VGG:用于大规模图像识别的超深卷积网络
Posted 三维重建学习笔记
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了VGG:用于大规模图像识别的超深卷积网络相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Abstract
main contribution:使用非常小的卷积滤波器(3x3)增加网络的深度,通过将深度推到16-19层,显著提升了网络的效果
achievement:在2014年ImageNet挑战赛上面分别获得定位和分类的第一名和第二名,可以很好的推广到其它数据集
Convnet Configuration
Input:224 x 224 RGB图像,预处理是每个像素减去通过训练集计算的平均RGB值
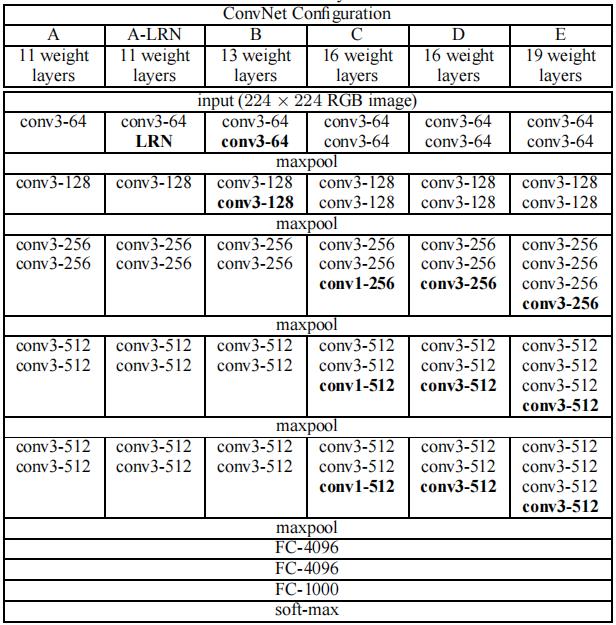
通过将一个7x7的卷积层替换为3个3x3的卷积层,有两个好处。第一,加入了三个线性层而不是一个单一的层,使得决策函数更具有鉴别性。其次,减少了参数的数量,假设3个3x3的卷积层,输入输出都是C通道,一共有3*(3*3*C*C) = 27C^2个参数。但是对于一个7x7的卷积层,一共有49C^2个参数。
Classification Experiments
Conclusion
网络结构非常简单,整个网络都使用了相同大小的卷积核(3x3)和最大池化尺寸(2x2),减少了网络参数,但是仍然会导致占用很多内存。可以根据论文里面的网络配置进行复现,也可以直接调用torchvision里面的模型,如下所示:
class VGG(nn.Module):def __init__(self, features, num_classes=1000, init_weights=True):super(VGG, self).__init__()self.features = featuresself.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((7, 7))self.classifier = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(512 * 7 * 7, 4096),nn.ReLU(True),nn.Dropout(),nn.Linear(4096, 4096),nn.ReLU(True),nn.Dropout(),nn.Linear(4096, num_classes),)if init_weights:self._initialize_weights()def forward(self, x):x = self.features(x)x = self.avgpool(x)x = torch.flatten(x, 1)x = self.classifier(x)return xdef _initialize_weights(self):for m in self.modules():if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d):nn.init.kaiming_normal_(m.weight, mode='fan_out', nonlinearity='relu')if m.bias is not None:nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d):nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1)nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)elif isinstance(m, nn.Linear):nn.init.normal_(m.weight, 0, 0.01)nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)def make_layers(cfg, batch_norm=False):layers = []in_channels = 3for v in cfg:if v == 'M':layers += [nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2)]else:conv2d = nn.Conv2d(in_channels, v, kernel_size=3, padding=1)if batch_norm:layers += [conv2d, nn.BatchNorm2d(v), nn.ReLU(inplace=True)]else:layers += [conv2d, nn.ReLU(inplace=True)]in_channels = vreturn nn.Sequential(*layers)cfgs = {'A': [64, 'M', 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],'B': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 'M'],'D': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 'M'],'E': [64, 64, 'M', 128, 128, 'M', 256, 256, 256, 256, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M', 512, 512, 512, 512, 'M'],}def _vgg(arch, cfg, batch_norm, pretrained, progress, **kwargs):if pretrained:kwargs['init_weights'] = Falsemodel = VGG(make_layers(cfgs[cfg], batch_norm=batch_norm), **kwargs)if pretrained:state_dict = load_state_dict_from_url(model_urls[arch],progress=progress)model.load_state_dict(state_dict)return modeldef vgg16(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):r"""VGG 16-layer model (configuration "D")`"Very Deep Convolutional Networks For Large-Scale Image Recognition" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1556.pdf>`_Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNetprogress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr"""return _vgg('vgg16', 'D', False, pretrained, progress, **kwargs)def vgg16_bn(pretrained=False, progress=True, **kwargs):r"""VGG 16-layer model (configuration "D") with batch normalization`"Very Deep Convolutional Networks For Large-Scale Image Recognition" <https://arxiv.org/pdf/1409.1556.pdf>`_Args:pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNetprogress (bool): If True, displays a progress bar of the download to stderr"""return _vgg('vgg16_bn', 'D', True, pretrained, progress, **kwargs)
以上是关于VGG:用于大规模图像识别的超深卷积网络的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章