Android-面试题Fragment详解
Posted 帅次
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Android-面试题Fragment详解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、为什么要有Fragment?
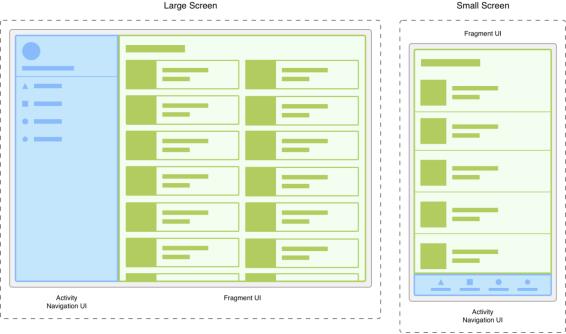
android运行在各种各样的设备中,有小屏幕的手机,还有大屏幕的平板,电视等。同样的界面在手机上显示可能很好看,在大屏幕的平板上就未必了,手机的界面放在平板上可能会有过分被拉长、控件间距过大等情况。针对屏幕尺寸的差距,Fragment的出现能做到一个App可以同时适应手机和平板。这就是为什么要有Fragment的原因。
android.app.Fragment在API 级别 11 中 添加,已在API 级别 28 中弃用。
二、Fragment为什么被称为第五大组件
Fragment比Activity更节省内存,其切换模式也更加舒适,使用频率不低于四大组件,且有自己的生命周期,而且必须依附于Activity,不能独立存在。
特点:
-
Fragment依赖于Activity,不能独立存在
-
一个Activity可以有多个Fragment
-
一个Fragment可以被多个Activity重用
-
Fragment有自己的生命周期,并能接收输入事件
-
可以在Activity运行时动态地添加或删除Fragment
三、Activity创建Fragment的方式
静态创建
- 定义Fragment的xml布局文件
- 自定义Fragment类,继承Fragment类或其子类,同时实现onCreateView()方法,在方法中通过inflater.inflate加载布局文件,接着返回其View
- 在需要加载Fragment的Activity对应布局文件中<fragment>的name属性设为全限定类名,即包名.fragment
- 最后在Activity调用setContentView()加载布局文件即可
样例:
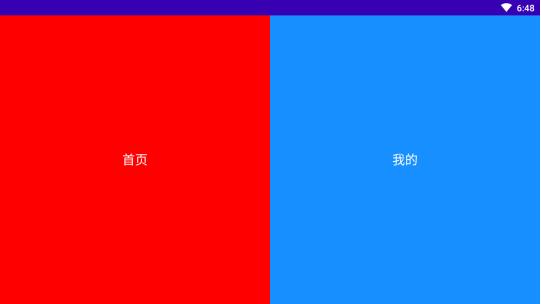
1.定义Fragment的xml布局文件(新建fragment_home.xml和fragment_mine.xml)
fragment_home.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="@color/color_ff0000"
android:gravity="center"
>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tv_on"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="首页"
android:onClick="onClick"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:textSize="@dimen/text_size_20"/>
</LinearLayout>fragment_mine.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:background="@color/color_188FFF"
android:gravity="center"
>
<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="我的"
android:textColor="@color/white"
android:textSize="@dimen/text_size_20"/>
</LinearLayout>2.自定义Fragment类,继承Fragment类或其子类,同时实现onCreateView()方法,在方法中通过inflater.inflate加载布局文件,接着返回其View
public class HomeFragment extends Fragment {
private TextView tv_on;
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_home, container,false);
MLog.e(this.getClass().getName()+"onCreateView");
tv_on = view.findViewById(R.id.tv_on);
tv_on.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
MLog.e(this.getClass().getName()+"准备关闭");
}
});
return view;
}
}
3.在需要加载Fragment的Activity对应布局文件中<fragment>的name属性设为全限定类名,即包名.fragment.HomeFragment
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/ll_bg"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:background="@color/color_666666"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragmen_home"
android:name="com.scc.demo.fragment.HomeFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
<fragment
android:id="@+id/fragmen_mine"
android:name="com.scc.demo.fragment.MineFragment"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
</LinearLayout>4.最后在Activity调用setContentView()加载布局文件即可
public class FragmentActivity extends ActivityBase {
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
MLog.e(this.getClass().getName()+"onCreate");
setContentView(R.layout.activity_fragment);
}
}动态创建
-
获得FragmentManager对象,通过getSupportFragmentManager()
-
获得FragmentTransaction对象,通过fm.beginTransaction()
-
调用add()方法或者repalce()方法加载Fragment;
-
最后调用commit()方法提交事务
样例:

1.activity的布局文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent">
<FrameLayout
android:id="@+id/fl_frame"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_above="@+id/rg_bottom_tab"/>
<RadioGroup
android:id="@+id/rg_bottom_tab"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="56dp"
android:layout_alignParentBottom="true"
android:background="#dcdcdc"
android:orientation="horizontal">
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rb_home"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:button="@null"
android:checked="true"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="首页"
android:textSize="@dimen/text_size_18" />
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rb_list"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:button="@null"
android:checked="true"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="列表"
android:textSize="@dimen/text_size_18" />
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rb_news"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:button="@null"
android:checked="true"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="消息"
android:textSize="@dimen/text_size_18" />
<RadioButton
android:id="@+id/rb_mine"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:layout_weight="1"
android:button="@null"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="我的"
android:textSize="@dimen/text_size_18" />
</RadioGroup>
</RelativeLayout>2.自定义Fragment
package com.scc.demo.fragment;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.TextView;
import com.scc.demo.R;
import com.scc.demo.utils.MLog;
public class HomeFragment extends Fragment {
private TextView tv_on;
public static HomeFragment newInstance(String param){
HomeFragment fragment = new HomeFragment();
Bundle args = new Bundle();
args.putString("param", param);
fragment.setArguments(args);
return fragment;
}
public HomeFragment(){}
@Override
public View onCreateView(LayoutInflater inflater, ViewGroup container, Bundle savedInstanceState) {
View view = inflater.inflate(R.layout.fragment_home, container,false);
MLog.e(this.getClass().getName()+"onCreateView");
Bundle bundle = getArguments();
String param = bundle.getString("param");
tv_on = view.findViewById(R.id.tv_on);
tv_on.setText("首页"+param);
tv_on.setOnClickListener(new View.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
MLog.e(this.getClass().getName()+"准备关闭");
}
});
return view;
}
}
3.获得FragmentManager对象,通过getFragmentManager()
package com.scc.demo.actvitiy;
import android.app.Fragment;
import android.app.FragmentManager;
import android.app.FragmentTransaction;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.SparseArray;
import android.widget.RadioGroup;
import com.scc.demo.R;
import com.scc.demo.fragment.HomeFragment;
import com.scc.demo.fragment.ListFragment;
import com.scc.demo.fragment.MineFragment;
import com.scc.demo.fragment.NewsFragment;
import com.scc.demo.utils.MLog;
public class FragmentActivity extends ActivityBase {
private RadioGroup rg_bottom_tab;
private SparseArray<Fragment> mFragmentList;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_fragment);
MLog.e(this.getClass().getName()+"onCreate");
initView();
}
public void initView(){
rg_bottom_tab = findViewById(R.id.rg_bottom_tab);
mFragmentList = new SparseArray<>();
mFragmentList.append(R.id.rb_home, HomeFragment.newInstance("我最帅"));
mFragmentList.append(R.id.rb_list, ListFragment.newInstance("我最美"));
mFragmentList.append(R.id.rb_news, NewsFragment.newInstance("我最新"));
mFragmentList.append(R.id.rb_mine, MineFragment.newInstance("这里是我的"));
rg_bottom_tab.setOnCheckedChangeListener(new RadioGroup.OnCheckedChangeListener() {
@Override
public void onCheckedChanged(RadioGroup group, int checkedId) {
// 具体的fragment切换逻辑可以根据应用调整,例如使用show()/hide()
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction transaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
transaction.replace(R.id.fl_frame, mFragmentList.
get(checkedId));
transaction.commit();
}
});
// 默认显示第一个
FragmentManager fragmentManager = getFragmentManager();
FragmentTransaction transaction = fragmentManager.beginTransaction();
transaction.add(R.id.fl_frame, mFragmentList.get(R.id.rb_home)).commit();
}
}四、FragmentPageAdapter和FragmentPageStateAdapter的区别
FragmentPageAdapter在每次切换页面的的时候,是将Fragment进行分离,适合页面较少的Fragment使用以保存一些内存,对系统内存不会多大影响。
FragmentPageStateAdapter在每次切换页面的时候,是将Fragment进行回收,适合页面较多的Fragment使用,这样就不会消耗更多的内存。
五、Fragment生命周期
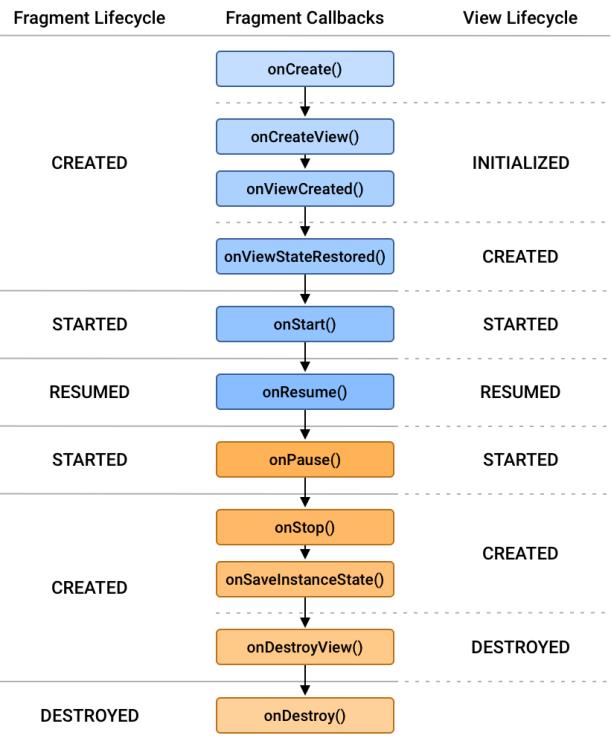
被调用以使Fragment恢复到恢复状态(与用户交互)的核心生命周期方法系列是:
onAttach(Activity) 一旦Fragment与其活动相关联,就会调用。
onCreate(Bundle) 调用以进行Fragment的初始创建。
onCreateView(LayoutInflater, ViewGroup, Bundle) 创建并返回与Fragment关联的视图层次结构。
onActivityCreated(Bundle)告诉Fragment它的活动已经完成了它自己的Activity.onCreate().
onViewStateRestored(Bundle) 告诉Fragment其视图层次结构的所有保存状态都已恢复。
onStart() 使Fragment对用户可见(基于正在启动的包含活动)。
onResume() 使Fragment开始与用户交互(基于其包含的活动正在恢复)。
由于不再使用Fragment,它会经历一系列反向回调:
onPause() Fragment不再与用户交互,因为其活动被暂停或片段操作正在活动中修改它。
onStop() Fragment不再对用户可见,因为其活动正在停止或片段操作正在活动中修改它。
onDestroyView() 允许Fragment清理与其视图关联的资源。
onDestroy() 调用对Fragment状态进行最终清理。
onDetach() 在Fragment不再与其活动相关联之前立即调用。
六、Fragment的通信
Fragment调用Activity中的方法:getActivity返回当前与此Fragment关联的 Activity。
Activity调用Fragment中的方法:接口回调
Fragment调用Fragment中的方法:通过Activity中的FragmentManager
七、Fragment的状态保存
Fragment负责管理与 Fragment功能相关的少量动态状态。你可以使用 Fragment.onSaveInstanceState(Bundle).类似 Activity.onSaveInstanceState(Bundle),你的包将数据通过配置的变化和处理死亡和娱乐保留,并在你的碎片的可用 onCreate(Bundle),onCreateView(LayoutInflater,ViewGroup, Bundle)和 onViewCreated(View,Bundle) 方法。
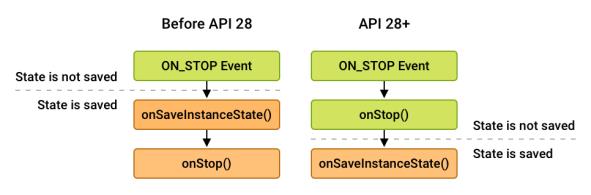
如上图所示,onStop()回调的顺序 和状态的保存因onSaveInstanceState()API 级别而异。对于 API 28 之前的所有 API 级别,onSaveInstanceState()在onStop(). 对于 API 级别 28 及更高级别,调用顺序相反。
八、Fragment的replace、add、remove方法
replace:替代Fragment的栈顶页面
add:添加Fragment到栈顶页面
remove:移除Fragment栈顶页面
九、Fragment的优势
Fragment可以使你能够将activity分离成多个可重用的组件,每个都有它自己的生命周期和UI。
Fragment可以轻松得创建动态灵活的UI设计,可以适应于不同的屏幕尺寸。从手机到平板电脑。
Fragment是一个独立的模块,紧紧地与activity绑定在一起。可以运行中动态地移除、加入、交换等。
Fragment提供一个新的方式让你在不同的安卓设备上统一你的UI。
Fragment 解决Activity间的切换不流畅,轻量切换。
Fragment 替代TabActivity做导航,性能更好。
Fragment 在4.2.版本中新增嵌套fragment使用方法,能够生成更好的界面效果。
Fragment做局部内容更新更方便,原来为了到达这一点要把多个布局放到一个activity里面,现在可以用多Fragment来代替,只有在需要的时候才加载Fragment,提高性能。
可以从startActivityForResult中接收到返回结果,但是View不能。
总结下来:
模块化(Modularity):我们不必把所有代码全部写在Activity中,而是把代码写在各自的Fragment中。
可重用(Reusability):多个Activity可以重用一个Fragment。
可适配(Adaptability):根据硬件的屏幕尺寸、屏幕方向,能够方便地实现不同的布局,这样用户体验更好。
十、androidx包访问Fragment
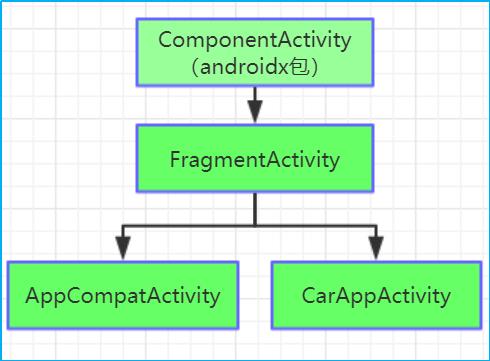
在Activity中访问
每个FragmentActivity及其子类(如AppCompatActivity)都可以通过getSupportFragmentManager()方法访问FragmentManager。
在Fragment中访问
Fragment也能够托管一个或多个子Fragment。在Fragment内,你可以通过getChildFragmentManager()获取对管理Fragment子级的FragmentManager的引用。如果你需要访问其宿主FragmentManager,可以使用getParentFragmentManager()。
以上是关于Android-面试题Fragment详解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章