Android P update_engine分析 --boot_control的操作
Posted Give.Me.Five
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android P update_engine分析 --boot_control的操作相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
上篇update_engine的启动时,有看到关于boot_control的初始化,我们知道boot_control是切换AB分区的关键实现者,那这篇就来专门介绍boot_control, 从boot_control的启动与初始化,boot_control针对配置的读写操作,以及最后boot_control的AB切换 这三个小模块来分析。
boot_control的初始化
我们接着上篇的boot_control的初始化开始分析, boot_control::CreateBootControl()的实现:
std::unique_ptr<BootControlInterface> CreateBootControl() {
std::unique_ptr<BootControlandroid> boot_control(new BootControlAndroid());
if (!boot_control->Init()) {
...
} // namespace boot_control
bool BootControlAndroid::Init() {
module_ = IBootControl::getService();
...
}
首先是new了一个BootControlAndroid的实现,然后调用Init()函数,这个就是通IBootControl::getService(), 这个是标准的HAL的获取服务句柄的写法。那看看IBootControl的服务的启动。
具体HAL服务路径:hardware/interface/boot/1.0
HAL服务也是标准的HIDL流程,通过android.hardware.boot@1.0-service.rc 来启动,但它还需要加载boot_control_module_t来实现其实际的操作。
Return<uint32_t> BootControl::getNumberSlots() {
return mModule->getNumberSlots(mModule);
}
Return<uint32_t> BootControl::getCurrentSlot() {
return mModule->getCurrentSlot(mModule);
}
BootControl相当于是对boot_control_module_t 加了一层封装的服务,实现实现部分还是得看boot_control_module_t的实现。因为每个芯片平台实现的方法不一样。我们就找标准qcom的实现方式,路径为:hardware/qcom/bootctrl.
看看module的接口与定义:
boot_control_module_t HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM = {
.common = {
.tag = HARDWARE_MODULE_TAG,
.module_api_version = 1,
.hal_api_version = 0,
.id = BOOT_CONTROL_HARDWARE_MODULE_ID,
.name = "Boot control HAL",
.author = "Code Aurora Forum",
.methods = &boot_control_module_methods,
},
.init = boot_control_init,
.getNumberSlots = get_number_slots,
.getCurrentSlot = get_current_slot,
.markBootSuccessful = mark_boot_successful,
.setActiveBootSlot = set_active_boot_slot,
.setSlotAsUnbootable = set_slot_as_unbootable,
.isSlotBootable = is_slot_bootable,
.getSuffix = get_suffix,
.isSlotMarkedSuccessful = is_slot_marked_successful,
};
上面是所有boot_control 对外实现的接口,我们来看看boot_control_init:
void boot_control_init(struct boot_control_module *module)
{
if (!module) {
ALOGE("Invalid argument passed to %s", __func__);
return;
}
return;
}
boot_control_init 里没有做什么事情,那这里boot_control 初始化就分析完了。
高通平台boot_control针对配置的读写操作
boot_control 对AB分区的实际保存与读写,最具有代表性的函数是setActiveBootSlot, 那我们就从这个函数入手,在上面HAL_MODULE_INFO_SYM 里可以看出 setActiveBootSlot实际调用的是set_active_boot_slot:
int set_active_boot_slot(struct boot_control_module *module, unsigned slot)
{
map<string, vector<string>> ptn_map;
vector<string> ptn_vec;
const char ptn_list[][MAX_GPT_NAME_SIZE] = { AB_PTN_LIST };
uint32_t i;
int rc = -1;
//先判断是否是ufs
int is_ufs = gpt_utils_is_ufs_device();
map<string, vector<string>>::iterator map_iter;
vector<string>::iterator string_iter;
//检查slot是否合法,是否属于A/B 对应的slot
if (boot_control_check_slot_sanity(module, slot)) {
ALOGE("%s: Bad arguments", __func__);
goto error;
}
//遍历ptn_list里的分区列表,将需要更改的分区都加入到此ptn_vec列表中
for (i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE(ptn_list); i++) {
//XBL is handled differrently for ufs devices so ignore it
if (is_ufs && !strncmp(ptn_list[i], PTN_XBL, strlen(PTN_XBL)))
continue;
//The partition list will be the list of _a partitions
string cur_ptn = ptn_list[i];
cur_ptn.append(AB_SLOT_A_SUFFIX);
ptn_vec.push_back(cur_ptn);
}
//获取真正存储设备里的真实分区列表放在ptn_map中
if (gpt_utils_get_partition_map(ptn_vec, ptn_map)) {
ALOGE("%s: Failed to get partition map",
__func__);
goto error;
}
//遍历ptn_map中的所有分区项,将其设置为slot项。
for (map_iter = ptn_map.begin(); map_iter != ptn_map.end(); map_iter++){
if (map_iter->second.size() < 1)
continue;
if (boot_ctl_set_active_slot_for_partitions(map_iter->second, slot)) {
ALOGE("%s: Failed to set active slot for partitions ", __func__);;
goto error;
}
}
//如果是ufs,需要特殊处理,在xbl中设置为slot为启动项。
if (is_ufs) {
if (!strncmp(slot_suffix_arr[slot], AB_SLOT_A_SUFFIX,
strlen(AB_SLOT_A_SUFFIX))){
//Set xbl_a as the boot lun
rc = gpt_utils_set_xbl_boot_partition(NORMAL_BOOT);
} else if (!strncmp(slot_suffix_arr[slot], AB_SLOT_B_SUFFIX,
strlen(AB_SLOT_B_SUFFIX))){
//Set xbl_b as the boot lun
rc = gpt_utils_set_xbl_boot_partition(BACKUP_BOOT);
...
}
return 0;
error:
return -1;
}
通过上面注释的解释,我们发现最重要切换分区的项是boot_ctl_set_active_slot_for_partitions 和 gpt_utils_set_xbl_boot_partition。
static int boot_ctl_set_active_slot_for_partitions(vector<string> part_list,
unsigned slot)
{
char buf[PATH_MAX] = {0};
struct gpt_disk *disk = NULL;
char slotA[MAX_GPT_NAME_SIZE + 1] = {0};
char slotB[MAX_GPT_NAME_SIZE + 1] = {0};
char active_guid[TYPE_GUID_SIZE + 1] = {0};
char inactive_guid[TYPE_GUID_SIZE + 1] = {0};
//Pointer to the partition entry of current 'A' partition
uint8_t *pentryA = NULL;
uint8_t *pentryA_bak = NULL;
//Pointer to partition entry of current 'B' partition
uint8_t *pentryB = NULL;
uint8_t *pentryB_bak = NULL;
struct stat st;
vector<string>::iterator partition_iterator;
for (partition_iterator = part_list.begin();
partition_iterator != part_list.end();
partition_iterator++) {
//Chop off the slot suffix from the partition name to
//make the string easier to work with.
string prefix = *partition_iterator;
if (prefix.size() < (strlen(AB_SLOT_A_SUFFIX) + 1)) {
ALOGE("Invalid partition name: %s", prefix.c_str());
goto error;
}
prefix.resize(prefix.size() - strlen(AB_SLOT_A_SUFFIX));
//检查AB 分区对应的块设备是否存在
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf) - 1, "%s/%s%s", BOOT_DEV_DIR,
prefix.c_str(),
AB_SLOT_A_SUFFIX);
if (stat(buf, &st))
continue;
memset(buf, '\\0', sizeof(buf));
snprintf(buf, sizeof(buf) - 1, "%s/%s%s", BOOT_DEV_DIR,
prefix.c_str(),
AB_SLOT_B_SUFFIX);
if (stat(buf, &st))
continue;
//设置slotA slotB的全名 ,类似boot_a, boot_b
memset(slotA, 0, sizeof(slotA));
memset(slotB, 0, sizeof(slotA));
snprintf(slotA, sizeof(slotA) - 1, "%s%s", prefix.c_str(),
AB_SLOT_A_SUFFIX);
snprintf(slotB, sizeof(slotB) - 1,"%s%s", prefix.c_str(),
AB_SLOT_B_SUFFIX);
//获取磁盘的分区表信息
if (!disk) {
disk = boot_ctl_get_disk_info(slotA);
if (!disk)
goto error;
}
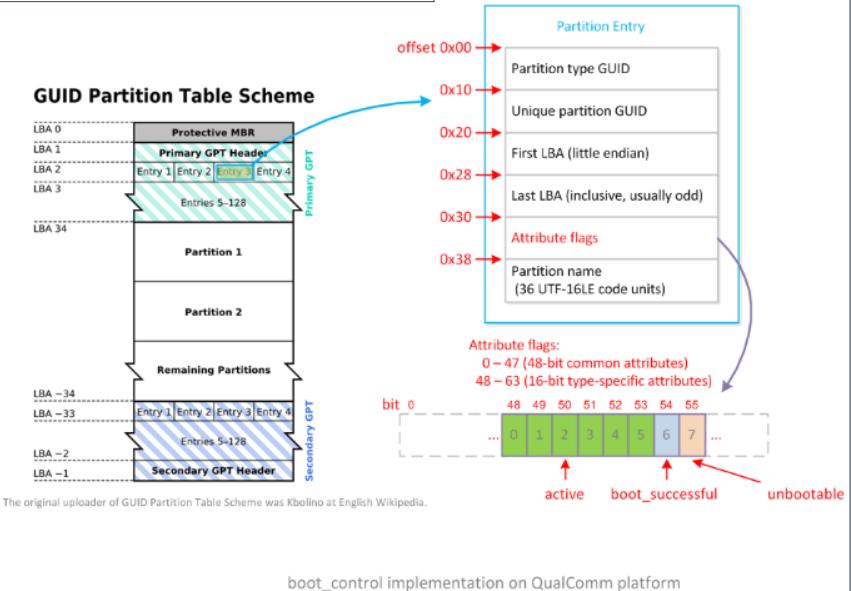
//qcom里分区表里有两块分区表信息,在磁盘头尾分别一块,为primary_GPT和SECONDARY_GPT 两个分区表信息,分别保存在pentryA/B 和 pentryA/B_bak中
pentryA = gpt_disk_get_pentry(disk, slotA, PRIMARY_GPT);
pentryA_bak = gpt_disk_get_pentry(disk, slotA, SECONDARY_GPT);
pentryB = gpt_disk_get_pentry(disk, slotB, PRIMARY_GPT);
pentryB_bak = gpt_disk_get_pentry(disk, slotB, SECONDARY_GPT);
if ( !pentryA || !pentryA_bak || !pentryB || !pentryB_bak) {
//None of these should be NULL since we have already
//checked for A & B versions earlier.
ALOGE("Slot pentries for %s not found.",
prefix.c_str());
goto error;
}
//将当前激活的guid 和 非激活的guid 分别存储在active_guid和 inactive_guid中。
memset(active_guid, '\\0', sizeof(active_guid));
memset(inactive_guid, '\\0', sizeof(inactive_guid));
if (get_partition_attribute(slotA, ATTR_SLOT_ACTIVE) == 1) {
//A is the current active slot
memcpy((void*)active_guid, (const void*)pentryA,
TYPE_GUID_SIZE);
memcpy((void*)inactive_guid,(const void*)pentryB,
TYPE_GUID_SIZE);
} else if (get_partition_attribute(slotB,
ATTR_SLOT_ACTIVE) == 1) {
//B is the current active slot
memcpy((void*)active_guid, (const void*)pentryB,
TYPE_GUID_SIZE);
memcpy((void*)inactive_guid, (const void*)pentryA,
TYPE_GUID_SIZE);
} else {
ALOGE("Both A & B are inactive..Aborting");
goto error;
}
//更新slot为最新的激活slot
if (!strncmp(slot_suffix_arr[slot], AB_SLOT_A_SUFFIX,
strlen(AB_SLOT_A_SUFFIX))){
//Mark A as active in primary table
UPDATE_SLOT(pentryA, active_guid, SLOT_ACTIVE);
//Mark A as active in backup table
UPDATE_SLOT(pentryA_bak, active_guid, SLOT_ACTIVE);
//Mark B as inactive in primary table
UPDATE_SLOT(pentryB, inactive_guid, SLOT_INACTIVE);
//Mark B as inactive in backup table
UPDATE_SLOT(pentryB_bak, inactive_guid, SLOT_INACTIVE);
} else if (!strncmp(slot_suffix_arr[slot], AB_SLOT_B_SUFFIX,
strlen(AB_SLOT_B_SUFFIX))){
//Mark B as active in primary table
UPDATE_SLOT(pentryB, active_guid, SLOT_ACTIVE);
//Mark B as active in backup table
UPDATE_SLOT(pentryB_bak, active_guid, SLOT_ACTIVE);
//Mark A as inavtive in primary table
UPDATE_SLOT(pentryA, inactive_guid, SLOT_INACTIVE);
//Mark A as inactive in backup table
UPDATE_SLOT(pentryA_bak, inactive_guid, SLOT_INACTIVE);
} else {
//Something has gone terribly terribly wrong
ALOGE("%s: Unknown slot suffix!", __func__);
goto error;
}
//更新分区表信息的CRC信息
if (disk) {
if (gpt_disk_update_crc(disk) != 0) {
ALOGE("%s: Failed to update gpt_disk crc",
__func__);
goto error;
}
}
}
//将信息写入磁盘信息中
if (disk) {
if (gpt_disk_commit(disk)) {
ALOGE("Failed to commit disk entry");
goto error;
}
gpt_disk_free(disk);
}
return 0;
error:
if (disk)
gpt_disk_free(disk);
return -1;
}
从上面的注释中可以看到,首先根据分区名如boot_a, 获取到对应分区表信息,高通的分区表信息是有两份的,一份在磁盘的第二块上,另一份在磁盘的最后一块上,做为备份分区表信息。通过更新分区表信息中的FLAG 为 SLOT_ACTIVE 或 SLOT_INACTIVE 来设置分区为激活状态,还是非激活状态。最后将disk分区表信息写回到磁盘上。这样就完成了分区表的更新。
标准google平台boot_control针对配置的读写操作
从上面高通平台来看,主要是基于GPT分区表去修改,设置flag的方式,读取GPT表信息来来配置从boot_control信息。那我们来看看从标准平台是如果配置boot_control信息的。还是从setActiveBootSlot来分析:
int BootControl_setActiveBootSlot(boot_control_module_t* module, unsigned int slot) {
//获取bootctl_module的接口
boot_control_private_t* const bootctrl_module = reinterpret_cast<boot_control_private_t*>(module);
if (slot >= kMaxNumSlots || slot >= bootctrl_module->num_slots) {
// Invalid slot number.
return -1;
}
bootloader_control bootctrl;
//从misc分区中读取当前bootctrl的信息
if (!LoadBootloaderControl(bootctrl_module->misc_device, &bootctrl)) return -1;
// 如果是激活分区,就将Priorty设置为15,如果是非激活分区,就将优先级设置为14.
const unsigned int kActivePriority = 15;
const unsigned int kActiveTries = 6;
for (unsigned int i = 0; i < bootctrl_module->num_slots; ++i) {
if (i != slot) {
if (bootctrl.slot_info[i].priority >= kActivePriority)
bootctrl.slot_info[i].priority = kActivePriority - 1;
}
}
// Note that setting a slot as active doesn't change the successful bit.
// The successful bit will only be changed by setSlotAsUnbootable().
bootctrl.slot_info[slot].priority = kActivePriority;
bootctrl.slot_info[slot].tries_remaining = kActiveTries;
// Setting the current slot as active is a way to revert the operation that
// set *another* slot as active at the end of an updater. This is commonly
// used to cancel the pending update. We should only reset the verity_corrpted
// bit when attempting a new slot, otherwise the verity bit on the current
// slot would be flip.
if (slot != bootctrl_module->current_slot) bootctrl.slot_info[slot].verity_corrupted = 0;
//然后将更新后的bootctrl信息更新回misc分区中
if (!UpdateAndSaveBootloaderControl(bootctrl_module->misc_device, &bootctrl)) return -1;
return 0;
}
struct slot_metadata {
// Slot priority with 15 meaning highest priority, 1 lowest
// priority and 0 the slot is unbootable.
uint8_t priority : 4;
// Number of times left attempting to boot this slot.
uint8_t tries_remaining : 3;
// 1 if this slot has booted successfully, 0 otherwise.
uint8_t successful_boot : 1;
// 1 if this slot is corrupted from a dm-verity corruption, 0
// otherwise.
uint8_t verity_corrupted : 1;
// Reserved for further use.
uint8_t reserved : 7;
} __attribute__((packed));
struct bootloader_control {
// NUL terminated active slot suffix.
char slot_suffix[4];
// Bootloader Control AB magic number (see BOOT_CTRL_MAGIC).
uint32_t magic;
// Version of struct being used (see BOOT_CTRL_VERSION).
uint8_t version;
// Number of slots being managed.
uint8_t nb_slot : 3;
// Number of times left attempting to boot recovery.
uint8_t recovery_tries_remaining : 3;
// Ensure 4-bytes alignment for slot_info field.
uint8_t reserved0[2];
// Per-slot information. Up to 4 slots.
struct slot_metadata slot_info[4];
// Reserved for further use.
uint8_t reserved1[8];
// CRC32 of all 28 bytes preceding this field (little endian
// format).
uint32_t crc32_le;
} __attribute__((packed));
从上面的可以看到,google标准平台就是将bootloader_control 的结构体信息保存在misc分区中,通过读写这块信息,来配置当前slot信息。
总结来说,bootcontrol 每家芯片实现的方式有些许差异。但都是适配boot_control的HAL层接口。
以上是关于Android P update_engine分析 --boot_control的操作的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章