java_注解与反射
Posted 偶像java练习生
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java_注解与反射相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
注解
-
springboot,mybatis .spring ,底层用的都是反射
-
注解还能给程序看
3. 注解单词是Annotation,注释是comment
什么是注解
内置注解
@Deprecated 方法以废弃,不鼓励程序员使用,有更好的替代方法
@Override 重写注解
@SuppressWarnings(“all”) 镇压警告

内置注解

元注解
@Target 目标注解,有方法:method ,all :全部,
@Retention 表示需要在什么级别保存该注释信息
@Documented 是否生成文档注释
@Inherited 表示子类可以注释父类中的注解

1.自定义注解都用RUNTIME
public enum ElementType {
/** Class, interface (including annotation type), or enum declaration */
TYPE, //class,interface
/** Field declaration (includes enum constants) */
FIELD,//字段
/** Method declaration */
METHOD,方法
/** Formal parameter declaration */
PARAMETER,参数
/** Constructor declaration */
CONSTRUCTOR,构造器
/** Local variable declaration */
LOCAL_VARIABLE,本地变量
/** Annotation type declaration */
ANNOTATION_TYPE,注解类型
/** Package declaration */
PACKAGE,包
/**
* Type parameter declaration
*
* @since 1.8
*/
TYPE_PARAMETER,类型参数
/**
* Use of a type
*
* @since 1.8
*/
TYPE_USE用户的一些参数
}
package com.kuang.lesson4;
import java.lang.annotation.*;
//测试元注解
@MyAnnotation
public class Test02 {
@MyAnnotation
public void test(){
}
}
//定义一个注解
//target 表示我们的注解可以用在哪个地方
@Target(value ={ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})//只能在方法上使用
//@Retention 表示我们的注解在什么地方才有效
// runtime 运行时有效 > class 编译成class 才有效>sources 源码才有效
@Retention(value = RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) //这个注解在运行的时候还有效
@Documented //表示是否将我们的注解生辰在JavaDoc 中
@Inherited //子类可以继承父类的注解
@interface MyAnnotation{
}
自定义注解
@Interface
代码案例
package com.kuang.lesson4;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
//自定义注解
public class Test03 {
//注解可以显示赋值,如果没有默认值,我们就必须给注解赋值
@MyAnnotation2(age=18,name="秦僵")
public void test(){
}
@MyAnnotation3("")
public void test2(){
}
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@interface MyAnnotation2{
//这个里面并不是方法
//注解的参数:参数类型+参数名()
String name() default ""; //如果有默认值则不用写name
int age() ;
int id() default -1;//如果默认值为-1,代表不存在,indexof,如果找不到就返回-1
String [] school() default {"西部开源","清华大学"};
}
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@interface MyAnnotation3{
//如果只有一个值可以省略其他的,直接填“ ”就可以了。value 才能省略
// @MyAnnotation3("")
// public void test2(){
//
// }
String value();
}
反射机制
什么是反射(Reflection )?
主要是指程序可以访问、检测和修改它本身状态或行为的一种能力
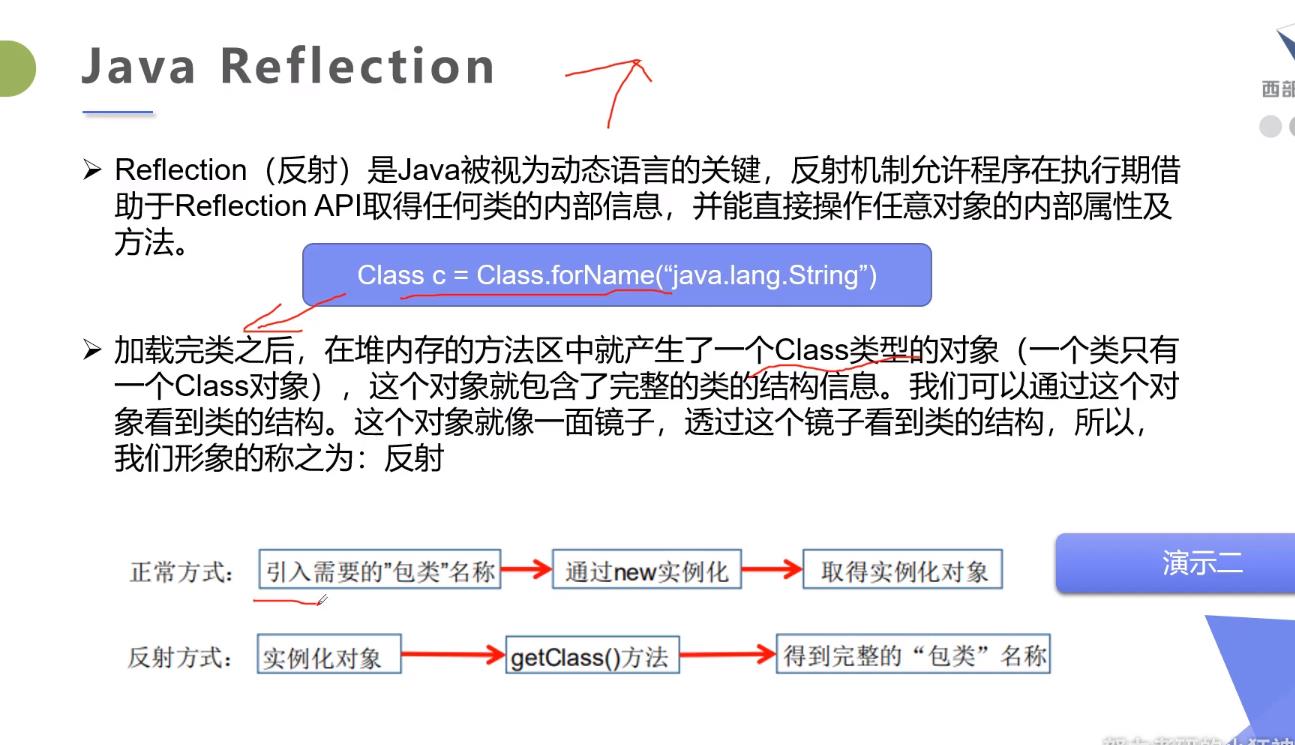
Java反射?
在Java运行时环境中,对于任意一个类,能否知道这个类有哪些属性和方法?对于任意一个对象,能否调用它的任意一个方法
Java反射机制主要提供了以下功能:
* 1.在运行时判断任意一个对象所属的类。
* 2.在运行时构造任意一个类的对象。
* 3.在运行时判断任意一个类所具有的成员变量和方法。
* 4.在运行时调用任意一个对象的方法。
- 有了反射使java 有动态性

静态与动态语言

Java Reflection
java 反射急着提供的功能



package com.kuang.reflection;
//什么叫反射
public class Test02 extends Object{
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//通过反射获取class
Class c1 = Class.forName("com.kuang.reflection.User");
System.out.println(c1);
Class c2 = Class.forName("com.kuang.reflection.User");
Class c3 = Class.forName("com.kuang.reflection.User");
//一个类在内存中只有一个Class 对象
//一个类被加载后,类的整个结构都会被分装在Class对象中
//如果hashCode 一样,他们就是同一个类,
System.out.println(c2.hashCode());
System.out.println(c3.hashCode());
System.out.println(c1.hashCode());
//class com.kuang.reflection.User
//1163157884
//1163157884
//1163157884
}
}
//
//实体类 pojo,entity
class User{
private String name;
private int id;
private int age;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, int id, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.id = id;
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\\'' +
", id=" + id +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
Class 类
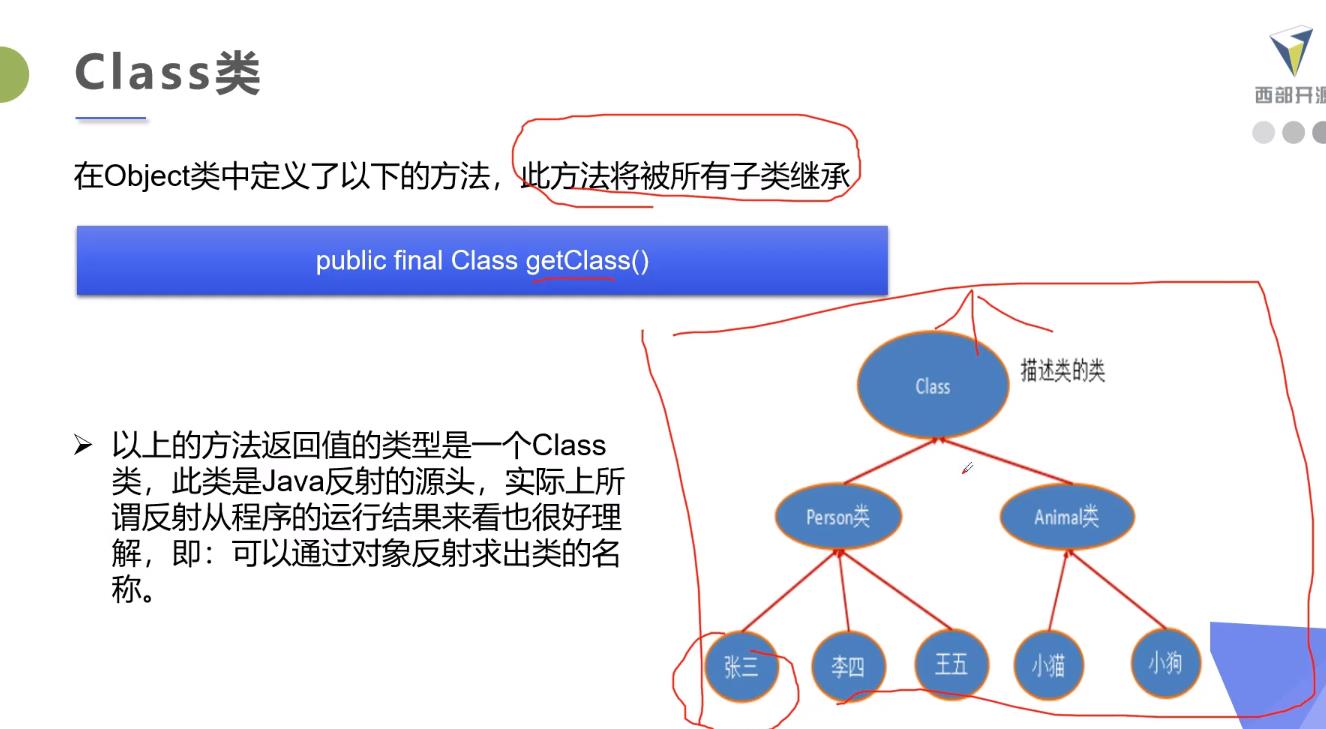

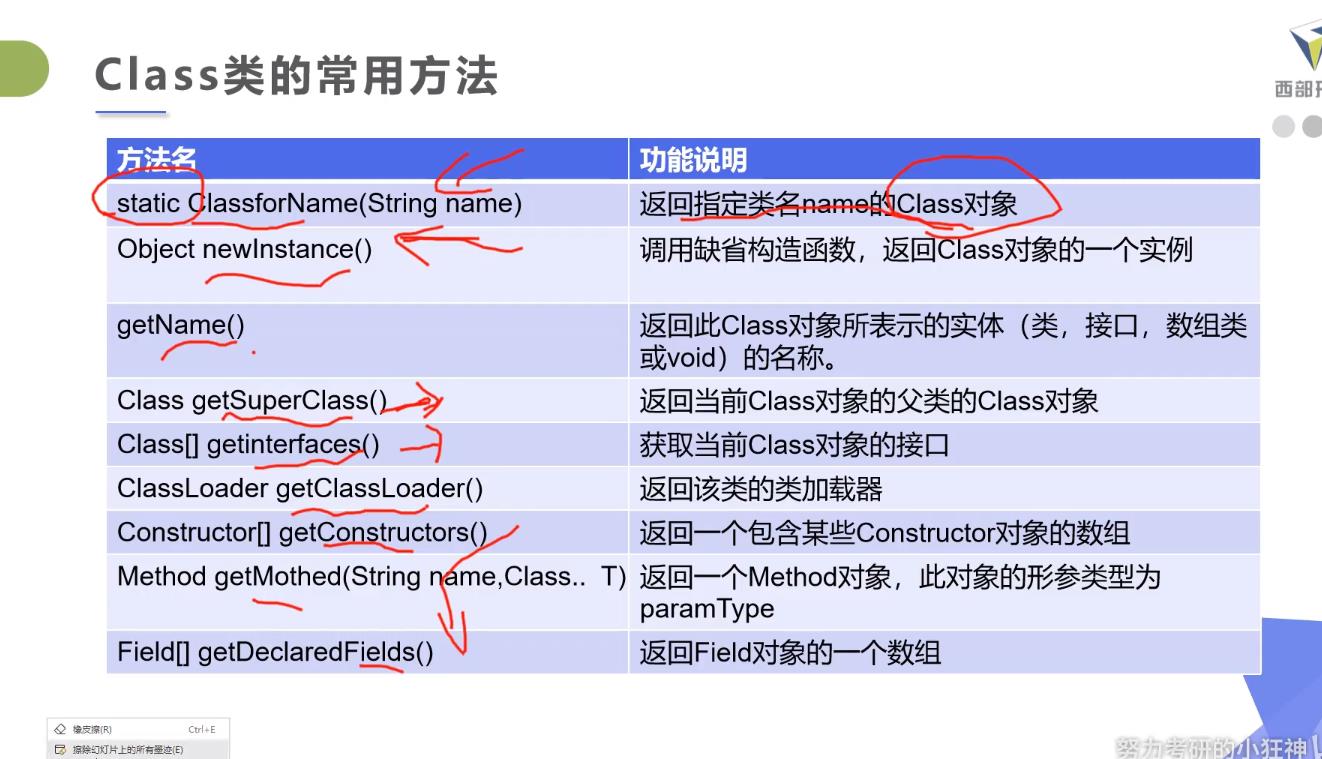

package com.kuang.reflection;
//测试class 类的创建方式有哪些
public class Test03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Person person = new Student();
System.out.println("这个人是:"+person.name);
//方式1 :通过对象获得
Class c1 = person.getClass();
System.out.println(c1.hashCode());
//方式2: forName 获得
Class c2 = Class.forName("com.kuang.reflection.Student");
System.out.println(c2.hashCode());
//方式3:通过类名.class 获得
Class<Student> c3 = Student.class;
System.out.println(c3.hashCode());
//方式4:基本内置类型的包装类都有一个type 属性
Class<Integer> c4 = Integer.TYPE;
System.out.println(c4);
//获得父类类型
Class c5 = c1.getSuperclass();
System.out.println(c5);
}
}
class Person{
String name;
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Person() {
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\\'' +
'}';
}
}
class Student extends Person{
public Student(){
this.name = "学生";
}
}
class Teacher extends Person{
public Teacher(){
this.name = "老师";
}
}
输出结果:
这个人是:学生
1163157884
1163157884
1163157884
int
class com.kuang.reflection.Person
Process finished with exit code 0
那些类型可以有class 对象
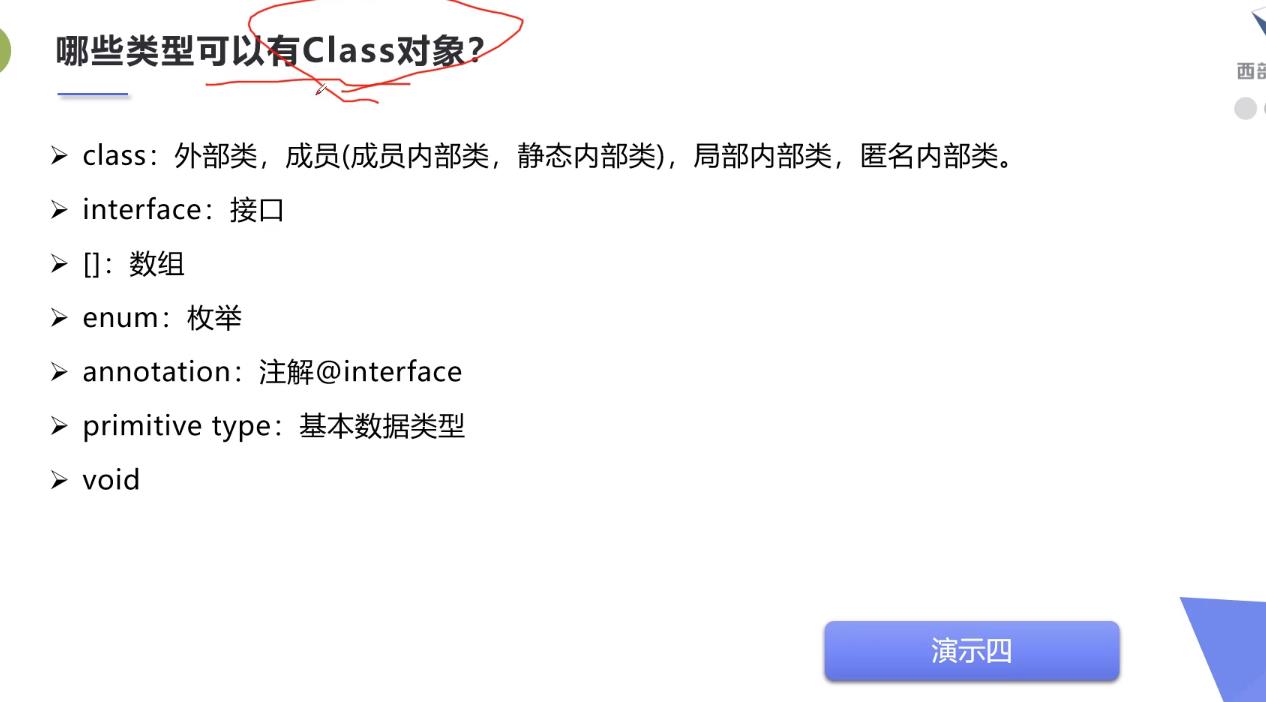
package com.kuang.reflection;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.util.Comparator;
//所有类型的Class
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class c1 = Object.class;//接口也可以获取类的对象
Class c2 = Comparator.class;//一维数组也可以获取类的对象
Class c3 = String[].class;//二维数组也可以获取类的对象
Class c4 = int[][].class;//注解类型也可以获取class
Class c5 = Override.class;//枚举类型
Class c6 = ElementType.class;//基本数据类型
Class c7 = Integer.class;//void 类型
Class c8 = void.class;//Class 类型
Class c9 = Class.class;
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
System.out.println(c3);
System.out.println(c4);
System.out.println(c5);
System.out.println(c6);
System.out.println(c7);
System.out.println(c8);
System.out.println(c9);
//只要元素类型与维度一样,就是同一个Class
int [] a = new int[10];
int[] b = new int[100];
System.out.println(a.getClass().hashCode());
System.out.println(b.getClass().hashCode());
}
}
返回结果:
class java.lang.Object
interface java.util.Comparator
class [Ljava.lang.String;
class [[I
interface java.lang.Override
class java.lang.annotation.ElementType
class java.lang.Integer
void
class java.lang.Class
1163157884
1163157884
Process finished with exit code 0
以上是关于java_注解与反射的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章