NodeJS入门:常用模块汇总之http模块
Posted 安之ccy
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了NodeJS入门:常用模块汇总之http模块相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
http模块是nodejs中非常重要的模块,本文从3个demo入手,入门学习http模块
简单demo
主要步骤:
- 引入http模块
- 创建服务器
- 服务器监听某指定端口
- 给出响应
- 结束响应
代码:
// 引入模块
const http = require("http");
// 创建服务器
http.createServer((req,res)=>{
console.log(req.url);
// 响应
res.write("hello world!");
// 结束响应
res.end();
}).listen(5000,()=>console.log("服务器已运行..."))
// 监听5000端口
效果:
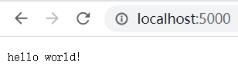
- 运行项目,控制台打印出:“服务器已运行…”
- 到浏览器打开localhost:5000,可以看到页面上显示的"hello world!"
- 打印出req.url :
'/'和页面标题默认图标favicon.ico路径
接收html文件、json数据的demo
文件解释:
- index.html:主页面
- about.html:"关于我们"页面
- index.js:服务器配置和响应设置
代码:
index.html
<h1>欢迎来到我的主页</h1>
about.html:
<h1>欢迎来到关于我们的页面</h1>
简单功能测试
index.js:
- 创建服务器对象、设置端口、服务器响应后返回一个html标签,让页面显示"good morning"
// 引入需要的模块
const path = require("path");
const http = require("http");
const fs = require("fs");
// 创建变量存储服务器对象
const server = http.createServer((req,res)=>{
console.log(req.url);
// 结束响应,返回响应的数据
res.end("<h1>good morning</h1>")
})
// 定义监听端口
// 如果环境变量中有定义端口,则使用环境变量中的端口,如果没有,就使用9999端口
const port = process.env.PROT || 9999;
// 监听
server.listen(port,()=>{
console.log(`服务器的${port}端口正在运行...`)
})
运行效果:
项目启动,控制台打印"服务器的9999端口正在运行…"
在浏览器打开localhost:9999,页面显示
good morning
加载html文件
简单的功能测试完毕,现在加入"加载index.html"的响应:
// 加载index页面
if (req.url === '/'){
fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname,"public","index.html"),(err,data)=>{
if (err) throw err;
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type':"text/html"})
res.end(data);
})
}
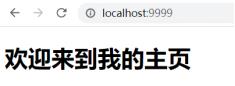
效果:
浏览器访问localhost:9999,加载index.html页面,显示如下:
接着是about.html页面的加载:
// 加载about页面
if (req.url === '/about'){
fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname,"public","about.html"),(err,data)=>{
if (err) throw err;
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type':"text/html"})
res.end(data);
})
}
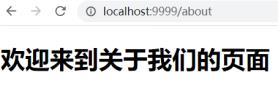
效果:
浏览器访问localhost:9999/about,加载about.html页面,显示如下:
加载json数据
然后是json数据的读取:
if (req.url = "/api/user") {
const data = [
{
name: "ccy",
age: 25
},
{
name: "ccy1",
age: 25
}
];
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': "application/json" })
res.end(JSON.stringify(data));
}
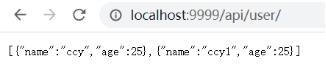
效果:
浏览器访问localhost:9999/api/user,加载该json数据,显示为:
index.js完整代码:
// 引入需要的模块
const path = require("path");
const http = require("http");
const fs = require("fs");
// 创建变量存储服务器对象
const server = http.createServer((req,res)=>{
// 加载index页面
if (req.url === '/'){
fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname,"public","index.html"),(err,data)=>{
if (err) throw err;
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type':"text/html"})
res.end(data);
})
}
// 加载about页面
if (req.url === '/about'){
fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname,"public","about.html"),(err,data)=>{
if (err) throw err;
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-Type':"text/html"})
res.end(data);
})
}
// 加载json数据
if (req.url = "/api/user") {
const data = [
{
name: "ccy",
age: 25
},
{
name: "ccy1",
age: 25
}
];
res.writeHead(200, { 'Content-Type': "application/json" })
res.end(JSON.stringify(data));
}
})
// 定义监听端口
// 如果环境变量中有定义端口,则使用环境变量中的端口,如果没有,就使用9999端口
const port = process.env.PROT || 9999;
// 监听
server.listen(port,()=>{
console.log(`服务器的${port}端口正在运行...`)
})
根据文件后缀名加载
如果文件找不到,就显示404,因此我们加一个404的html:
404.html
<h1>404 NOT FOUND</h1>
在前一个例子的基础上加上文件后缀名的判断,此处用switch来做判断
不同类型的文件对应的content-type都不同,此处仅列举几个类型,如:
| 文件类型 | content-type |
|---|---|
| ‘.js’ | text/javascript |
| ‘.css’ | text/css |
| ‘.json’ | application/json |
| ‘.png’ | image/png |
| ‘.jpg’ | image/jpg |
// 动态加载
// 创建变量存储文件路径
let filePath = path.join(__dirname, "public", req.url === '/' ? "index.html" : req.url);
// 初始化content-type
let contentType = "text/html";
// 文件扩展名
let extName = path.extname(filePath);
// 通过验证拓展名,设置contentType
switch (extName){
case ".js":
contentType = 'text/javascript';
break;
case ".css":
contentType = 'text/css';
break;
case '.json':
contentType = 'application/json';
break;
case '.png':
contentType = 'image/png';
break;
case '.jpg':
contentType = 'image/jpg';
break;
}
// 读取文件
fs.readFile(filePath,(err,data)=>{
if (err) {
if(err.code === 'ENOENT'){
// 没有找到页面,就加载404.html
fs.readFile(path.join(__dirname,"public","404.html"),(err,data)=>{
if (err) throw err;
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-type':"text/html"});
res.end(data,"utf8")
})
}else{
// 其他服务器错误
res.writeHead(500);
res.end(`服务器错误:${err.code}`);
}
}else{
// 文件读取成功
res.writeHead(200, {'Content-type':contentType});
res.end(data, 'utf8');
}
})
效果:
在浏览器访问localhost:9999/index.html,加载index.html文件,显示如下:
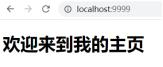
在浏览器访问localhost:9999/about.html,加载about.html文件,显示如下:

在浏览器访问localhost:9999/404.html,加载404.html文件,显示如下:
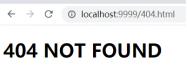
如果文件名输入错误,也会加载404.html文件
由于是根据后缀名来判断和加载文件的,因此访问时需要输入后缀名
切记要结束响应,将数据返回给客户端
以上是关于NodeJS入门:常用模块汇总之http模块的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
NodeJS入门:常用模块汇总之(path / fs / os / url模块)
NodeJS入门:常用模块汇总之(path / fs / os / url模块)