JDBC从零开始的保姆级教程!!!
Posted 大忽悠爱忽悠
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JDBC从零开始的保姆级教程!!!相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
JDBC从零开始的保姆级教程!!!
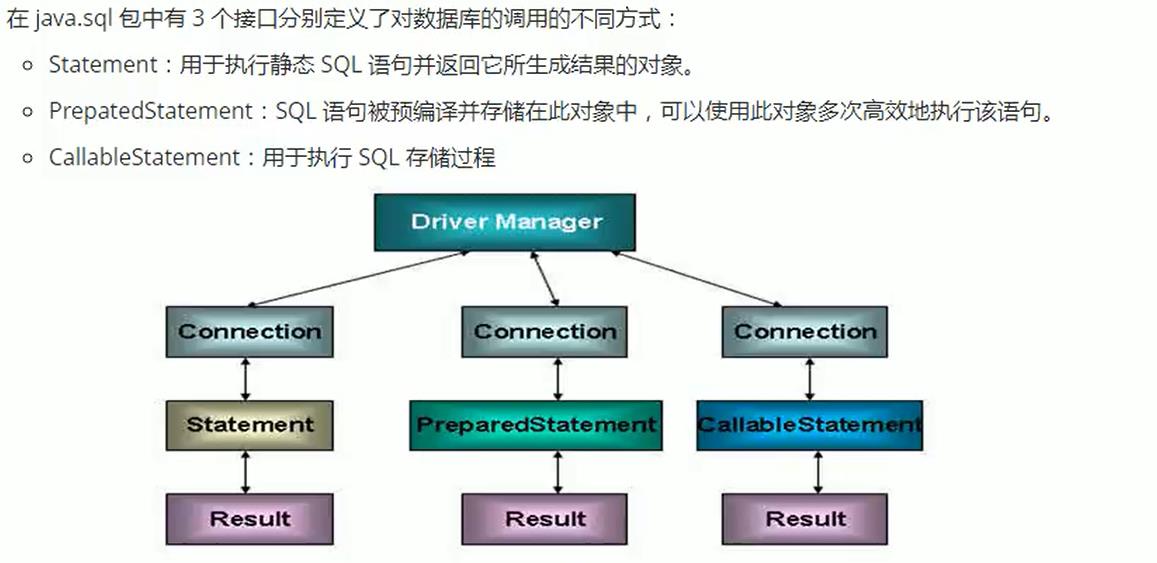
JAVA与数据库的连接方式
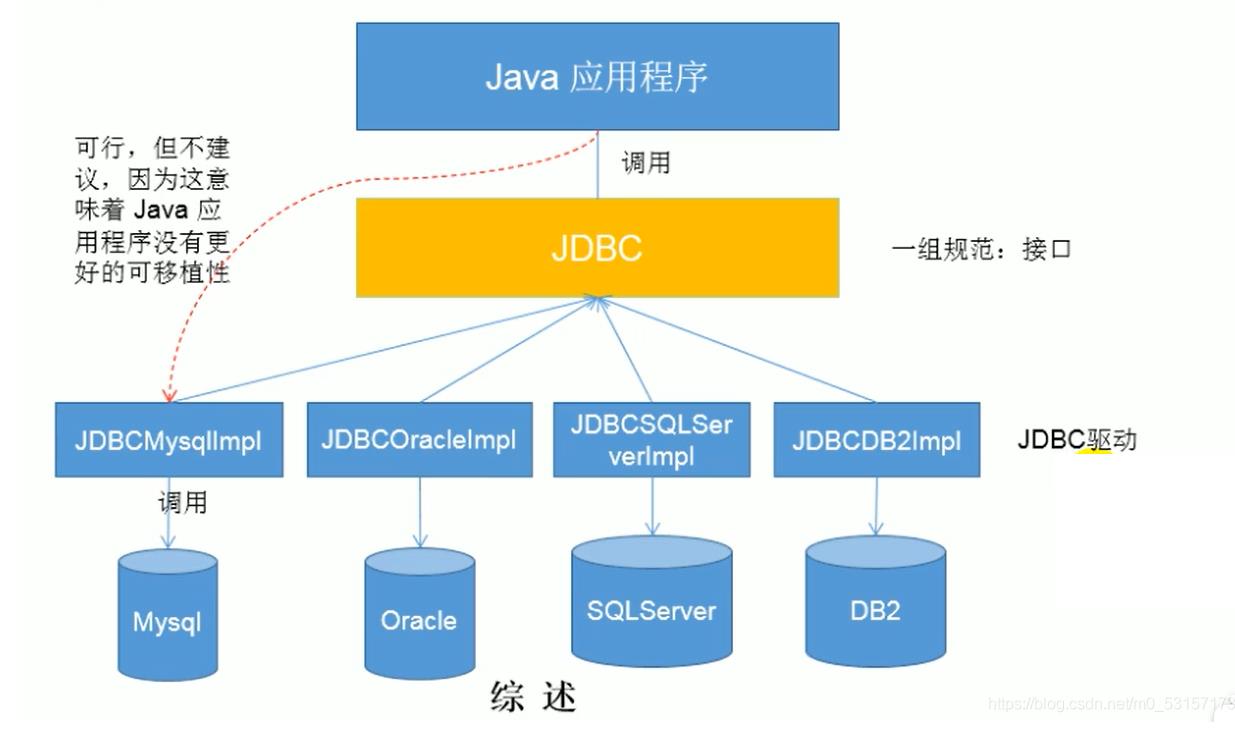
JDBC体系结构

JDBC程序编写步骤
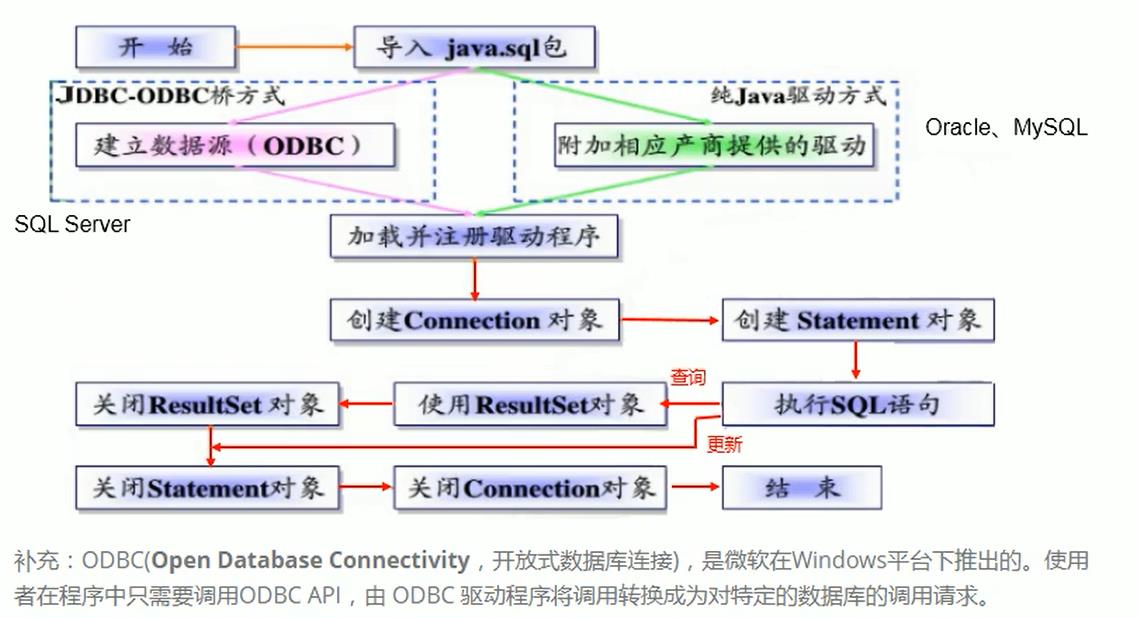
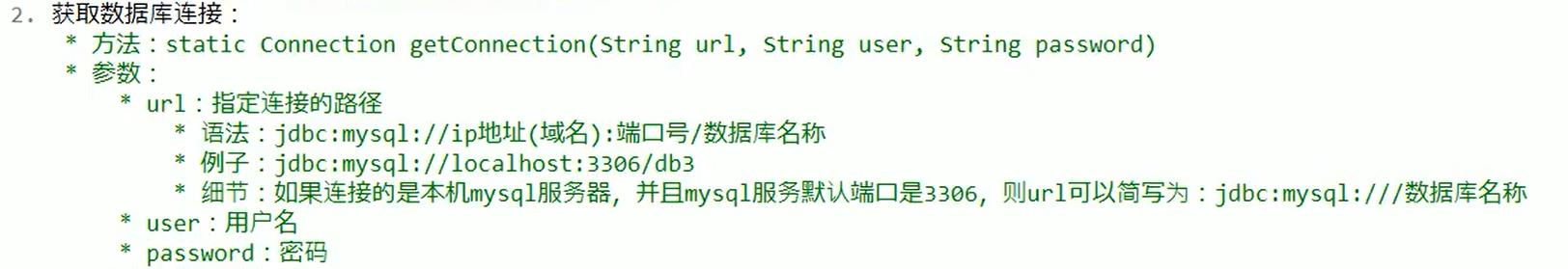
获取数据库连接方式一
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class MAIN
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException
{
//获取driver的实现类对象
Driver driver=new com.mysql.jdbc.Driver();
//jbdc:mysql :协议
//localhost: ip地址
// 3306: 默认mysql的端口号
//test1: test1数据库
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test1";
//将用户名和密码封装在properties中
Properties info=new Properties();
info.setProperty("user","root");
info.setProperty("password","126433");
Connection conn=driver.connect(url,info);
System.out.println(conn);
}
}
数据库连接方式二
对方式一的迭代,避免第三方的api,使得程序有更好的可移植性
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class MAIN
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//1.获取Driver实现类对象,使用反射
Class clazz=Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Driver driver=(Driver)clazz.newInstance();
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test1";
Properties info=new Properties();
info.setProperty("user","root");
info.setProperty("password","126433");
Connection conn=driver.connect(url,info);
System.out.println(conn);
}
}
数据库连接的方式三
使用DriverManger替换Driver
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class MAIN
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//1.提供另外三个连接的基本信息
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test1";
String user="root";
String password="126433";
//2.获取Driver实现类对象,使用反射
Class clazz=Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
Driver driver=(Driver)clazz.newInstance();
//注册驱动
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);
//获取连接
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
System.out.println(conn);
}
}
数据库连接方式四
可以只是加载驱动,而非显示的注册驱动了
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class MAIN
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, SQLException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
//1.提供另外三个连接的基本信息
String url="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test1";
String user="root";
String password="126433";
//2.加载Driver
Class clazz=Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//相较于方式三,可以省略如下的操作:
/* Driver driver=(Driver)clazz.newInstance();
//注册驱动
DriverManager.registerDriver(driver);*/
//获取连接
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
System.out.println(conn);
}
}
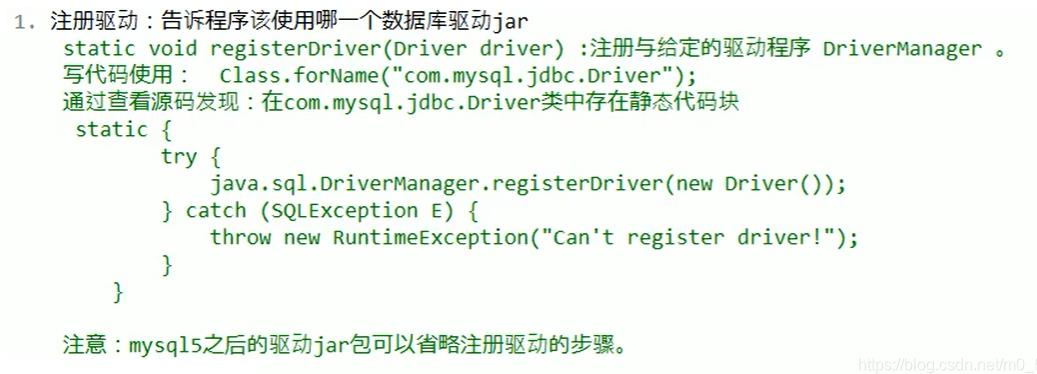
为什么可以省略呢?
因为在mysql的Driver实现类中,静态代码块声明了如下的操作:
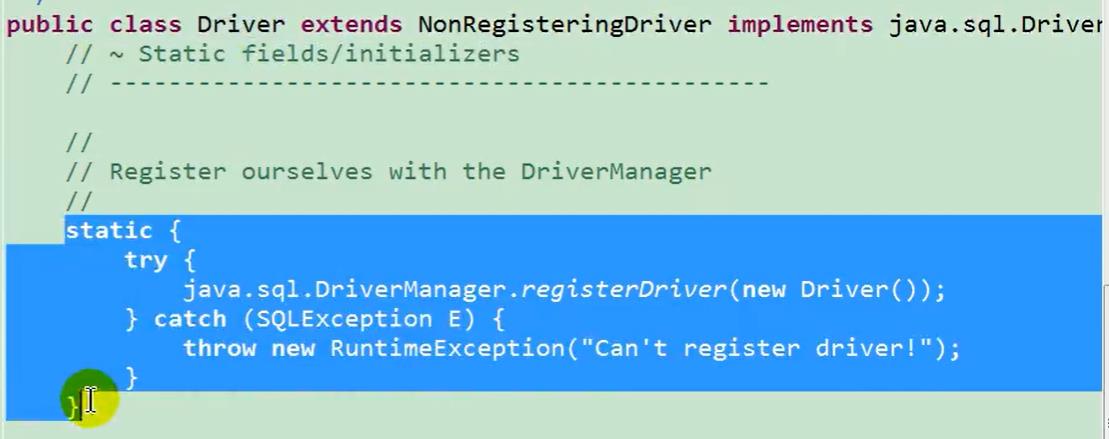
数据库连接方式五—final版本
将数据库连接需要的四个基本信息声明在配置文件中,通过读取配置文件的方式,获取连接
配置文件:
user=root
password=126433
url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test1
driverClass=com.jdbc.mysql.Driver
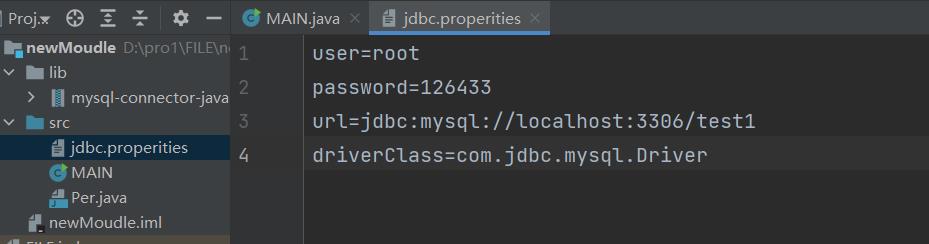
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
public class MAIN
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
//MAIN是当前的类
InputStream is=MAIN.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properities");
Properties pros=new Properties();
pros.load(is);
String user=pros.getProperty("user");
String password=pros.getProperty("password");
String url=pros.getProperty("url");
String driverClass=pros.getProperty("driverClass");
//加载驱动
Class.forName(driverClass);
//获取连接
Connection conn=DriverManager.getConnection(url,user,password);
System.out.println(conn);
}
}
final版的好处
实现了数据和代码的分离,实现了解耦
如果需要修改配置文件信息,可以避免程序重新打包
操作和访问数据库

DriverManger : 驱动管理对象
功能1:
功能2:
演示:
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.导入驱动jar包
//2.注册驱动
//java5版本后可以省略下面这行代码
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//3.获取数据库连接对象
//Connection conn= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/test1","root","126433");
Connection conn= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///test1","root","126433");
//4.定义sql语句
//注意: 嵌套字符串,外双里单
//这里被双引号包裹的sql语句结尾不用加分号
String sql="update depart set name='大忽悠总裁办' where wID=105";
//5.获取执行sql的对象 Statement
Statement stmt=conn.createStatement();
//6.执行sql
int count=stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
//7.处理结果
System.out.println(count);
//8.释放资源
stmt.close();
conn.close();
}
Connection :数据库连接对象
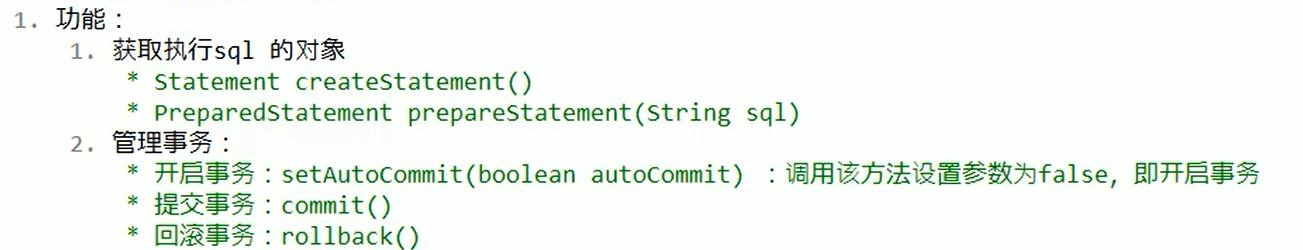
Statement : 执行sql的对象

DDL语句默认返回0
insert语句练习:
public class newMain {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Connection conn=null;
Statement stmt=null;
//1.注册驱动
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//2.定义sql语句
String sql="INSERT INTO depart VALUES(110,'小朋友副总裁办')";
try {
//3.获取connection对象
conn= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///test1","root","126433");
//4.获取sql对象,执行Statement
stmt=conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql
int count=stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
if(count>0)
System.out.println("添加成功!!");
else
System.out.println("添加失败");
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//7.释放资源
//避免空指针异常
if(stmt!=null) {
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null) {
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
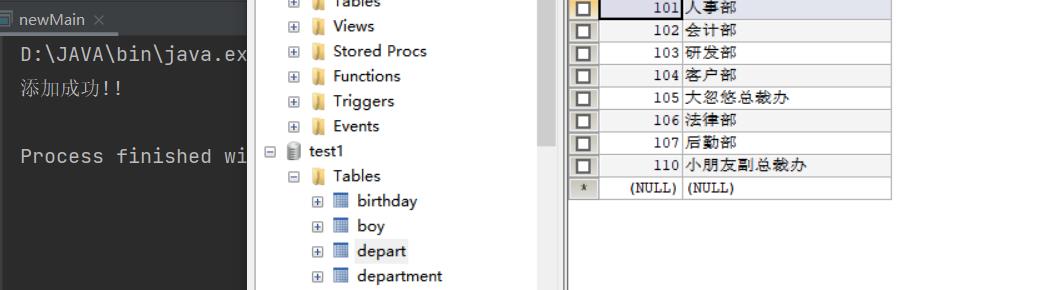
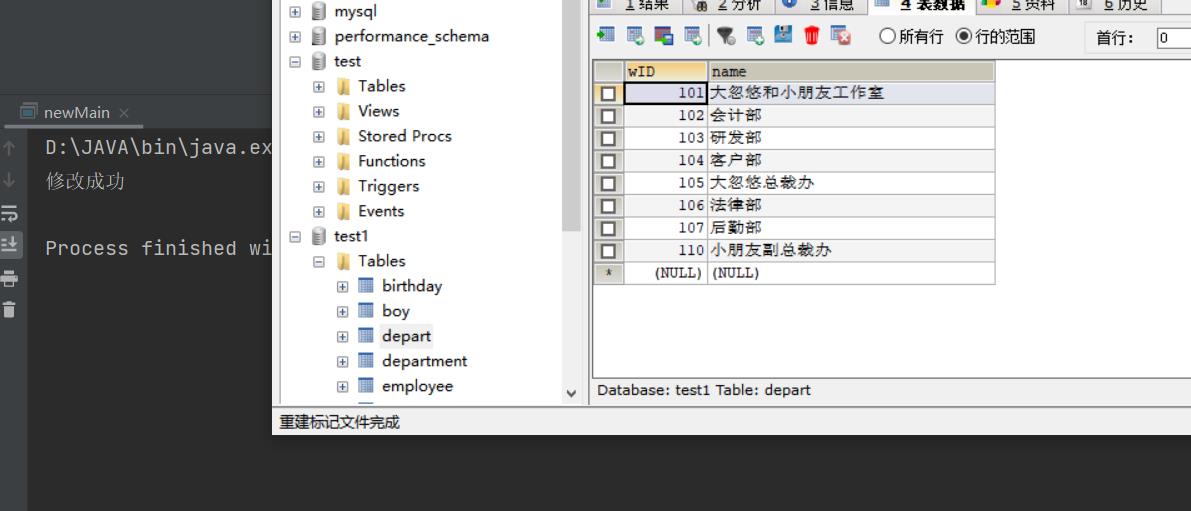
update语句练习:
public class newMain {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Connection conn=null;
Statement stmt=null;
//1.注册驱动
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取connection对象
conn= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///test1","root","126433");
//3.定义sql语句
String sql="update depart set name='大忽悠和小朋友工作室' where wID=101";
//4.获取sql对象
stmt=conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql语句
int count=stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
if(count>0)
System.out.println("修改成功");
else
System.out.println("修改失败");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//7.释放资源
if(stmt!=null)
{
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null)
{
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
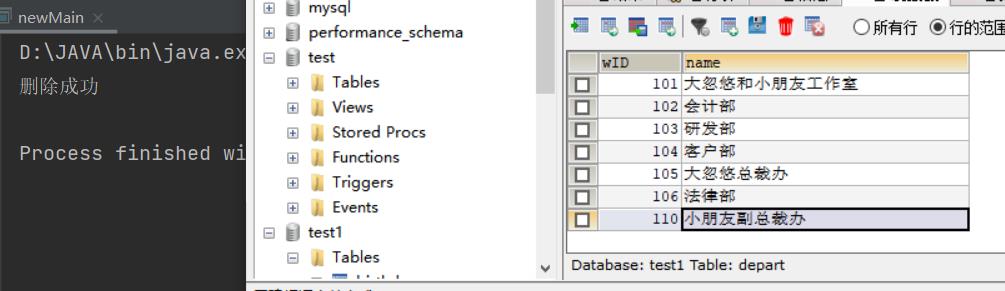
delete语句练习:
public class newMain {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Connection conn=null;
Statement stmt=null;
//1.注册驱动
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取connection对象
conn= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///test1","root","126433");
//3.定义sql语句
String sql="delete from depart where name like '%后%'";
//4.获取sql对象
stmt=conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql语句
int count=stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
if(count>0)
System.out.println("删除成功");
else
System.out.println("删除失败");
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//7.释放资源
if(stmt!=null)
{
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null)
{
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
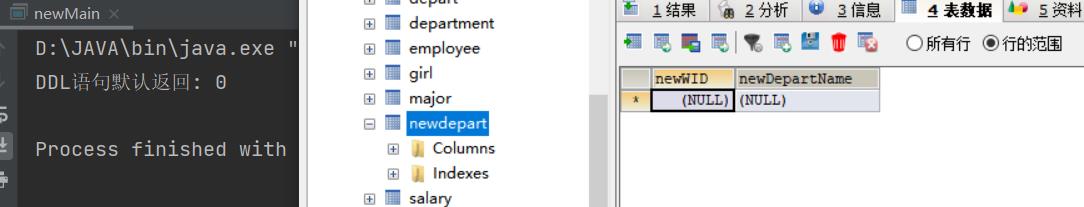
DDL语句之建表练习:
public class newMain {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Connection conn=null;
Statement stmt=null;
//1.注册驱动
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取connection对象
conn= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///test1","root","126433");
//3.定义sql语句
String sql="create table newDepart(newWID int primary key,newDepartName varchar(20))";
//4.获取sql对象
stmt=conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql语句
int count=stmt.executeUpdate(sql);
System.out.println("DDL语句默认返回: "+count);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}finally {
//7.释放资源
if(stmt!=null)
{
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(conn!=null)
{
try {
conn.close();
} catch (SQLException throwables) {
throwables.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}
ResultSet: 结果集对象,封装查询结果

演示:
public class newMain {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Connection conn=null;
Statement stmt=null;
ResultSet rs=null;
//1.注册驱动
try {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
//2.获取conncetion对象
conn= DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql:///test1","root","126433");
//3.定义sql语句---查询语句
String sql="select *from depart";
//4.获取执行sql的对象
stmt=conn.createStatement();
//5.执行sql语句---返回一个查询到的结果集
rs=stmt.executeQuery(sql);
//6.处理结果
//6.1让游标向下移动一行
rs.next();
//6.2获取资源
int wID=rs.getInt(1);
String name=rs.getString("name");
System.out.println("查询到的部门编号:"+wID+" 查询到部门名称:"+name);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
以上是关于JDBC从零开始的保姆级教程!!!的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章