二叉树
Posted 保护眼睛
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了二叉树相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
二叉树
- 树基本概念和基本性质
- 二叉树基本概念和基本性质
- 为什么常常使用二叉树取代树结构?
- 二叉树的基本操作
- 由字符串创建一颗二叉树
- 二叉树生成字符串
- 层序遍历二叉树
- 检查两棵二叉树是否相同
- 二叉树的最大深度
- 二叉树的最大宽度
- 一棵树是否是完全二叉树
- 判断一棵二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
- 一棵二叉树是否是对称二叉树
- 一棵树是不是另一颗树的子树
- 分层遍历二叉树
- 找出二叉树的最近公共祖先
- 二叉树搜索树转换成排序双向链表
- 根据一棵树的前序遍历与中序遍历构造二叉树
- 根据一棵树的中序遍历与后序遍历构造二叉树
- 二叉树的前序遍历的非递归实现
- 二叉树的后序遍历的非递归实现
- 二叉树的中序遍历的非递归实现
- 求二叉树的右视图
- 求二叉树的左视图
- 求二叉树的镜像二叉树
- 欢迎指正,相互关注啊😄
上篇👇
栈和队列-上
树基本概念和基本性质
树是一种特殊的数据结构,它可以用来描述有分支的结构,是由一个或一个以上的节点所组成的有限的集合。
空集合也是树,称为空树。空树中没有节点;
孩子节点或子节点:一个节点含有的子树的根节点称为该节点的子节点;
节点的度:一个节点含有的子节点的个数称为该节点的度;
叶节点或终端节点:度为0的节点称为叶节点;
非终端节点或分支节点:度不为0的节点;
双亲节点或父节点:若一个节点含有子节点,则这个节点称为其子节点的父节点;
兄弟节点:具有相同父节点的节点互称为兄弟节点;
树的度:一棵树中,最大的节点的度称为树的度;
节点的层次:从根开始定义起,根为第1层,根的子节点为第2层,以此类推;
树的高度或深度:树中节点的最大层次;
堂兄弟节点:双亲在同一层的节点互为堂兄弟;
节点的祖先:从根到该节点所经分支上的所有节点;
子孙:以某节点为根的子树中任一节点都称为该节点的子孙;
森林:由m棵互不相交的树的集合称为森林。
二叉树基本概念和基本性质
二叉树(binary tree)是指树中节点的度不大于2的有序树,它是一种最简单且最重要的树。二叉树的递归定义为:二叉树是一棵空树,或者是一棵由一个根节点和两棵互不相交的,分别称作根的左子树和右子树组成的非空树;左子树和右子树又同样都是二叉树。
性质1:二叉树的第i层上至多有2i-1(i≥1)个节点。
性质2:深度为h的二叉树中至多含有2h-1个节点。
性质3:若在任意一棵二叉树中,有n0个叶子节点,有n2个度为2的节点,则必有n0=n2+1 。
性质4:具有n个节点的完全二叉树深为log2x+1(其中x表示不大于n的最大整数)。
性质5:若对一棵有n个节点的完全二叉树进行顺序编号(1≤i≤n),那么,对于编号为i(i≥1)的节点:
当i=1时,该节点为根,它无双亲节点 。
当i>1时,该节点的双亲节点的编号为i/2 。
若2i≤n,则有编号为2i的左节点,否则没有左节点 。
若2i+1≤n,则有编号为2i+1的右节点,否则没有右节点 。
为什么常常使用二叉树取代树结构?
一般的树状结构在计算机内存中的存储方式以链表为主。对于n元数来说,因为每个节点的分支度都不相同,所以为了方便起见,我们必需取n为链接个数的最大固定长度,每个节点的数据结构如下:

假设n元树由m个节点,那么此树共享了n* m个链接字段。另外因为除了树根以外,每一个非空链接都指向一个节点,所以得知空连接的个数为n* m-(m-1)= m*(n-1)+1,n元树的链接浪费率为:
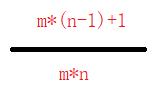
有以下结论:
n = 2时,二元树的浪费率约为1/2;
n = 3时,二元树的浪费率约为2/3;
n = 4时,二元树的浪费率约为3/4;
… … … …
当n = 2时,它的链接浪费率最低,所以为了改进内存空间浪费的缺点,我们常常使用二叉树结构来取代树状结构。
二叉树的基本操作
/**
* user:ypc;
* date:2021-05-11;
* time: 17:51;
*/
public class TreeNode {
int val;
TreeNode left;
TreeNode right;
TreeNode(int val) {
this.val = val;
}
}
class Tree {
// 前序遍历
void preOrderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
preOrderTraversal(root.left);
preOrderTraversal(root.right);
}
// 中序遍历
void inOrderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
preOrderTraversal(root.left);
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
preOrderTraversal(root.right);
}
// 后序遍历
void postOrderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
preOrderTraversal(root.left);
preOrderTraversal(root.right);
System.out.print(root.val + " ");
}
// 求结点个数
static int size = 0;
int getSize1(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
size++;
getSize1(root.left);
getSize1(root.right);
return size;
}
// 求结点个数
int getSize2(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return (getSize2(root.left) + 1 + getSize2(root.right));
}
// 求叶子结点个数
static int leafSize = 0;
int getLeafSize1(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return -1;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) leafSize++;
getSize2(root.left);
getSize2(root.right);
return leafSize;
}
// 求叶子结点个数
int getLeafSize2(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
if (root.left == null && root.right == null) return 1;
return (getLeafSize2(root.right) + getLeafSize2(root.right));
}
// 求第 k 层结点个数
int getKLevelSize(TreeNode root, int k) {
if (root == null) return 0;
if (k == 1) return 1;
return getKLevelSize(root.right, k - 1) + getKLevelSize(root.left, k - 1);
}
// 获取二叉树的高度
int getHeight(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return getHeight(root.left) + 1 > getHeight(root.right) + 1 ? getHeight(root.left) + 1 : getHeight(root.right) + 1;
}
TreeNode find(TreeNode root, int val) {
if (root == null) return null;
if (root.val == val) return root;
TreeNode l = find(root.left, val);
if (l != null) return l;
TreeNode r = find(root.right, val);
if (r != null) return r;
return null;
}
}
由字符串创建一颗二叉树
class TestDemo {
//根据字符串创建二叉树
public int i = 0;
public Node createTree(String s) {
Node root = null;
if (s.charAt(i) != '#') {
root = new Node(s.charAt(i));
i++;
root.left = createTree(s);
root.right = createTree(s);
} else {
i++;
}
return root;
}
}
二叉树生成字符串
//根据二叉树创建字符串
public void tree2strChild(Node root,StringBuilder sb){
if(root == null)return;
sb.append(root.val);
if(root.left == null){
if(root.right == null){
return;
}else{
sb.append("(");
sb.append(")");
}
}else{
sb.append("(");
tree2strChild(root.left,sb);
sb.append(")");
}
if(root.right == null){
return;
}else{
sb.append("(");
tree2strChild(root.right,sb);
sb.append(")");
}
}
public String tree2str(Node root) {
StringBuilder sb =new StringBuilder();
if(root == null)return sb.toString();
tree2strChild(root,sb);
return sb.toString();
}
层序遍历二叉树
//层序遍历二叉树
public void levelOrderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
System.out.print(cur.val + " ");
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
}
}
}
检查两棵二叉树是否相同
//检查两棵树是否相同
public boolean isSameTree(TreeNode t1, TreeNode t2) {
if (t1 == null && t2 == null) return true;
if (t1 != null && t2 == null) return false;
if (t1 == null && t2 != null) return false;
if (t1.val != t2.val) return false;
boolean l = isSameTree(t1.left, t2.left);
boolean r = isSameTree(t1.right, t2.right);
return (l == true && r == true);
}
二叉树的最大深度
// 获取二叉树的高度
int getHeight(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
return getHeight(root.left) > getHeight(root.right) ? getHeight(root.left) + 1 : getHeight(root.right) + 1;
}
二叉树的最大宽度
//求二叉树的最大宽度
public int widthOfBinaryTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return 0;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
Queue<Integer> indexQueue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
indexQueue.offer(1);
int result = 0;
int width = 0;
while (queue.size() > 0) {
int initialIndex = indexQueue.peek();
int leafSize = queue.size();
int index = initialIndex;
while (leafSize > 0) {
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
index = indexQueue.poll();
if (cur != null) {
if (cur.left != null) {
queue.offer(cur.left);
indexQueue.offer(index * 2);
}
if (cur.right != null) {
queue.offer(cur.right);
indexQueue.offer(index * 2 + 1);
}
}
leafSize--;
}
width = index - initialIndex + 1;
result = Math.max(result, width);
}
return result;
}
一棵树是否是完全二叉树
//是否是完全二叉树
public boolean isCompleteTree(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)return true;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>();
queue.offer(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
if(cur!=null){
queue.offer(cur.left);
queue.offer(cur.right);
}else{
break;
}
}
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
TreeNode cur = queue.poll();
if(cur != null){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
判断一棵二叉树是否是平衡二叉树
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null)return true;
int l = getDepth(root.left);
int r = getDepth(root.right);
return Math.abs(l-r)<2&&isBalanced(root.right)&&isBalanced(root.left);
}
public int getDepth(TreeNode root){
if(root == null)return 0;
int l = getDepth(root.left);
int r = getDepth(root.right);
return l>r?l+1:r+1;
}
一棵二叉树是否是对称二叉树
//两棵树是否对称
public boolean isSymmetricChild(TreeNode left, TreeNode right) {
if (right == null && left == null) return true;
if (left == null || right != null) return false;
if (left.val != right.val) return false;
return isSymmetricChild(left.left, right.right) && isSymmetricChild(right.left, left.right);
}
public boolean isSymmetric(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) return true;
return isSymmetricChild(root.left, root.right);
}
一棵树是不是另一颗树的子树
以上是关于二叉树的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章