java_父类
Posted 偶像java练习生
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java_父类相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
继承

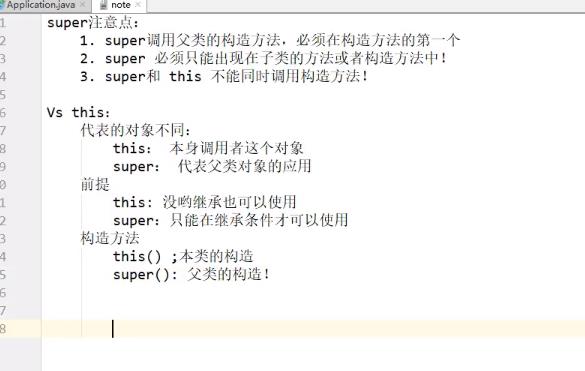
- 子类构造器中默认调用父类构造器 super();
重写
- 需要有继承关系,子类重写父类的方法
- 方法名必须相同
- 参数列表必须相同
- 修饰符,范围可以扩大: public ->Protected>defaule ->private
- 抛出的异常:范围,可以被缩小,但不能扩大:ClassNotFoundException --> Exception(大)
重写,子类的方法和父类必要一致;方法体不同!
为什么需要重写:
1.父类的功能,子类不一定需要,或者不一定满足!
代码如下:
public class Application {
//静态的方法和非静态的方法区别很大
//静态方法: //方法的调用只和左边,定义的有关,类加载的时候就出来了
//非静态:重写
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方法的调用只和左边,定义的数据类型有关
A a = new A();
a.test();
//父类的引用指向子类
B b = new A();
b.test();
}
}
package chongxie;
//继承
public class A extends B{
public void test() throws ClassNotFoundException{
System.out.println("A=>test()");
}
}
package chongxie;
//重写都是方法的重写,和属性无关,
//重写的关键词方法只能是public 的
public class B {
protected void test() throws Exception{
System.out.println("B=>test()");
}
}
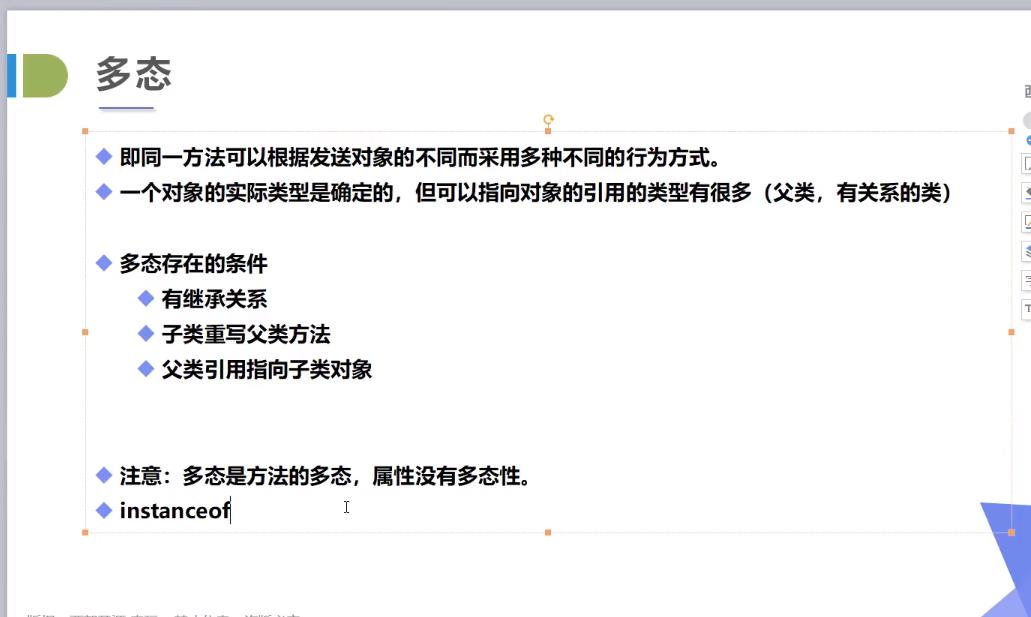
多态
package demo05;
public class Student extends Person{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//一个对象的是实际类型是确定的
//new Student();
//new Person();
//可以指向的引用类型就不确定了;父类的引用指向子类
//Student 能调用的方法都是自己的或者继承父类的!
Student s1 = new Student();
//Person 父类型,可以指向父类,但是不能调用子类独有的方法
Person s2 = new Student();
Object s3 = new Student();
//一个类的实际对象是可以确定的,而指向这个对象的引用类型可以是任意类型
s2.run();//子类重写了父类的方法,执行子类的方法
s1.run();
//对象能执行哪些方法,主要看对象左边的类型,和右边关系不大!
((Student) s2).eat();
s1.eat();
}
@Override
public void run(){
System.out.println("son");
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("ear");
}
}
package demo05;
public class Person {
public void run(){
System.out.println("run");
}
}
多态注意事项
- 多态是方法的多态,属性没有多态
- 父类和子类,有联系,(String 与 Person 不能转换)
- 存在条件:继承关系,方法需要重写,父类引用指向子类对象!Father f1 = new Son();
哪些方法不能重写
1. static 方法,属于类,他不属于实例
2. final 常量:
3. private 方法,
instanceof
类型转换 | 引用类型的转换
类型转换:强制转换,自动转换

package demo05;
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//类型之间的转换:基本类型转换, 高低 64,32, 15
//高转低 ->强转 , 低转高不需要、
//父类代表高的,子代表低的
Person studet1 =new Student();
studet1.go();//红色报错
//student 将这个对象转换为Student 类型,我们就可以使用Student 类型方法了!
Student student = (Student)studet1;
student.go();//红色报错
//子类转换为父类,可能丢失自己的本来的一些方法
Student student2= new Student();
student2.go();
Person person = student2;
person.go();
/*
1.父类的引用指向子类的对象
2.把子类转换为父类,向上转型
3.把父类转换为子类,向下转型;强制转换可能丢失一些方法;
4.方便方法的调用,减少重复的代码
抽象:封装,继承,多态! 抽象类,接口
*/
// //object >String
// //Object >Person >Teacher
// //Object >Person >Student
// Object object = new Student();
// //System.out.printLn(X instanceof Y);//能不能编译通过,就是判断X 与Y 是否有父子关系
//
// System.out.println(object instanceof Student);
// System.out.println(object instanceof Person);
// System.out.println(object instanceof Object);
// System.out.println(object instanceof Teacher);
// System.out.println(object instanceof String);
//
// System.out.println("=================>>>>>>>>>>");
//
// Person person = new Student();
// System.out.println(person instanceof Student);
// System.out.println(person instanceof Person);
// System.out.println(person instanceof Object);
// System.out.println(person instanceof Teacher);
// // System.out.println(person instanceof String);
//
// System.out.println("=================>>>>>>>>>>");
// Student student = new Student();
// System.out.println(student instanceof Student);
// System.out.println(student instanceof Person);
// System.out.println(student instanceof Object);
// //System.out.println(student instanceof Teacher);
// // System.out.println(person instanceof String);
//
}
}
以上是关于java_父类的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章