Part3-1-3 Vue.js 响应式原理
Posted 沿着路走到底
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Part3-1-3 Vue.js 响应式原理相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
数据响应式
数据模型仅仅是普通的 javascript 对象,而当我们修改数据时,视图会进行更新,避免了繁琐的 Dom 操作,提供开发效率。
双向绑定
数据改变,视图改变;视图改变,数据也随之改变。
我们可以使用 v-model 在表单元素上 创建双向数据绑定。
数据驱动
数据驱动是 Vue 最独特的特性之一。
开发过程中仅需要关注数据本身,不需要关心数据是如何渲染到视图。
数据响应式核心原理-Vue2
Object.defineProperty
https://cn.vuejs.org/v2/guide/reactivity.html
无法 shim 是指 无法做降级处理。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>defineProperty 多个成员</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
hello
</div>
<script>
// 模拟 Vue 中的 data 选项
let data = {
msg: 'hello',
count: 10
}
// 模拟 Vue 的实例
let vm = {}
proxyData(data)
function proxyData(data) {
// 遍历 data 对象的所有属性
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => {
// 把 data 中的属性,转换成 vm 的 setter/setter
Object.defineProperty(vm, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get () {
console.log('get: ', key, data[key])
return data[key]
},
set (newValue) {
console.log('set: ', key, newValue)
if (newValue === data[key]) {
return
}
data[key] = newValue
// 数据更改,更新 DOM 的值
document.querySelector('#app').textContent = data[key]
}
})
})
}
// 测试
vm.msg = 'Hello World'
console.log(vm.msg)
</script>
</body>
</html>数据响应式核心原理-Vue3
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="ie=edge">
<title>Proxy</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app">
hello
</div>
<script>
// 模拟 Vue 中的 data 选项
let data = {
msg: 'hello',
count: 0
}
// 模拟 Vue 实例
let vm = new Proxy(data, {
// 执行代理行为的函数
// 当访问 vm 的成员会执行
get (target, key) {
console.log('get, key: ', key, target[key])
return target[key]
},
// 当设置 vm 的成员会执行
set (target, key, newValue) {
console.log('set, key: ', key, newValue)
if (target[key] === newValue) {
return
}
target[key] = newValue
document.querySelector('#app').textContent = target[key]
}
})
// 测试
vm.msg = 'Hello World'
console.log(vm.msg)
</script>
</body>
</html>发布订阅模式
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="cn">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>发布订阅模式</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 事件触发器
class EventEmitter {
constructor () {
// { 'click': [fn1, fn2], 'change': [fn] }
this.subs = Object.create(null)
}
// 注册事件
$on (eventType, handler) {
this.subs[eventType] = this.subs[eventType] || []
this.subs[eventType].push(handler)
}
// 触发事件
$emit (eventType) {
if (this.subs[eventType]) {
this.subs[eventType].forEach(handler => {
handler()
})
}
}
}
// 测试
let em = new EventEmitter()
em.$on('click', () => {
console.log('click1')
})
em.$on('click', () => {
console.log('click2')
})
em.$emit('click')
</script>
</body>
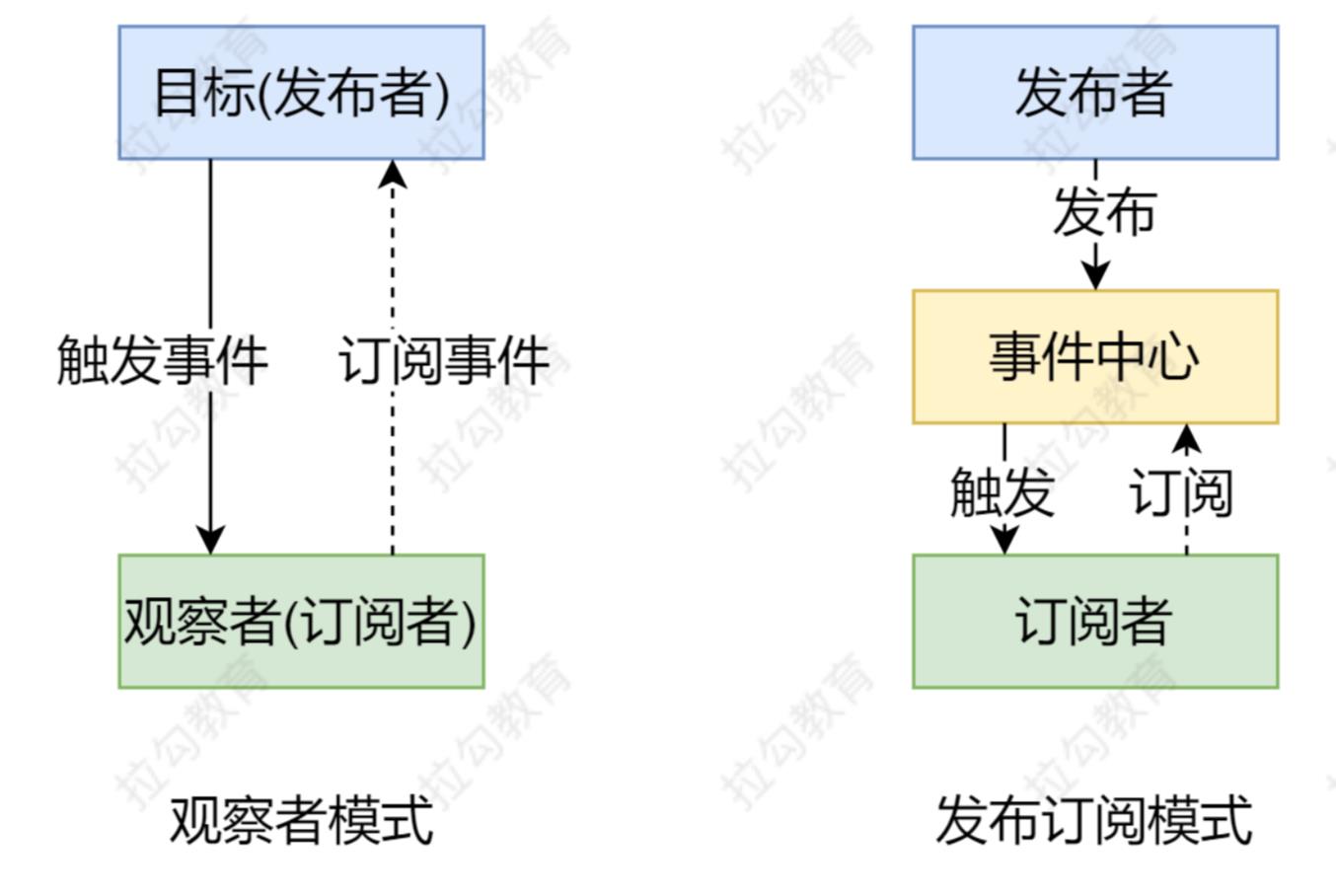
</html>观察者模式
观察者(订阅者) -- Watcher
update():当事件发生时,具体要做的事情
目标(发布者) -- Dep
subs 数组:存储所有的观察者
addSub():添加观察者
notify():当事件发生,调用所有观察者的 update() 方法
没有事件中心
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>观察者模式</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
// 发布者-目标
class Dep {
constructor () {
// 记录所有的订阅者
this.subs = []
}
// 添加订阅者
addSub (sub) {
if (sub && sub.update) {
this.subs.push(sub)
}
}
// 发布通知
notify () {
this.subs.forEach(sub => {
sub.update()
})
}
}
// 订阅者-观察者
class Watcher {
update () {
console.log('update')
}
}
// 测试
let dep = new Dep()
let watcher = new Watcher()
dep.addSub(watcher)
dep.notify()
</script>
</body>
</html>总结
观察者模式是由具体目标调度,比如当事件触发,Dep 就会去调用观察者的方法,所以观察者模
式的订阅者与发布者之间是存在依赖的。
发布/订阅模式由统一调度中心调用,因此发布者和订阅者不需要知道对方的存在。
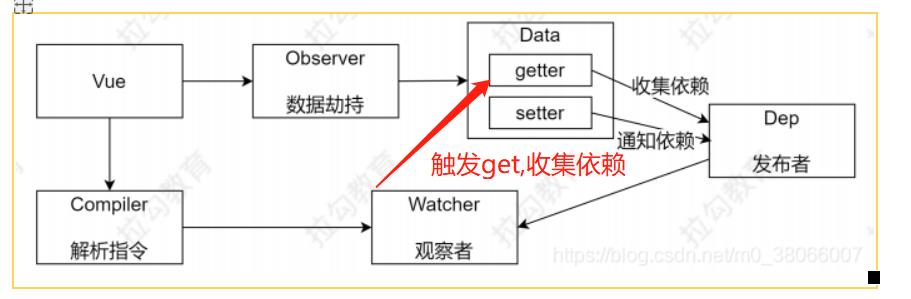
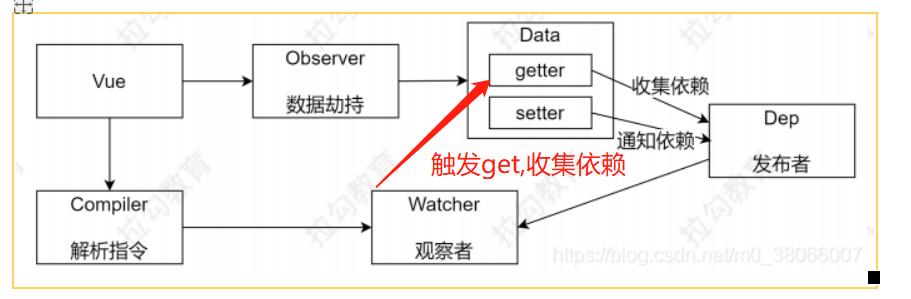
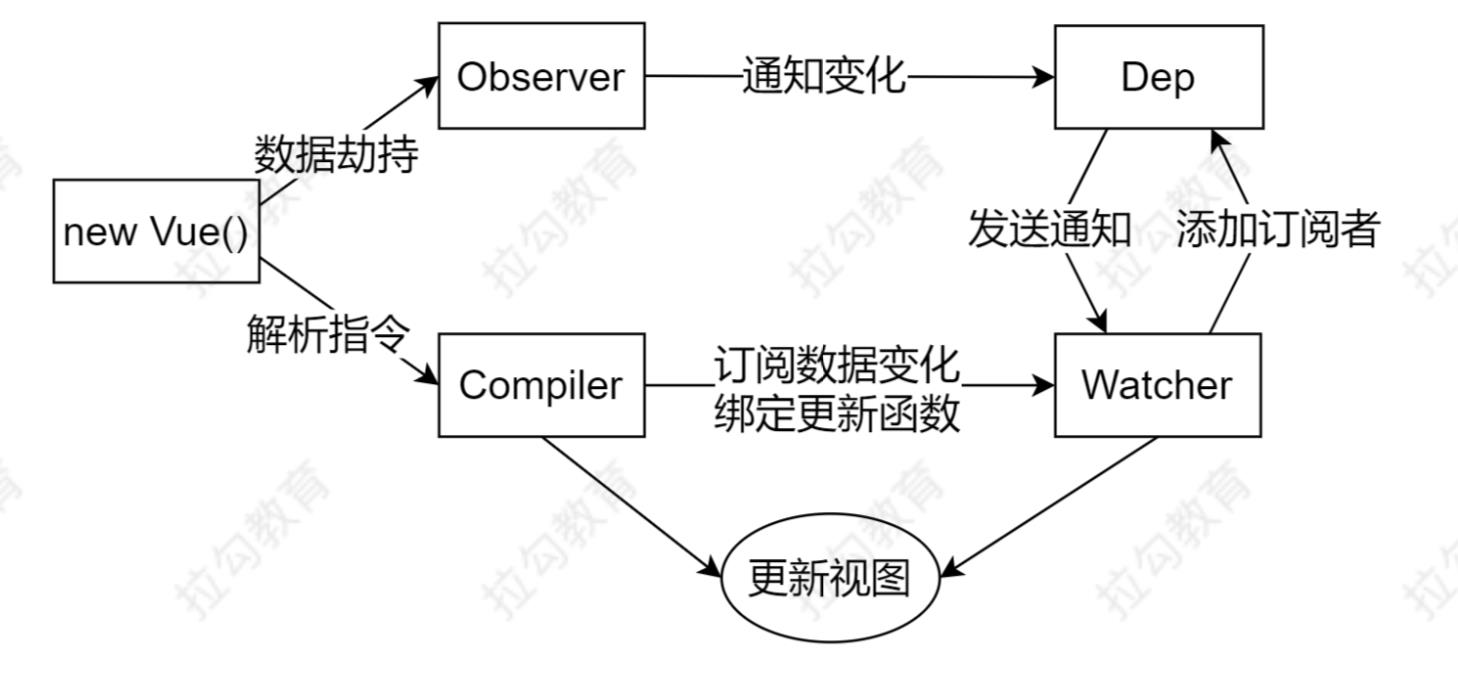
Vue 响应式原理模拟
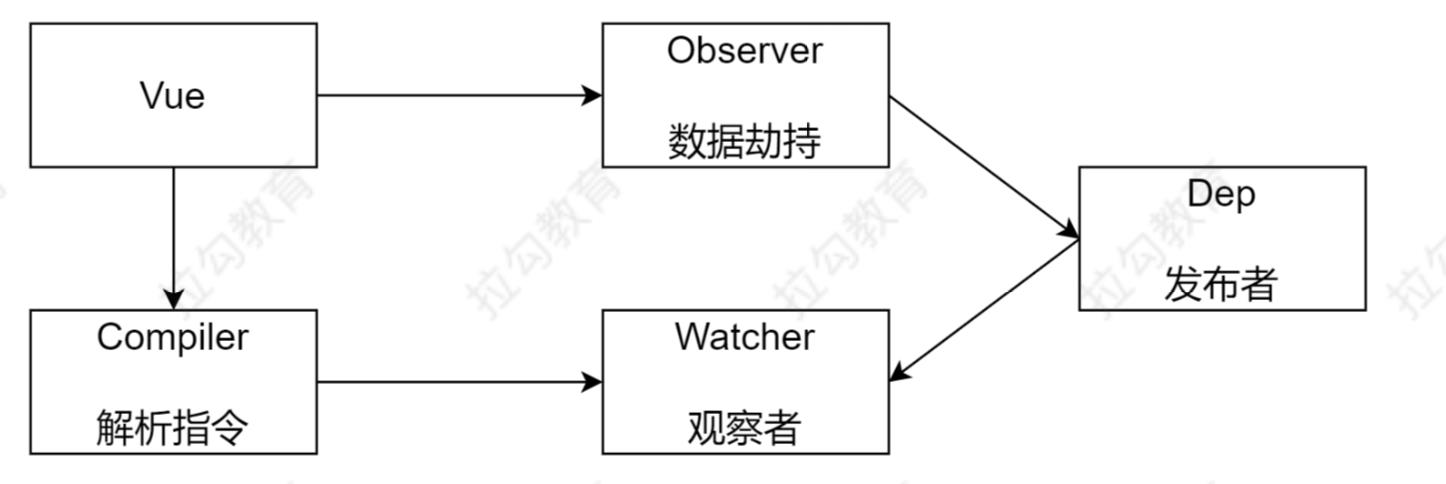
Vue
把 data 中的成员注入到 Vue 实例,并且把 data 中的成员转成 getter/setter
Observer
能够对数据对象的所有属性进行监听,如有变动可拿到最新值并通知 Dep
Compiler
解析每个元素中的指令/插值表达式,并替换成相应的数据
Dep
添加观察者(watcher),当数据变化通知所有观察者
Watcher
数据变化更新视图
Vue.js
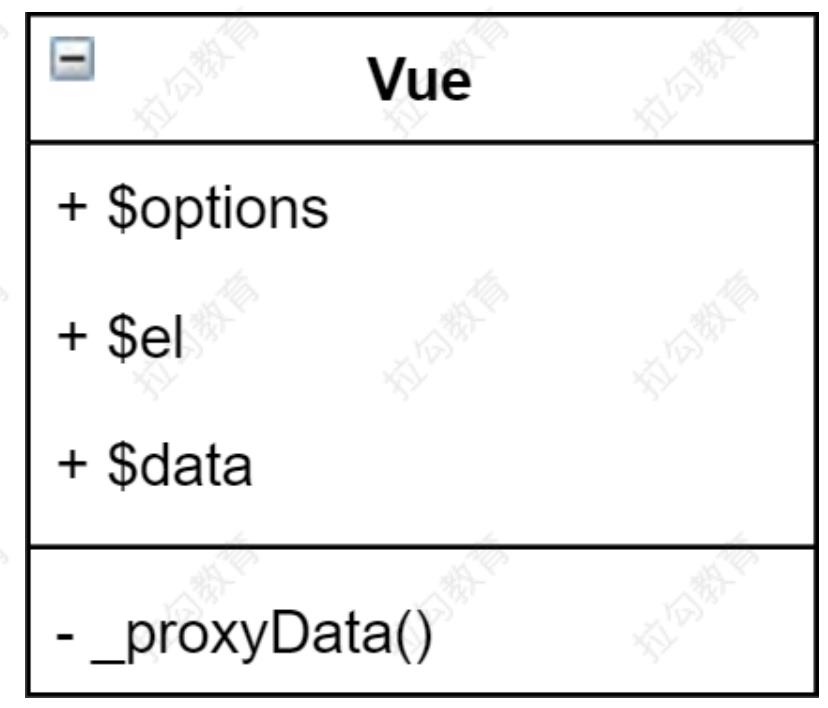
代码分析
class Vue {
constructor(options) {
// 1. 通过属性保存选项的数据
this.$options = options || {}
this.$data = options.data || {}
this.$el = typeof options.el === 'string' ? document.querySelector(options.el) : options.el
// 2. 把data中的成员转换成getter和setter,注入到vue实例中
this._proxyData(this.$data)
// 3. 调用observer对象,监听数据的变化
new Observer(this.$data)
// 4. 调用compiler对象,解析指令和差值表达式
new Compiler(this)
}
_proxyData(data) {
// 遍历data中的所有属性
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => {
// 把data的属性注入到vue实例中
Object.defineProperty(this, key, {
enumerable: true,
configurable: true,
get() {
return data[key]
},
set(newValue) {
if (newValue === data[key]) {
return
}
data[key] = newValue
}
})
})
}
}observer.js
功能
负责把 data 选项中的属性转换成响应式数据
data 中的某个属性也是对象,把该属性转换成响应式数据
数据变化发送通知
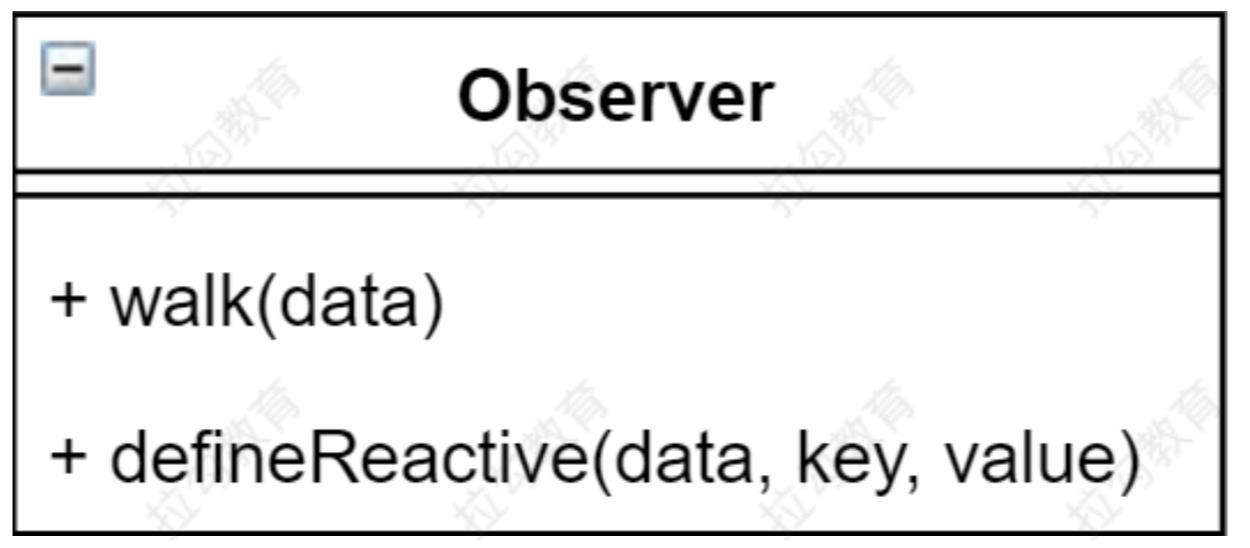
代码分析
class Observer {
constructor (data) {
this.walk(data)
}
walk (data) {
// 1. 判断data是否是对象
if (!data || typeof data !== 'object') {
return
}
// 2. 遍历data对象的所有属性
Object.keys(data).forEach(key => {
this.defineReactive(data, key, data[key])
})
}
defineReactive (obj, key, val) {
let that = this
// 负责收集依赖,并发送通知
let dep = new Dep()
// 如果val是对象,把val内部的属性转换成响应式数据
this.walk(val)
Object.defineProperty(obj, key, {
enumerable: true, // 可枚举
configurable: true, // 可配置
get () {
// 收集依赖
Dep.target && dep.addSub(Dep.target)
// 如果 return obj[key],又会触发 get ,使得堆栈溢出
return val
},
set (newValue) {
if (newValue === val) {
return
}
val = newValue
that.walk(newValue)
// 发送通知
dep.notify()
}
})
}
}compiler.js

代码分析
class Compiler {
constructor (vm) {
this.el = vm.$el
this.vm = vm
this.compile(this.el)
}
// 编译模板,处理文本节点和元素节点
compile (el) {
let childNodes = el.childNodes
Array.from(childNodes).forEach(node => {
// 处理文本节点
if (this.isTextNode(node)) {
this.compileText(node)
} else if (this.isElementNode(node)) {
// 处理元素节点
this.compileElement(node)
}
// 判断node节点,是否有子节点,如果有子节点,要递归调用compile
if (node.childNodes && node.childNodes.length) {
this.compile(node)
}
})
}
// 编译元素节点,处理指令
compileElement (node) {
// console.log(node.attributes)
// 遍历所有的属性节点
Array.from(node.attributes).forEach(attr => {
// 判断是否是指令
let attrName = attr.name
if (this.isDirective(attrName)) {
// v-text --> text
attrName = attrName.substr(2)
let key = attr.value
this.update(node, key, attrName)
}
})
}
update (node, key, attrName) {
let updateFn = this[attrName + 'Updater']
updateFn && updateFn.call(this, node, this.vm[key], key)
}
// 处理 v-text 指令
textUpdater (node, value, key) {
node.textContent = value
new Watcher(this.vm, key, (newValue) => {
node.textContent = newValue
})
}
// v-model
modelUpdater (node, value, key) {
node.value = value
new Watcher(this.vm, key, (newValue) => {
node.value = newValue
})
// 双向绑定
node.addEventListener('input', () => {
this.vm[key] = node.value
})
}
// 编译文本节点,处理差值表达式
compileText (node) {
// console.dir(node)
// {{ msg }}
let reg = /\\{\\{(.+?)\\}\\}/
let value = node.textContent
if (reg.test(value)) {
let key = RegExp.$1.trim()
node.textContent = value.replace(reg, this.vm[key])
// 创建watcher对象,当数据改变更新视图
new Watcher(this.vm, key, (newValue) => {
node.textContent = newValue
})
}
}
// 判断元素属性是否是指令
isDirective (attrName) {
return attrName.startsWith('v-')
}
// 判断节点是否是文本节点
isTextNode (node) {
return node.nodeType === 3
}
// 判断节点是否是元素节点
isElementNode (node) {
return node.nodeType === 1
}
}Dep(Dependency)
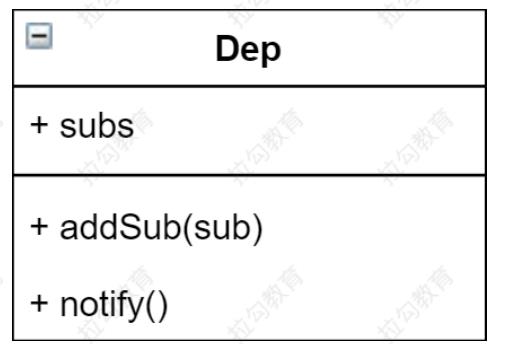
代码分析
class Dep {
constructor () {
// 存储所有的观察者
this.subs = []
}
// 添加观察者
addSub (sub) {
if (sub && sub.update) {
this.subs.push(sub)
}
}
// 发送通知
notify () {
this.subs.forEach(sub => {
sub.update()
})
}
}watcher.js
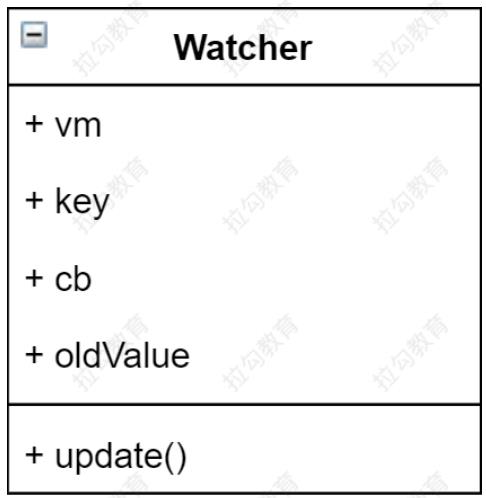
代码分析
class Watcher {
constructor (vm, key, cb) {
this.vm = vm
// data中的属性名称
this.key = key
// 回调函数负责更新视图
this.cb = cb
// 把watcher对象记录到Dep类的静态属性target
Dep.target = this
// 触发get方法,在get方法中会调用addSub
this.oldValue = vm[key]
/ 在 get 方法里收集依赖后,把 target 销毁,以防后面重复添加
Dep.target = null
}
// 当数据发生变化的时候更新视图
update () {
let newValue = this.vm[this.key]
if (this.oldValue === newValue) {
return
}
this.cb(newValue)
}
}总结
Vue
记录传入的选项,设置 $data/$el
把 data 的成员注入到 Vue 实例
负责调用 Observer 实现数据响应式处理(数据劫持) 负责调用 Compiler 编译指令/插值表达式等
Observer
数据劫持
负责把 data 中的成员转换成 getter/setter
负责把多层属性转换成 getter/setter
如果给属性赋值为新对象,把新对象的成员设置为 getter/setter
添加 Dep 和 Watcher 的依赖关系
数据变化发送通知
Compiler
负责编译模板,解析指令/插值表达式
负责页面的首次渲染过程
当数据变化后重新渲染
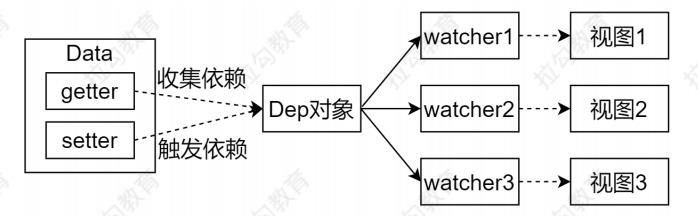
Dep
收集依赖,添加订阅者(watcher)
通知所有订阅者
Watcher
自身实例化的时候往dep对象中添加自己
当数据变化dep通知所有的 Watcher 实例更新视图
1
以上是关于Part3-1-3 Vue.js 响应式原理的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章