std::alloc 二级配置器
Posted Jqivin
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了std::alloc 二级配置器相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
一、关于二级配置器的介绍
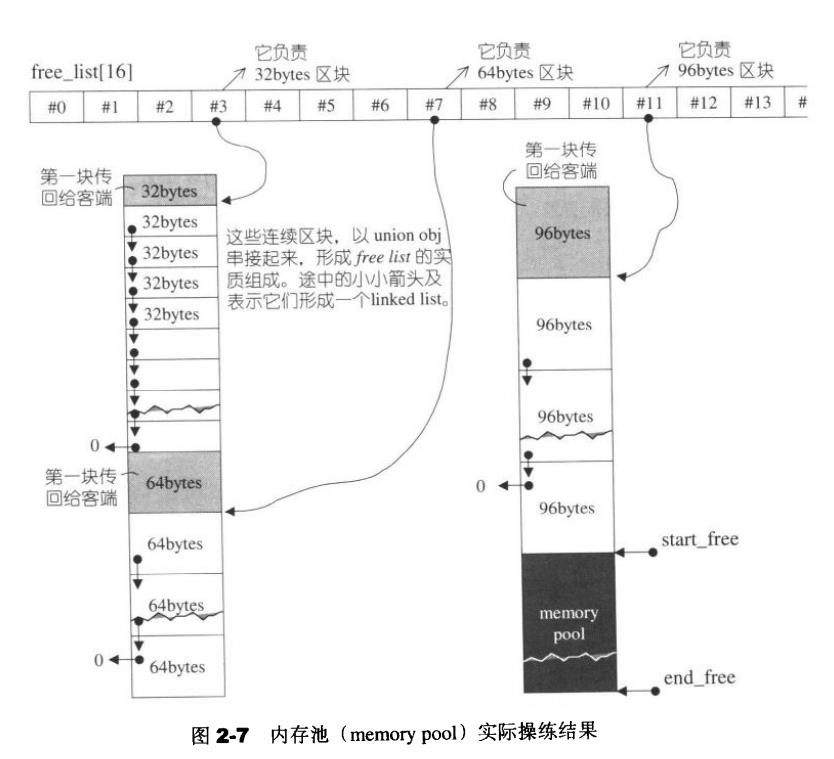
SGI第二级配置器的做法是,如果区块够大,超过128 bytes时,就移交第一级配置器处理。当区块小于128 bytes 时,则以内存池 ( memory pool)管理,每次配置一大块内存,并维护对应之自由链表( free-list )。下次若再有相同大小的内存需求,就直接从free-lists中拨出。如果客端释还小额区块,就由配置器回收到free_lists中。是的,别忘了,配置器除了负责配置,也负责回收。为了方便管理,SGI第二级配置器会主动将任何小额区块的内存需求量上调至8的倍数(例如客端要求30 bytes,就自动调整为32 bytes) ,并维护16个free_lists,各自管理大小分别为: 8, 16,24 ,32,40,48 ,56,64,72,80,8 8,96, 104,112,120,128 bytes的小额区块。
二、结构
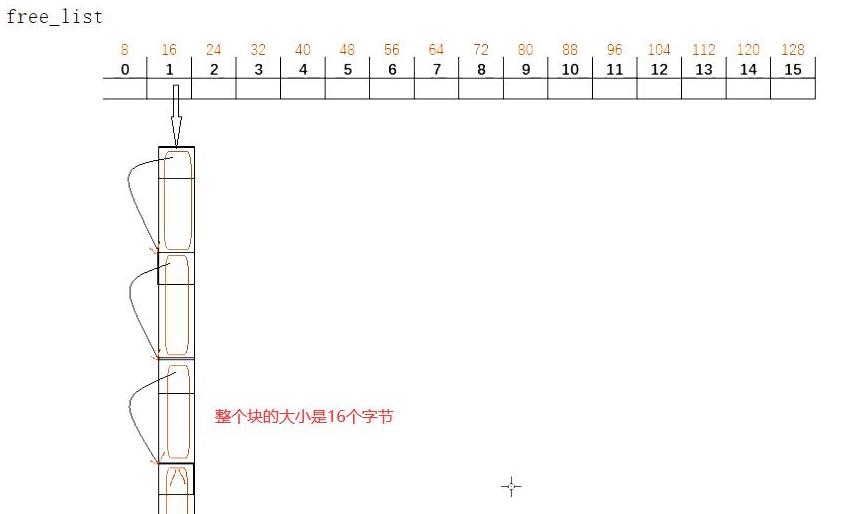
自由链表结构:
//自由链表中所连接的每个链表的结点类型
union obj
{
union obj* free_list_link; //next的作用
char client_data[1]; //没有什么作用,可以删除掉
};
//自由链表的表的结构,别忘了是静态的结构
static union obj* volatile free_list[__NFREELISTS];
内存池的结构
//内存池的结构
static char* start_free; //内存池的开始位置 ,定义成char类型,每次+1就表示增加一个字节
static char* end_free; //内存池的结束的位置
static size_t heap_size; //总共从堆区申请的空间
三、主要接口和函数的介绍
1.allocate 空间配置函数
//和一级配置器名字一样
static void* allocate(size_t n)
{
if (n <= 0)
return;
if (n > 128)
{
return _malloc_alloc_template<ints>::allocate(n);
}
obj* volatile* my_free_list = nullptr; //二级指针,因为free_list就是二级指针
obj* result = nullptr;
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n);
result = *my_free_list;
if (result == nullptr)
{
void *r = refill(ROUND_UP(n)); //参数是一块空间的大小
return r;
}
*my_free_list = result->free_list_link; //相当于头删,第一块要返回给用户
return result;
}
2. deallocate 空间释放函数
static void* deallocate(void* p, size_t n)
{
if (n > (size_t)__MAX_BYTES)
{
malloc_alloc::deallocate(p, n);
return;
}
//头插法,插回原来的free_list中
obj* q = (obj*)p;
obj* volatile* my_free_list = nullptr;
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n);
q->free_list_link = *my_free_list;
*my_free_list = q;
return;
}
3.reallocate 重新分配函数
static void* reallocate(void* p, size_t old_sz, size_t new_sz)
{
//
if (old_sz > 128 && new_sz > 128)
{
return malloc_alloc::reallocate(p, old_sz, new_sz);
}
if (ROUND_UP(old_sz) == ROUND_UP(new_sz))
{
return p;
}
/*
* 包括三种情况
* old_sz > 128 new_size < 128
* old_sz < 128 new_size > 128
* old_sz < 128 new_size < 128
* 不管new_sz是否大于128,我们都调用二级配置器,如果大于128,二级配置器会调动一级配置器的
*/
size_t sz = old_sz > new_sz ? new_sz : old_sz; //较小的内存大小
void* s = allocate(new_sz); //申请新的内存
memmove(s, p, sz); //将旧的拷贝到新的中 p->s
deallocate(p); //释放旧的,如果大于128,调用一级配置器,小于128,调用二级配置器
return s;
}
4.refill函数
作用:该函数的作用就是重新填充free_list[目标值],将从chunk_alloc返回的大块的内存空间进行重新的分块处理,一块一块的链接到free_list上
//能进行到这里就说明free_list[目标值]必然是空的,在allocate函数中有显示
//该函数的作用就是重新填充free_list[目标值],将从chunk_alloc返回的大块的内存空间进行重新的分块处理,一块一块的链接到free_list上
static void* refill(size_t n)
{
int nobjs = 20; //希望申请20个连续的块
char* chunk = (char*)chunk_alloc(n,nobjs); //nobjs passed by reference ,要定义成char* 因为下面chunk+n才能知道前进n字节
//只分配一个区块,这个区块直接给用户就行了
if (1 == nobjs)
{
return chunk;
}
obj* volatile* my_free_list = nullptr;
obj* result = (obj*)chunk; //保存返回给用户的那一块,所以下面的*my_free_list = next_obj = (chunk + n); +n 表示指向下一块,第一块返回用户
obj* current_obj = nullptr, * next_obj = nullptr;
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(n); //找到正确的下标,开始工作了
*my_free_list = next_obj = (obj*)(chunk + n); //不是result->free_list_link,因为此时result->free_list_link还没有值,这是一块全新的空间
current_obj = *my_free_list;
int i = 0;
for (i = 1; ; i++)
{
current_obj = next_obj;
next_obj = (obj*)((char*)next_obj + n);
if (i == nobjs - 1)
{
current_obj->free_list_link = nullptr; //到头了,这时候next指向尾
break;
}
else
{
current_obj->free_list_link = next_obj; //连接上
}
}
return result;
}
5.chunk_alloc函数
作用:
- 最重要的一个函数
- 该函数的作用就是:管理内存池,主要被refill调用,从内存池中取出空间给free_list使用返回值是一大块空间,
- 如果有nobjs*n那么大的空间最好,没有那么大也没关系,返回<n块,再不济返回一块,如果内存池的空间能返回的空间一块都不够就把剩下的空间连接到free_list的相应的部位,再申请一大块空间 ,如果成功最好,没有成功的话,说明没有内存了,这时候我们在free_list当前n在free_list之后的位置)中寻找(因为后面的比当前的空间大),如果后面有,我们就“借一块”,如果没有的话,我们就找一级配置器帮忙,因为一级配置器如果没空间会调用储备的内存,如果在一级配置器里还是没空间,一级配置器一生气就抛出异常,或者exit(1);
/*
* 最重要的一个函数
* 该函数的作用就是:管理内存池,主要被refill调用,从内存池中取出空间给free_list使用
* 返回值是一大块空间,如果有nobjs*n最好,没有那么大也没关系,返回<n块,再不济返回一块,如果内存池的空间能返回的空间一块都不够
* 就把剩下的空间连接到free_list的相应的部位,再申请一大块空间 ,如果成功最好,没有成功的话,说明没有内存了,这时候我们在free_list
* (当前n在free_list之后的位置)中寻找(因为后面的比当前的空间大),如果后面有,我们就“借一块”,如果没有的话,我们就找一级配置器
* 帮忙,因为一级配置器如果没空间会调用储备的内存,如果在一级配置器里还是没空间,一级配置器一生气就抛出异常,或者exit(1);
*/
static void* chunk_alloc(size_t n,int & nobjs)
{
char* result = nullptr;
size_t bytes_left = end_free - start_free; //内存池中剩余的字节数
size_t total_bytes = n * nobjs; //refill想要申请的字节数
if (bytes_left > total_bytes) // 内存池可以提供 20 块
{
result = start_free;
start_free = start_free + bytes_left; //start_free向下移动
return result;
}
else if (bytes_left >= n) // 不足20块但大于 1 块
{
nobjs = bytes_left / n; //改变nobjs的值
result = start_free;
total_bytes = n * nobjs;
start_free = start_free + total_bytes;
return result;
}
else //不足一块
{
size_t bytes_to_get = 2 * total_bytes + ROUND_UP(heap_size >> 4); //?
//不足16,可能只有8了,把剩下的连在0下标的链表上边
if (bytes_left > 0)
{
obj* volatile* my_free_list = nullptr;
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(bytes_left);
((obj*)start_free)->free_list_link = *my_free_list;
*my_free_list = (obj*)start_free; //注意:每次都要强转
}
start_free = (char*)malloc(bytes_to_get);// 申请资源,先不调用一级配置器
if (start_free == nullptr) //失败,从free_list当前位置之后中寻找看有没有空闲的空间
{
obj* volatile* my_free_list = nullptr;
for (int i = n ; i <= __MAX_BYTES; i += __ALIGN)
{
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(i);
obj* p = *my_free_list;
if (p != nullptr)
{
*my_free_list = p->free_list_link;//my_free_list指向他的下一个,只卸掉一块
start_free = (char*)p; //类型转换
end_free = start_free + i;
return chunk_alloc(n, nobjs); //现在有空间了,回到上面的函数中进行分配,然后返回,此时objs还未改变
}
}
//山穷水尽了,调用之前储备的空间
start_free = (char*)malloc_alloc::allocate(bytes_to_get);
//如果之前储备的空间也没有了,就结束进程
}
//能来到这说明上面的之前储备的空间申请成功或者在堆区空间申请成功
end_free = start_free + bytes_to_get;
heap_size += bytes_to_get;
return chunk_alloc(n,nobjs);
}
}
二级配置器的测试
SGI空间配置器 jqw_alloc.h的代码
#pragma once
#include<iostream>
namespace jqw
{
#if 0
#include<new>
#define _THROW_BAD_ALLOC throw std::bad_alloc;
#elif !defined(_THROW_BAD_ALLOC)
//#include<iostream>
#define _THROW_BAD_ALLOC std::cerr<<"out of memory" <<std::endl;exit(1)
#endif
//非类型模板化,inst没有任何意义
template <int inst>
class _malloc_alloc_template
{
private:
static void* oom_malloc(size_t n)
{
void (*my_malloc_handler)() = nullptr;
void* result = nullptr;
for (;;)
{
my_malloc_handler = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;
if (my_malloc_handler == nullptr)
{
_THROW_BAD_ALLOC;
}
(*my_malloc_handler)();
result = malloc(n);
//如果申请到了空间,就返回申请到的空间,否则再次进入循环,继续释放空间
if (result != nullptr)
{
return result;
}
}
}
static void* oom_realloc(void* p, size_t new_sz)
{
void (*my_malloc_handler)() = nullptr;
void* result = nullptr;
for (;;)
{
my_malloc_handler = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;
if (my_malloc_handler == nullptr)
{
_THROW_BAD_ALLOC;
}
(*my_malloc_handler)();
result = realloc(p, new_sz);
//如果申请到了空间,就返回申请到的空间,否则再次进入循环,继续释放空间
if (result != nullptr)
{
return result;
}
}
}
//返回值为void,无参的函数指针,在类外把它初始化为空 -- 静态成员初始化要在类外
static void(*__malloc_alloc_oom_handler)();
public:
//申请空间,如果检测到有内存调用malloc,没有就调用oom_malloc
static void* allocate(size_t n)
{
void* result = malloc(n);
if (result == nullptr)
{
result = oom_malloc(n);
}
return result;
}
//释放空间,一级配置器直接使用free()
static void* deallocate(void* p, size_t /* n */)
{
free(p);
}
//重新分配空间
static void* reallocate(void* p, size_t /* old_sz */, size_t new_size)
{
void* result = realloc(p, new_size);
if (result == nullptr)
{
result = oom_realloc(p, new_size);
}
return result;
}
typedef void(*malloc_handler)(); //定义一个函数指针
//返回值是一个函数指针,参数也是一个函数指针
//static void(*set_alloc_handler)(void(*f)()); //与下面的等价
//在这个函数的作用是吧原来的__malloc_alloc_oom_handler返回(可能别的函数收到这个返回值就把这个函数指针的内容运行 -- 释放空间)
//然后再把传过来的指针给给__malloc_alloc_oom_handler,供下次使用
static malloc_handler set_alloc_handler(malloc_handler f)
{
malloc_handler old = __malloc_alloc_oom_handler;
__malloc_alloc_oom_handler = f;
return old;
}
};
//静态成员的类外定义
template <int inst>
void(*_malloc_alloc_template<inst>::__malloc_alloc_oom_handler)() = nullptr;
typedef _malloc_alloc_template<0> malloc_alloc;
//
//二级配置器
enum {__ALIGN = 8}; //自由链表每次增加的字节数 //对其的意思
enum{__MAX_BYTES = 128}; //自由链表中最大的字节数
enum{__NFREELISTS = __MAX_BYTES / __ALIGN}; //自由链表的元素个数
template<bool threads,int ints>
class __default_alloc_template
{
private:
//自由链表中所连接的每个链表的结点类型
union obj
{
union obj* free_list_link; //next的作用
char client_data[1]; //没有什么作用,可以删除掉
};
private:
//自由链表的表的结构,别忘了是静态的结构
static union obj* volatile free_list[__NFREELISTS];
//内存池的结构
static char* start_free; //内存池的开始位置 ,定义成char类型,每次+1就表示增加一个字节
static char* end_free; //内存池的结束的位置
static size_t heap_size; //总共从堆区申请的空间
static size_t FREELIST_INDEX(size_t n)
{
return (n + __ALIGN - 1) / __ALIGN - 1;
}
static size_t ROUND_UP(size_t n)
{
//return (n + __ALIGN - 1) & ~(__ALIGN - 1);
return ((n + __ALIGN - 1) / __ALIGN) * 8;
}
/*
* 最重要的一个函数
* 该函数的作用就是:管理内存池,主要被refill调用,从内存池中取出空间给free_list使用
* 返回值是一大块空间,如果有nobjs*n最好,没有那么大也没关系,返回<n块,再不济返回一块,如果内存池的空间能返回的空间一块都不够
* 就把剩下的空间连接到free_list的相应的部位,再申请一大块空间 ,如果成功最好,没有成功的话,说明没有内存了,这时候我们在free_list
* (当前n在free_list之后的位置)中寻找(因为后面的比当前的空间大),如果后面有,我们就“借一块”,如果没有的话,我们就找一级配置器
* 帮忙,因为一级配置器如果没空间会调用储备的内存,如果在一级配置器里还是没空间,一级配置器一生气就抛出异常,或者exit(1);
*/
static void* chunk_alloc(size_t n,int & nobjs)
{
char* result = nullptr;
size_t bytes_left = end_free - start_free; //内存池中剩余的字节数
size_t total_bytes = n * nobjs; //refill想要申请的字节数
if (bytes_left > total_bytes) // 内存池可以提供 20 块
{
result = start_free;
start_free = start_free + bytes_left; //start_free向下移动
return result;
}
else if (bytes_left >= n) // 不足20块但大于 1 块
{
nobjs = bytes_left / n; //改变nobjs的值
result = start_free;
total_bytes = n * nobjs;
start_free = start_free + total_bytes;
return result;
}
else //不足一块
{
size_t bytes_to_get = 2 * total_bytes + ROUND_UP(heap_size >> 4); //?
//不足16,可能只有8了,把剩下的连在0下标的链表上边
if (bytes_left > 0)
{
obj* volatile* my_free_list = nullptr;
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(bytes_left);
((obj*)start_free)->free_list_link = *my_free_list;
*my_free_list = (obj*)start_free; //注意:每次都要强转
}
start_free = (char*)malloc(bytes_to_get);// 申请资源,先不调用一级配置器
if (start_free == nullptr) //失败,从free_list当前位置之后中寻找看有没有空闲的空间
{
obj* volatile* my_free_list = nullptr;
for (int i = n ; i <= __MAX_BYTES; i += __ALIGN)
{
my_free_list = free_list + FREELIST_INDEX(i);
obj* p = *my_free_list;
if (p != nullptr)
{
*my_free_list = p->free_list_link;//my_free_list指向他的下一个,只卸掉一块
start_free = (char*)p; //类型转换
end_free = start_free + i;
return chunk_alloc(n, nobjs); //现在有空间了,回到上面的函数中进行分配,然后返回,此时objs还未改变
}
以上是关于std::alloc 二级配置器的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
第一个代码中的错误,但第二个正确“在抛出 'std::bad_alloc' what() 的实例后调用终止:std::bad_alloc Aborted(core dumped)”