LINUX基础实践第三部分答案
Posted 分布式技术学习沙龙
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LINUX基础实践第三部分答案相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
8.进程查询、清除的题组:
1)通过ps命令的两种选项形式查看进程信息(ps -aux |-elf)
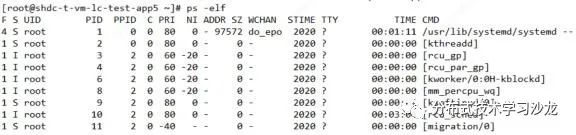
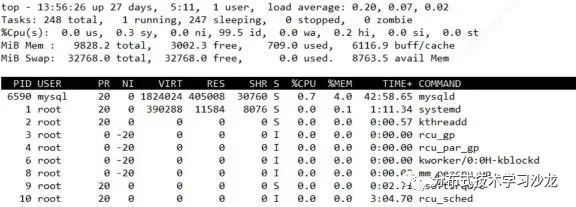
2)通过top命令查看进程
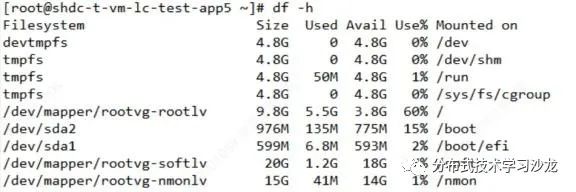
3)查看磁盘的使用情况
df -lh
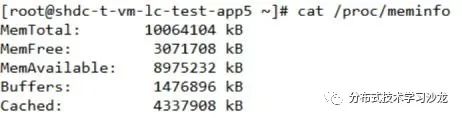
4)如何查看系统的负荷及内存使用状况

表示最近1分钟,5分钟,15分钟系统的平均负载;
3/330 3代表此时运行队列中的进程个数;330代表系统中进程总数
17247 代表到此为止创建的最后一个进程的ID
top命令

5)通过pgrep命令查看sshd服务的进程号

6)查看系统进程树
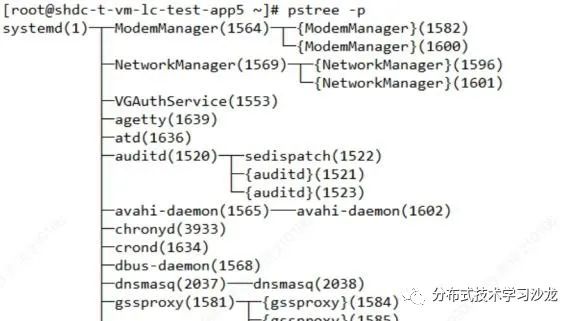
7)使dd if=/dev/zero of=/root/file bs=1M count=8190 命令操作在前台运行
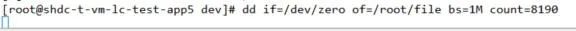
8)将第5题命令操作调入到后台并暂停

显示太快,换以下命令运行

9)使dd if=/dev/zero of=/root/file2 bs=1M count=1024 命令操作在后台运行
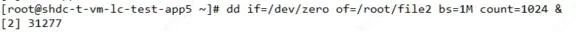
10)查看后台的任务列表

11)恢复dd if=/dev/zero of=/root/file bs=1M count=8190 让其在后台继续运行
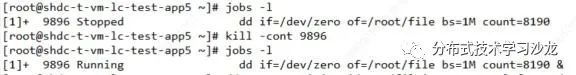
12)查询dd if=/dev/zero of=/root/file bs=1M count=8190 命令的进程并通过kill杀死

13)用两种方法强制踢出某个用户(kill、pkill)
1.who或w查询登录用户
[root@CentOS-WD /]# who
wu**** tty2 2021-01-06 22:10 (tty2)
wu**** pts/1 2021-01-06 22:34 (**.**.**.**)
[root@CentOS-WD /]# pkill -kill -t pts/1
w查询确认
[root@CentOS-WD /]# who
wu**** tty2 2021-01-06 22:10 (tty2)
2.who查询登录用户
[root@CentOS-WD /]# who
wu**** tty2 2021-01-06 22:10 (tty2)
wu**** pts/1 2021-01-06 22:37 (**.**.**.**)
[root@CentOS-WD /]# ps -ef|grep pts/1 查找该用户全部进程
wu**** 6820 6816 0 22:37 ? 00:00:00 sshd: wu****@pts/1
wu**** 6821 6820 0 22:37 pts/1 00:00:00 -bash
root 6899 6565 0 22:37 pts/0 00:00:00 grep --color=auto pts/1
[root@CentOS-WD /]# kill -9 6821 终止该用户shell进程
[root@CentOS-WD /]# who
wu**** tty2 2021-01-06 22:10 (tty2)
9.awk、sed、alias、find综合运用题组:
1)创建目录/data/oldboy,并且在该目录下创建文件oldboy.txt,然后在文件lodboy.txt里写入内容:
“inet addr:10.0.0.8” Bcast:10.0.0.255 Mask:255.255.255.0"(不包括引号)。
Mkdir /data -> cd /data -> mkdir /oldboy -> cd /oldboy -> touch oldboy.txt -> vi oldboy.txt ->写入内容 -> wq
2)题1中的oldboy.txt文件内容通过命令过滤只输出如下内容:
10.0.0.8 10.0.0.255 255.255.255.0
awk -F '[ :]+' '{print $3,$5,$7}' oldboy.txt
10.0.0.8 10.0.0.255 255.255.255.0
或者sed -r 's/[a-zA-Z:]+//g' oldboy.txt
3)将题1的oldboy目录移动到/tmp目录下,并将/etc/passwd文件复制到/tmp/oldboy下。
Cd /data -> mv oldboy /tmp
cp /etc/passwd /tmp/oldboy
4)在题3的基础上使用awk取passwd文件的地10行到20行的第三列重定向到/tmp/oldboy/test.txt 文件里面。
awk 'NR>=10 && NR<=20' /tmp/oldboy/passwd| awk -F ":" '{print $3}' >>/tmp/oldboy/test.txt

5)在题3的基础上要求用命令rm删除文件时提示如下禁止使用rm的提示,并是该效果永久生效。(提示:别名设置)
[root@python01 oldboy]# rm -f passwd
1.Do not use rm command
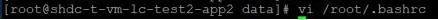
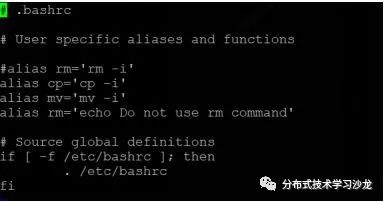
2. source /etc/profile
3. rm

6)在题3的基础上,删除/tmp/oldboy/下除passwd以外的其他文件。
[root@CentOS-WD oldboy]# ll
total 12
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 55 Jan 6 22:47 oldboy.txt
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 3147 Jan 6 22:50 passwd
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 37 Jan 6 22:51 test.txt
[root@CentOS-WD oldboy]# find /tmp/oldboy/ -type f ! -name "passwd"|xargs m -f
[root@CentOS-WD oldboy]# ll
total 4
-rw-r--r--. 1 root root 3147 Jan 6 22:50 passwd
或find /tmp/oldboy -type f ! -name 'passwd' |xargs rm -rf
7)在题3的基础上,请打印/etc/passwd 文件中的第2-5行(awk、sed、head三种方法)
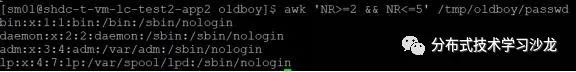
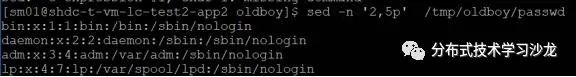
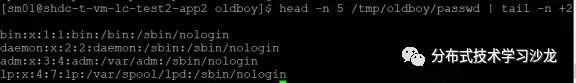
8)在题3的基础上,使用命令调换passwd文件里root位置和/bin/bash位置?即将所有的第一列和最后一列位置调换?
Awk -F ":" '{a=$1;$1=$NF;$NF=a;print}'/ tmp/oldboy/passwd | tr " " ":" 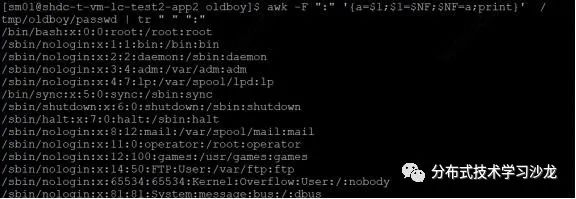
9)把/data目录及其子目录下所有以拓展名.txt结尾的文件中包含oldgirl的字符串全部替换为oldboy
find /data -type f -name '*.txt' | xargs sed -i 's/oldgirl/oldboy/g'
10)查找/oldboy下所有七天以前的以log结尾的大于1M的文件移动到/emp目录下。
find /data/oldboy -name "*.log" -size +1M -mtime +7 -exec mv {} /emp ;
10.Shell脚本运用综合题组:
1)基本操作的shell运用,实现以下功能
(1)使用for循环在/oldboy目录下批量创建10个html文件,其中每个文件需要包含10个随机小写字母加固定字符串oldboy
脚本:
#!/bin/bash
key="abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz"
randpass(){
if [ -z "$1" ];then
echo "randpass函数需要一个参数,用来指定提取的随机数个数."
return 127
fi
#调用$1参数,循环提取任意个数据字符,用随机数对26取余数,返回的结果为[0-25].
pass=""
for i in `seq $1`
do
num=$[RANDOM%${#key}]
local tmp=${key:num:1}
pass=${pass}${tmp}
done
echo $pass
}
for i in $(seq 1 10)
do
touch /tmp/shell/oldboy/oldboy$i.html
passwd="$(randpass 10)"oldboy
echo $passwd > /tmp/shell/oldboy/oldboy$i.html
done
exit 0
检查输出:
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 shell]# sh test1.sh
test1
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 shell]# cd oldboy
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 oldboy]# dir
oldboy10.html oldboy2.html oldboy4.html oldboy6.html oldboy8.html
oldboy1.html oldboy3.html oldboy5.html oldboy7.html oldboy9.html
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 oldboy]# cat oldboy10.html
svricioikxoldoldboy
(2)结果文件名中的oldboy字符串全部改成oldgirl(最好用for循环实现),并且将扩展名html全部改成大写
脚本:
#!/bin/bash
for i in $(seq 1 10)
do
mv /tmp/shell/oldboy/oldboy$i.html /tmp/shell/oldboy/oldboy$i.HTML
sed -i 's/boy/girl/g' /tmp/shell/oldboy/oldboy$i.HTML
done
exit 0
检查输出:
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 shell]# sh test2.sh
test2
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 shell]# dir
oldboy test1.sh test2.sh test.sh
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 shell]# cd oldboy
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 oldboy]# dir
oldboy10.HTML oldboy2.HTML oldboy4.HTML oldboy6.HTML oldboy8.HTML
oldboy1.HTML oldboy3.HTML oldboy5.HTML oldboy7.HTML oldboy9.HTML
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 oldboy]# cat oldboy10.HTML
svricioikxoldgirl
(3)批量创建10个系统帐号oldboy01-oldboy10并设置密码(密码为随机数,要求字符和数字等混合)
脚本:
#!/bin/bash
#功能描述(Description):使用字串截取的方式生成随机密码
#定义变量:10个数字+52个字符+3个符号
key="abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ0123456789@#$"
randpass(){
if [ -z "$1" ];then
echo "randpass函数需要一个参数,用来指定提取的随机数个数."
return 127
fi
#调用$1参数,循环提取任意个数据字符.
#用随机数对65取余数,返回的结果为[0-64].
pass=""
for i in `seq $1`
do
num=$[RANDOM%${#key}]
local tmp=${key:num:1}
pass=${pass}${tmp}
done
echo $pass
}
#创建10个测试账户,为账户配置随机密码并显示
for i in $(seq 1 10)
do
#userdel oldboy$i
#rm -r /home/oldboy$i
#rm /var/spool/mail/oldboy$i
useradd oldboy$i
passwd=$(randpass 10)
echo $passwd | passwd --stdin oldboy$i
echo oldboy$i $passwd
done
exit 0
检查输出:
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 shell]# sh test3.sh
Changing password for user oldboy1.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
oldboy1 #t1o96pN1G
Changing password for user oldboy2.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
oldboy2 X7pah6yp13
Changing password for user oldboy3.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
oldboy3 qMya611J1F
Changing password for user oldboy4.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
oldboy4 t5Ly66a11m
Changing password for user oldboy5.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
oldboy5 0DUx61$97k
Changing password for user oldboy6.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
oldboy6 jwL55UTboX
Changing password for user oldboy7.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
oldboy7 rPiJk55EiM
Changing password for user oldboy8.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
oldboy8 Vsx9557bgh
Changing password for user oldboy9.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
oldboy9 JkMA55dDB$
Changing password for user oldboy10.
passwd: all authentication tokens updated successfully.
oldboy10 Q7xy55ZzJk
(4)编写一个名为move的脚本程序,格式move <file1> <file2>。如果file1不存在,给出提示;否则移动file1至file2。
脚本:
#!/bin/bash
function move(){
cp $file1 $file2
}
read -p "please input file1:" file1
if [ -f $file1 ];then
read -p "please input file2:" file2
move
else
echo "file1 not exist,please check"
exit 0
fi
exit 0
检查输出:
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 shell]# dir
aaa oldboy test1.sh test2.sh test3.sh test4.sh test.sh t.sh
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 shell]# sh test4.sh
test4
please input file1:hhh
file1 not exist,please check
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 shell]# sh test4.sh
test4
please input file1:passwd
file1 not exist,please check
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 shell]# sh test4.sh
test4
please input file1:aaa
please input file2:bbb
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 shell]# dir
aaa bbb oldboy test1.sh test2.sh test3.sh test4.sh test.sh t.sh
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 shell]# sh test4.sh
test4
please input file1:ccc
file1 not exist,please check
2)运用shell,搜集系统状态以及性能数据
(1)写一个Shell脚本,判断10.0.0.0/24网络里,当前在线的IP有哪些?
脚本:
#!/bin/bash
rm /tmp/shell/up
touch /tmp/shell/up
rm /tmp/shell/down
touch /tmp/shell/down
for I in `seq 1 255`
do
ping -c 1 10.0.0.$I
if [ $? -eq 0 ]
then
echo -e "10.0.0.$I is up." >> /tmp/shell/up
else
echo -e "10.0.0.$I is down." >> /tmp/shell/down
fi
done
检查输出:
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 shell]# cat up
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 shell]#(由于没有在线ip,显示为空)
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 shell]# cat down
10.*.*.* is down.
以下省略到最后几行
10.*.*.255 is down.
a.使用shell数组方法实现,检测策略尽量模拟用户访问。
b.每10秒钟做一次所有的检测,无法访问的输出报警。
脚本:
#!/bin/bash
[ -f /etc/init.d/functions ]&&. /etc/init.d/functions
array_url=(
web.abc
10.2**.**.**:8**3/*me/Per**Page
10.2**.**.**:8*
http://10.2**.**.**/C*/**
)
curl_ip(){
curl -o /dev/null -s --connect-timeout 5 -w '%{http_code}' $1
}
main(){
for I in `seq 1 5
do
echo $I
for n in ${array_url[*]}
do
CURL=$(curl_ip $n|egrep "200|301"|wc -l)
if [ $CURL -eq 1 ];then
echo "curl $n" ok > /dev/null
# action "curl $n" /bin/true
else
action "curl $n" /bin/false
fi
done
sleep 10
done
}
main
检查输出:
[root@shdc-t-vm-lc-test-app5 shell]# sh test22.sh
1
curl 10.**.**.**:9*3/Ho*/Pers*Page
2
curl 10.**.**.**:9*3/Ho*/Pers*Page
3
curl 10.**.**.**:9*3/Ho*/Pers*Page
4
curl 10.**.**.**:9*3/Ho*/Pers*Page
5
curl 10.**.**.**:9*3/Ho*/Pers*Page
(3)巡检CPU、内存使用率,30秒一轮,持续检查5分钟。低于5%情况记一条日志到文件(时间戳、绝对值、百分比、结论),其余情况程序显示告警。
#! /bin/bash
LOG_FILE="/tmp/shell/log"
check_interval=30
max_usage_ration_memory=5
max_usage_ration_cpu=5
function monitor_memory() {
memory_total=$(grep MemTotal /proc/meminfo | awk '{print $2}' )
memory_free=$(grep MemFree /proc/meminfo | awk '{print $2}' )
memory_usage=$((100-memory_free*100/memory_total))
echo "Current memory usage: $memory_usage at $(date)" 2>&1 | tee -a "$1"
if [[ "$memory_usage" -gt "$max_usage_ration_memory" ]]
then
echo "Current Memory usage is high "
return 1
else
echo "$(date) $memory_free $memory_usage warning" >>/tmp/shell/log
return 0
fi
}
function get_cpu_info() {
grep -i "^cpu[0-9]+" /proc/stat | awk '{used+=$2+$3+$4; unused+=$5+$6+$7+$8} END {print used, unused}'
}
function monitor_cpu() {
cpu_info_1=$(get_cpu_info)
sleep "$check_interval"
cpu_info_2=$(get_cpu_info)
cpu_usage=$(echo "$cpu_info_1" "$cpu_info_2" | awk '{used=$3-$1;total+=$3+$4-$1-$2; print int(used*100/total)}')
echo "Current cpu usage: $cpu_usage at $(date)" 2>&1 | tee -a "$1"
if [[ "$cpu_usage" -gt "$max_usage_ration_cpu" ]]
then
echo "Current CPU usage is high "
return 1
else
echo "$(date) $cpu_free $cpu_usage warning" >>/tmp/shell/log
return 0
fi
}
check_time=10
(4)写脚本,每小时将/etc目录下所有文件,备份到/testdir独立的子目录下,并要求子目录格式含时间戳( BAK202012151000)。同时结合定时器设置,实现每天清除2天前的备份。
#!/bin/bash
cd '/tmp/shell/testdir'
for f in $(ls /etc)
do
if [ -d $f ]
then
cp -r $f /testdir
fi
done
2天前的备份。
以上是关于LINUX基础实践第三部分答案的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
《Linux系统管理与应用》课程知识点整理+书后习题全文解答(Linux知识点大纲)