Day275.Thread和Object类中的重要方法 -Juc
Posted 阿昌喜欢吃黄桃
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Day275.Thread和Object类中的重要方法 -Juc相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Thread和Object类中的重要方法【一】
1、引入面试题思考

2、方法概览
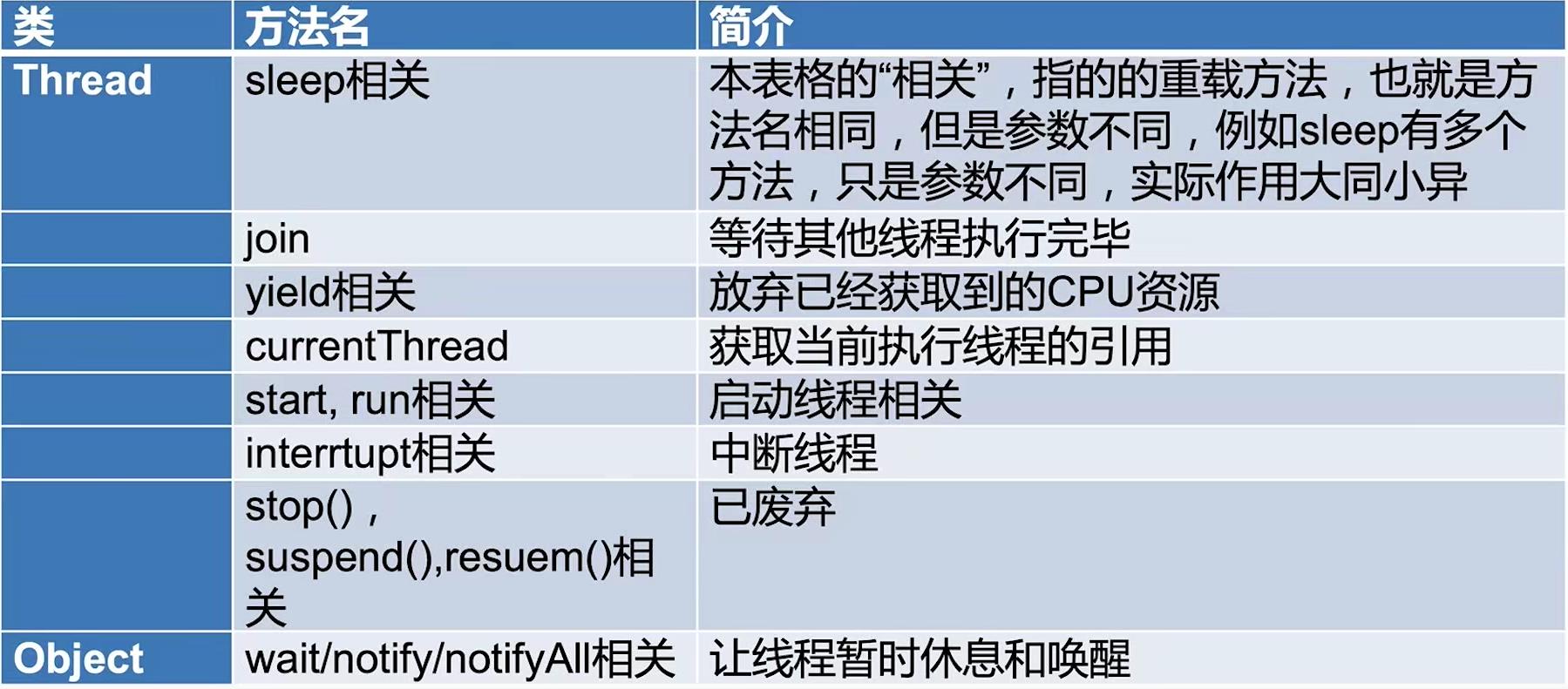
3、wait、notify、notifyAll
-
作用、用法:控制一些线程休息(阻塞)、唤醒
-
在Synchronized修饰的方法中执行
-
阻塞阶段:wait- 阻塞阶段—唤醒条件:

- 阻塞阶段—唤醒条件:
-
唤醒阶段:notify、notifyAll-
notify:唤醒单个正在等待某对象monitor(监听)的线程,若有多个线程都在等待,他只能唤醒
单个 -
notifyAll:一次唤醒正在等待某对象monitor(监听)的
所有线程
-
-
遇到中断:执行了wait()方法之后,再此期间被中断了
-
-
代码演示:
-
普通用法:-
/****** @author 阿昌 @create 2021-05-22 19:31 ******* * 展示wait和notify的基本用法 * 1、研究代码执行顺序 * 2、证明wait释放锁 */ public class Wait { //object对象 public static Object object = new Object(); //线程1 static class Thread1 extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { synchronized (object){ System.out.println("线程1 开始执行"); try { //释放锁 object.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } System.out.println("线程1 拿到锁"); } } } //线程2 static class Thread2 extends Thread{ @Override public void run() { synchronized (object){ //唤醒 线程1 object.notify(); System.out.println("线程2 调用了notify()"); } } } //主函数 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { Thread1 thread1 = new Thread1(); Thread2 thread2 = new Thread2(); thread1.start(); Thread.sleep(200); thread2.start(); } } -
结果:
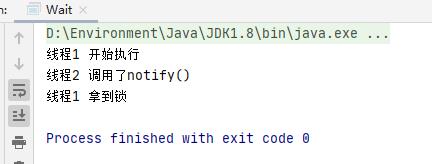
-
-
notify和notifyAll展示:-
使用notifyAll():/****** @author 阿昌 @create 2021-05-22 19:48 ******* * 3个线程,线程1和线程2首先被阻塞,线程3去唤醒线程1、线程2;唤醒的方式有notify、notifyAll * start全执行,不代表此线程先启动 */ public class WaitNotifyAll implements Runnable { public static Object resourceA = new Object(); @Override public void run() { synchronized (resourceA){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获取到锁"); try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"等待下一步开始"); //释放锁 resourceA.wait(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"即将程序结束"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } //主函数 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { WaitNotifyAll r = new WaitNotifyAll(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(r); Thread thread2 = new Thread(r); Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { synchronized (resourceA){ //【使用notifyAll】 唤醒其他所有阻塞线程 resourceA.notifyAll(); System.out.println("线程3 唤醒了其他所有线程"); } } }); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); Thread.sleep(200); thread3.start(); } }所有线程执行完毕,都被notifyAll唤醒
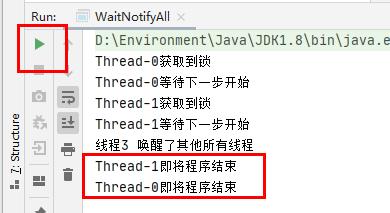
-
使用notify():/****** @author 阿昌 @create 2021-05-22 19:48 ******* * 3个线程,线程1和线程2首先被阻塞,线程3去唤醒线程1、线程2;唤醒的方式有notify、notifyAll * start全执行,不代表此线程先启动 */ public class WaitNotifyAll implements Runnable { public static Object resourceA = new Object(); @Override public void run() { synchronized (resourceA){ System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"获取到锁"); try { System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"等待下一步开始"); //释放锁 resourceA.wait(); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"即将程序结束"); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } //主函数 public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException { WaitNotifyAll r = new WaitNotifyAll(); Thread thread1 = new Thread(r); Thread thread2 = new Thread(r); Thread thread3 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { synchronized (resourceA){ //使用【notify】唤醒单个阻塞线程 resourceA.notify(); System.out.println("线程3 唤醒了其他所有线程"); } } }); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); Thread.sleep(200); thread3.start(); } }线程依然还被阻塞中,因为Thread-0还在阻塞,没有被notify唤醒
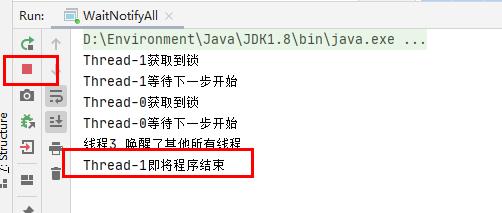
-
-
只释放当前monitor展示:-
/****** @author 阿昌 @create 2021-05-22 20:06 ******* * 证明wait只释放当前的那把锁 */ public class WaitNotifyReleaeOwnMonitor { public static Object resourceA = new Object(); public static Object resourceB = new Object(); public static void main(String[] args) { Thread thread1 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { synchronized (resourceA) { System.out.println("线程1 拿到resourceA锁"); synchronized (resourceB) { System.out.println("线程1 拿到resourceB锁"); try { System.out.println("线程1 释放resourceA锁"); resourceA.wait(); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } } }); Thread thread2 = new Thread(new Runnable() { @Override public void run() { try { Thread.sleep(1000); } catch (InterruptedException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } synchronized (resourceA) { System.out.println("线程2 拿到resourceA锁"); System.out.println("线程2 尝试获取resourceB锁"); synchronized (resourceB) { System.out.println("线程2 拿到resourceB锁"); } } } }); thread1.start(); thread2.start(); } }线程2没有获取到resourceB,因为resourceB没有被释放,他在线程1手上,所有线程2还在被阻塞等到拿到resourceB
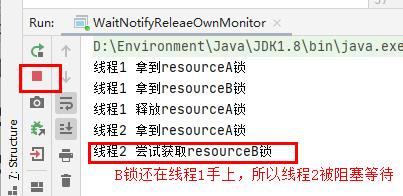
-
-
- 特点、性质:
- 使用必须
先拥有monitor锁 - notify只能唤醒其中
一个 - 属于
Object类,任何对象都属于object类,所以所有对象都可以调用wait、notify、notifyAll方法 - 类似功能的
Condition - 如果一个线程,同时持有
多个锁的情况,需要合理释放锁,不然会导致死锁发生
- 使用必须
- 原理:
wait原理图:
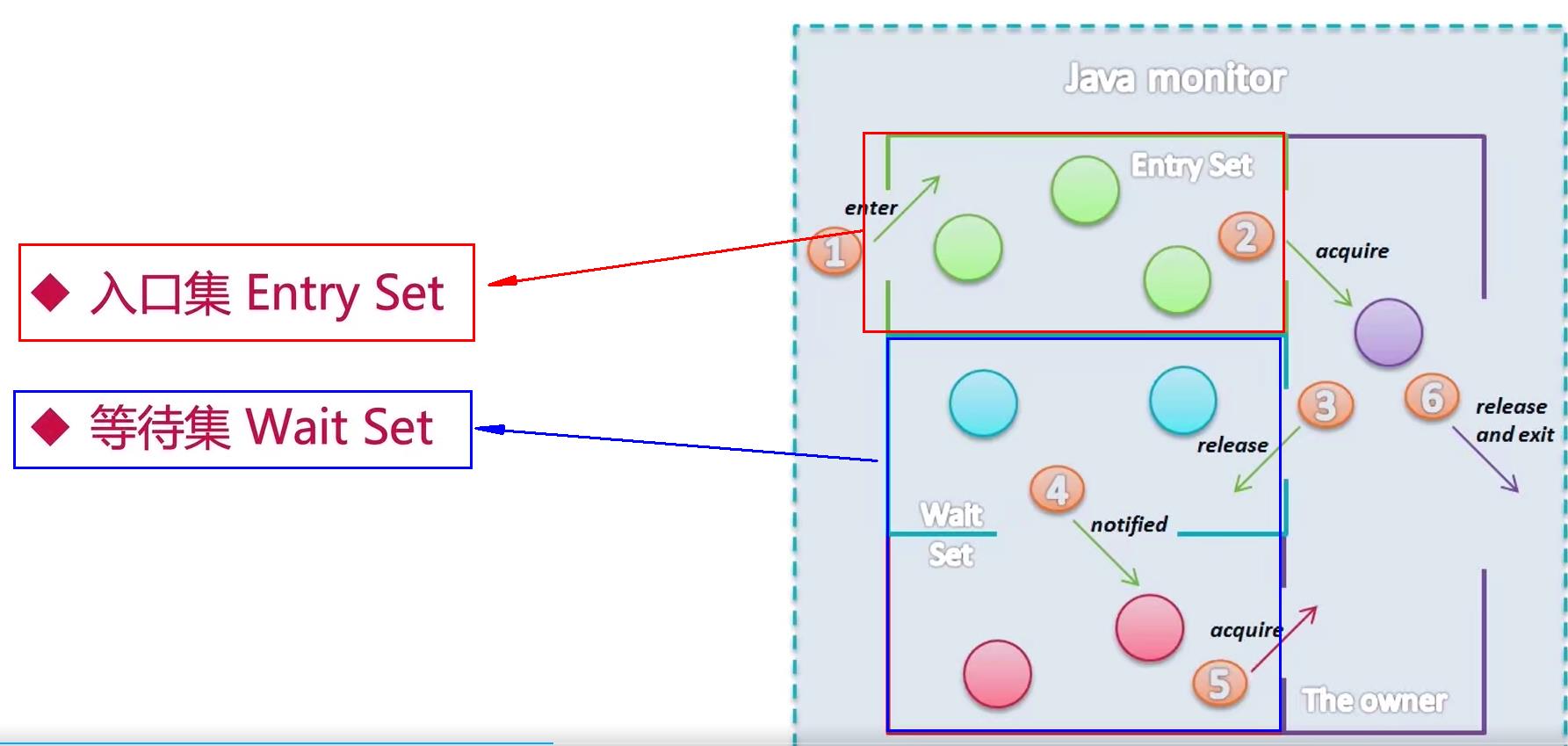
-
注意点:
- 进入blocked状态的情况
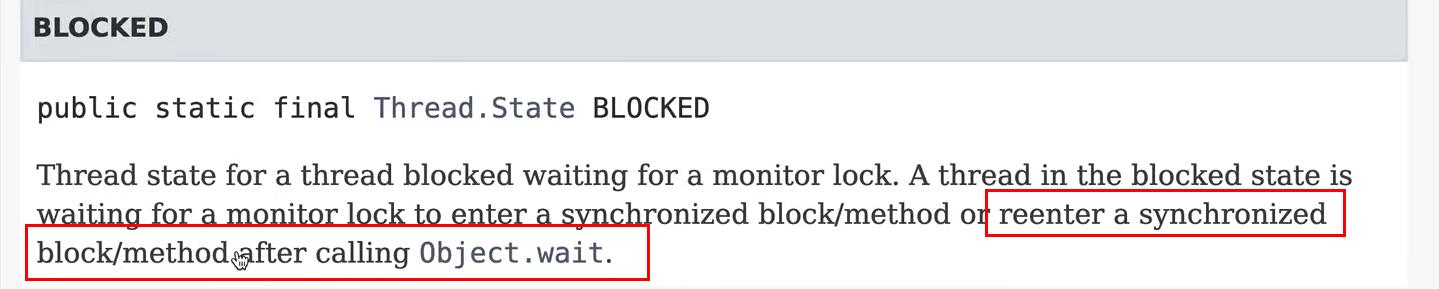
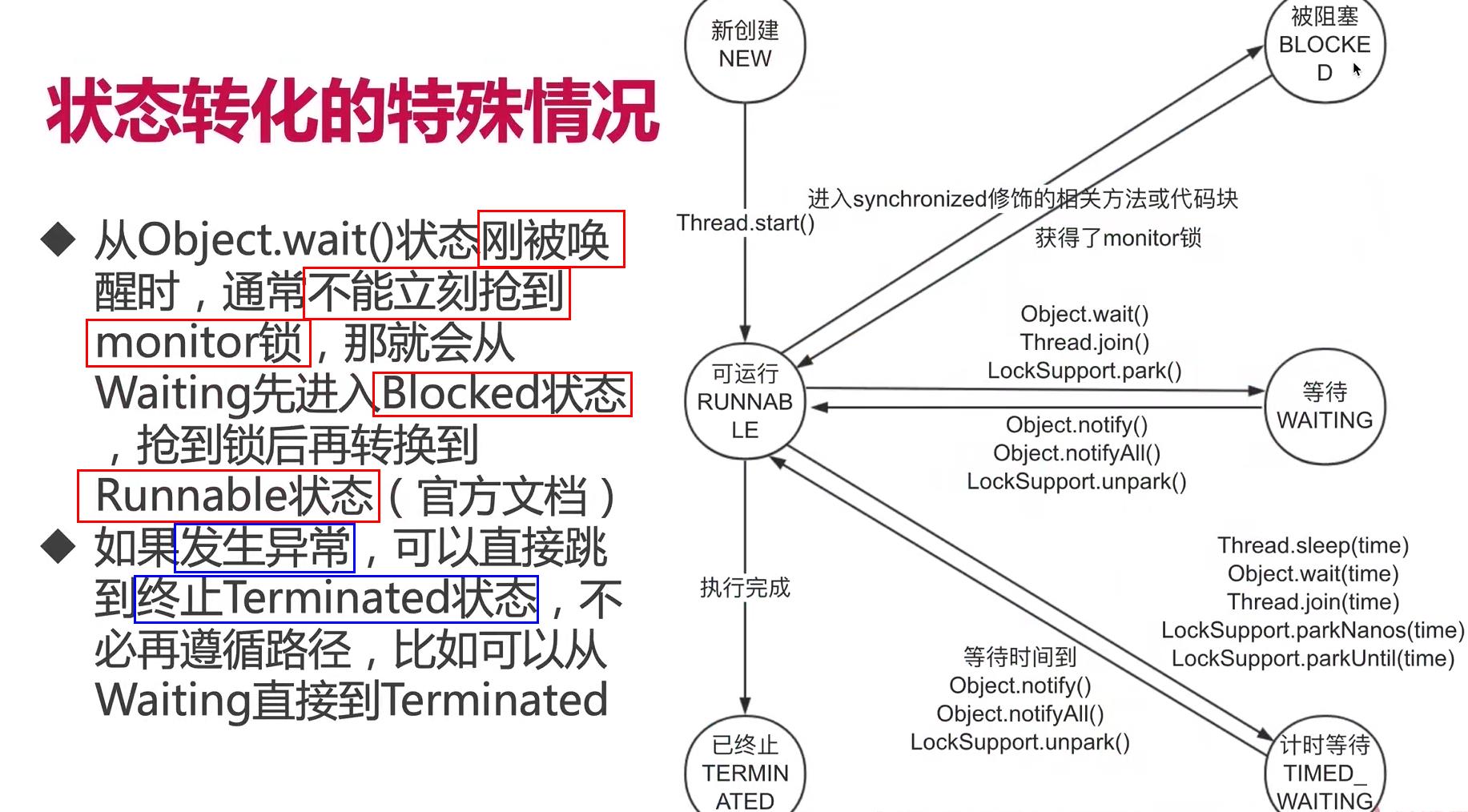
4、生产者消费者设计模式
1)为什么要有这个设计模式
保证生产消费平衡,通过一个异步的队列来实现
2)什么是生产者消费者模式
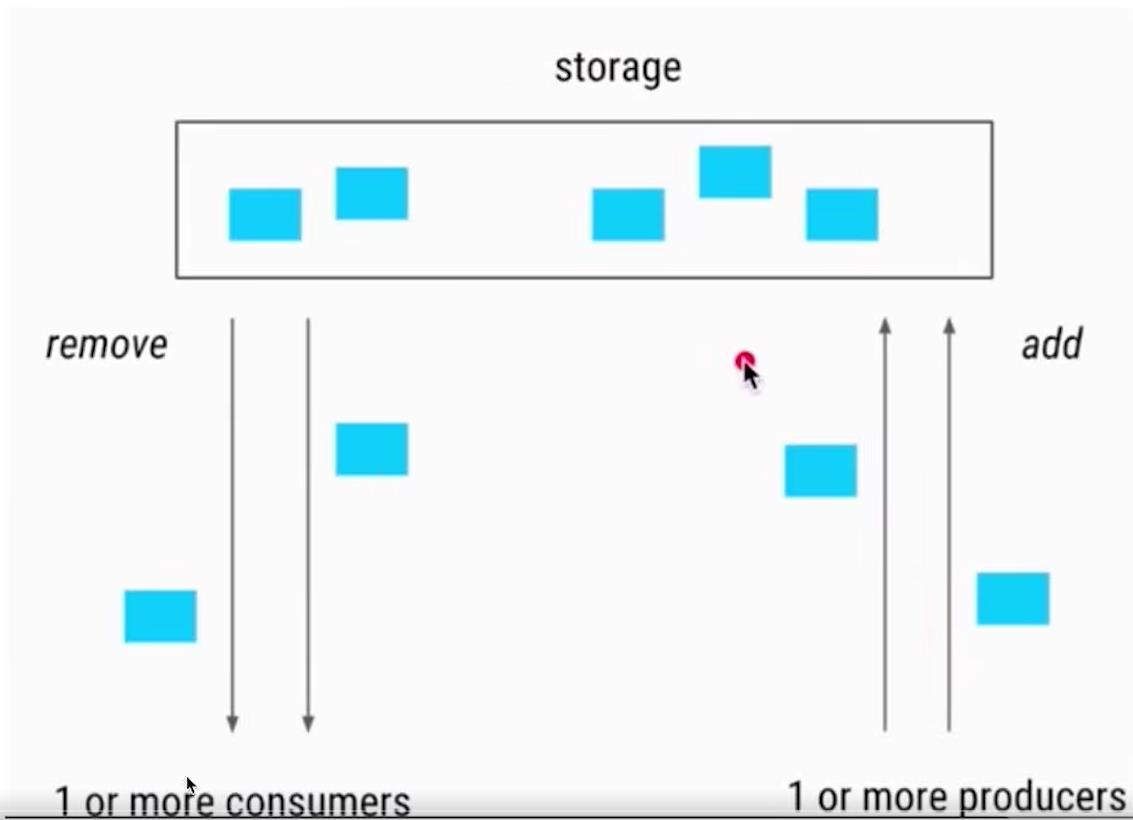
生产者生成往queue队列中放,queue队列满了生产阻塞;
消费者消费queue队列,queue队列没了消费阻塞;
生产者生成会向消费者通知消费;
消费者消费会向生成者通知生成
![[外链图片转存失败,源站可能有防盗链机制,建议将图片保存下来直接上传(img-dm3xj1E4-1621690023212)(C:/Users/PePe/AppData/Roaming/Typora/typora-user-images/image-20210522205650646.png)]](https://image.cha138.com/20210717/718c8675b01546cab0ee00c2dec83551.jpg)
3)手写代码,通过wait/notify实现生产者消费者模式
/******
@author 阿昌
@create 2021-05-22 20:58
*******
* 用wait/notify来实现 生产者消费者模式
*/
public class ProducerConsumerModel {
//主函数
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventStorage eventStorage = new EventStorage();
Consumer1 consumer = new Consumer1(eventStorage);
Producer1 producer = new Producer1(eventStorage);
Thread threadConsumer = new Thread(consumer);
Thread threadProducer = new Thread(producer);
threadConsumer.start();
threadProducer.start();
}
}
//生产者
class Producer1 implements Runnable{
private EventStorage storage;
public Producer1(EventStorage storage) {
this.storage = storage;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
storage.put();
}
}
}
//消费者
class Consumer1 implements Runnable{
private EventStorage storage;
public Consumer1(EventStorage storage) {
this.storage = storage;
}
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
storage.take();
}
}
}
//队列
class EventStorage{
private int maxSize;
private LinkedList storage;
public EventStorage(){
this.maxSize=10;
storage = new LinkedList<>();
}
//生成产品
public synchronized void put(){
//如果满了
while (storage.size()==maxSize){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//如果没满
storage.add(new Date());
System.out.println("生产者生产了产品,仓库里有了"+storage.size()+"个产品");
notify();
}
//消费产品
public synchronized void take(){
//如果空了
while (storage.size()<=0){
try {
wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//如果没空
System.out.println("消费者消费了产品,拿到了"+storage.poll()+",现在仓库还剩下"+storage.size());
notify();
}
}
- 结果

以上是关于Day275.Thread和Object类中的重要方法 -Juc的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章