Android 源码分析 应用程序启动的过程
Posted 小图包
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android 源码分析 应用程序启动的过程相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
记录进阶解密学习,再看源码层面思路不会那么杂乱无章,有了一个很清晰的脉络。
启动过程
启动过程可以分为两步:
-
AMS 发送启动应用程序进程请求
AMS 如果想要启动应用程序进程,就需要向 Zygote 进程发送创建应用程序进程的请求,AMS 会通过调用 startProcessLocked 方法向 Zygote 进程发送请求。
-
Zygote 接收请求并创建应用程序进程
出处。
一 AMS 发送启动应用程序进程请求
时序图如下
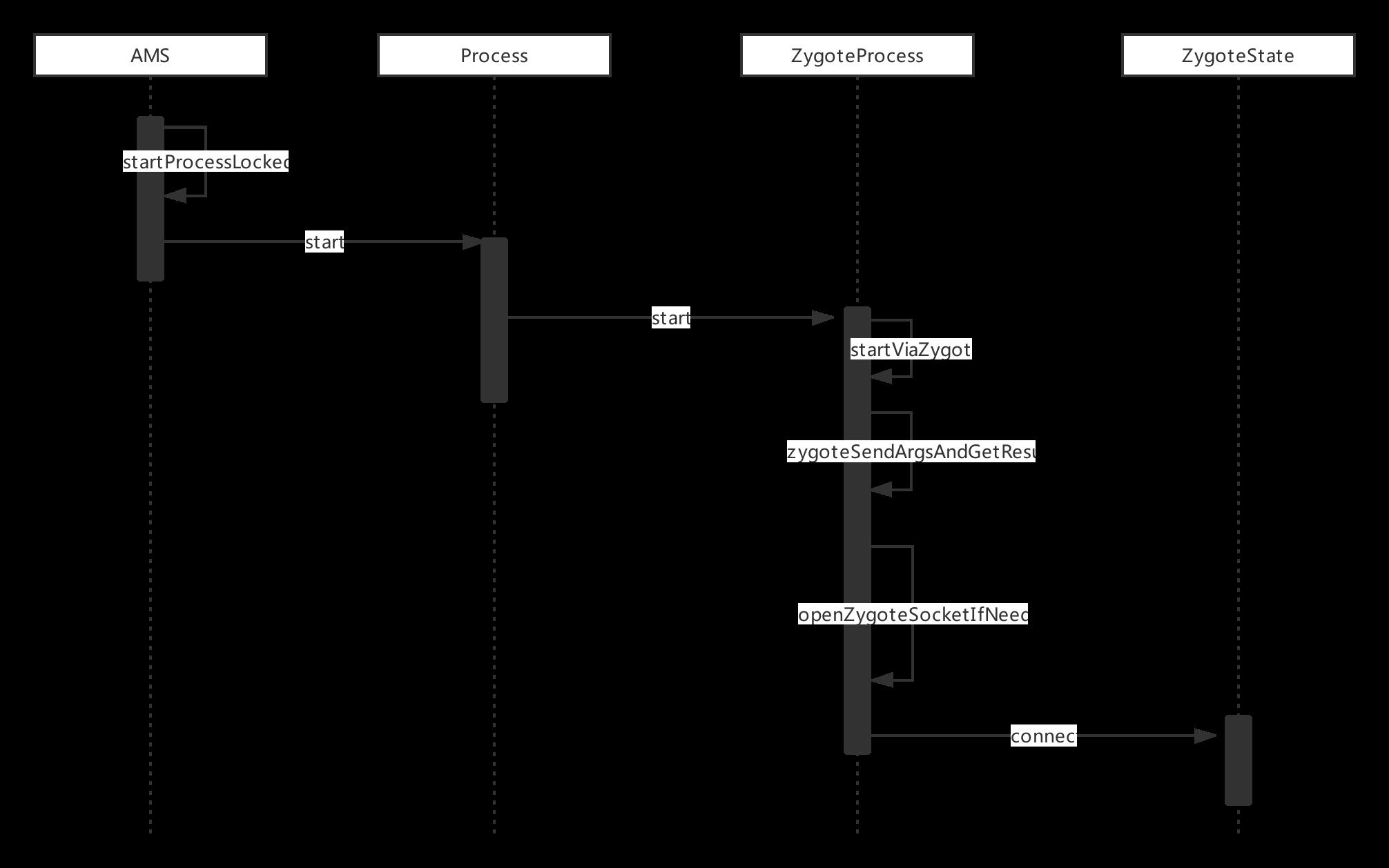
AMS 启动应用程序进程,向 Zygote 进程发送创建应用程序进程的请求, AMS 会通过调用 startProcessLocked 函数向 Zygote 进程发送请求 代码如下:
//com.android.server.am; ActivityManagerService.java
/**
* 启动进程的函数
* @param app
* @param hostingType
* @param hostingNameStr
* @param abiOverride
* @param entryPoint
* @param entryPointArgs
*/
private final void startProcessLocked(
ProcessRecord app, String hostingType,
String hostingNameStr, String abiOverride,
String entryPoint, String[] entryPointArgs){
...
try {
try {
final int userId = UserHandle.getUserId(app.uid);
AppGlobals.getPackageManager().checkPackageStartable(app.info.packageName, userId);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
throw e.rethrowAsRuntimeException();
}
1. 获取要创建的应用程序进程的 用户 id
int uid = app.uid;
int[] gids = null;
int mountExternal = Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_NONE;
if (!app.isolated) {
...
2. 对 gids 进行创建和赋值
if (ArrayUtils.isEmpty(permGids)) {
gids = new int[3];
} else {
gids = new int[permGids.length + 3];
System.arraycopy(permGids, 0, gids, 3, permGids.length);
}
gids[0] = UserHandle.getSharedAppGid(UserHandle.getAppId(uid));
gids[1] = UserHandle.getCacheAppGid(UserHandle.getAppId(uid));
gids[2] = UserHandle.getUserGid(UserHandle.getUserId(uid));
}
...
boolean isActivityProcess = (entryPoint == null);
3. 如果 entryPoint == null 那么将 ActivityThread 全类名赋值给 entryPoint
if (entryPoint == null) entryPoint = "android.app.ActivityThread";
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "Start proc: " +
app.processName);
checkTime(startTime, "startProcess: asking zygote to start proc");
ProcessStartResult startResult;
if (hostingType.equals("webview_service")) {
startResult = startWebView(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, null, entryPointArgs);
} else {
4. 在 AMS 中调用 start 函数进行通知 Zygote fork 进程
startResult = Process.start(entryPoint,
app.processName, uid, uid, gids, debugFlags, mountExternal,
app.info.targetSdkVersion, seInfo, requiredAbi, instructionSet,
app.info.dataDir, invokeWith, entryPointArgs);
}
...
}
总结上面主要做了4个步骤
1 获取创建应用程序进程的用户 ID
2 对用户组 ID(gids)进行创建和赋值
3 如果 entryPoint 为 null ,就把 ActivityThread 全类名赋值给它
4 调用 Process 的 start 函数
我们看下 Process 的 start 函数:
//android.os; Process.java
public static final ProcessStartResult start(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, int[] gids,
int debugFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String abi,
String instructionSet,
String appDataDir,
String invokeWith,
String[] zygoteArgs) {
1. 通过 ZygoteProcess 调用 start 函数
return zygoteProcess.start(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
debugFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, invokeWith, zygoteArgs);
}
ZygoteProcess 的Start 调用了startViaZygote 方法
//android.os; ZygoteProcess.java
public final Process.ProcessStartResult start(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
int uid, int gid, int[] gids,
int debugFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String abi,
String instructionSet,
String appDataDir,
String invokeWith,
String[] zygoteArgs) {
try {
1
return startViaZygote(processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,
debugFlags, mountExternal, targetSdkVersion, seInfo,
abi, instructionSet, appDataDir, invokeWith, zygoteArgs);
} catch (ZygoteStartFailedEx ex) {
Log.e(LOG_TAG,
"Starting VM process through Zygote failed");
throw new RuntimeException(
"Starting VM process through Zygote failed", ex);
}
}
private Process.ProcessStartResult startViaZygote(final String processClass,
final String niceName,
final int uid, final int gid,
final int[] gids,
int debugFlags, int mountExternal,
int targetSdkVersion,
String seInfo,
String abi,
String instructionSet,
String appDataDir,
String invokeWith,
String[] extraArgs)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
//创建字符串列表argsForZygote 并将应用进程的启动参数保存到argsForZygote
ArrayList<String> argsForZygote = new ArrayList<String>();
// --runtime-args, --setuid=, --setgid=,
// and --setgroups= must go first
argsForZygote.add("--runtime-args");
argsForZygote.add("--setuid=" + uid);
argsForZygote.add("--setgid=" + gid);
synchronized(mLock) {
2
return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi), argsForZygote);
}
}
看2 处的openZygoteSocketIfNeeded
//android.os; ZygoteProcess.java
@GuardedBy("mLock")
private ZygoteState openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(String abi) throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
Preconditions.checkState(Thread.holdsLock(mLock), "ZygoteProcess lock not held");
if (primaryZygoteState == null || primaryZygoteState.isClosed()) {
try {
1
primaryZygoteState = ZygoteState.connect(mSocket);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Error connecting to primary zygote", ioe);
}
}
2
if (primaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) {
return primaryZygoteState;
}
// 如果不匹配,则尝试连接 zygote 辅模式
if (secondaryZygoteState == null || secondaryZygoteState.isClosed()) {
try {
3
secondaryZygoteState = ZygoteState.connect(mSecondarySocket);
} catch (IOException ioe) {
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Error connecting to secondary zygote", ioe);
}
}
4
if (secondaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) {
return secondaryZygoteState;
}
//如果都不匹配那么就抛一个异常
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Unsupported zygote ABI: " + abi);
}
总结如上方法
1 连接 zygote 名称为 "zygote" 服务端的 Socket ,建立进程间通信
2 连接 Zygote 主模式返回的 ZygoteState 是否与启动应用程序进程所需要的 ABI 匹配
3 如果不匹配那么就尝试连接 name 为 "zygote_secondary" 的 Socket
4 连接 Zygote 辅模式返回的 ZygoteState 是否与启动应用程序进程所需要的 ABI 匹配
连接成功zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult 做了些什么
//android.os; ZygoteProcess.java
private static Process.ProcessStartResult zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(
ZygoteState zygoteState, ArrayList<String> args)
throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {
...
final BufferedWriter writer = zygoteState.writer;
final DataInputStream inputStream = zygoteState.inputStream;
writer.write(Integer.toString(args.size()));
writer.newLine();
for (int i = 0; i < sz; i++) {
String arg = args.get(i);
writer.write(arg);
writer.newLine();
}
writer.flush();
...
}
return result;
} catch (IOException ex) {
zygoteState.close();
throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx(ex);
}
}
zygote 进程的服务端 Socket 连接成功,那么就将存储起来的应用程序进程启动参数写入到 ZygoteState 中 .ZygoteState是ZygoteProcess的静态内部类,表示与Zygote的状态。
二 Zygote 接收请求并创建应用程序进程
SystemServer 跟应用进程启动在 Zygote 处理 的方式相似,看下时序图
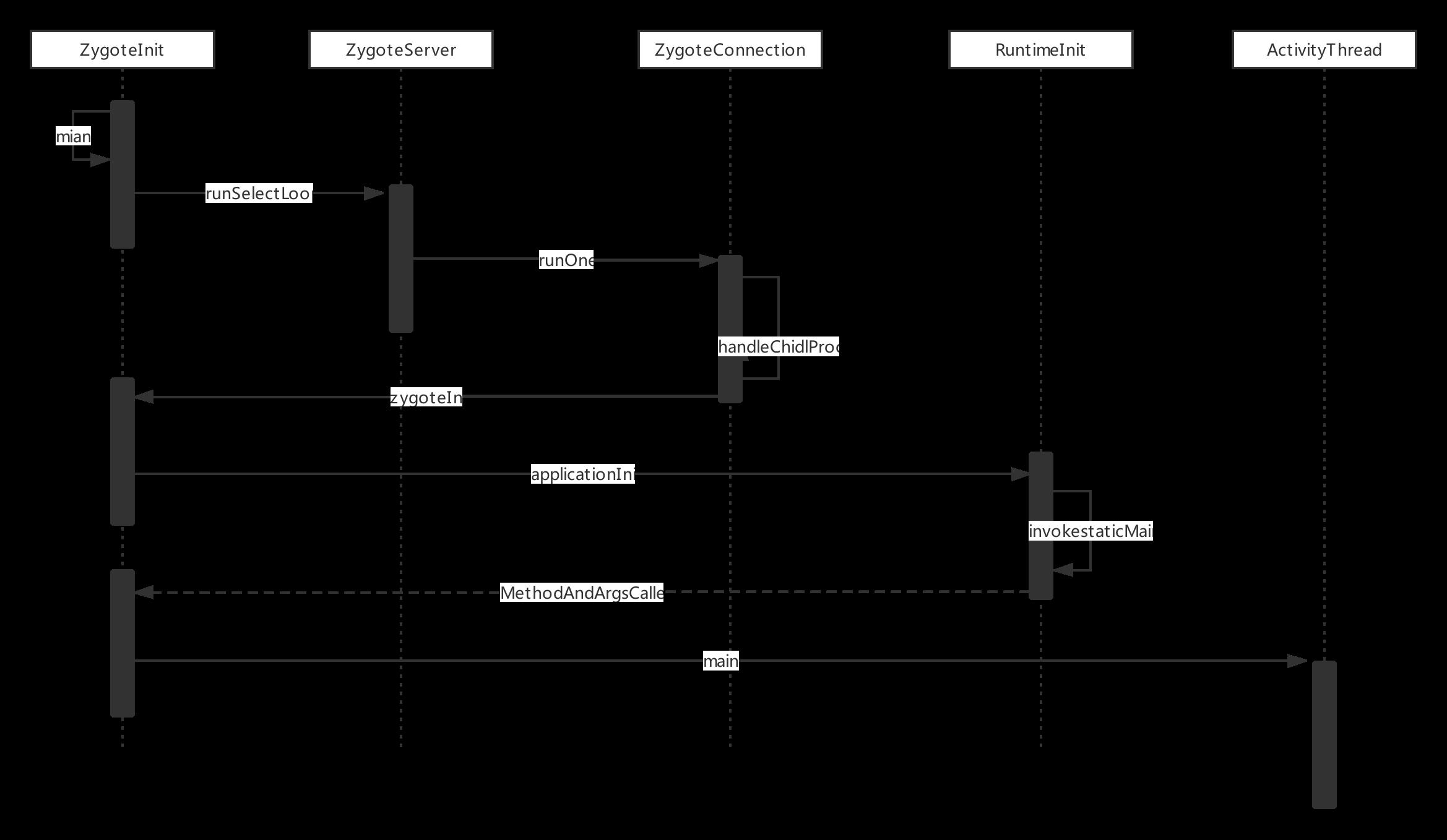
服务端的Socket的创建
//com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.java
public static void main(String argv[]) {
....
try {
1
zygoteServer.registerServerSocket(socketName);
if (!enableLazyPreload) {
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceBegin("ZygotePreload");
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_START,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
2
preload(bootTimingsTraceLog);
EventLog.writeEvent(LOG_BOOT_PROGRESS_PRELOAD_END,
SystemClock.uptimeMillis());
bootTimingsTraceLog.traceEnd(); // ZygotePreload
} else {
Zygote.resetNicePriority();
}
...
if (startSystemServer) {
3
startSystemServer(abiList, socketName, zygoteServer);
}
Log.i(TAG, "Accepting command socket connections");
4
zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
//清理或者关闭对应的 Socket
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
} catch (Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
caller.run();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
}
}
总结如上步骤
1 创建服务端的 Socket ,名称为 "zygote"
2 用来预加载资源
3 启动 SystemServer 进程
4 等待 AMS 请求创建新的应用程序进程
看下zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList); 方法
// com.android.internal.os ZygoteInit.main->runSelectLoop
void runSelectLoop(String abiList) throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
ArrayList<FileDescriptor> fds = new ArrayList<FileDescriptor>();
ArrayList<ZygoteConnection> peers = new ArrayList<ZygoteConnection>();
1
fds.add(mServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());
peers.add(null);
死循环等待 AMS 的请求
while (true) {
StructPollfd[] pollFds = new StructPollfd[fds.size()];
2
for (int i = 0; i < pollFds.length; ++i) {
pollFds[i] = new StructPollfd();
pollFds[i].fd = fds.get(i);
pollFds[i].events = (short) POLLIN;
}
try {
Os.poll(pollFds, -1);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException("poll failed", ex);
}
3
for (int i = pollFds.length - 1; i >= 0; --i) {
if ((pollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) == 0) {
continue;
}
//如果 i == 0 那么就认为 服务端 Socket 与客户端连接上了,就是与 AMS 建立了连接
if (i == 0) {
4
ZygoteConnection newPeer = acceptCommandPeer(abiList);
//将 ZygoteConnection 添加到 Socket 连接列表中
peers.add(newPeer);
//将 ZygoteConnection 的文件描述符 添加到 fds 列表中
fds.add(newPeer.getFileDesciptor());
} else {//如果不等于 0 ,那么就说明 AMS 向 Zygote 发送了一个创建应用进程的请求
5
boolean done = peers.get(i).runOnce(this);
if (done) {
peers.remove(i);
fds.remove(i);
}
}
}
}
}
上述方法的主要作用
1. 添加获得该 Socket 的 fd 字段的值
2. 将 fds 信息转存到 pollFds 数组中。
3 对 pollFds 信息进行遍历
4 添加到 Socket 连接列表中
5 调用 ZygoteConnection 的 runOnce 函数来创建一个新的应用进程,并在成功创建后将这个连接从 Socket 连接列表中 peers、fd 列表中关闭
如果 AMS 发来了一个新的请求任务,会走5 处通过 peers.get(i).runOnce(this); 来处理请求数据,我们看 runOnce 函数具体实现:
//com.android.internal.os; ZygoteConnection.java
boolean runOnce(ZygoteServer zygoteServer) throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
String args[];
Arguments parsedArgs = null;
FileDescriptor[] descriptors;
try {
1. 获取应用程序进程的启动参数
args = readArgumentList();
descriptors = mSocket.getAncillaryFileDescriptors();
} catch (IOException ex) {
Log.w(TAG, "IOException on command socket " + ex.getMessage());
closeSocket();
return true;
}
...
int pid = -1;
FileDescriptor childPipeFd = null;
FileDescriptor serverPipeFd = null;
try {
2. 将获取到启动应用程序进程的启动参数 args 数组 封装到 Arguments 类型的 parsedArgs 对象中
parsedArgs = new Arguments(args);
...
fd = null;
3. 通过 Zygote 来创建应用程序进程
pid = Zygote.forkAndSpecialize(parsedArgs.uid, parsedArgs.gid, parsedArgs.gids,
parsedArgs.debugFlags, rlimits, parsedArgs.mountExternal, parsedArgs.seInfo,
parsedArgs.niceName, fdsToClose, fdsToIgnore, parsedArgs.instructionSet,
parsedArgs.appDataDir);
} catch (ErrnoException ex) {
...
}
try {
//当前代码逻辑运行在被创建出来的子进程中
if (pid == 0) {
// in child
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
serverPipeFd = null;
4. 处理应用程序进程
handleChildProc(parsedArgs, descriptors, childPipeFd, newStderr);
// should never get here, the child is expected to either
// throw Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller or exec().
return true;
} else {
// in parent...pid of < 0 means failure
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
childPipeFd = null;
return handleParentProc(pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd, parsedArgs);
}
} finally {
IoUtils.closeQuietly(childPipeFd);
IoUtils.closeQuietly(serverPipeFd);
}
}
Zygote.forkAndSpecialize主要通过创建fork当前程序创建一个子程序的,如果pid等于0 则说明当前的 代码逻辑运行在新创建的子进程的应用程序当中。我们这里来看下 handleChildProc怎么处理应用程序进程
//com.android.internal.os; ZygoteConnection.java
private void handleChildProc(Arguments parsedArgs,
FileDescriptor[] descriptors, FileDescriptor pipeFd, PrintStream newStderr)
throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
...
if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null) {
...
} else {
//调用 ZygoteInit 的 zygoteInit 函数
ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.targetSdkVersion,
parsedArgs.remainingArgs, null /* classLoader */);
}
}
// com.android.internal.os ZygoteInit
public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv,
ClassLoader classLoader) throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
if (RuntimeInit.DEBUG) {
Slog.d(RuntimeInit.TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
}
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ZygoteInit");
RuntimeInit.redirectLogStreams();
RuntimeInit.commonInit();
1. 启动 Binder 线程池
ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit();
2. 进入 ActivityThread 的 main 方法
RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, argv, classLoader);
}
1 处先启动 Binder 线程池,用于进程间通信,接下来看applicationInit 处理了什么
//com.android.internal.os RuntimeInit.java
protected static void applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller {
...
invokeStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader);
}
private static void invokeStaticMain(String className, String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader)
throws Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller
{
Class<?> cl;
try {
1
cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(
"Missing class when invoking static main " + className,
ex);
}
Method m;
try {
2
m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
} catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
...
} catch (SecurityException ex) {
...
}
int modifiers = m.getModifiers();
if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) {
...
}
3
throw new Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
}
总结如上方法做了3件事:
1 通过 className("android.app.ActivityThread" )反射得到 ActivityThread 类
2 获取ActivityThread的main的方法,并将main的方法传入3处的Zygote中的MethodAndArhsCaller类的构造方法当中
3将 m 、argv 传入 MethodAndArgsCaller,然后抛一个异常,并在 ZygoteInit.main 中进行捕获异常
//com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit.java
public static void main(String argv[]) {
....
try {
1
zygoteServer.registerServerSocket(socketName);
2
zygoteServer.runSelectLoop(abiList);
} catch (Zygote.MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {
3
caller.run();
} catch (Throwable ex) {
Log.e(TAG, "System zygote died with exception", ex);
zygoteServer.closeServerSocket();
throw ex;
}
}
1 创建服务端的 Socket ,名称为 "zygote"
2. 等待 AMS 请求
3. 捕获到 RuntimeInit applicationInit 中的异常
看 RuntimeInit applicationInit 中的异常,然后看它的 run 函数
com.android.internal.os Zygote.java
public static class MethodAndArgsCaller extends Exception
implements Runnable {
/** method to call */
private final Method mMethod;
/** argument array */
private final String[] mArgs;
public MethodAndArgsCaller(Method method, String[] args) {
mMethod = method;
mArgs = args;
}
public void run() {
try {
1. 这里就开始执行 ActivityThread main 方法了
mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { mArgs });
} catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
} catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
Throwable cause = ex.getCause();
if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
throw (RuntimeException) cause;
} else if (cause instanceof Error) {
throw (Error) cause;
}
throw new RuntimeException(ex);
}
}
}
至此应用程序的进程创建和 应用程序进程的入口 ActivityThread main 都已经执行,我们看下ActivityThread消息的创建处理
//android.app; ActivityThread.java
//通过 ZygoteInit 反射调用执行的
public static void main(String[] args) {
...
1
Looper.prepareMainLooper();
2
ActivityThread thread = new ActivityThread();
thread.attach(false);
3
if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {
sMainThreadHandler = thread.getHandler();
}
4
Looper.loop();
throw new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited");
}
1 主线程消息循环 Looper 创建
2 创建 ActivityThread 对象
3 拿到H类的Hander并且 赋值给sMainThreadHandler
4 开启 Looper开启了循环,使得Looper开始处理消息。
通过对系统源码的源码的分析,对系统进程、系统桌面 Launcher 进程、应用程序进程的启动过程,Binder,Hander的更加深的理解, 后续将对四大组件启动流程进行分析.
以上是关于Android 源码分析 应用程序启动的过程的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章