Android源码分析 SystemServer 进程启动
Posted 小图包
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android源码分析 SystemServer 进程启动相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
最近学习进阶解密 总结SystemService启动 加深理解记忆
SystemService启动之前,我们先看一下 Zygote进程做了些什么
Zygote进程
在android系统中,DVM和ART、应用程序进程以及运行系统的关键服务SystemServer进程都是有Zygote进程来创建的,我们也将它称为孵化器。它通过fork的形式来创建应用程序进程和SystemServer进程,犹豫Zygote进程在启动时会创建DVM或者ART,因此通过fork而创建的应用程序进程和SystemServer进程可以在内部获取一个DVM或者ART的实例副本。Zygote进程启动共做了如下几件事:
1 创建AppRuntime并调用其start方法,启动Zygote进程;
2 创建Java虚拟机并为Java虚拟机注册JNI方法;
3 通过JNI调用ZygoteInit的main函数进入Zygote的Java框架层;
4 通过registerZygoteSocket方法创建服务端Socket,并通过runSelectLoop方法等待AMS的请求来5 创建新的应用程序进程;
6 启动SystemServer进程。
如下是时序图
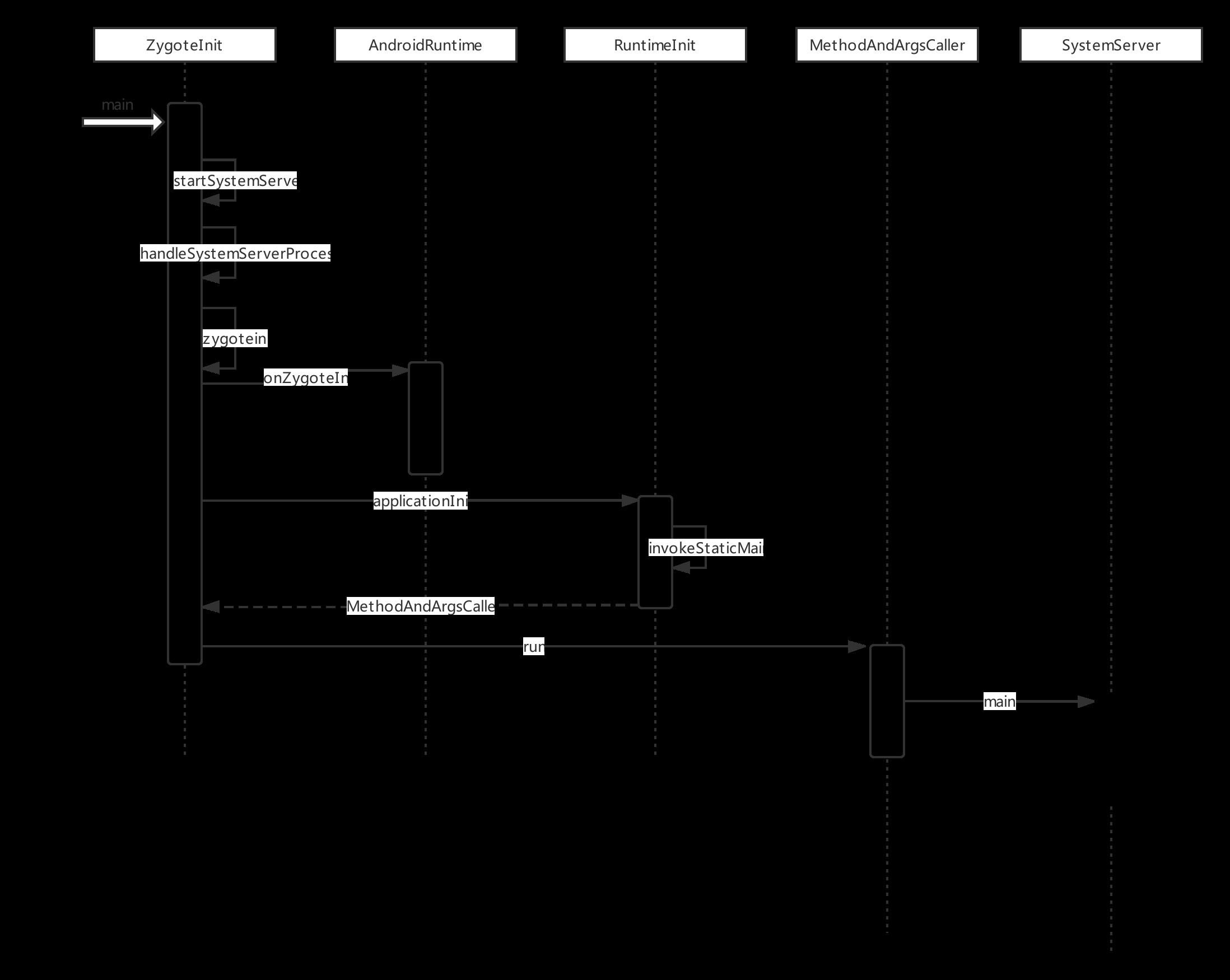
一 Zygote 开创 Java 框架层入口
启动 Zygote 的入口,其实就是 ZygoteInit.java ,我们看它的 main 函数实现。
//com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.java
public static void main(String argv[]) {
....
try {
1. 创建服务端的 Socket ,名称为 "zygote"
zygoteServer.registerServerSocket(socketName);
if (!enableLazyPreload) {
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygotePreload");
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
2 用来预加载资源
preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygotePreload
} else {
Zygote.resetNicePriority();
}
...
if (startSystemServer) {
3. 启动 SystemServer 进程
startSystemServer(abiList, socketName, zygoteServer);
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
4. 等待 AMS 请求
zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
//清理或者关闭对应的 Socket
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
} catch (Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
caller.run();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
}
}
ZygoteInit.main() 做了做了四件事
1 创建一个 Server 端为 ”zygote“ 名称的 Socket,用于等待 AMS 请求 Zygote 来创建新的应用程序进程。
2 预处理加载类跟资源。
3 根据 JNI 传递过来的信息来判断是否启动 SystemServer
4 等待 AMS 请求,用于创建新的应用程序进程。
1. zygoteServer.registerServerSocket(socketName);
看下registerServerSocket做了什么
//com.android.internal.os ZygoteServer.java
void registerServerSocket(String socketName) {
if (mServerSocket == null) {
int fileDesc;
1 拿到 Socket 名称
final String fullSocketName = ANDROID_SOCKET_PREFIX + socketName;
try {
2. 得到 Socket 环境变量的值
String env = System.getenv(fullSocketName);
3. 将 Socket 环境变量的值转换为文件描述符的参数
fileDesc = Integer.parseInt(env);
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(fullSocketName + " unset or invalid", ex);
}
try {
4. 创建文件描述符
FileDescriptor fd = new FileDescriptor();
5 Socket 转换出来的信息传递给文件描述符,用于获取具体信息
fd.setInt$(fileDesc);
6 创建服务端 Socket
mServerSocket = new LocalServerSocket(fd);
} catch (IOException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Error binding to local socket '" + fileDesc + "'", ex);
}
}
}
registerServerSocket主要做了6件事情
1 拿到拼接之后的 Socket 名称(ANDROID_SOCKET_zygote)
2 把funSocketName Socket 名称转换为系统环境变量的值
3 将 Socket 的系统环境变量的值转换为文件描述符的参数
4 创建 FileDescriptor 文件描述符
5 传入之前文件抓换参数
6 创建LocalServerSocket,并将文件操作符传递出去
最后服务端 Socket 就创建成功了,在这个服务端上并处等待 AMS 请求 zygote 进程来创建新的应用程序进程。
2. 启动 SystemServer 进程
回头在看 ZygoteInit main 函数的注释 3
//com.android.internal.os ZygoteInit.main->startSystemServer
private static boolean startSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName, ZygoteServer zygoteServer)
throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller, RuntimeException {);
...
1. 启动 SystemServer 的参数
String args[] = {
"--setuid=1000",
"--setgid=1000",
"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1023,1032,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010",
"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,
"--nice-name=system_server",
"--runtime-args",
"com.android.server.SystemServer", //全类名路径
};
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs = null;
int pid;
try {
parsedArgs = new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args);
ZygoteConnection.applyDebuggerSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
ZygoteConnection.applyInvokeWithSystemProperty(parsedArgs);
2创建一个子进程,也就是 SystemServer 进程
pid = Zygote.forkSystemServer(
parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid,
parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags,
null,
parsedArgs.permittedCapabilities,
parsedArgs.effectiveCapabilities);
} catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
/* For child process */
/**
* 如果当前代码运行在子进程中 ,也就是 SystemServer 进程中
*/
if (pid == 0) {
if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {
waitForSecondaryZygote(socketName);
}
//关闭 Zygote 进程创建的 Socket
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
3
handleSystemServerProcess(parsedArgs);
}
return true;
}
总结startSystemServer 做了些什么
1 用来创建args数组,这个数组用来保存启动SystemServer
2 通过fork函数在当前线程SystemServer进程。
3 Zygote.forkSystemServer 创建的pid为0 已经运行到了SystemServer 进程中
3. zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
SystemServer 进程启动成功之后, 会ZygoteInit.Main() 中执行 runSelectLoop 方法
// com.android.internal.os ZygoteInit.main->runSelectLoop
void runSelectLoop(String abiList) throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
ArrayList<FileDescriptor> fds = new ArrayList<FileDescriptor>();
ArrayList<ZygoteConnection> peers = new ArrayList<ZygoteConnection>();
1. 添加获得该 Socket 的 fd 字段的值
fds.add(mServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());
peers.add(null);
while (true) {
StructPollfd[] pollFds = new StructPollfd[fds.size()];
2 通过遍历将fds的信息转移到pooFds数组中
for (int i = 0; i < pollFds.length; ++i) {
pollFds[i] = new StructPollfd();
pollFds[i].fd = fds.get(i);
pollFds[i].events = (short) POLLIN;
}
try {
Os.poll(pollFds, -1);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("poll failed", ex);
}
for (int i = pollFds.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if ((pollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) == 0) {
continue;
}
3 如果 i == 0 那么就认为 服务端 Socket 与客户端连接上了,就是与 AMS 建立了连接
if (i == 0) {
4 ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList);
//将 ZygoteConnection 添加到 Socket 连接列表中
peers.add(newPeer);
fds.add(newPeer.getFileDesciptor());
} else {//如果不等于 0 ,那么就说明 AMS 向 Zygote 发送了一个创建应用进程的请求
5 调用 ZygoteConnection 的 runOnce 函数来创建一个新的应用进程,并在成功创建后将这个连接从 Socket 连接列表中 peers、fd 列表中关闭
*/
boolean done = peers.get(i).runOnce(this);
if (done) {
peers.remove(i);
fds.remove(i);
}
}
}
}
}
总结 上面的函数
1 mServerSocket 就是我们在 registerZygoteSocket 函数中创建的服务器端 Socket,调用 mServerSocket.getFileDescriptor() 函数用来获得该 Socket 的 fd 字段的值并添加到 fds 列表中。接下来就无限循环用来等待 AMS 请求 Zygote 进程创建的新的应用程序进程。
2 将 fds 信息转存到 pollFds 数组中。
3 对 pollFds 信息进行遍历,如果 i == 0 那么就认为 服务端 Socket 与客户端连接上了,就是与 AMS 建立了连接,否则就说明 AMS 向 Zygote 发送了一个创建应用进程的请求,并在成功创建后将这个连接从 Socket 连接列表中 peers、fd 列表中关闭。
二 SystemServer 进程处理过程
进入处理 SystemServer 是在 ZygoteInit.main() -> startSystemServer() 函数的 handleSystemServerProcess 中
那SystemServer成功启动的了之后那后续做了些什么呢 ?
1 启动Binder线程池。这样就可以与其他进程进行通信;
2 创建SystemServiceManager。其用于对系统的服务进行创建、启动和生命周期管理;
3 启动各种系统服务。BootstrapServices(AMS、PMS等),CoreServices(BatteryService、WebViewUpdateService等),OtherServices(CameraSevice、Audioservice、WindowManagerService等)。
//com.android.internal.os ZygoteInit.main
private static void handleSystemServerProcess(
ZygoteConnection.Arguments parsedArgs)
throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
...
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
...
} else {
ClassLoader cl = null;
if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
1. 创建了 PathClassLoader
cl = createPathClassLoader(systemServerClasspath, parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion);
Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl);
}
2. 调用自己的 zygoteInit 函数
ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion, parsedArgs.remainingArgs, cl);
}
/* should never reach here */
}
我们来看ZygoteInit.zygoteInit的方法
// com.android.internal.os ZygoteInit
public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv,
ClassLoader classLoader) throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
if (RuntimeInit.DEBUG) {
Slog.d(RuntimeInit.TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.redirectLogStreams();
RuntimeInit.commonInit();
1. 启动 Binder 线程池
ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit();
2. 进入 SystemServer 的 main 方法
RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
}
ZygoteInit. zygoteInit的中
1 用于启动 Binder 线程池,这样 SystemServer 就能通过 Binder 与其它进程进行通信
2 反射调用 SystemServer main 函数。
看RuntimeInit.applicationInit
//com.android.internal.os RuntimeInit.java
protected static void applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
....
invokeStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader);
}
private static void invokeStaticMain(String className, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller
{
Class<?> cl;
try {
1. 通过 className(com.android.server.SystemServer )反射得到SystemServer 类
className 通过 AMS 等其它地方传递过来的,并不是唯一
cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing class when invoking static main " + className,
ex);
}
Method m;
try {
2. 拿到 SystemServer main 函数
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
...
} catch (SecurityException ex) {
...
}
int modifiers = m.getModifiers();
if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) {
...
}
3. 将 m 、argv 传入 MethodAndArgsCaller,然后抛一个异常,并在 ZygoteInit.main 中进行捕获异常
throw new Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
}
3位置处异常是在 ZygoteInit.java main 函数进行捕获
//com.android.internal.os ZygoteInit.java
public static void main(String argv[]) {
...
if (startSystemServer) {
1. 启动 SystemServer 进程
startSystemServer(abiList, socketName, zygoteServer);
}
....
2. 捕获异常
} catch (Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
3. 执行 run 函数
caller.run();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
}
}
现在来看3处的 caller.run();
com.android.internal.os Zygote.java
public static class MethodAndArgsCaller extends Exception
implements Runnable {
public void run() {
try {
这里就开始执行 SystemServer main 方法了
mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { mArgs });
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
Throwable cause = ex.getCause();
if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) cause;
} else if (cause instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) cause;
}
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
我们再看SystemServer.java main()的Main实现
//com.android.server SystemServer.java
public static void main(String[] args) {
//调用内部 run 函数
new SystemServer().run();
}
//com.android.server SystemServer.java
private void run() {
try {
...
创建 主线程的消息 Looper
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
// Initialize native services.
1. 加载动态库 libandroid_servers .so
System.loadLibrary("android_servers");
// Check whether we failed to shut down last time we tried.
// This call may not return.
performPendingShutdown();
// Initialize the system context.
createSystemContext();
2. 创建 SystemServiceManager 它会对系统服务进行创建、启动和生命周期管理
mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
mSystemServiceManager.setRuntimeRestarted(mRuntimeRestart);
LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
// Prepare the thread pool for init tasks that can be parallelized
SystemServerInitThreadPool.get();
} finally {
traceEnd(); // InitBeforeStartServices
}
// Start services.
try {
traceBeginAndSlog("StartServices");
3. SystemServiceManager启动了 AMS 、PowerMS、PackageMS 等服务
startBootstrapServices();
4. 启动了 DropBoxManagerService、BatteryService、UsageStatsService 和 WebViewUpdateService
startCoreServices();
5. 启动了CameraService、AlarmManagerService、VrManagerService 等服务。
startOtherServices();
SystemServerInitThreadPool.shutdown();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
throw ex;
} finally {
traceEnd();
}
...
// Loop forever.
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
上面代码可以总结如下
1 创建消息 Looper
2 加载动态库 libandroid_servers .so
3 创建 SystemServiceManager 它会对系统服务进行创建、启动和生命周期管理
4 通过 SystemServiceManager 启动 AMS 、PowerMS、PackageMS 等服务
5 启动 DropBoxManagerService、BatteryService、UsageStatsService 和 WebViewUpdateService 等核心服务,他们父类都是 SystemServer
6 启动 CameraService、AlarmManagerService、VrManagerService 等服务
以上是关于Android源码分析 SystemServer 进程启动的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章