C语言复习之模拟ArrayList的demo
Posted 你是小KS
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C语言复习之模拟ArrayList的demo相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1.声明
当前内容主要复习和使用C语言模拟实现ArrayList的基本操作
主要实现
- ArrayList的自动扩容
- ArrayList的数据添加,数删除的操作
2.demo
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#ifndef true
#include <stdbool.h>
#endif
/*
内容:使用c语言模拟ArrayList
时间:2021/05/02
作者:hy
*/
typedef struct {
char *name;
int id;
char *(*toString)();
} Person;
typedef Person *Item;// 添加对象时
//typedef int Item;// 添加数字类型时
void formatPerson(Item *p) {
if (p == NULL) {
printf("NULL");
return;
}
Person *lp = (Person *) p;
if(lp->name && lp->id){
printf("Person [name=%s,id=%i]", lp->name, lp->id);
}
}
// 一个person的比较器
bool personCompare(const Person *p1, const Person *p2){
// 只要一个为null则返回false
if(p1==NULL || p2==NULL){
return false;
}
// 内存地址一致
if(p1==p2){
return true;
}
// 内存地址不一致
if(p1->id==p2->id){
return true;
}
return false;
}
Person *newPerson() {
return NULL;
}
typedef struct {
Item *datas;
int size;
int capital;
size_t t;
bool (*compare)(const Item *, const Item *);
} ArrayList;
/*重新改变数组长度*/
static void resize(ArrayList *list, int newCapital);
/*容量缩小为原来的1.5倍,条件为删除数据时,数据不足容量的一半时*/
static void capitalToSmall(ArrayList *list);
/*容量扩大为原来的1.5倍,条件为添加数据时,且容量超过时*/
static void capitalToBig(ArrayList *list);
/*拷贝原数据到现在的数据中*/
static void copyItemFromOld(Item *oldItems, Item *newItems, int len);
/*通过下标删除数据*/
bool listRemoveByIndex(ArrayList *lp, int index);
/*释放集合内存*/
void listFree(ArrayList *list);
bool isEmpty(ArrayList *list);
/*判断当前集合是否为空*/
bool isEmpty(ArrayList *list) {
if (list == NULL || list->size == 0 || list->datas == NULL) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/*检查是否数组越界*/
bool checkOutOfArrayBound(ArrayList *lp, int index) {
if (isEmpty(lp)) {
return true;
}
if (index > lp->size - 1 || index < 0) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
/*获取对应数据的下标*/
int listGetIndexByItem(ArrayList *lp, Item *item) {
if (isEmpty(lp) || item == NULL) {
return -1;
}
bool (*eq)(const Item *, const Item *) =lp->compare;
for (int index = 0; index < lp->size; index++) {
Item *oItem = (Item *)lp->datas[index];
if (eq == NULL) {
if (oItem == item) {
return index;
}
} else {
if (eq(item, oItem)) {
return index;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
/*通过下标获取对应项*/
Item *listGetItemByIndex(ArrayList *lp, int index) {
if (isEmpty(lp) || checkOutOfArrayBound(lp, index)) {
return NULL;
}
return &(lp->datas[index]);
}
bool listRemoveByIndex(ArrayList *lp, int index) {
if (isEmpty(lp) || index < 0) {
// 找不到当前的数据只有不进行任何操作
return false;
}
Item item = lp->datas[index];
if (!item) {// 没有值
return false;
}
// 直接把index后面的向index-1处拷贝即可
for (int i = index; i < lp->size - 1; ++i) {
lp->datas[i] = lp->datas[i + 1];
}
lp->size--;
return true;
}
/*删除数据,通过数据*/
bool listRemoveByItem(ArrayList *lp, Item *item) {
int index = listGetIndexByItem(lp, item);
if (checkOutOfArrayBound(lp, index)) {
return false;
}
return listRemoveByIndex(lp, index);
}
static void copyItemFromOld(Item *oldItems, Item *newItems, int endIndex) {
for (int i = 0; i < endIndex; i++) {
newItems[i] = oldItems[i];
}
}
/*容量缩小为原来的1.5倍,条件为删除数据时,数据不足容量的一半时*/
static void capitalToSmall(ArrayList *list) {
int oldCapital = list->capital;
int newCapital = (int) (oldCapital / 1.5);
if (newCapital <= 10) {
return;
}
resize(list, newCapital);
}
/*容量扩大为原来的1.5倍,条件为添加数据时,且容量超过时*/
static void capitalToBig(ArrayList *list) {
int oldCapital = list->capital;
int newCapital = (int) (oldCapital * 1.5);
resize(list, newCapital);
}
static void resize(ArrayList *list, int newCapital) {
if (newCapital < 0) {
printf("upper size overflow ,the list is to big...\\n");
return;
}
Item *newItems = (Item *) malloc(list->t * newCapital);
Item *oldItems = list->datas;
copyItemFromOld(oldItems, newItems, list->size - 1);
free(list->datas);
list->datas = NULL;
list->datas = newItems;
list->capital = newCapital;
}
// 添加数据时
void add(ArrayList *list, Item item) {
// 这里可能不需要类型检测
if (sizeof(item) != list->t) {
//printf("传递类型(%d)与实际类型(%d)不匹配\\n",sizeof(elem),list->t);
}
// 添加数据时
int size = list->size;
if (size + 1 > list->capital) {
capitalToBig(list);
}
list->datas[size] = item;
list->size++;
}
// 释放ArrayList的空间
void listFree(ArrayList *list) {
if (list == NULL || list->size == 0 || list->datas == NULL) {
return;
}
free(list->datas);
list->size = 0;
list->t = 0;
free(list);
}
void printArrayList(ArrayList *list, void (*format)(Item)) {
if (list == NULL) {
printf("list is NULL\\n");
return;
}
//printf("%d\\n",list->size);
printf("ArrayList [");
int i;
for (i = 0; i < list->size; i++) {
//puts("println\\n");
Item *p = (Item *) list->datas[i];
if (p == NULL) {
continue;
}
//printf("%s,%d",p->name,p->id);
format(list->datas[i]);
if (i < list->size - 1) {
printf(",");
}
}
puts("]");
}
void formatInt(int i) {
printf("%d", i);
}
// 创建新的ArrayList集合
ArrayList *newArrayList(size_t t, bool (*compare)(const Item *, const Item *)) {
ArrayList *list = (ArrayList *) malloc(sizeof(ArrayList));
// default 10可能需要扩容
int defaultCapital = 10;
list->datas = (Item *) malloc(defaultCapital * t);
list->size = 0;
list->t = t;
list->capital = defaultCapital;
list->compare=compare;
//printf("size_t=%d\\n",t);
return list;
}
int main() {
ArrayList *plist = newArrayList(sizeof(Person),personCompare);
Person p1 = {"龙1", 1001};
Person p2 = {"龙2", 1002};
Person p3 = {"龙3", 1003};
Person p4 = {"龙4", 1004};
Person p5 = {"龙5", 1005};
Person p6 = {"龙6", 1006};
Person p7 = {"龙7", 1007};
Person p8 = {"龙8", 1008};
Person p9 = {"龙9", 1009};
Person p10 = {"龙10", 1010};
Person p11 = {"龙11", 1011};
Person p12 = {"龙12", 1012};
add(plist, &p1);
add(plist, &p2);
add(plist, &p3);
add(plist, &p4);
add(plist, &p5);
add(plist, &p6);
/*add(plist, &p7);
add(plist, &p8);
add(plist, &p9);
add(plist, &p10);
add(plist, &p11);*/
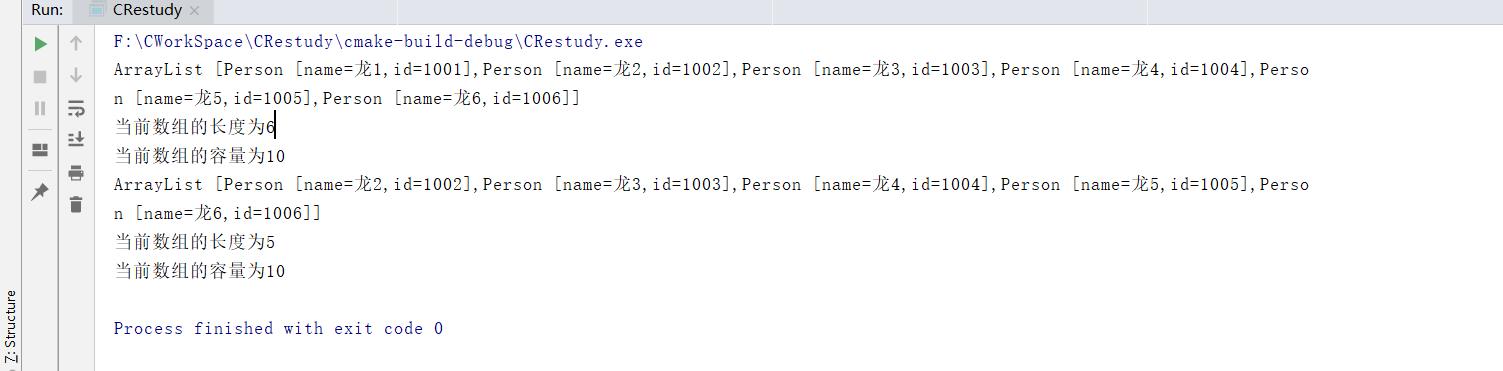
printArrayList(plist, formatPerson);
printf("当前数组的长度为%d\\n", plist->size);
printf("当前数组的容量为%d\\n", plist->capital);
listRemoveByItem(plist, (Item *)(&p1)); // 移除测试成功
printArrayList(plist, formatPerson);
printf("当前数组的长度为%d\\n", plist->size);
printf("当前数组的容量为%d\\n", plist->capital);
listFree(plist);
return 0;
}
3.测试
以上是关于C语言复习之模拟ArrayList的demo的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章