Spring源码剖析-Autowired自动注入原理
Posted 墨家巨子@俏如来
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring源码剖析-Autowired自动注入原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
这篇文章接上一篇文章属性注入讲一讲 @Autowired 注解的实现源码,这个也是面试被问的比较多的。
Bean的后置处理器
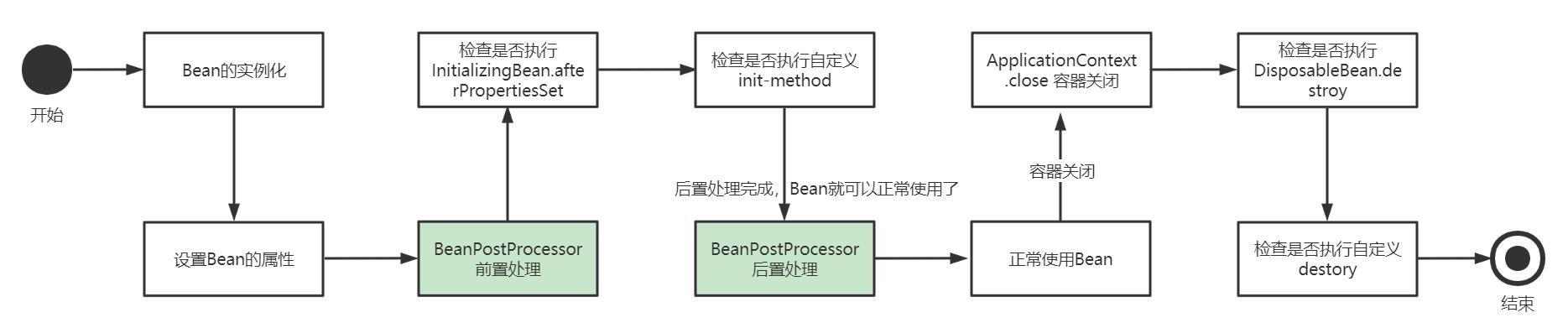
BeanPostProcessor 通常被叫做Bean的后置处理器,是Spring提供给我们的扩展接口,它允许我们在Bean调用初始化方法前,后对 Bean 做一些扩展逻辑。BeanPostProcessor提供了postProcessBeforeInitialization 前置处理和postProcessAfterInitialization后置处理 两个方法,我们可以实现该接口,复写这两个方法来定义自己的逻辑,Bean的生命周期如下:
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
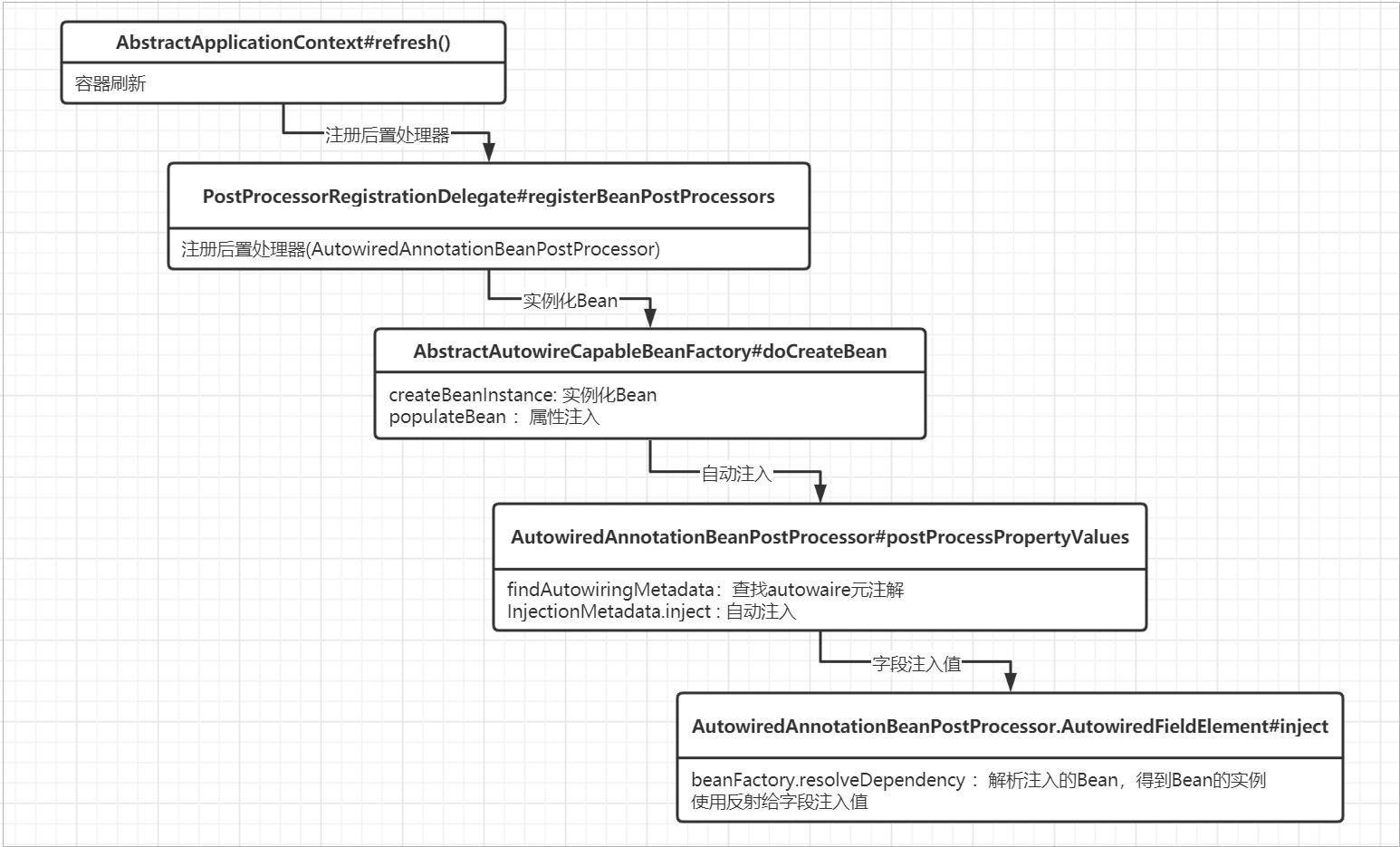
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor是用来处理@Autowired注解注入的后置处理器,这里先上一个 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的工作流程图,后面可以根据这个图来看源码。
注册AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor是用来处理@Autowired注解注入的后置处理器,它是在 AbstractApplicationContext#refresh()容器刷新流程中registerBeanPostProcessors() 方法中完成注册,源码如下
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
Object var1 = this.startupShutdownMonitor;
synchronized(this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
this.prepareRefresh();
//【第一步】Bean的加载和注册
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory();
this.prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
this.postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
this.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
//【第二步】注册Bean后置处理器,注册到DefaultListableBeanFactory(它的父类)中的一个List存放后置处理器
this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
this.initMessageSource();
this.initApplicationEventMulticaster();
this.onRefresh();
this.registerListeners();
//【第三步】实例化单利且lazy-init=false的Bean
this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
this.finishRefresh();
} catch (BeansException var9) {
if (this.logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
this.logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - cancelling refresh attempt: " + var9);
}
this.destroyBeans();
this.cancelRefresh(var9);
throw var9;
} finally {
this.resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}
上面标记了三个步骤:
- ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = this.obtainFreshBeanFactory() : 加载解析注册Bean
- this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory) : 注册BeanPostProcessors后置处理器
- this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory):实例化Bean 以及属性注入
我们现在来看一下 this.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory) 注册BeanPostProcessors后置处理器的源码
protected void registerBeanPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, this);
}
通过PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate去注册
public static void registerBeanPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, AbstractApplicationContext applicationContext) {
String[] postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Register BeanPostProcessorChecker that logs an info message when
// a bean is created during BeanPostProcessor instantiation, i.e. when
// a bean is not eligible for getting processed by all BeanPostProcessors.
//后置处理器个数
int beanProcessorTargetCount = beanFactory.getBeanPostProcessorCount() + 1 + postProcessorNames.length;
//把BeanPostProcessorChecker后置处理器添加IOC容器中 , 它是用来实例化期间创建 bean 时记录信息消息,当 bean 没有资格被所有 BeanPostProcessor 处理时。
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessorChecker(beanFactory, beanProcessorTargetCount));
//实现 PriorityOrdered、 // Ordered 和其余的 BeanPostProcessor。
// Separate between BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
//实现了 priorityOrdered 接口的优先级最高的处理器,PriorityOrdered是Ordered接口的扩展,表示优先级排序:
// PriorityOrdered对象总是在普通Ordered对象之前应用
List<BeanPostProcessor> priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
//框架内部后置处理器
List<BeanPostProcessor> internalPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
//具有排序的后置处理器,实现了Ordered 接口,order值越小,越先执行
List<String> orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
//没有指定顺序的后置处理器
List<String> nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
//得到后置处理器Bean的实例
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor在这里被实例化
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
//如果是实现了 PriorityOrdered 的后置处理器,添加到priorityOrderedPostProcessors集合中
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
//合并BeanDefinition的后置处理器
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
//添加实现了 Ordered 的后置处理器
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
//没有任何顺序的后置处理器
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
//首先,注册实现 PriorityOrdered 的 BeanPostProcessors。
//后置处理器排序
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
//注册priorityOrdered后置处理器
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, priorityOrderedPostProcessors);
// Next, register the BeanPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
//接下来,注册实现 Ordered 的 BeanPostProcessors。
List<BeanPostProcessor> orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
//处理实现了 ordered的后置处理器
for (String ppName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
//得到后置处理器Bean
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
//添加到集合中
orderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
//排序后置处理器
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
//注册后置初期
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, orderedPostProcessors);
// Now, register all regular BeanPostProcessors.
//现在,注册所有常规 BeanPostProcessor。
List<BeanPostProcessor> nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
//
for (String ppName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
//得到Bean的实例
BeanPostProcessor pp = beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanPostProcessor.class);
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(pp);
if (pp instanceof MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor) {
internalPostProcessors.add(pp);
}
}
//注册常规后置处理器
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, nonOrderedPostProcessors);
// Finally, re-register all internal BeanPostProcessors.
sortPostProcessors(internalPostProcessors, beanFactory);
//最后,重新注册所有内部 BeanPostProcessor。
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory, internalPostProcessors);
// Re-register post-processor for detecting inner beans as ApplicationListeners,
// moving it to the end of the processor chain (for picking up proxies etc).
//ApplicationListener检测器,也是一个BeanPostProcessor
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new ApplicationListenerDetector(applicationContext));
}
这里根据类型:BeanPostProcessor.class 找到了所有的后置处理器,然后通过beanFactory.getBean创建Bean的实例,根据优先级依次注册到AbstractBeanFactory中的List<BeanPostProcessor> beanPostProcessors = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<>() 集合中 , 注册顺序如下:
- 注册实现了PriorityOrdered 接口的优先级最高的后置处理器
- 注册实现了 Ordered接口的有序的后置处理器
- 注册常规后置处理器
- 注册内部使用的后置处理器MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor
对于AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor而言,它是属于PriorityOrdered的范畴,优先被注册,我们来看一下他的构造器
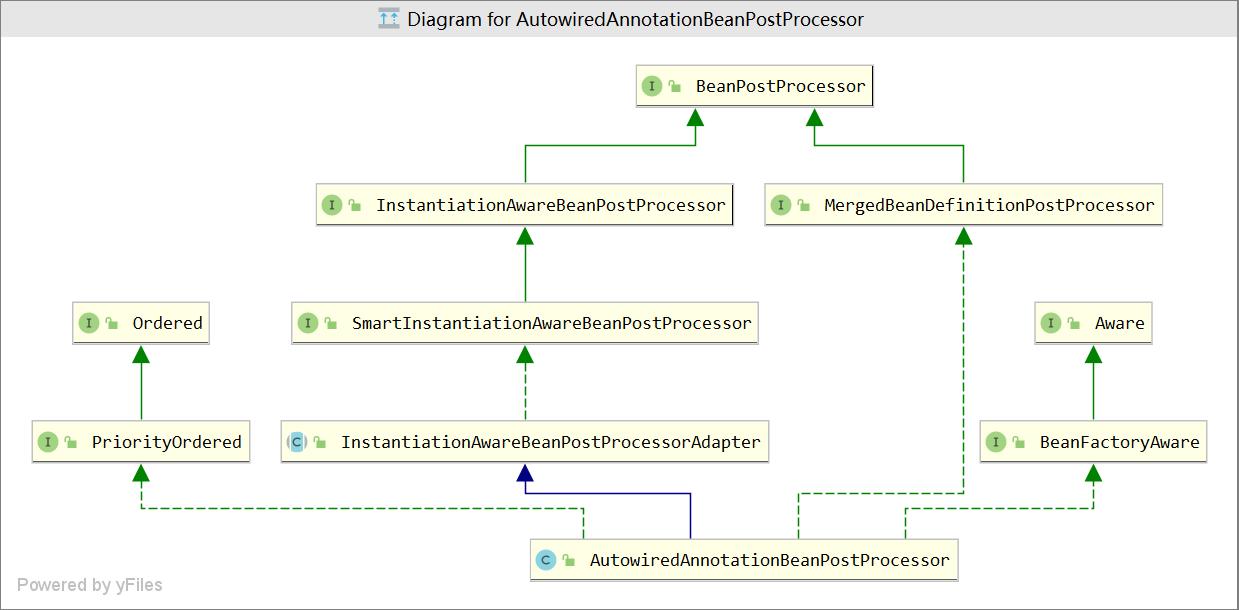
public class AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor extends InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessorAdapter
implements MergedBeanDefinitionPostProcessor, PriorityOrdered, BeanFactoryAware {
...省略...
/**
* Create a new AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
* for Spring's standard {@link Autowired} annotation.
* <p>Also supports JSR-330's {@link javax.inject.Inject} annotation, if available.
*/
//为 Spring 的标准Autowired注释创建一个新的 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() {
//增加要注入的注解类型
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Autowired.class);
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add(Value.class);
try {
//支持 JSR-330 的javax.inject.Inject注释
this.autowiredAnnotationTypes.add((Class<? extends Annotation>)
ClassUtils.forName("javax.inject.Inject", AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class.getClassLoader()));
logger.info("JSR-330 'javax.inject.Inject' annotation found and supported for autowiring");
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// JSR-330 API not available - simply skip.
}
}
可以看得出来,它支持 Autowired 和 Value 两种注解的处理,同时支持 JSR-330 的javax.inject.Inject注释下面是继承体系图:
属性注入
上面我们知道了 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 是在什么时候被实例化和被注册到IOC容器中,接下来我们来分析一下 AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 的工作流程。
前面文章我们分析过IOC启动流程,在refresh()中
- 调用 obtainFreshBeanFactory(); 对Bean进行加载,解析,注册
- 调用registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory); 注册后置处理器
- 调用 this.finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory); 对单利Bean进行创建。Bean创建成功后,会进行属性注入, 属性注入是在 AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory#populateBean 中完成。
我们今天要研究的@Autowire 注解的处理就是在populateBean方法中完成的。
protected void populateBean(String beanName, RootBeanDefinition mbd, @Nullable BeanWrapper bw) {
//省略....
if (hasInstAwareBpps) {
//得到所有的后置处理器
for (BeanPostProcessor bp : getBeanPostProcessors()) {
//如果是InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor类型
if (bp instanceof InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) {
InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor ibp = (InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor) bp;
//后置处理器处理属性【AutowireAnnotationBeanPostProcess就是在这里调用】
pvs = ibp.postProcessPropertyValues(pvs, filteredPds, bw.getWrappedInstance(), beanName);
if (pvs == null) {
return;
}
}
}
}
处理autowired
下面是:AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#postProcessPropertyValues 源码
@Override
public PropertyValues postProcessPropertyValues(
PropertyValues pvs, PropertyDescriptor[] pds, Object bean, String beanName) throws BeanCreationException {
//查找找 autowire 元数据,利用反射根据bean的class得到bean的元注解信息
InjectionMetadata metadata = findAutowiringMetadata(beanName, bean.getClass(), pvs);
try {
//注入
metadata.inject(bean, beanName, pvs);
}
catch (BeanCreationException ex) {
throw ex;
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new BeanCreationException(beanName, "Injection of autowired dependencies failed", ex);
}
return pvs;
}
这里首先通过findAutowiringMetadata方法查找autowire的元注解信息InjectionMetadata,然后调用InjectionMetadata.inject 执行注入,跟一下findAutowiringMetadata方法,
查找元注解
AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor#findAutowiringMetadata 源码如下
private InjectionMetadata findAutowiringMetadata(String beanName, Class<?> clazz, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) {
// Fall back to class name as cache key, for backwards compatibility with custom callers.
//获取Bean的名字,如果没有以类名作为名字
String cacheKey = (StringUtils.hasLength(beanName) ? beanName : clazz.getName());
//从 自动注入元数据缓存map中查找InjectionMetadata
// Quick check on the concurrent map first, with minimal locking.
InjectionMetadata metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
synchronized (this.injectionMetadataCache) {
metadata = this.injectionMetadataCache.get(cacheKey);
if (InjectionMetadata.needsRefresh(metadata, clazz)) {
if (metadata != null) {
metadata.clear(pvs);
}
//构建自动装配元数据,利用反射获取
metadata = buildAutowiringMetadata(clazz);
//缓存自动装配元数据
this.injectionMetadataCache.put(cacheKey, metadata);
}
}
}
return metadata;
}
查找元注解比较简单,先从缓存中获取,如果缓存中没有就调用 buildAutowiringMetadata 查找元注解信息然后加入缓存。
private InjectionMetadata buildAutowiringMetadata(final Class<?> clazz) {
LinkedList<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> elements = new LinkedList<>();
Class<?> targetClass = clazz;
do {
final LinkedList<InjectionMetadata.InjectedElement> currElements = new LinkedList<>();
ReflectionUtils.doWithLocalFields(targetClass, field -> {
//查找@autowired注解的属性,以及要注入的对象
AnnotationAttributes ann = findAutowiredAnnotation(field);
if (ann != null) {
if (Modifier.isStatic(field.getModifiers())) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Autowired annotation is not supported on static fields: " + field);
}
return;
}
boolean required = determineRequiredStatus(ann);
//添加到 currElements 集合中
currElements.add(new AutowiredFieldElement(field, required));
}
});
...省略...,
//把注解封的属性封装成jectionMetadata
return new InjectionMetadata(clazz, elements);
}
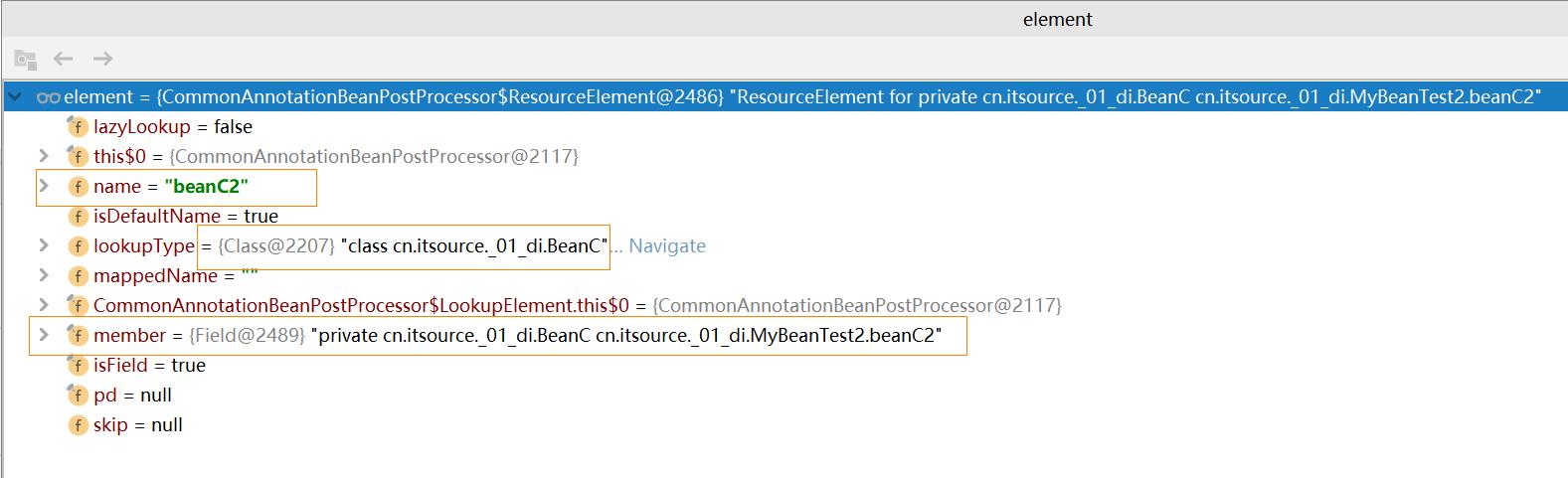
根据Bean的class使用反射查找到Bean中的@Autowire注解信息,以及注入的Bean ,创建成 一个一个的AutowiredFieldElement ,封装到InjectionMetadata 返回。Element结构如下:
属性注入
我们接着看一下 InjectionMetadata#inject 注入方法
public void inject(Object target, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
//得到要注入的属性集合
Collection<InjectedElement> checkedElements = this.checkedElements;
Collection<InjectedElement> elementsToIterate =
(checkedElements != null ? checkedElements : this.injectedElements);
if (!elementsToIterate.isEmpty()) {
boolean debug = logger.isDebugEnabled();
for (InjectedElement element : elementsToIterate) {
if (debug) {
logger.debug("Processing injected element of bean '" + beanName + "': " + element);
}
//调用InjectedElement的inject方法注入
element.inject(target, beanName, pvs);
}
}
}
这里得到了Bean的依赖的属性,即InjectedElement 集合,然后一个一个调用inject进行注入值。代码来到:AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.AutowiredFieldElement#inject
@Override
protected void inject(Object bean, @Nullable String beanName, @Nullable PropertyValues pvs) throws Throwable {
Field field = (Field) this.member;
Object value;
if (this.cached) {
value = resolvedCachedArgument(beanName, this.cachedFieldValue);
}
else {
//DependencyDescriptor 依赖描述符
DependencyDescriptor desc = new DependencyDescriptor(field, this.required);
desc.setContainingClass(bean.getClass());
Set<String> autowiredBeanNames = new LinkedHashSet<>(1);
Assert.state(beanFactory != null, "No BeanFactory available");
//类型转换器
TypeConverter typeConverter = beanFactory.getTypeConverter();
try {
//得到容器中的Bean实例
value = beanFactory.resolveDependency(desc, beanName, autowiredBeanNames, typeConverter);
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
throw new UnsatisfiedDependencyException(null, beanName, new InjectionPoint(field), ex);
}
synchronized (this) {
if (!this.cached) {
//走缓存流程
if (value != null || this.required) {
this.cachedFieldValue = desc;
//注册依赖的Bean
registerDependentBeans(beanName, autowiredBeanNames);
if (autowiredBeanNames.size() == 1) {
String autowiredBeanName = autowiredBeanNames.iterator().next();
if (beanFactory.containsBean(autowiredBeanName) &&
beanFactory<以上是关于Spring源码剖析-Autowired自动注入原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章