[An Introduction to GCC 学习笔记] 04 Verbose选项-c链接次序
Posted 漫小牛
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了[An Introduction to GCC 学习笔记] 04 Verbose选项-c链接次序相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1 Verbose Compilation
- The ‘-V’ option can be used to display detailed information about the exact sequence of commands used to compile and link a program.
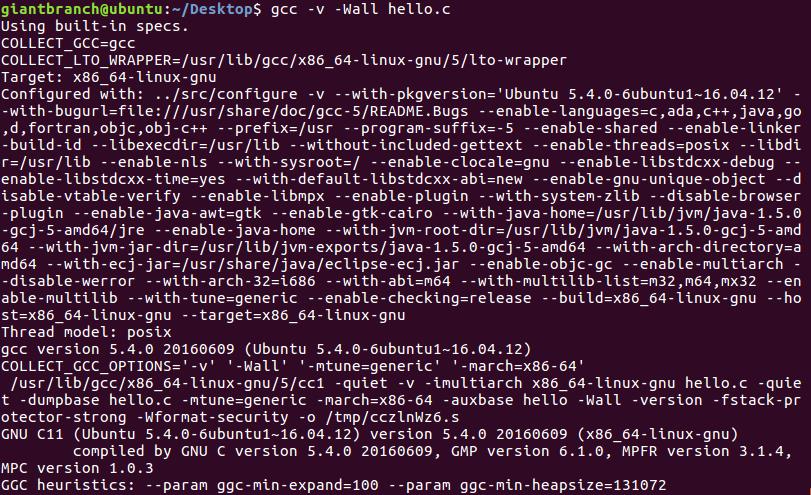
- The output produced by ‘-v’ can be useful whenever there is a problem with the compilation process itself. It displays the full directory paths used to search for header files and libraries, the predefined preprocessor symbols, and the object files and libraries used for linking.
2 Compiling Files Independently(独立编译文件)
- If a program is stored in a single file then any change to an individual function requires the whole program to be recompiled to produce a new executable. The recompilation of large source files can be very time-consuming.
- When programs are stored in independent source files, only the files which have changed need to be recompiled after the source code has been modified. In this approach, the source files are compiled separately and then linked together - a two stage process.
- In the first stage, a file is complied without creating an executable. The result is referred to as an object file, and has the extension ‘,o’ when using GCC.
- In the second stage, the object files are merged together by a separate program called the linker. The linker combines all the object files together to create a single executable.
- An object file contains machine code where any references to the memory addresses of functions(or variables) in other files are left undefined. This allows source files to be compiled without direct reference to each other. The linker fills in these missing address when it produces the executable.
3 Creating Object Files From Source Files
- The command-line option ‘-c’ is used to compile a source file to an object file.
$ gcc -Wall -c main
- There is no need to use the option ‘-o’ to specify the name of the output file in this case. When compiling with ‘-c’ the compiler automatically creates an objct file whose name the same as the source file, with ‘.o’ instead of the original extension.
- There is no need to put the header file on the command line, since it is automatically included by the #include statements in the souce files.
4 Creating Executables From Object Files
- The final step in creating an executable file is to use gcc to link the object files together and fill the missing addresses of external functions. To link object files together, they are simply listed on the command line:
$ gcc main.o hello_fn.o -o hello
- To perform the linking step, gcc uses the link ld, which is a separate program.
5 Link Order of Object Files
- On Unix-like systems, the traditional behavior of compilers and linkers is to search for external functions from left to right in the object files specified on the command line. This means that the object file which contains the definition of a function should appear after any files which call that function.
- Most current compilers and linkers will search all object files, regardless of order, but since not all compilers do this it is best to follow the convention of ordering object files from left to right.
- This is worth keeping in mind if you ever encounter unexpected problems with undefined references, and all the necessary object files appear to be present on the command line.
以上是关于[An Introduction to GCC 学习笔记] 04 Verbose选项-c链接次序的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
[An Introduction to GCC 学习笔记] 09 -Wall
[An Introduction to GCC 学习笔记] 14 优化问题3
[An Introduction to GCC 学习笔记] 14 优化问题3
[An Introduction to GCC 学习笔记] 13 优化问题2