数据结构--顺序表的实现(c语言实现)
Posted 我是晓伍
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了数据结构--顺序表的实现(c语言实现)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
最近终于开始学数据结构了,开个坑记录一下
首先,顺序表是一段物理地址连续的存储单元依次存储数据元素的线性结构,一般情况下采用数组存储。在数组上完成数据的增删查改。
顺序表一般可以分为:
1.静态顺序表:使用定长数组存储。
2.动态顺序表:使用动态开辟的数组存储。
我实现的就是一个动态顺序表。
首先要思考这个鬼东西要能做什么,增删查改这肯定是必须的了,其他的接口我依次列出:
//初始化
void SeqListInit(SL *ps);
//破坏顺序表
void SeqListDestory(SL *ps);
//头插
void SeqListPushFront(SL *ps, SeqListDataType data);
//头删
void SeqListPopFront(SL *ps);
//尾插
void SeqListPushBack(SL *ps, SeqListDataType data);
//尾删
void SeqListPopBack(SL *ps);
//任意位置插入
void SeqListInsert(SL *ps, int pos, SeqListDataType data);
//任意位置删除
void SeqListErase(SL *ps, int pos);
//扩容
void SeqListExpan(SL *ps);
//打印
void SeqListPrint(const SL *ps);
//查找
void SeqListFind(SL *ps, SeqListDataType data);
虽然看着很多,但仔细一想,头部插入删除和尾部插入删除都只需要调用任意位置插入删除就行了。
我们首先先新建三个文件:
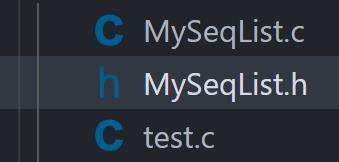
这张图中,第二个文件用来提供头文件及所有的宏定义,函数声明,第一个文件用来实现函数的功能,而test.c则用来测试函数是否有问题。
一个顺序表结构,其中需要一个变量记录元素个数,需要一个变量记录容量,还需要一个数组存储数据,当个数等于容量时,我们就扩容,达到动态存储的功能。
首先为了后期维护,我们把顺序表中的数组里变量通过宏定义设置为SeqListDataType,如下:
typedef int SeqListDataType;
接着设置一个初始容量为
#define CAPACITY_INIT 4
这之后可以先做出一个顺序表结构体出来
//顺序表
typedef struct SeqList
{
SeqListDataType *array; //用于存放数据
int size; //元素个数
int capacity; //容量
} SL;
再接下来跟上一堆函数声明,这个MySeqList.h就做完了
MySeqList.h
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <string.h>
#define CAPACITY_INIT 4
typedef int SeqListDataType;
//顺序表
typedef struct SeqList
{
SeqListDataType *array; //用于存放数据
int size; //元素个数
int capacity; //容量
} SL;
//初始化
void SeqListInit(SL *ps);
//破坏顺序表
void SeqListDestory(SL *ps);
//头插
void SeqListPushFront(SL *ps, SeqListDataType data);
//头删
void SeqListPopFront(SL *ps);
//尾插
void SeqListPushBack(SL *ps, SeqListDataType data);
//尾删
void SeqListPopBack(SL *ps);
//任意位置插入
void SeqListInsert(SL *ps, int pos, SeqListDataType data);
//任意位置删除
void SeqListErase(SL *ps, int pos);
//扩容
void SeqListExpan(SL *ps);
//打印
void SeqListPrint(const SL *ps);
//查找
void SeqListFind(SL *ps, SeqListDataType data);
下一步要做的就是一一实现各个接口的功能了,我们最好实现一个就测试一下,否则到最后来测试出现bug会非常难找。
初始化
void SeqListInit(SL *ps)
{
//开辟空间
ps->array = (int *)malloc(CAPACITY_INIT * sizeof(SeqListDataType));
//开辟失败就简单点,直接埋了程序qwq
if (ps->array == NULL)
{
printf("%s\\n", strerror(errno));
exit(-1);
}
//初始化个数
ps->size = 0;
// 初始化容量
ps->capacity = CAPACITY_INIT;
}
扩容
扩容要在什么时候扩呢?答的好!每次插入元素都要判断一次容量是否满了,满了就扩容,那我们先把扩容写出来。
void SeqListExpan(SL *ps)
{
//数组容量是上一次的两倍
ps->array = (SeqListDataType *)realloc(ps->array, 2 * ps->capacity * sizeof(SeqListDataType));
if (ps->array == NULL)
{
printf("%s\\n", strerror(errno));
exit(-1);
}
//别忘了这个也要扩大一倍
ps->capacity = ps->capacity * 2;
}
接下来是
任意位置的增加删除
void SeqListInsert(SL *ps, int pos, SeqListDataType data)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
//位置为0就是头插,位置为ps->size就是尾插
assert((pos >= 0) && (pos <= ps->size));
//判断容量是否足够
if (ps->size >= ps->capacity)
{
SeqListExpan(ps);
}
int end = ps->size - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
ps->array[end + 1] = ps->array[end];
end--;
}
ps->array[pos] = data;
ps->size++;
}
void SeqListErase(SL *ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
assert((pos >= 0) && (pos < ps->size));
int begin = pos + 1;
while (begin <= ps->size - 1)
{
ps->array[begin - 1] = ps->array[begin];
begin++;
}
ps->size--;
}
测试一下
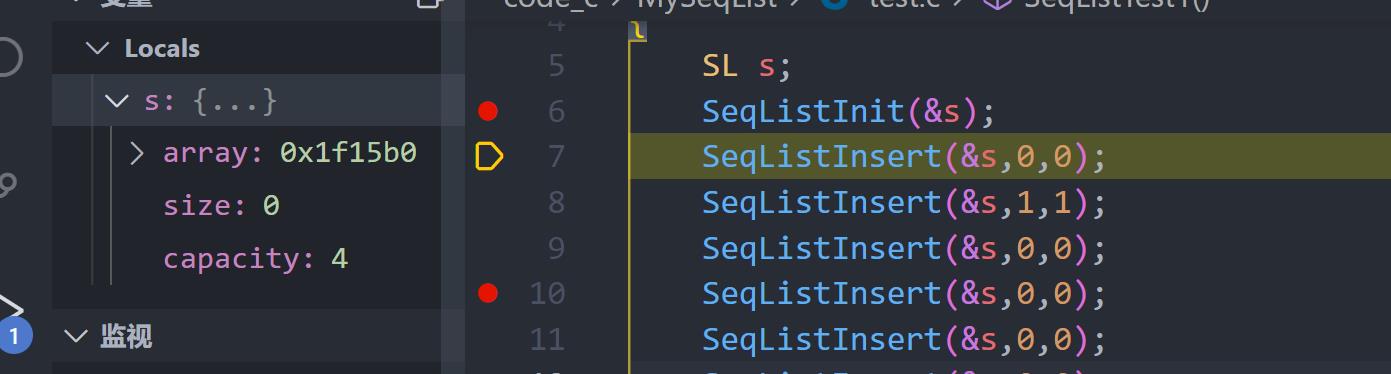
初始化没问题!
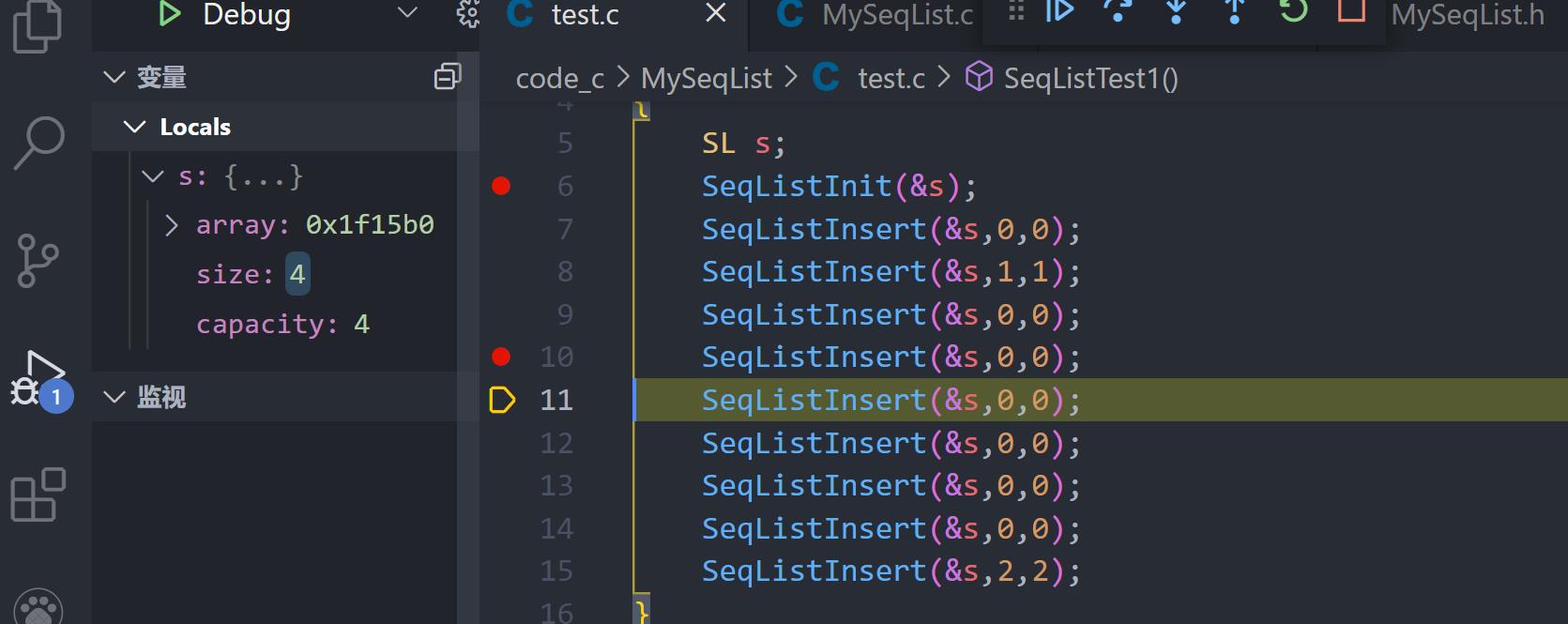
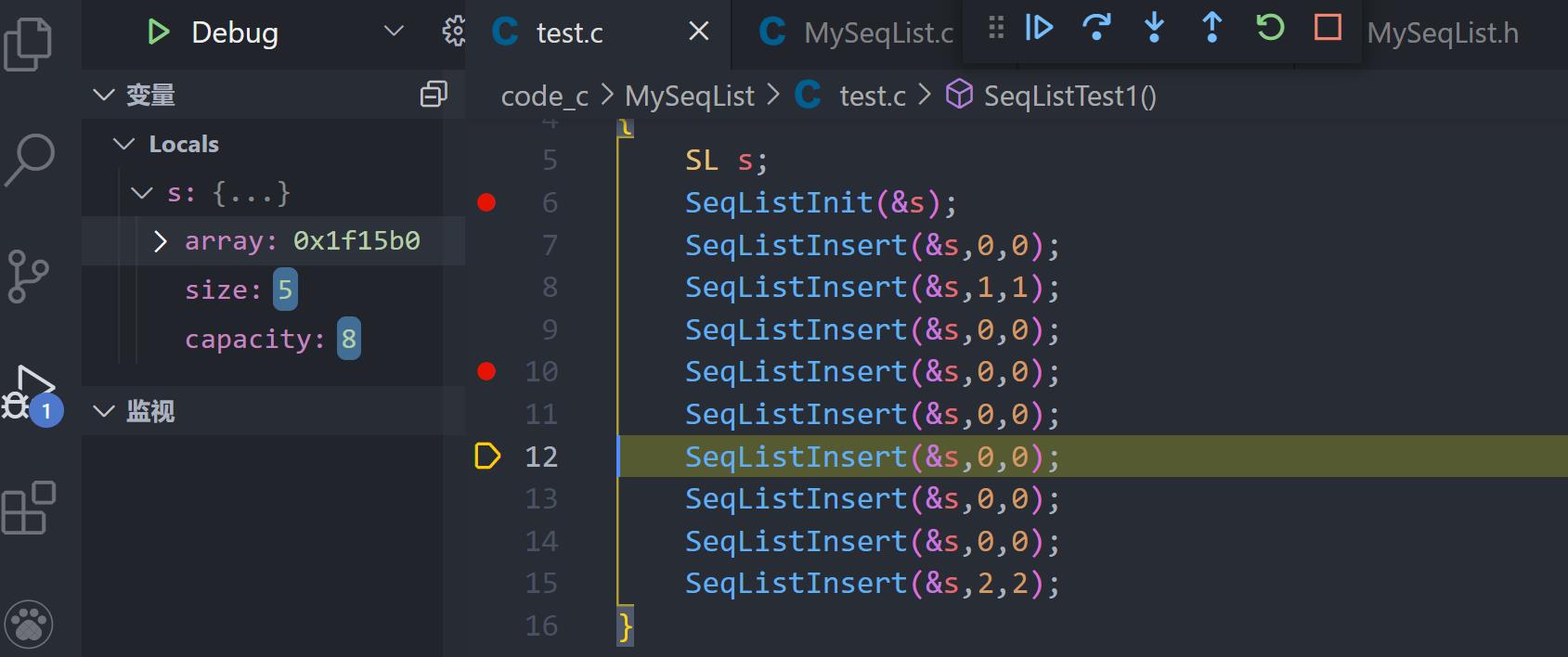
扩容没问题!
那立刻写一个打印函数测试这个增删有没有问题(打印函数真简单)
void SeqListPrint(const SL *ps)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->array[i]);
}
}
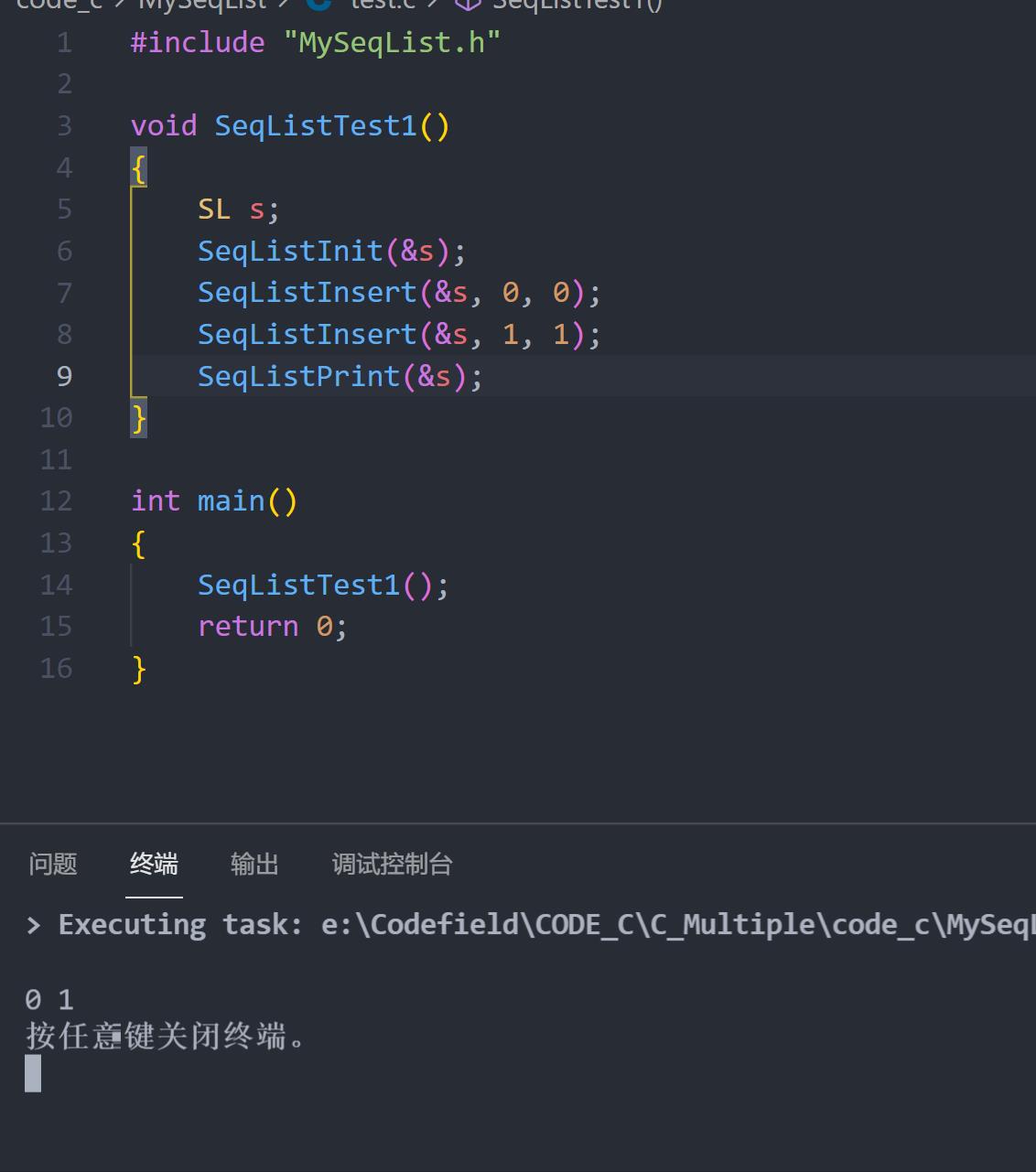
增改和打印都没问题!
接下来是头插头删和尾插尾删,已经没有什么难度了,就是直接调用任意位置的增加删除就好了。
MySeqList.c
#include "MySeqList.h"
void SeqListInit(SL *ps)
{
//开辟空间
ps->array = (int *)malloc(CAPACITY_INIT * sizeof(SeqListDataType));
//开辟失败就简单点,直接埋了程序qwq
if (ps->array == NULL)
{
printf("%s\\n", strerror(errno));
exit(-1);
}
//初始化个数
ps->size = 0;
// 初始化容量
ps->capacity = CAPACITY_INIT;
}
void SeqListExpan(SL *ps)
{
//数组容量是上一次的两倍
ps->array = (SeqListDataType *)realloc(ps->array, 2 * ps->capacity * sizeof(SeqListDataType));
if (ps->array == NULL)
{
printf("%s\\n", strerror(errno));
exit(-1);
}
//别忘了这个也要扩大一倍
ps->capacity = ps->capacity * 2;
}
void SeqListPushFront(SL *ps, SeqListDataType data)
{
SeqListInsert(ps, 0, data);
}
void SeqListPrint(const SL *ps)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
printf("%d ", ps->array[i]);
}
}
void SeqListPopFront(SL *ps)
{
SeqListErase(ps, 0);
}
void SeqListDestory(SL *ps)
{
free(ps->array);
ps->array = NULL;
ps->size = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
void SeqListPushBack(SL *ps, SeqListDataType data)
{
SeqListInsert(ps, ps->size, data);
}
void SeqListPopBack(SL *ps)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
ps->size--;
}
void SeqListInsert(SL *ps, int pos, SeqListDataType data)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
//位置为0就是头插,位置为ps->size就是尾插
assert((pos >= 0) && (pos <= ps->size));
//判断容量是否足够
if (ps->size >= ps->capacity)
{
SeqListExpan(ps);
}
int end = ps->size - 1;
while (end >= pos)
{
ps->array[end + 1] = ps->array[end];
end--;
}
ps->array[pos] = data;
ps->size++;
}
void SeqListErase(SL *ps, int pos)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
assert((pos >= 0) && (pos < ps->size));
int begin = pos + 1;
while (begin <= ps->size - 1)
{
ps->array[begin - 1] = ps->array[begin];
begin++;
}
ps->size--;
}
void SeqListFind(SL *ps, SeqListDataType data)
{
assert(ps != NULL);
for (int i = 0; i < ps->size; i++)
{
if (ps->array[i] == data)
{
printf("%d ", i);
}
}
}
反思
其实实现这个还是没什么难度的,最主要的地方就是当插入或者删除的时候需要挪动数据,这里的循环一定要控制准了qwq。
顺序表的优缺点

over
以上是关于数据结构--顺序表的实现(c语言实现)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章