java多线程 线程池ThreadPoolExecutor
Posted 500年
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了java多线程 线程池ThreadPoolExecutor相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
java多线程 线程池
线程复用、可以控制最大并发数、管理线程
线程池:三大方法、7大参数、4种拒绝策略
1、三大方法
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
public class ExecutorsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//ExecutorService threadPool = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
//ExecutorService threadPool =Executors.newFixedThreadPool(5);
ExecutorService threadPool =Executors.newCachedThreadPool();
try {
for (int i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 执行");
});
}
} finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
}
2、七大参数
2.1、源码解析
public ThreadPoolExecutor(int corePoolSize, // 核心线程池大小
int maximumPoolSize, // 最大核心线程池大小
long keepAliveTime, // 超时没有人调用就会释放
TimeUnit unit, // 超时单位
BlockingQueue<Runnable> workQueue, // 阻塞队列
ThreadFactory threadFactory, // 线程工厂,创建线程的,一般不用动
RejectedExecutionHandler handler // 拒绝策略
) {
if (corePoolSize < 0 ||
maximumPoolSize <= 0 ||
maximumPoolSize < corePoolSize ||
keepAliveTime < 0)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
if (workQueue == null || threadFactory == null || handler == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.acc = System.getSecurityManager() == null ?
null :
AccessController.getContext();
this.corePoolSize = corePoolSize;
this.maximumPoolSize = maximumPoolSize;
this.workQueue = workQueue;
this.keepAliveTime = unit.toNanos(keepAliveTime);
this.threadFactory = threadFactory;
this.handler = handler;
}
2.2、图例
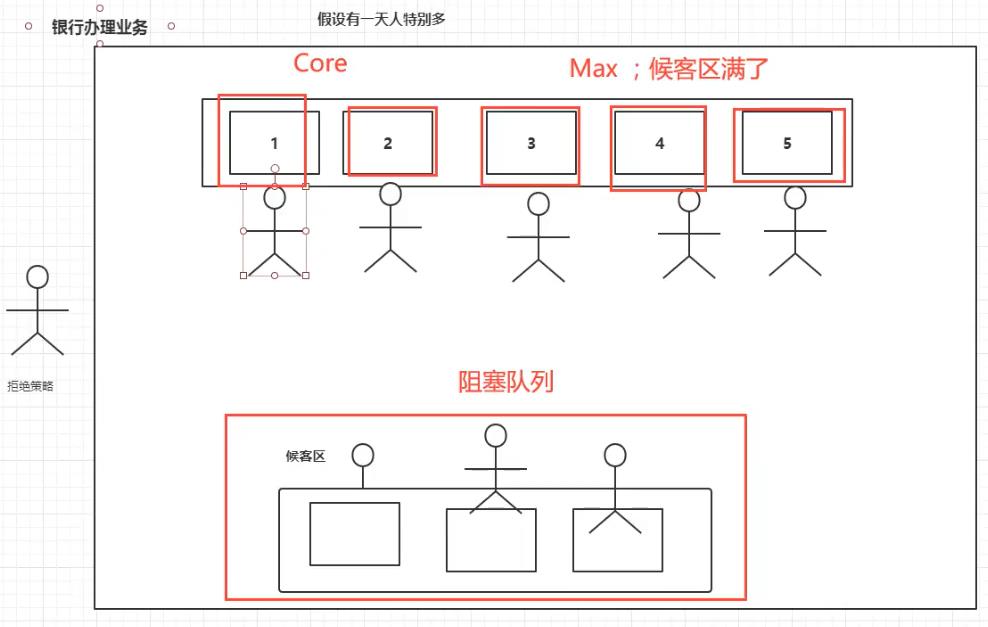
2.3、手写ThreadPoolExecutor实例
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.LinkedBlockingDeque;
import java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
public class ExecutorsDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ThreadPoolExecutor threadPool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(2, 5, 3, TimeUnit.SECONDS,
new LinkedBlockingDeque<>(3), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy());
try {
for (int i = 1; i <= 9; i++) {
threadPool.execute(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 执行");
});
}
} finally {
threadPool.shutdown();
}
}
}
3、4种拒绝策略
new ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy() // 银行满了,还有人进来,不处理这个人,抛出异常
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy() // 哪来的去哪里
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy() // 队列满了,丢掉任务,不会抛出异常!
new ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy() // 队列满了,尝试和最早的竞争,竞争即便是失败了,也不抛出异常。
扩展内容
最大线程到底如何定义
1、CPU密集型,几核,就是几,可以保持cpu的效率最高。
2、IO密集型,判断程序十分耗IO的任务数
比如:程序 15个大型任务 十分消耗IO资源。 此处最大线程数可取 30,这样就有多余资源处理其他任务。
// java获取CUP数量
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
特别鸣谢:狂神说Java老师的无私奉献
.
.
.
上一篇 java多线程(六) SynchronousQueue同步队列
下一篇 java多线程(八)ForkJoin分支合并
以上是关于java多线程 线程池ThreadPoolExecutor的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章