JUC并发编程--- 阻塞队列和同步队列使用
Posted 小样5411
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JUC并发编程--- 阻塞队列和同步队列使用相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
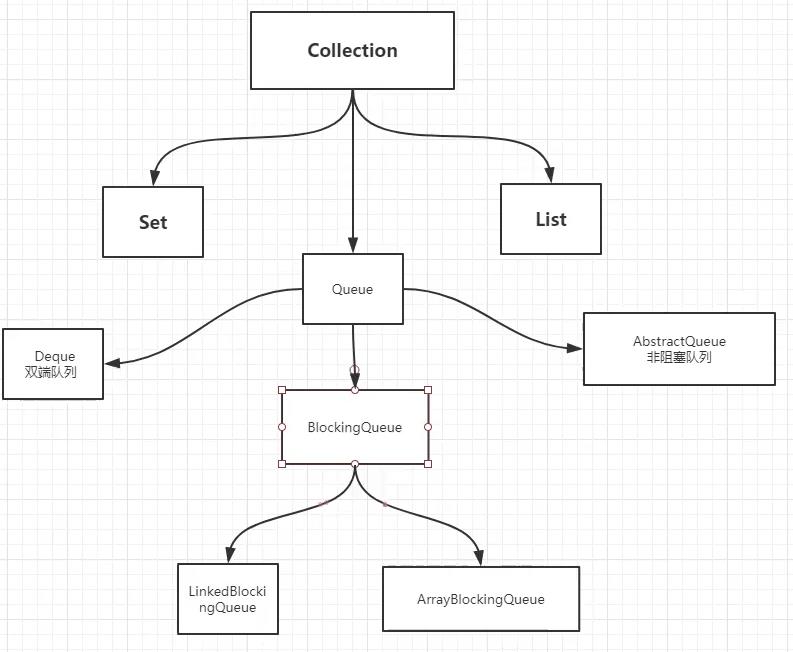
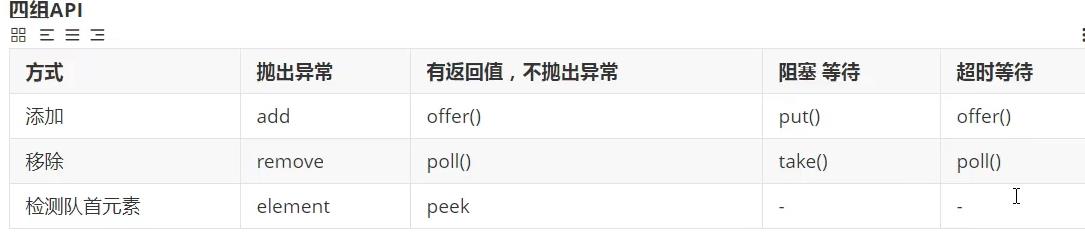
主要涉及一些方法,根据开发实际情况,选择用哪个方法
一、阻塞队列
抛出异常
add与remove,设置队列大小为3,已经添加3个再添加就会抛出异常,remove同理,如果队列没有还remove就会抛出异常java.util.NoSuchElementException
但如果我们不要抛出异常呢,就可以用有返回值的,不能添加就返回false,不抛异常
package com.yx.queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class BlockingQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test1();
}
private static void test1() {
//创建一个队列大小为3的队列
ArrayBlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("a"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("b"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("c"));
//System.out.println(blockingQueue.add("d"));//添加第四个就会抛出异常java.lang.IllegalStateException: Queue full
System.out.println("===========");
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.remove());//抛出异常java.util.NoSuchElementException
}
}
有返回值不抛出异常
offer()与poll()
package com.yx.queue;
import java.util.concurrent.ArrayBlockingQueue;
public class BlockingQueue {
public static void main(String[] args) {
test2();
}
private static void test2() {
//创建一个队列大小为3的队列
ArrayBlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("a"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("b"));
System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("c"));
//System.out.println(blockingQueue.offer("d"));//返回false,不跑出异常,表示添加不成功
System.out.println("============");
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());//返回null,不抛出异常
}
}
阻塞等待
put()与take(),一直阻塞,程序不停止
private static void test3() throws InterruptedException {
//创建一个队列大小为3的队列
ArrayBlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
blockingQueue.put("a");
blockingQueue.put("b");
blockingQueue.put("c");
//blockingQueue.put("d");//队列没有位置一直阻塞
System.out.println("================");
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.take());
}


等待,等待超时
offer(),poll()
private static void test4() throws InterruptedException {
//创建一个队列大小为3的队列
ArrayBlockingQueue blockingQueue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(3);
blockingQueue.offer("a");
blockingQueue.offer("b");
blockingQueue.offer("c");
blockingQueue.offer("d",2, TimeUnit.SECONDS);//等待两秒就退出
System.out.println("================");
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
System.out.println(blockingQueue.poll());
blockingQueue.poll(2,TimeUnit.SECONDS);//等待两秒就退出
}
二、同步队列
SynchronousQueue同步队列
该同步队列没有容量,进去一个元素,必须等待取出之后,才能再往里面放一个元素
package com.yx.queue;
import java.util.concurrent.BlockingQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.SynchronousQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class SynchronousQueueDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BlockingQueue<String> blockingQueue = new SynchronousQueue<>();
new Thread(()->{
try {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->put 1");
blockingQueue.put("1");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->put 2");
blockingQueue.put("2");
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->put 3");
blockingQueue.put("3");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"A").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->take->"+blockingQueue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->take->"+blockingQueue.take());
TimeUnit.SECONDS.sleep(2);
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->take->"+blockingQueue.take());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
},"B").start();
}
}

以上是关于JUC并发编程--- 阻塞队列和同步队列使用的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章