Fragment 生命周期源码分析
Posted 进击的包籽
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Fragment 生命周期源码分析相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
- 本次分析Fragment 1.3.4版本,不同版本源码会不同!
- Fragment官方文档
dependencies {
val fragment_version = "1.3.4"
// Java language implementation
implementation("androidx.fragment:fragment:$fragment_version")
// Kotlin
implementation("androidx.fragment:fragment-ktx:$fragment_version")
// Testing Fragments in Isolation
debugImplementation("androidx.fragment:fragment-testing:$fragment_version")
}
- Fragment 无论是单独使用还是配合Viewpager,对于Android开发来说非常熟悉了,但生命周期,一般就网上看到的一张图,想必大家也经常看到;
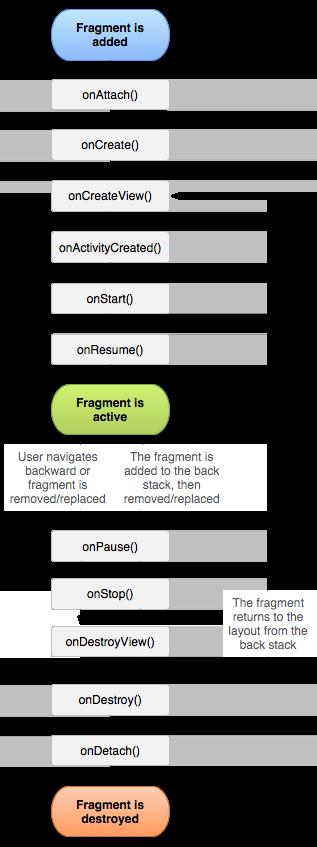
- 那Fragment的生命周期在什么时候调用的,commit之后怎么走到生命周期的每一个方法,需要看源码才知道,本文就此分析。
1.supportFragmentManager
- 只有使用 FragmentActivity 才有 supportFragmentManager 。
override fun onCreate(savedInstanceState: Bundle?) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState)
setContentView(R.layout.test_activity3_activity)
if (savedInstanceState == null) {
supportFragmentManager.beginTransaction()
.replace(R.id.container, TestActivity3Fragment.newInstance())
.commitNow()
}
}
1.1 getSupportFragmentManager
- FragmentActivity里面的 mFragments 可不是Fragment数组哦,他是 FragmentController ,这个很重要,先记住他。
/* FragmentActivity类 */
//创建FragmentController
final FragmentController mFragments = FragmentController.createController(new HostCallbacks());
/**
* Return the FragmentManager for interacting with fragments associated
* with this activity.
*/
@NonNull
public FragmentManager getSupportFragmentManager() {
return mFragments.getSupportFragmentManager();
}
1.2 FragmentController类
- new HostCallbacks() 传进去,再获取 SupportFragmentManager。
public class FragmentController {
private final FragmentHostCallback<?> mHost;
/**
* Returns a {@link FragmentController}.
*/
@NonNull
public static FragmentController createController(@NonNull FragmentHostCallback<?> callbacks) {
return new FragmentController(checkNotNull(callbacks, "callbacks == null"));
}
private FragmentController(FragmentHostCallback<?> callbacks) {
mHost = callbacks;
}
/**
* 通过mHost获取FragmentManager
* Returns a {@link FragmentManager} for this controller.
*/
@NonNull
public FragmentManager getSupportFragmentManager() {
return mHost.mFragmentManager;
}
}
1.3 FragmentHostCallback类
- FragmentHostCallback 里获取 mFragmentManager。
- FragmentManagerImpl 继承FragmentManager,但什么都没做。
public abstract class FragmentHostCallback<E> extends FragmentContainer {
@Nullable private final Activity mActivity;
@NonNull private final Context mContext;
@NonNull private final Handler mHandler;
private final int mWindowAnimations;
final FragmentManager mFragmentManager = new FragmentManagerImpl();
}
//继承FragmentManager,但什么都没做
class FragmentManagerImpl extends FragmentManager {
}
- 到此就获取一个fragmentManager。
2.beginTransaction
- 每次处理Fragment的事务都是新建一个 BackStackRecord 回退栈 ,只能用一次。
@NonNull
public FragmentTransaction beginTransaction() {
return new BackStackRecord(this);
}
2.1 FragmentTransaction类
- BackStackRecord 类是继承 抽象类FragmentTransaction,这里有非常重要的各个OP常量,还有内部类OP。
- add,hide,remove等操作也是在这个类,他们都会封装进Op,用数组mOps 保存。
public abstract class FragmentTransaction {
static final int OP_NULL = 0;
static final int OP_ADD = 1;
static final int OP_REPLACE = 2;
static final int OP_REMOVE = 3;
static final int OP_HIDE = 4;
static final int OP_SHOW = 5;
static final int OP_DETACH = 6;
static final int OP_ATTACH = 7;
static final int OP_SET_PRIMARY_NAV = 8;
static final int OP_UNSET_PRIMARY_NAV = 9;
static final int OP_SET_MAX_LIFECYCLE = 10;
.
.
ArrayList<Op> mOps = new ArrayList<>();
}
2.2 Op类
- Op这个类对于后面add,hide,remove等操作很重要。
static final class Op {
int mCmd;
Fragment mFragment;
int mEnterAnim;
int mExitAnim;
int mPopEnterAnim;
int mPopExitAnim;
Lifecycle.State mOldMaxState;
Lifecycle.State mCurrentMaxState;
Op() {
}
.
.
}
2.3 BackStackRecord类
- 这个类就是真正执行提交事务的类,提交事务会把自己一起传给FragmentManager。
- 还实现了 FragmentManager.OpGenerator 接口。
final class BackStackRecord extends FragmentTransaction implements
FragmentManager.BackStackEntry, FragmentManager.OpGenerator {
final FragmentManager mManager;
@Override
public int commit() {
return commitInternal(false);
}
@Override
public int commitAllowingStateLoss() {
return commitInternal(true);
}
@Override
public void commitNow() {
disallowAddToBackStack();
mManager.execSingleAction(this, false);
}
@Override
public void commitNowAllowingStateLoss() {
disallowAddToBackStack();
mManager.execSingleAction(this, true);
}
}
3.add,hide,replace,remove
3.1 封装,addOp
- 这里就分析一个replace,其他也是差不多的。
- 这里做的就是把要替换的控件id,fragment,tag,操作对应的常量封装进Op类里。
/*FragmentTransaction*/
/**
* Calls {@link #replace(int, Fragment, String)} with a null tag.
*/
@NonNull
public FragmentTransaction replace(@IdRes int containerViewId, @NonNull Fragment fragment) {
return replace(containerViewId, fragment, null);
}
@NonNull
public FragmentTransaction replace(@IdRes int containerViewId, @NonNull Fragment fragment,
@Nullable String tag) {
//判断数据有效性
if (containerViewId == 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Must use non-zero containerViewId");
}
doAddOp(containerViewId, fragment, tag, OP_REPLACE);
return this;
}
void doAddOp(int containerViewId, Fragment fragment, @Nullable String tag, int opcmd) {
.
.
//封装进Op
addOp(new Op(opcmd, fragment));
}
/**
* mOps 数组保持着这些操作
* 把fragment进入退出动画一起加上,
* 可以去setCustomAnimations方法看
*/
void addOp(Op op) {
mOps.add(op);
op.mEnterAnim = mEnterAnim;
op.mExitAnim = mExitAnim;
op.mPopEnterAnim = mPopEnterAnim;
op.mPopExitAnim = mPopExitAnim;
}
4.commit
4.1 四种提交方式
- 提交事务有四种,分别是,先不分析四种区别,不是本次重点。
1. commit()
2. commitAllowingStateLoss()
3. commitNow()
4. commitNowAllowingStateLoss()
4.2 提交事务
- commit 只能操作一次,一次就把add,hide,replace等操作一起提交。
- 提交事务其实就是把自己一起丢给FragmentManager执行。
@Override
public int commit() {
return commitInternal(false);
}
int commitInternal(boolean allowStateLoss) {
//只能commit一次,否则抛异常
if (mCommitted) throw new IllegalStateException("commit already called");
if (FragmentManager.isLoggingEnabled(Log.VERBOSE)) {
Log.v(TAG, "Commit: " + this);
LogWriter logw = new LogWriter(TAG);
PrintWriter pw = new PrintWriter(logw);
dump(" ", pw);
pw.close();
}
mCommitted = true;
//是否加入回退栈
if (mAddToBackStack) {
// 放入回退栈标记的index
mIndex = mManager.allocBackStackIndex();
} else {
mIndex = -1;
}
//操作入队
mManager.enqueueAction(this, allowStateLoss);
return mIndex;
}
4.3 handler 发送
- commit 是在主线程异步执行,就是通过handler执行。
/*FragmentManager*/
//保存操作
private final ArrayList<OpGenerator> mPendingActions = new ArrayList<>();
void enqueueAction(@NonNull OpGenerator action, boolean allowStateLoss) {
if (!allowStateLoss) {
if (mHost == null) {
if (mDestroyed) {
//FragmentManager 已经 销毁
throw new IllegalStateException("FragmentManager has been destroyed");
} else {
//FragmentManager 还没绑定
throw new IllegalStateException("FragmentManager has not been attached to a "
+ "host.");
}
}
checkStateLoss();
}
//加锁
synchronized (mPendingActions) {
if (mHost == null) {
//commitAllowingStateLoss会走这里
if (allowStateLoss) {
// This FragmentManager isn't attached, so drop the entire transaction.
return;
}
throw new IllegalStateException("Activity has been destroyed");
}
//加入到数组
mPendingActions.add(action);
//最终来到这里
scheduleCommit();
}
}
- 到这终于看到handler了,用post(Runnable)发送出去。
void scheduleCommit() {
synchronized (mPendingActions) {
boolean postponeReady =
mPostponedTransactions != null && !mPostponedTransactions.isEmpty();
boolean pendingReady = mPendingActions.size() == 1;
if (postponeReady || pendingReady) {
//handler处理
mHost.getHandler().removeCallbacks(mExecCommit);
mHost.getHandler().post(mExecCommit);
updateOnBackPressedCallbackEnabled();
}
}
}
4.4 执行execPendingActions
private Runnable mExecCommit = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
execPendingActions(true);
}
};
/**
* Only call from main thread!
*/
boolean execPendingActions(boolean allowStateLoss) {
ensureExecReady(allowStateLoss);
boolean didSomething = false;
//把事务放入临时变量
while (generateOpsForPendingActions(mTmpRecords, mTmpIsPop)) {
mExecutingActions = true;
try {
//优化整理事务
removeRedundantOperationsAndExecute(mTmpRecords, mTmpIsPop);
} finally {
cleanupExec();
}
didSomething = true;
}
...
return didSomething;
}
4.5 整理事务
- removeRedundantOperationsAndExecute 有一大段注释,注释的意思就是说这方法删除冗余的操作,合并重复的操作,就是优化整理
- 重点看到 record.expandOps 方法。
- 拿出 Op 里面记录的操作,对不同操作处理,added增加或者移除,替换就是先移除再添加,具体可以看源码,这里就不贴全部了,有点多。
/*FragmentManager*/
/**
* Remove redundant BackStackRecord operations and executes them. This method merges operations
* of proximate records that allow reordering. See
...
*/
private void removeRedundantOperationsAndExecute(@NonNull ArrayList<BackStackRecord> records,
@NonNull ArrayList<Boolean> isRecordPop) {
...
executeOpsTogether(records, isRecordPop, startIndex, recordNum);
...
private void executeOpsTogether(@NonNull ArrayList<BackStackRecord> records,
@NonNull ArrayList<Boolean> isRecordPop, int startIndex, int endIndex) {
//展开整理
oldPrimaryNav = record.expandOps(mTmpAddedFragments, oldPrimaryNav);
...
}
//展开整理
Fragment expandOps(ArrayList<Fragment> added, Fragment oldPrimaryNav) {
for (int opNum = 0; opNum < mOps.size(); opNum++) {
final Op op = mOps.get(opNum);
switch (op.mCmd) {
//添加
case OP_ADD:
case OP_ATTACH:
added.add(op.mFragment);
break;
//移除
case OP_REMOVE:
case OP_DETACH: {
added.remove(op.mFragment);
if (op.mFragment == oldPrimaryNav) {
mOps.add(opNum, new Op(OP_UNSET_PRIMARY_NAV, op.mFragment));
opNum++;
oldPrimaryNav = null;
}
}
break;
//替换
case OP_REPLACE: {
...
}
break;
case OP_SET_PRIMARY_NAV: {
...
}
break;
}
}
return oldPrimaryNav;
}
4.6 执行事务
- 这里的FragmentManager.executeOps方法,再进入 BackStackRecord.executeOps方法,根据Op信息,处理再回到FragmentManager.moveToState方法。
/*FragmentManager*/
private void executeOpsTogether(@NonNull ArrayList<BackStackRecord> records,
@NonNull ArrayList<Boolean> isRecordPop, int startIndex, int endIndex) {
...
executeOps(records, isRecordPop, startIndex, endIndex);
...
}
private static void executeOps(@NonNull ArrayList<BackStackRecord> records,
@NonNull ArrayList<Boolean> isRecordPop, int startIndex, int endIndex) {
..
record.executeOps();
/*BackStackRecord*/
void executeOps() {
final int numOps = mOps.size();
for (int opNum = 0; opNum < numOps; opNum++) {
final Op op = mOps.get(opNum);
final Fragment f = op.mFragment;
...
switch (op.mCmd) {
case OP_ADD:
f.