Java并发多线程编程——并发容器ConcurrentLinkedQueue
Posted 小志的博客
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java并发多线程编程——并发容器ConcurrentLinkedQueue相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
一、ConcurrentLinkedQueue的理解
- ConcurrentLinkedQueue属于java.util.concurrent包;
- 要实现一个线程安全的队列有两种实现方式:一种是加锁,这种实现方式就是我们常说的阻塞队列;另一种是使用循环CAS算法实现,这种方式实现队列称之为非阻塞队列;而ConcurrentLinkedQueue就是一种非阻塞队列。
- ConcurrentLinkedQueue是基于链接节点的无界线程安全队列 。 这个队列排列元素FIFO(先进先出)
- 下图为jdk1.8API的解释:

二、ConcurrentLinkedQueue的类图
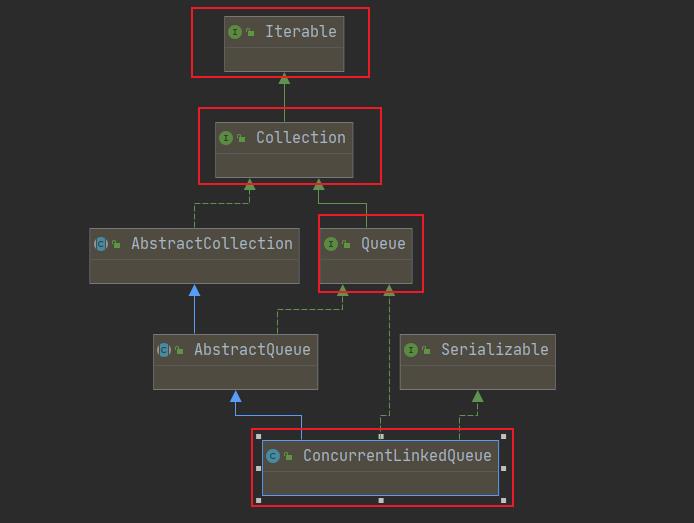
- 由上图可知ConcurrentLinkedQueue实现了Queue接口,Queue继承Collection接口,Collection继承Iterable接口;
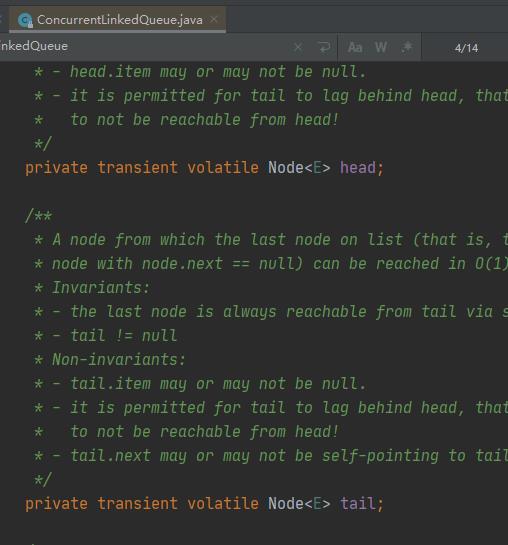
- 由上图可知ConcurrentLinkedQueue由head节点和tail节点组成。head头结点,负责出列, tail尾节点,负责入列。
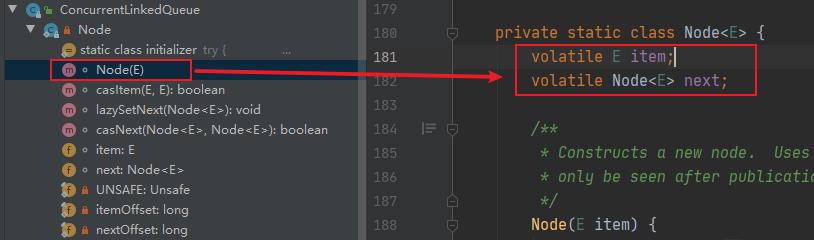
- 由上图可知每个节点(Node)由节点元素(item)和指向下一个节点的引用(next)组成,节点与节点之间就是通过这个next关联起来,从而组成一张链表结构的队列。
三、ConcurrentLinkedQueue类中常用的方法
1、构造方法
- public ConcurrentLinkedQueue() 创建一个 ConcurrentLinkedQueue为空的ConcurrentLinkedQueue。
- public ConcurrentLinkedQueue(Collection<? extends E> c) 创建一个 ConcurrentLinkedQueue最初包含给定集合的元素,以集合的迭代器的遍历顺序添加。
2、常用方法
- public boolean offer(E e) 在该队列的尾部插入指定的元素。 即入队列;
- public E poll() 检索并删除此队列的头部,如果此队列为空,则返回 null 。 即出队列;
四、ConcurrentLinkedQueue中常用方法的原理
1、offer(E e)方法
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the tail of this queue.
* As the queue is unbounded, this method will never return {@code false}.
*
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Queue#offer})
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified element is null
*/
public boolean offer(E e) {
//判断节点是否为null
checkNotNull(e);
//创建入队节点,该节点也由节点元素(item)和指向下一个节点的引用(next)组成
final Node<E> newNode = new Node<E>(e);
// 循环CAS直到入队成功
for (Node<E> t = tail, p = t;;) {//p用来表示队列的尾节点,初始情况下p和t都等于tail节点
Node<E> q = p.next;//q等于p指向下一个节点的引用(next)
if (q == null) {//判断p是否为尾节点
//q等于新节点
if (p.casNext(null, newNode)) {
if (p != t)
//更新尾节点为最新元素
casTail(t, newNode);
return true;
}
}
else if (p == q)
//将head的next设置为新的head
p = (t != (t = tail)) ? t : head;
else
//寻找尾节点
p = (p != t && t != (t = tail)) ? t : q;
}
}
- 总结:offer(E e)方法即入队列方法,主要是先定位出尾节点, 然后CAS算法将入队节点设置成尾节点的next节点,如不成功则重试。
2、poll() 方法
public E poll() {
restartFromHead:
for (;;) {
for (Node<E> h = head, p = h, q;;) {
E item = p.item;
//item != null && item设置为null,表示出列成功
if (item != null && p.casItem(item, null)) {
if (p != h) // hop two nodes at a time
//出列成功需要对head进行移动
updateHead(h, ((q = p.next) != null) ? q : p);
return item;
}
else if ((q = p.next) == null) {
updateHead(h, p);
return null;
}
else if (p == q)
//操作失败,回到循环之前
continue restartFromHead;
else
//移动head节点
p = q;
}
}
}
- 总结:offer(E e)方法即入队列方法,主要是先定位出尾节点, 然后CAS算法将入队节点设置成尾节点的next节点,如不成功则重试。
五、单链表(Linked List)的详细理解
源码原理如不是很了解可参考lz如下博文:
以上是关于Java并发多线程编程——并发容器ConcurrentLinkedQueue的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章