Java:@Repeatable注解的使用和反射获取
Posted 你是小KS
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Java:@Repeatable注解的使用和反射获取相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
当前环境:JDK1.8
1. 声明
当前内容主要用于本人学习和复习java的基础知识,主要为@Repeatable注解的使用,以及部分注解的使用
主要参考:Oracle官方文档
主要为:
- 使用@Repeatable和获取@Repeatable修饰的注解属性
- 在类变量前面使用注解(这个好像无法反射获取)
2. @Repeatable基本demo
首先需要一个代表单数的注解
import java.lang.annotation.Repeatable;
import com.sun.istack.NotNull;
@Repeatable(Authors.class)
public @interface Author {
// 添加非空校验
@NotNull
String name();
@NotNull
String createTime();
}
然后在一个代表复数的注解中的value方法中返回上面这个单数的注解类数组
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
// 注意当前的Authors中如果不加这句话那马不可使用反射方式获取Author的注解
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Authors {
Author[] value();
}
这里需要注意的是,如果想要在运行的时候获取@Author注解必须在Authors的上面添加这个@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)(这个注解不能放在Author上面)
并且,@Author上面不能有与当前的@Repeatable的注解中有相同的注解,否则编译报错
@NotNull注解强制用户输入必要的参数
最后的使用
@Author(createTime = "2021-07-03", name = "hy")
@Author(createTime = "2021-07-03", name = "zs")
public class Book {
private String author;
private String name;
public String getAuthor() {
return author;
}
public void setAuthor(String author) {
this.author = author;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
这样就可以在一个类上面使用相同的注解了(感觉就是,将注解替换为了@Authors)
反射获取@Author注解中的方法返回值
/**
*
* @author hy
* @createTime 2021-07-03 08:49:07
* @description 主要为再测试java中的注解
*
*/
public class AnnotationTest {
// 默认运行的时候是可以得到的
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book book = new Book();
Class<? extends Book> clazz = book.getClass();
// Annotation[] declaredAnnotations = clazz.getDeclaredAnnotations();
// 注意下面的操作无法获取当前的注解
Annotation[] annotations = clazz.getAnnotations();
System.out.println("获取到所有的注解" + annotations.length);
Author[] annotationsByType = clazz.getAnnotationsByType(Author.class);
System.out.println(annotationsByType);
if (annotationsByType == null || annotationsByType.length == 0) {
System.out.println("未获取到当前注解为Author的属性");
return;
}
if (annotationsByType != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < annotationsByType.length; i++) {
Author author = annotationsByType[i];
String createTime = author.createTime();
String name = author.name();
System.out.println(name + ":" + createTime);
}
}
}
}
执行结果:
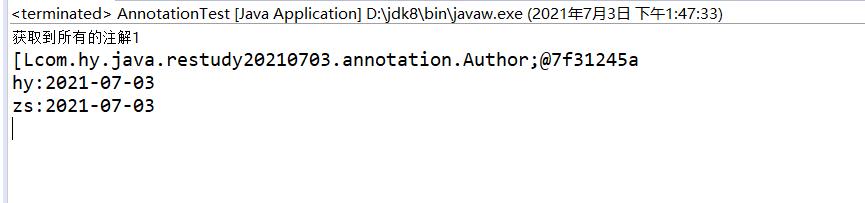
3.在变量前使用注解
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
import com.sun.istack.Nullable;
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(value = { java.lang.annotation.ElementType.FIELD, java.lang.annotation.ElementType.METHOD,
java.lang.annotation.ElementType.PARAMETER, java.lang.annotation.ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE })
public @interface Note {
@Nullable
String value() default "";
}
基本使用
import com.sun.istack.NotNull;
/**
*
* @author hy
* @createTime 2021-07-03 09:58:41
* @description 当前内容主要为测试和使用annotation注解修饰变量
*
*/
public class NewAnnotationTest /* implements @Readonly List<T> 不支持这个格式的操作*/ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
@Note("备注") // 注解可以放在当前的变量的前面
Book book = new Book();
Note annotation = book.getClass().getDeclaredAnnotation(Note.class);
Annotation[] annotations = book.getClass().getAnnotations();
System.out.println(annotation);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(annotations));
// 如何获取本地变量声明
}
public static void print(@NotNull String str) {
String string = str.toString();
System.out.println(string);
}
}
可以在方法内部的变量的类型前面使用注解,主要靠的是java.lang.annotation.ElementType.LOCAL_VARIABLE,但是又无法通过变量方式访问这个标记,本人通过javap方式发现编译中有Note注解,但是里面的内容消失了
以上是关于Java:@Repeatable注解的使用和反射获取的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章