Nacos源码Sofa-JRaft
Posted 程序猿阿越
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Nacos源码Sofa-JRaft相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
前言
当Nacos使用嵌入数据源( -DembeddedStorage=true,每个节点有一个数据源),以集群方式启动(-Dnacos.standalone=false)时,使用raft协议,来保证数据一致性。
为了把Nacos相关源码看懂,先看一下sofa-jraft对于Raft算法的实现。(1.4.1之前使用的是nacos自己实现的raft算法,1.4.1开始使用了sofa-jraft框架)
一、Closure
Status代表一段逻辑运行成功或失败,State为空或State.code是0代表成功。
public class Status implements Copiable<Status> {
private static class State {
int code;
String msg;
}
private State state;
public Status() {
this.state = null;
}
public static Status OK() {
return new Status();
}
public boolean isOk() {
return this.state == null || this.state.code == 0;
}
}
Closure是一个回调函数,run方法是在后续程序执行完成后执行的回调方法,入参Status告知后续执行成功或失败。
/**
* Callback closure.
*/
public interface Closure {
/**
* Called when task is done.
*
* @param status the task status.
*/
void run(final Status status);
}
在JRaft里Closure会被反复包装,回调层数很多。当存在多层Closure传递时,可以认为Closure组成了一个栈,每创建一个Closure都入栈一次。最后在调用最外层的Closure.run时,就是将所有Closure出栈,调用他们的run方法。
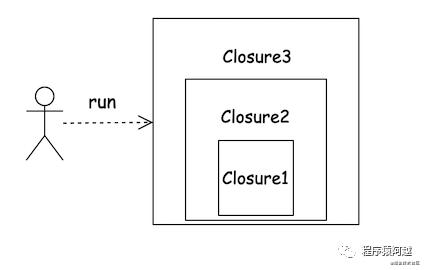
比如上面Closure3持有Closure2持有Closure1,Closure1是负责响应客户端的,其他两层包含一些其他业务逻辑,最终也会调用Closure1。当外部执行业务成功后,持有Closure3调用run方法,将依次调用3->2->1。
二、JRaft使用
这里以sofa-jraft提供的jraft-example里的CounterServer,看看如何使用JRaft实现分布式计数器。
1、RaftServer创建
public class CounterServer {
private RaftGroupService raftGroupService;
private Node node; // 当前节点
private CounterStateMachine fsm;
public CounterServer(final String dataPath, final String groupId, final String serverIdStr,
final String initConfStr) throws IOException {
// 解析参数
// serverIdStr = 当前节点ip:port
PeerId serverId = new PeerId();
if (!serverId.parse(serverIdStr)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Fail to parse serverId:" + serverIdStr);
}
// initConfStr = 集群节点列表 = node1:port,node2:port,node3:port
Configuration initConf = new Configuration();
if (!initConf.parse(initConfStr)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Fail to parse initConf:" + initConfStr);
}
// 初始化路径
FileUtils.forceMkdir(new File(dataPath));
// 这里让 raft RPC 和业务 RPC 使用同一个 RPC server, 通常也可以分开
final RpcServer rpcServer = RaftRpcServerFactory.createRaftRpcServer(serverId.getEndpoint());
// 注册业务处理器
CounterService counterService = new CounterServiceImpl(this);
rpcServer.registerProcessor(new GetValueRequestProcessor(counterService));
rpcServer.registerProcessor(new IncrementAndGetRequestProcessor(counterService));
// 初始化状态机
this.fsm = new CounterStateMachine();
NodeOptions nodeOptions = new NodeOptions();
// 设置状态机到启动参数
nodeOptions.setFsm(this.fsm);
// 设置存储路径
// 日志, 必须
nodeOptions.setLogUri(dataPath + File.separator + "log");
// 元信息, 必须
nodeOptions.setRaftMetaUri(dataPath + File.separator + "raft_meta");
// snapshot, 可选, 一般都推荐
nodeOptions.setSnapshotUri(dataPath + File.separator + "snapshot");
// 设置选举超时时间为 1 秒
nodeOptions.setElectionTimeoutMs(1000);
// 关闭 CLI 服务。
nodeOptions.setDisableCli(false);
// 每隔30秒做一次 snapshot
nodeOptions.setSnapshotIntervalSecs(30);
// 设置初始集群配置
nodeOptions.setInitialConf(initConf);
// 初始化 raft group 服务框架
this.raftGroupService = new RaftGroupService(groupId, serverId, nodeOptions, rpcServer);
// 启动
this.node = this.raftGroupService.start();
}
}
这里启动配置比较多,主要分为几类:
RpcServer:通过jraft提供的RaftRpcServerFactory创建一个Rpc服务Server,这个工厂是根据Sofa自己的SPI机制加载的,正常实现是BoltRaftRpcFactory,内部用的是sofa-bolt提供的Rpc服务。
Raft通讯和业务通讯,使用同一个RpcServer,如当前CountServer。
Raft通讯使用JRaft提供的RpcServer,业务Server使用SpringBoot开发HttpServer,如Nacos。
RpcProcessor(GetValueRequestProcessor):Rpc请求处理器,只有当业务通讯也使用sofa-jraft提供的RpcServer才需要。可以实现com.alipay.sofa.jraft.rpc.RpcProcessor接口,根据目标请求参数,处理业务请求。
StateMachine(CounterStateMachine):使用sofa-jraft必须实现的状态机接口,用于实际业务数据存储和读取。非常重要的一个接口。
NodeOptions:当前raft节点配置选项。
RaftGroupService:持有Node和RpcServer,负责启动和关闭Raft服务。
Node:实现类是NodeImpl,主要负责提交议案(apply)和线性一致性读(readIndex)。
2、状态机
使用sofa-jraft需要实现自己的StateMachine。
最重要的方法是onApply方法。当Node提交Task,对应的log被提交到Raft集群后,当quorum节点成功commit log,触发这个方法来应用状态(当前节点存储数据)。CounterStateMachine在onApply方法中,执行原子计数器的相关功能,包括get和addAndGet。
public class CounterStateMachine extends StateMachineAdapter {
// 原子计数器
private final AtomicLong value = new AtomicLong(0);
@Override
public void onApply(final Iterator iter) {
while (iter.hasNext()) {
long current = 0;
CounterOperation counterOperation = null;
CounterClosure closure = null;
// iter.done() != null代表当前节点是leader
// 可以通过closure直接拿到请求数据,不需要反序列化请求报文
if (iter.done() != null) {
closure = (CounterClosure) iter.done();
counterOperation = closure.getCounterOperation();
} else {
// iter.done == null 代表当前节点是follower,需要反序列化请求报文
final ByteBuffer data = iter.getData();
counterOperation = SerializerManager.getSerializer(SerializerManager.Hessian2).deserialize(
data.array(), CounterOperation.class.getName());
}
// 执行业务逻辑
switch (counterOperation.getOp()) {
case GET:
// get
current = this.value.get();
break;
case INCREMENT:
// addAndGet
final long delta = counterOperation.getDelta();
final long prev = this.value.get();
current = this.value.addAndGet(delta);
break;
}
// 如果closure不为空,代表当前节点是leader,需要调用closure.run来通知客户端
if (closure != null) {
closure.success(current);// 设置响应参数
closure.run(Status.OK()); // 执行Closure回调
}
// 执行下一个任务
iter.next();
}
}
sofa-jraft提供了数据快照功能,Snapshot是表示一个快照,就是对数据当前值的一个记录,会存盘保存,提供冷备数据功能。生成快照有这么几个作用:
当有新的 Node 加入集群的时候,不用只靠日志复制、回放去和 Leader 保持数据一致,而是通过安装 Leader 的快照来跳过早期大量日志的回放;
Leader 用快照替代 Log 复制可以减少网络上的数据量;
用快照替代早期的 Log 可以节省存储空间;
StateMachine提供了两个方法,onSnapshotLoad用于加载快照,onSnapshotSave用于保存快照,触发时机由sofa-jraft框架选择。
// CounterStateMachine将内存中的计数写入磁盘
@Override
public void onSnapshotSave(final SnapshotWriter writer, final Closure done) {
final long currVal = this.value.get();
Utils.runInThread(() -> {
final CounterSnapshotFile snapshot = new CounterSnapshotFile(writer.getPath() + File.separator + "data");
if (snapshot.save(currVal)) {
if (writer.addFile("data")) {
done.run(Status.OK());
} else {
done.run(new Status(RaftError.EIO, "Fail to add file to writer"));
}
} else {
done.run(new Status(RaftError.EIO, "Fail to save counter snapshot %s", snapshot.getPath()));
}
});
}
// CounterStateMachine加载快照到内存计数器
@Override
public boolean onSnapshotLoad(final SnapshotReader reader) {
if (isLeader()) {
return false;
}
if (reader.getFileMeta("data") == null) {
return false;
}
final CounterSnapshotFile snapshot = new CounterSnapshotFile(reader.getPath() + File.separator + "data");
try {
this.value.set(snapshot.load());
return true;
} catch (final IOException e) {
return false;
}
}
三、写
Raft共识算法为了保证强一致,所有的读写请求都必须提交到Leader节点执行。
1、用户代码时序
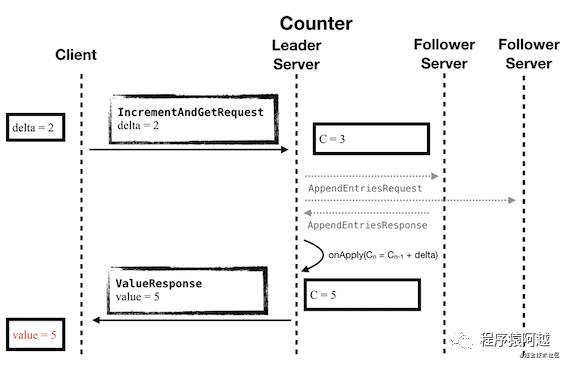
这里还是以CounterServer为例。
当客户端发起IncreamentAndGetRequest请求后,Leader节点会将这个请求封装为一个Task提交到Raft集群。
Raft框架执行日志复制。
Raft集群中大部分节点commit之后(日志复制),会调用所有节点的StateMachine的onApply方法应用状态,更新内存中的计数器。
作为Leader节点的onApply方法还需要响应客户端请求,返回ValueResponse。
接下来详细看看业务处理流程,这里先无视JRaft框架做了什么。
IncrementAndGetRequest请求参数,向raft集群发起写请求,对原子计数器执行addAndGet操作。
public class IncrementAndGetRequest {
// 增加步长
private long delta;
}
ValueResponse响应参数。
public class ValueResponse implements Serializable {
// 原子计数器的值
private long value;
// 是否成功
private boolean success;
// 重定向leader的ip:port
private String redirect;
// 错误信息
private String errorMsg;
}
IncrementAndGetRequestProcessor初始化RpcServer的时候,传入的请求处理器,用于处理业务请求IncrementAndGetRequest。这里用的是JRaft提供的RpcServer处理业务请求,当收到IncrementAndGetRequest类型请求参数,JRaft提供的RpcServer能自动识别并调用IncrementAndGetRequestProcessor。
如果是SpringBoot开发的HttpServer,RpcContext相当于HttpServletResponse,这里Closure的run方法就可以通过HttpServletResponse响应客户端。
public class IncrementAndGetRequestProcessor implements RpcProcessor<IncrementAndGetRequest> {
private final CounterService counterService;
public IncrementAndGetRequestProcessor(CounterService counterService) {
super();
this.counterService = counterService;
}
// 处理请求
@Override
public void handleRequest(final RpcContext rpcCtx, final IncrementAndGetRequest request) {
// Closure,当后续步骤执行完成后,通过RpcContext响应客户端
final CounterClosure closure = new CounterClosure() {
@Override
public void run(Status status) {
// 调用CounterClosure抽象类的getValueResponse方法,获取下面incrementAndGet执行的时候塞入的response
rpcCtx.sendResponse(getValueResponse());
}
};
this.counterService.incrementAndGet(request.getDelta(), closure);
}
// 返回关注的请求类型
@Override
public String interest() {
return IncrementAndGetRequest.class.getName();
}
}
CounterServiceImpl将请求入参转换为CounterOperation,封装为com.alipay.sofa.jraft.entity.Task提交到Raft集群,注意这里将上面最初用来响应客户端的Closure也传入了,未来某个时刻会执行Closure的run方法回调。
public class CounterServiceImpl implements CounterService {
private final CounterServer counterServer;
@Override
public void incrementAndGet(final long delta, final CounterClosure closure) {
// 将业务请求delta转换为CounterOperation
applyOperation(CounterOperation.createIncrement(delta), closure);
}
private void applyOperation(final CounterOperation op, final CounterClosure closure) {
if (!isLeader()) {
// 响应请求失败,往往应用应该将请求转发至Leader节点,然后响应closure成功
handlerNotLeaderError(closure);
return;
}
try {
// 设置请求入参到closure里
closure.setCounterOperation(op);
// 创建Task
final Task task = new Task();
// 把请求入参序列化为ByteBuffer
task.setData(ByteBuffer.wrap(SerializerManager.getSerializer(SerializerManager.Hessian2).serialize(op)));
// 把外部传入的closure放到Task的done成员变量里
task.setDone(closure);
// 将Task提交到当前Node处理,托管给JRaft框架
this.counterServer.getNode().apply(task);
} catch (CodecException e) {
// 如果发生编解码异常,这里直接响应客户端
closure.failure(errorMsg, StringUtils.EMPTY);
closure.run(new Status(RaftError.EINTERNAL, errorMsg));
}
}
}
Task在JRaft里是个比较重要的实体类。
ByteBuffer data:业务数据。
Closure done:回调方法,当raft执行完毕后(commit或fail),会调用这个回调方法。
long expecteTerm:期望任期,默认-1。如果非-1的情况下,当前term与期望term不同,会拒绝这个task。
public class Task {
/** Associated task data*/
private ByteBuffer data = LogEntry.EMPTY_DATA;
/** task closure, called when the data is successfully committed to the raft group or failures happen.*/
private Closure done;
/** Reject this task if expectedTerm doesn't match the current term of this Node if the value is not -1, default is -1.*/
private long expectedTerm = -1;
}
执行完Node.apply(Task)后,后续的步骤会托管给JRaft框架处理。Leader会将Log同步给follower节点,当n/2+1节点同步成功后,会触发StateMachine的onApply方法,继续走用户的业务逻辑。
再来回顾一下CounterStateMachine的onApply方法,作为Leader节点,这里将内存里的计数器增加delta并将增加后的结果current放入了CounterClosure,并执行Closure的run方法响应客户端。
@Override
public void onApply(final Iterator iter) {
while (iter.hasNext()) {
long current = 0;
CounterOperation counterOperation = null;
CounterClosure closure = null;
// iter.done() != null代表当前节点是leader
// 可以通过closure直接拿到请求数据,不需要反序列化请求报文
if (iter.done() != null) {
closure = (CounterClosure) iter.done();
counterOperation = closure.getCounterOperation();
} else {
// ... Follwer节点需要反序列化请求报文,且iter里不包含closure回调方法
}
// 执行业务逻辑
switch (counterOperation.getOp()) {
case INCREMENT:
final long delta = counterOperation.getDelta();
final long prev = this.value.get();
current = this.value.addAndGet(delta);
break;
}
// 如果closure不为空,代表当前节点是leader,需要调用closure.run来通知客户端
if (closure != null) {
closure.success(current);// 设置响应参数
closure.run(Status.OK());// 执行Closure回调
}
iter.next();
}
}
此外,当task对应的log被commit之后,这个onApply方法同样会在其他follower节点被触发,所以其他节点也会更新内存里的计数器。
2、从框架角度看写操作
从框架角度看写操作,Node.apply(Task)做了什么?
public interface Node extends Lifecycle<NodeOptions>, Describer {
/**
* [Thread-safe and wait-free]
*
* Apply task to the replicated-state-machine
*
* About the ownership:
* |task.data|: for the performance consideration, we will take away the
* content. If you want keep the content, copy it before call
* this function
* |task.done|: If the data is successfully committed to the raft group. We
* will pass the ownership to #{@link StateMachine#onApply(Iterator)}.
* Otherwise we will specify the error and call it.
*
* @param task task to apply
*/
void apply(final Task task);
}
从java doc来看,为了性能考虑,task里的ByteBuffer会被框架移除。另外如果data成功commit到Raft集群里,接下来会交给StateMachine的onApply方法处理,task里的Closure需要用户在onApply方法中调用。
再来看一下StateMachine的onApply方法的javadoc。
public interface StateMachine {
/**
* Update the StateMachine with a batch a tasks that can be accessed
* through |iterator|.
*
* Invoked when one or more tasks that were passed to Node#apply(Task) have been
* committed to the raft group (quorum of the group peers have received
* those tasks and stored them on the backing storage).
*
* Once this function returns to the caller, we will regard all the iterated
* tasks through |iter| have been successfully applied. And if you didn't
* apply all the the given tasks, we would regard this as a critical error
* and report a error whose type is ERROR_TYPE_STATE_MACHINE.
*
* @param iter iterator of states
*/
void onApply(final Iterator iter);
}
当Node#apply(Task)提交的任务被commit后(大多数成员已经收到这个Task且将Task保存到后端存储中),这个方法会被调用。
从apply(Task)到onApply的过程中,JRaft做了什么?
这个流程比较长,分为7个阶段来看,总体流程如下:
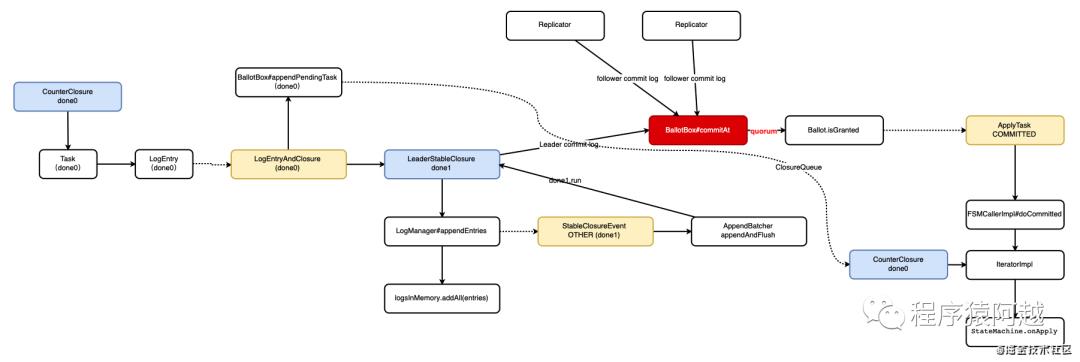
阶段一:封装LogEntryAndClosure
这里以CounterServer为例,当后续步骤处理完后(onApply处理完成后),会回调用户的CounterClosure,为了方便这里记用户的CounterClosure为done0。
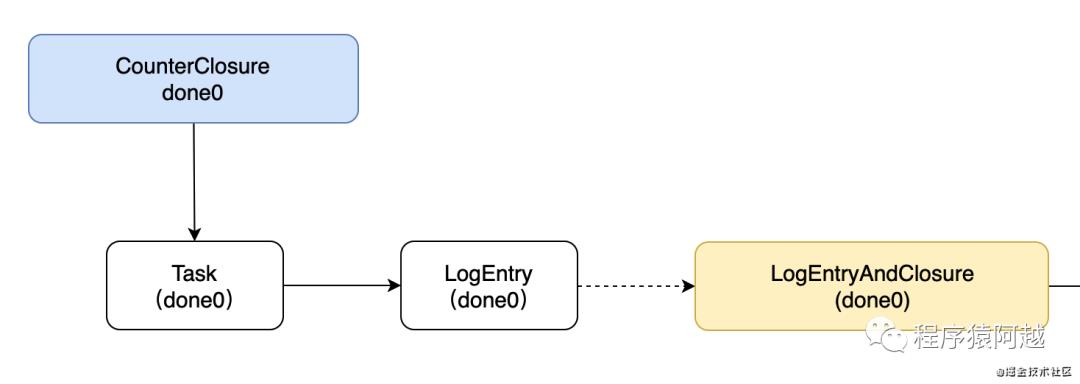
NodeImpl的apply方法,将用户传入的Task封装为LogEntryAndClosure,并放入一个Disruptor框架队列,至此用户代码结束,CounterServiceImpl处理完成。
// NodeImpl
@Override
public void apply(final Task task) {
// ...
final LogEntry entry = new LogEntry();
entry.setData(task.getData());
int retryTimes = 0;
try {
// 封装LogEntryAndClosure,包含Closure done(客户端closure回调)、LogEntry entry(客户端数据)、expectedTerm(客户端期望term任期,默认-1)
final EventTranslator<LogEntryAndClosure> translator = (event, sequence) -> {
event.reset();
event.done = task.getDone();
event.entry = entry;
event.expectedTerm = task.getExpectedTerm();
};
while (true) {
// 将LogEntryAndClosure提交到Disruptor框架队列
if (this.applyQueue.tryPublishEvent(translator)) {
break;
} else {
retryTimes++;
if (retryTimes > MAX_APPLY_RETRY_TIMES) {
return;
}
ThreadHelper.onSpinWait();
}
}
} catch (final Exception e) {
// ...
}
}
阶段二:log写内存并将done0放入投票箱
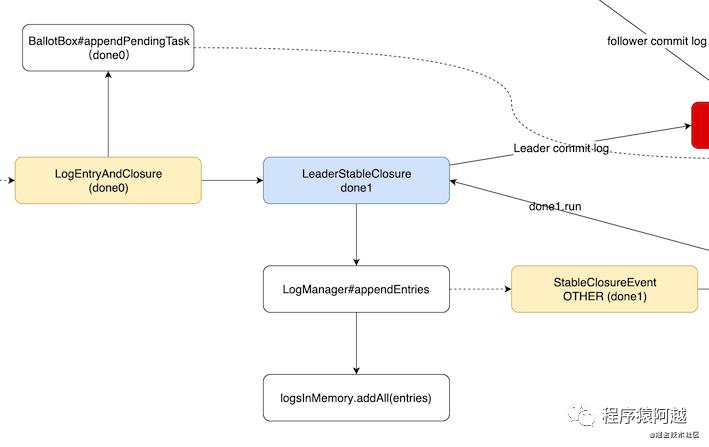
NodeImpl.LogEntryAndClosureHandler处理LogEntryAndClosure事件。
private class LogEntryAndClosureHandler implements EventHandler<LogEntryAndClosure> {
// task list for batch
private final List<LogEntryAndClosure> tasks = new ArrayList<>(NodeImpl.this.raftOptions.getApplyBatch());
@Override
public void onEvent(final LogEntryAndClosure event, final long sequence, final boolean endOfBatch)
throws Exception {
// ...
this.tasks.add(event);
if (this.tasks.size() >= NodeImpl.this.raftOptions.getApplyBatch() || endOfBatch) {
executeApplyingTasks(this.tasks);
this.tasks.clear();
}
}
}
executeApplyingTasks
校验当前节点是否是Leader
校验task的期望任期
把日志复制的信息放入投票箱BallotBox,注意这里把done0放进去了,BallotBox里会有个List存储这些需要回调的用户Closure,后期会放入用户StateMachine#onApply方法的入参Iterator里,让用户执行回调
最后,将日志交给LogManager处理,封装第二个Closure---LeaderStableClosure
private void executeApplyingTasks(final List<LogEntryAndClosure> tasks) {
this.writeLock.lock();
try {
final int size = tasks.size();
// 1. 如果当前节点不是Leader,返回失败
if (this.state != State.STATE_LEADER) {
final Status st = new Status();
if (this.state != State.STATE_TRANSFERRING) {
st.setError(RaftError.EPERM, "Is not leader.");
} else {
st.setError(RaftError.EBUSY, "Is transferring leadership.");
}
final List<LogEntryAndClosure> savedTasks = new ArrayList<>(tasks);
Utils.runInThread(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
savedTasks.get(i).done.run(st);
}
});
return;
}
final List<LogEntry> entries = new ArrayList<>(size);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
final LogEntryAndClosure task = tasks.get(i);
// 2. 如果期望任期不等于当前leader任期,返回失败
if (task.expectedTerm != -1 && task.expectedTerm != this.currTerm) {
task.expectedTerm, this.currTerm);
if (task.done != null) {
final Status st = new Status(RaftError.EPERM, "expected_term=%d doesn't match current_term=%d",
task.expectedTerm, this.currTerm);
Utils.runClosureInThread(task.done, st);
}
continue;
}
// 3. 日志复制前的信息,保存到ballotBox里的队列
if (!this.ballotBox.appendPendingTask(this.conf.getConf(),
this.conf.isStable() ? null : this.conf.getOldConf(), task.done)) {
Utils.runClosureInThread(task.done, new Status(RaftError.EINTERNAL, "Fail to append task."));
continue;
}
task.entry.getId().setTerm(this.currTerm);
task.entry.setType(EnumOutter.EntryType.ENTRY_TYPE_DATA);
entries.add(task.entry);
}
// 4. 把LogEntry交给LogManager管理,传入了一个LeaderStableClosure
this.logManager.appendEntries(entries, new LeaderStableClosure(entries));
checkAndSetConfiguration(true);
} finally {
this.writeLock.unlock();
}
}
进入LogManager#appendEntries,这一段逻辑是leader节点和follower节点公用的,入参closure不同导致回调逻辑不同。主要是将log先写入内存,然后发布StableClosureEvent事件。
public void appendEntries(final List<LogEntry> entries, final StableClosure done) {
// ...
boolean doUnlock = true;
this.writeLock.lock();
try {
//...
// 1. Log批量写入内存
if (!entries.isEmpty()) {
done.setFirstLogIndex(entries.get(0).getId().getIndex());
this.logsInMemory.addAll(entries);
}
done.setEntries(entries);
int retryTimes = 0;
// 2. 提交StableClosureEvent事件【注意done=LeaderStableClosure】
final EventTranslator<StableClosureEvent> translator = (event, sequence) -> {
event.reset();
event.type = EventType.OTHER;
event.done = done;
};
while (true) {
if (tryOfferEvent(done, translator)) {
break;
} else {
retryTimes++;
if (retryTimes > APPEND_LOG_RETRY_TIMES) {
return;
}
ThreadHelper.onSpinWait();
}
}
doUnlock = false;
if (!wakeupAllWaiter(this.writeLock)) {
notifyLastLogIndexListeners();
}
} finally {
if (doUnlock) {
this.writeLock.unlock();
}
}
}
阶段三:StableClosureEvent处理,将内存中的log落盘,leader commit log
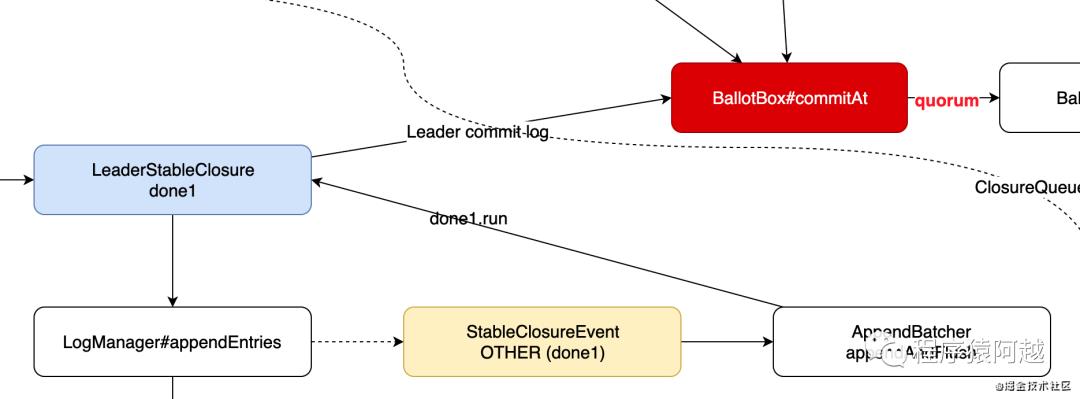
private class StableClosureEventHandler implements EventHandler<StableClosureEvent> {
LogId lastId = LogManagerImpl.this.diskId;
List<StableClosure> storage = new ArrayList<>(256);
AppendBatcher ab = new AppendBatcher(this.storage, 256, new ArrayList<>(),
LogManagerImpl.this.diskId);
@Override
public void onEvent(final StableClosureEvent event, final long sequence, final boolean endOfBatch)
throws Exception {
final StableClosure done = event.done;
if (done.getEntries() != null && !done.getEntries().isEmpty()) {
this.ab.append(done);
} else {
// ...
}
if (endOfBatch) {
// 将log写入磁盘并触发done回调
this.lastId = this.ab.flush();
setDiskId(this.lastId);
}
}
}
LogManagerImpl.AppendBatcher负责将log写入底层存储并触发Closure回调,这里会触发的是LeaderStableClosure。
private class AppendBatcher {
List<StableClosure> storage;
int cap;
int size;
int bufferSize;
List<LogEntry> toAppend;
LogId lastId;
public AppendBatcher(final List<StableClosure> storage, final int cap, final List<LogEntry> toAppend,
final LogId lastId) {
super();
this.storage = storage;
this.cap = cap;
this.toAppend = toAppend;
this.lastId = lastId;
}
LogId flush() {
if (this.size > 0) {
// 1. log写入底层存储
this.lastId = appendToStorage(this.toAppend);
for (int i = 0; i < this.size; i++) {
this.storage.get(i).getEntries().clear();
Status st = null;
try {
if (LogManagerImpl.this.hasError) {
st = new Status(RaftError.EIO, "Corrupted LogStorage");
} else {
st = Status.OK();
}
// 2. 触发回调
this.storage.get(i).run(st);
} catch (Throwable t) {
LOG.error("Fail to run closure with status: {}.", st, t);
}
}
this.toAppend.clear();
this.storage.clear();
}
this.size = 0;
this.bufferSize = 0;
return this.lastId;
}
void append(final StableClosure done) {
if (this.size == this.cap || this.bufferSize >= LogManagerImpl.this.raftOptions.getMaxAppendBufferSize()) {
flush();
}
this.storage.add(done);
this.size++;
this.toAppend.addAll(done.getEntries());
for (final LogEntry entry : done.getEntries()) {
this.bufferSize += entry.getData() != null ? entry.getData().remaining() : 0;
}
}
}
LeaderStableClosure调用BallotBox投票箱的commitAt方法提交,commitAt方法需要等到quorum节点提交后,才会处理后续步骤,后面再看。
class LeaderStableClosure extends LogManager.StableClosure {
public LeaderStableClosure(final List<LogEntry> entries) {
super(entries);
}
@Override
public void run(final Status status) {
if (status.isOk()) {
NodeImpl.this.ballotBox.commitAt(this.firstLogIndex, this.firstLogIndex + this.nEntries - 1,
NodeImpl.this.serverId);
} else {
LOG.error(...);
}
}
}
阶段四:Replicator日志同步
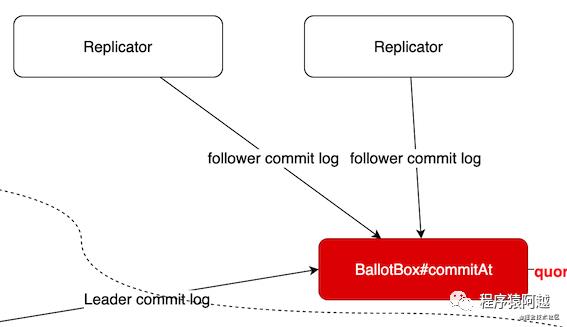
对于每个Follower,Leader节点都会创建一个Replicator实例负责向Follower做日志同步。Replicator会持续向Follower发送AppendEntries请求,负责向Follwer同步日志。
// Replicator
private boolean sendEntries(final long nextSendingIndex) {
final AppendEntriesRequest.Builder rb = AppendEntriesRequest.newBuilder();
// 设置AppendEntriesRequest请求参数
if (!fillCommonFields(rb, nextSendingIndex - 1, false)) {
installSnapshot();
return false;
}
ByteBufferCollector dataBuf = null;
final int maxEntriesSize = this.raftOptions.getMaxEntriesSize();
final RecyclableByteBufferList byteBufList = RecyclableByteBufferList.newInstance();
try {
for (int i = 0; i < maxEntriesSize; i++) {
// 设置log的元数据 任期、类型、数据报文长度
final RaftOutter.EntryMeta.Builder emb = RaftOutter.EntryMeta.newBuilder();
if (!prepareEntry(nextSendingIndex, i, emb, byteBufList)) {
break;
}
rb.addEntries(emb.build());
}
// 如果本次请求参数,没有日志需要同步,等待
if (rb.getEntriesCount() == 0) {
if (nextSendingIndex < this.options.getLogManager().getFirstLogIndex()) {
installSnapshot();
return false;
}
// _id is unlock in _wait_more
waitMoreEntries(nextSendingIndex);
return false;
}
if (byteBufList.getCapacity() > 0) {
dataBuf = ByteBufferCollector.allocateByRecyclers(byteBufList.getCapacity());
for (final ByteBuffer b : byteBufList) {
dataBuf.put(b);
}
final ByteBuffer buf = dataBuf.getBuffer();
buf.flip();
rb.setData(ZeroByteStringHelper.wrap(buf));
}
} finally {
RecycleUtil.recycle(byteBufList);
}
final AppendEntriesRequest request = rb.build();
this.statInfo.runningState = RunningState.APPENDING_ENTRIES;
this.statInfo.firstLogIndex = rb.getPrevLogIndex() + 1;
this.statInfo.lastLogIndex = rb.getPrevLogIndex() + rb.getEntriesCount();
final Recyclable recyclable = dataBuf;
final int v = this.version;
final long monotonicSendTimeMs = Utils.monotonicMs();
final int seq = getAndIncrementReqSeq();
Future<Message> rpcFuture = null;
try {
// 发送appendEntries请求给follower
rpcFuture = this.rpcService.appendEntries(this.options.getPeerId().getEndpoint(), request, -1,
new RpcResponseClosureAdapter<AppendEntriesResponse>() {
@Override
public void run(final Status status) {
RecycleUtil.recycle(recyclable);
// 处理follower响应
onRpcReturned(Replicator.this.id, RequestType.AppendEntries, status, request, getResponse(),
seq, v, monotonicSendTimeMs);
}
});
} catch (final Throwable t) {
RecycleUtil.recycle(recyclable);
ThrowUtil.throwException(t);
}
addInflight(RequestType.AppendEntries, nextSendingIndex, request.getEntriesCount(), request.getData().size(),
seq, rpcFuture);
return true;
}
在onRpcReturn回调方法里,Leader处理Follower复制结果。
static void onRpcReturned(final ThreadId id, final RequestType reqType, final Status status, final Message request,
final Message response, final int seq, final int stateVersion, final long rpcSendTime) {
// ...
final PriorityQueue<RpcResponse> holdingQueue = r.pendingResponses;
holdingQueue.add(new RpcResponse(reqType, seq, status, request, response, rpcSendTime));
boolean continueSendEntries = false;
try {
int processed = 0;
while (!holdingQueue.isEmpty()) {
final RpcResponse queuedPipelinedResponse = holdingQueue.peek();
// ...
holdingQueue.remove();
try {
switch (queuedPipelinedResponse.requestType) {
case AppendEntries:
// leader 当log复制成功后,触发
continueSendEntries = onAppendEntriesReturned(id, inflight, queuedPipelinedResponse.status,
(AppendEntriesRequest) queuedPipelinedResponse.request,
(AppendEntriesResponse) queuedPipelinedResponse.response, rpcSendTime, startTimeMs, r);
break;
// ...
}
} finally {
if (continueSendEntries) {
r.getAndIncrementRequiredNextSeq();
} else {
break;
}
}
}
} finally {
// ...
// 继续日志同步
if (continueSendEntries) {
r.sendEntries();
}
}
}
onAppendEntriesReturned处理follower返回的response,调用投票箱的commitAt方法继续投票。
private static boolean onAppendEntriesReturned(final ThreadId id, final Inflight inflight, final Status status,
final AppendEntriesRequest request,
final AppendEntriesResponse response, final long rpcSendTime,
final long startTimeMs, final Replicator r) {
if (inflight.startIndex != request.getPrevLogIndex() + 1) {
// ...
return false;
}
if (!status.isOk()) {
// ...
return false;
}
if (!response.getSuccess()) {
// ...
return false;
}
if (response.getTerm() != r.options.getTerm()) {
// ...
return false;
}
if (rpcSendTime > r.lastRpcSendTimestamp) {
r.lastRpcSendTimestamp = rpcSendTime;
}
final int entriesSize = request.getEntriesCount();
if (entriesSize > 0) {
if (r.options.getReplicatorType().isFollower()) {
// leader继续调用投票箱的commitAt方法
r.options.getBallotBox().commitAt(r.nextIndex, r.nextIndex + entriesSize - 1, r.options.getPeerId());
}
}
// ...
return true;
}
阶段五:过半节点commit,提交ApplyTask

无论是Leader提交,还是Follower响应日志复制请求后Leader处理响应结果,都会调用BallotBox投票箱的commitAt方法,这里主要是为了计数。当过半节点commit后,BallotBox投票箱会调用FSMCaller的onCommitted方法。
// BallotBox
// 场景1:leader自己的log commit完成了
// 场景2:replicator follower log commit完成了
public boolean commitAt(final long firstLogIndex, final long lastLogIndex, final PeerId peer) {
final long stamp = this.stampedLock.writeLock();
long lastCommittedIndex = 0;
try {
if (this.pendingIndex == 0) {
return false;
}
if (lastLogIndex < this.pendingIndex) {
return true;
}
if (lastLogIndex >= this.pendingIndex + this.pendingMetaQueue.size()) {
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
}
final long startAt = Math.max(this.pendingIndex, firstLogIndex);
Ballot.PosHint hint = new Ballot.PosHint();
for (long logIndex = startAt; logIndex <= lastLogIndex; logIndex++) {
final Ballot bl = this.pendingMetaQueue.get((int) (logIndex - this.pendingIndex));
hint = bl.grant(peer, hint);
// 当半数以上节点commit,这里lastCommittedIndex赋值为logIndex
if (bl.isGranted()) {
lastCommittedIndex = logIndex;
}
}
// 如果没有过半节点commit,这里会直接返回
if (lastCommittedIndex == 0) {
return true;
}
this.pendingMetaQueue.removeFromFirst((int) (lastCommittedIndex - this.pendingIndex) + 1);
this.pendingIndex = lastCommittedIndex + 1;
this.lastCommittedIndex = lastCommittedIndex;
} finally {
this.stampedLock.unlockWrite(stamp);
}
// 如果有过半节点commit,FSMCaller.onCommitted
this.waiter.onCommitted(lastCommittedIndex);
return true;
}
FSMCallerImpl#onCommitted提交一个ApplyTask事件,类型是COMMITTED。
// FSMCallerImpl
public boolean onCommitted(final long committedIndex) {
return enqueueTask((task, sequence) -> {
task.type = TaskType.COMMITTED;
task.committedIndex = committedIndex;
});
}
private boolean enqueueTask(final EventTranslator<ApplyTask> tpl) {
if (!this.taskQueue.tryPublishEvent(tpl)) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
阶段六:处理ApplyTask,组装IteratorImpl调用用户的StateMachine的onApply方法
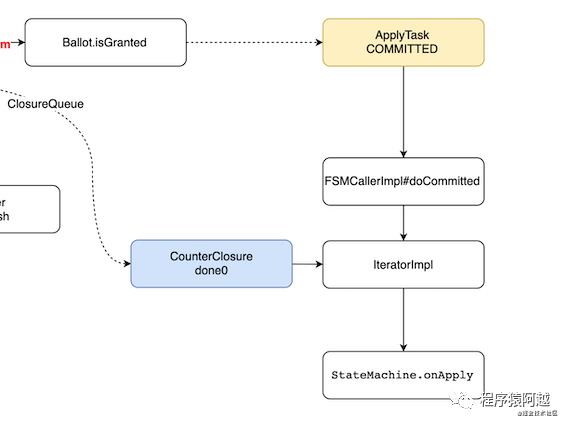
FSMCallerImpl.ApplyTaskHandler处理ApplyTask事件。
private class ApplyTaskHandler implements EventHandler<ApplyTask> {
private long maxCommittedIndex = -1;
@Override
public void onEvent(final ApplyTask event, final long sequence, final boolean endOfBatch) throws Exception {
this.maxCommittedIndex = runApplyTask(event, this.maxCommittedIndex, endOfBatch);
}
}
runApplyTask方法,调用doCommitted方法。
// FSMCallerImpl
private long runApplyTask(final ApplyTask task, long maxCommittedIndex, final boolean endOfBatch) {
CountDownLatch shutdown = null;
if (task.type == TaskType.COMMITTED) {
if (task.committedIndex > maxCommittedIndex) {
maxCommittedIndex = task.committedIndex;
}
} else {
// ...
}
try {
if (endOfBatch && maxCommittedIndex >= 0) {
this.currTask = TaskType.COMMITTED;
// 调用用户StateMachine的onApply方法
doCommitted(maxCommittedIndex);
maxCommittedIndex = -1L;
}
this.currTask = TaskType.IDLE;
return maxCommittedIndex;
} finally {
if (shutdown != null) {
shutdown.countDown();
}
}
}
doCommitted方法将原先存储的用户提交的Task里的Closure done,放入IteratorImpl,再循环迭代器调用用户StateMachine的onApply方法,由用户代码执行done0最外层回调。
// FSMCallerImpl
// 组装IteratorImpl,调用用户StateMachine的onApply方法
private void doCommitted(final long committedIndex) {
if (!this.error.getStatus().isOk()) {
return;
}
final long lastAppliedIndex = this.lastAppliedIndex.get();
if (lastAppliedIndex >= committedIndex) {
return;
}
final long startMs = Utils.monotonicMs();
try {
final List<Closure> closures = new ArrayList<>();
final List<TaskClosure> taskClosures = new ArrayList<>();
// 这里会将done0(用户代码最初Task里的done),放入closures
final long firstClosureIndex = this.closureQueue.popClosureUntil(committedIndex, closures, taskClosures);
final IteratorImpl iterImpl = new IteratorImpl(this.fsm, this.logManager, closures, firstClosureIndex,
lastAppliedIndex, committedIndex, this.applyingIndex);
while (iterImpl.isGood()) {
final LogEntry logEntry = iterImpl.entry();
// ...
// 调用用户StateMachine的onApply方法
doApplyTasks(iterImpl);
}
// ...
} finally {
this.nodeMetrics.recordLatency("fsm-commit", Utils.monotonicMs() - startMs);
}
}
private StateMachine fsm;
private void doApplyTasks(final IteratorImpl iterImpl) {
final IteratorWrapper iter = new IteratorWrapper(iterImpl);
final long startApplyMs = Utils.monotonicMs();
final long startIndex = iter.getIndex();
try {
// 调用用户StateMachine的onApply方法
this.fsm.onApply(iter);
} finally {
// ...
}
if (iter.hasNext()) {
LOG.error("");
}
iter.next();
}
阶段七:Follower应用日志
Leader会通过Replicator持续发送已经提交的commitedIndex,Follower发现applyIndex小于commitedIndex,同样会提交ApplyTask执行用户的StateMachine的onApply方法。
客户端NodeImpl的handleAppendEntriesRequest处理AppendEntriesRequest,会设置投票箱的committedIndex。
// NodeImpl
public Message handleAppendEntriesRequest(final AppendEntriesRequest request, final RpcRequestClosure done) {
// ...
if (entriesCount == 0) {
// 一个心跳请求或探测请求
this.ballotBox.setLastCommittedIndex(Math.min(request.getCommittedIndex(), prevLogIndex));
return respBuilder.build();
}
//...
}
投票箱发现committedIndex超过上次的committedIndex,会提交ApplyTask,之后就和Leader的处理一样了,会调用用户的StateMachine的onApply方法。
// BallotBox
private FSMCaller waiter;
public boolean setLastCommittedIndex(final long lastCommittedIndex) {
boolean doUnlock = true;
final long stamp = this.stampedLock.writeLock();
try {
// ...
if (lastCommittedIndex < this.lastCommittedIndex) {
return false;
}
if (lastCommittedIndex > this.lastCommittedIndex) {
this.lastCommittedIndex = lastCommittedIndex;
this.stampedLock.unlockWrite(stamp);
doUnlock = false;
// 这里会提交ApplyTask,和Leader的处理一样,最终会调用用户的StateMachine的onApply方法
this.waiter.onCommitted(lastCommittedIndex);
}
} finally {
if (doUnlock) {
this.stampedLock.unlockWrite(stamp);
}
}
return true;
}
四、读
为了实现线性一致读,所有的读请求应该转发到Leader节点。
1、用户代码时序
GetValueRequestProcessor负责处理GetValueRequest。这里封装了第一个Closure,负责响应客户端。
public class GetValueRequestProcessor implements RpcProcessor<GetValueRequest> {
private final CounterService counterService;
public GetValueRequestProcessor(CounterService counterService) {
super();
this.counterService = counterService;
}
@Override
public void handleRequest(final RpcContext rpcCtx, final GetValueRequest request) {
final CounterClosure closure = new CounterClosure() {
@Override
public void run(Status status) {
// 响应客户端
rpcCtx.sendResponse(getValueResponse());
}
};
this.counterService.get(request.isReadOnlySafe(), closure);
}
@Override
public String interest() {
return GetValueRequest.class.getName();
}
}
CounterServiceImpl通过NodeImpl.readIndex方法实现一致性读,这里封装了第二个Closure---ReadIndexClosure传入readIndex方法。
public class CounterServiceImpl implements CounterService {
private final CounterServer counterServer;
private final Executor readIndexExecutor;
@Override
public void get(final boolean readOnlySafe, final CounterClosure closure) {
// readOnlySafe = false,不走一致性读逻辑,直接返回当前节点的statemachine中的值
if(!readOnlySafe){
closure.success(getValue());
closure.run(Status.OK());
return;
}
// readOnlySafe = true,走一致性读逻辑
this.counterServer.getNode().readIndex(BytesUtil.EMPTY_BYTES, new ReadIndexClosure() {
@Override
public void run(Status status, long index, byte[] reqCtx) {
// 保证readIndex(commitIndex) <= applyIndex后,获取状态机中的值
if(status.isOk()){
closure.success(getValue());
closure.run(Status.OK());
return;
}
// 失败处理
CounterServiceImpl.this.readIndexExecutor.execute(() -> {
// 如果当前节点是Leader,提交task到Raft集群,如果成功了,会回调CounterStateMachine的onApply方法响应
if(isLeader()){
applyOperation(CounterOperation.createGet(), closure);
}else {
// 如果当前节点不是Leader,响应失败
handlerNotLeaderError(closure);
}
});
}
});
}
// 获取CounterStateMachine中的value
private long getValue() {
return this.counterServer.getFsm().getValue();
}
}
当readIndex执行完成后,执行用户的ReadIndexClosure回调。
如果判断status成功,表明readIndex已经小于等于applyIndex,会读取当前节点本地状态机中的值;
如果失败且当前节点还是Leader,则降级为走Raft流程保证一致性读(和前面IncreamentAndGet的流程一致);
如果失败且当前节点已经不是Leader节点,则返回失败;
2、从框架角度看读操作
从NodeImpl#readIndex到ReadIndexClosure被调用,JRaft做了什么?
NodeImpl交给ReadOnlyServiceImpl处理。
// NodeImpl
@Override
public void readIndex(final byte[] requestContext, final ReadIndexClosure done) {
if (this.shutdownLatch != null) {
Utils.runClosureInThread(done, new Status(RaftError.ENODESHUTDOWN, "Node is shutting down."));
throw new IllegalStateException("Node is shutting down");
}
this.readOnlyService.addRequest(requestContext, done);
}
ReadOnlyServiceImpl发布ReadIndexEvent事件,由内部类ReadIndexEventHandler处理。
至此readIndex方法返回,剩下的交给ReadIndexEvent事件处理器处理。
// ReadOnlyServiceImpl
@Override
public void addRequest(final byte[] reqCtx, final ReadIndexClosure closure) {
try {
EventTranslator<ReadIndexEvent> translator = (event, sequence) -> {
event.done = closure;
event.requestContext = new Bytes(reqCtx);
event.startTime = Utils.monotonicMs();
};
int retryTimes = 0;
while (true) {
if (this.readIndexQueue.tryPublishEvent(translator)) {
break;
} else {
retryTimes++;
if (retryTimes > MAX_ADD_REQUEST_RETRY_TIMES) {
Utils.runClosureInThread(closure,
new Status(RaftError.EBUSY, "Node is busy, has too many read-only requests."));
return;
}
ThreadHelper.onSpinWait();
}
}
} catch (final Exception e) {
Utils.runClosureInThread(closure, new Status(RaftError.EPERM, "Node is down."));
}
}
private class ReadIndexEventHandler implements EventHandler<ReadIndexEvent> {
private final List<ReadIndexEvent> events = new ArrayList<>(
ReadOnlyServiceImpl.this.raftOptions.getApplyBatch());
@Override
public void onEvent(final ReadIndexEvent newEvent, final long sequence, final boolean endOfBatch)
throws Exception {
this.events.add(newEvent);
if (this.events.size() >= ReadOnlyServiceImpl.this.raftOptions.getApplyBatch() || endOfBatch) {
executeReadIndexEvents(this.events);
this.events.clear();
}
}
}
ReadOnlyServiceImpl的executeReadIndexEvents方法构造ReadIndexRequest,交给Node处理。
注意这里封装了第三层Closure---ReadIndexResponseClosure。
// ReadOnlyServiceImpl
private void executeReadIndexEvents(final List<ReadIndexEvent> events) {
if (events.isEmpty()) {
return;
}
// 构造ReadIndex请求
final ReadIndexRequest.Builder rb = ReadIndexRequest.newBuilder() //
.setGroupId(this.node.getGroupId()) //
.setServerId(this.node.getServerId().toString());
final List<ReadIndexState> states = new ArrayList<>(events.size());
for (final ReadIndexEvent event : events) {
rb.addEntries(ZeroByteStringHelper.wrap(event.requestContext.get()));
states.add(new ReadIndexState(event.requestContext, event.done, event.startTime));
}
final ReadIndexRequest request = rb.build();
// 调用Node处理ReadIndex
this.node.handleReadIndexRequest(request, new ReadIndexResponseClosure(states, request));
}
NodeImpl根据当前节点状态,做不同的处理,如果当前节点是leader,走readLeader;如果当前节点是follower,走readFollower,两边逻辑不同。
// NodeImpl
@Override
public void handleReadIndexRequest(final ReadIndexRequest request, final RpcResponseClosure<ReadIndexResponse> done) {
final long startMs = Utils.monotonicMs();
this.readLock.lock();
try {
switch (this.state) {
case STATE_LEADER:
readLeader(request, ReadIndexResponse.newBuilder(), done);
break;
case STATE_FOLLOWER:
readFollower(request, done);
break;
// ...
}
} finally {
this.readLock.unlock();
}
}
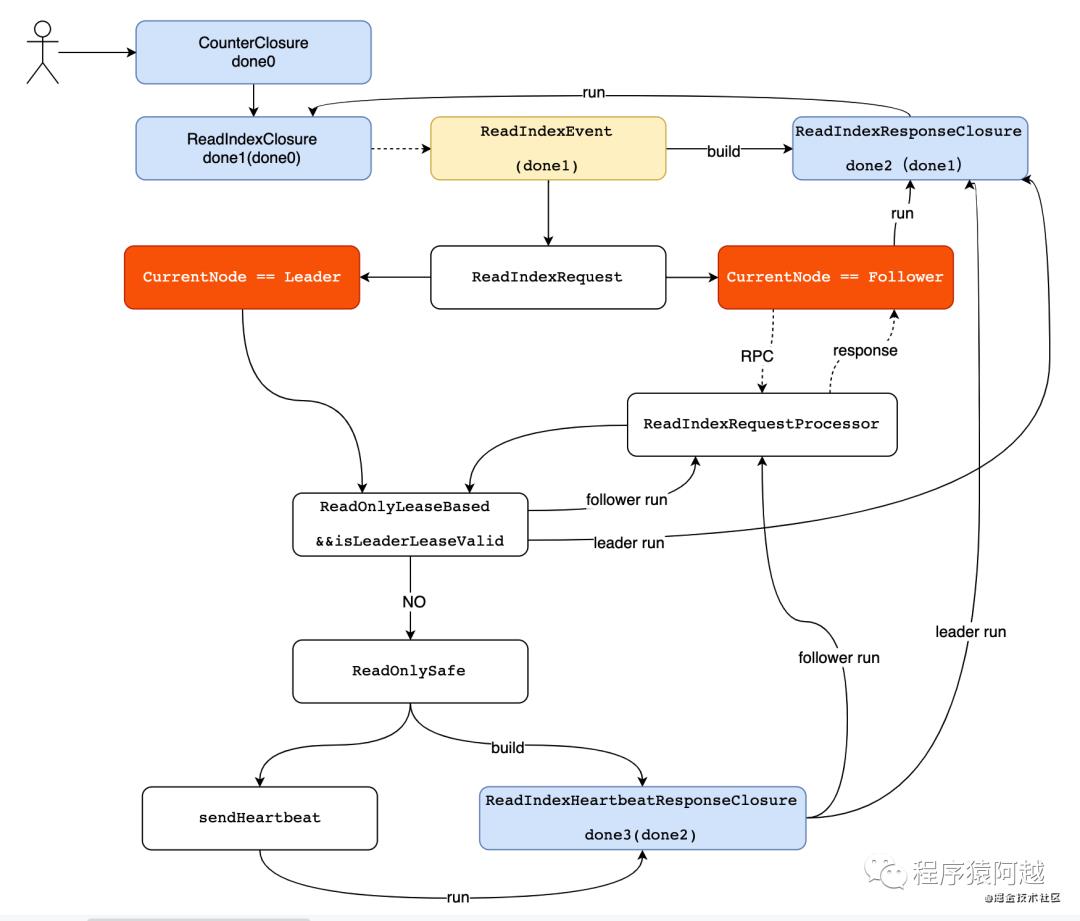
当前节点是Leader
如果当前节点是Leader,直接走NodeImpl的readLeader方法。follower发送ReadIndexRequest给leader,leader也会走这个方法。
// NodeImpl
private void readLeader(final ReadIndexRequest request, final ReadIndexResponse.Builder respBuilder,
final RpcResponseClosure<ReadIndexResponse> closure) {
// 如果只有一个节点,直接响应成功
final int quorum = getQuorum();
if (quorum <= 1) {
respBuilder.setSuccess(true) //
.setIndex(this.ballotBox.getLastCommittedIndex());
closure.setResponse(respBuilder.build());
closure.run(Status.OK());
return;
}
// 如果leader在自己任期内没有提交任何log,拒绝请求
final long lastCommittedIndex = this.ballotBox.getLastCommittedIndex();
if (this.logManager.getTerm(lastCommittedIndex) != this.currTerm) {
closure
.run(new Status(
RaftError.EAGAIN,
"ReadIndex request rejected because leader has not committed any log entry at its term, logIndex=%d, currTerm=%d.",
lastCommittedIndex, this.currTerm));
return;
}
respBuilder.setIndex(lastCommittedIndex);
// 如果是follower发来的ReadIndexRequest,如果follower不在当前raft集群内,响应失败
if (request.getPeerId() != null) {
final PeerId peer = new PeerId();
peer.parse(request.getServerId());
if (!this.conf.contains(peer) && !this.conf.containsLearner(peer)) {
closure
.run(new Status(RaftError.EPERM, "Peer %s is not in current configuration: %s.", peer, this.conf));
return;
}
}
ReadOnlyOption readOnlyOpt = this.raftOptions.getReadOnlyOptions();
// 如果ReadOnlyLeaseBased,但是leader不在有效期内,降级为普通readIndex请求,默认ReadOnlySafe
if (readOnlyOpt == ReadOnlyOption.ReadOnlyLeaseBased && !isLeaderLeaseValid()) {
readOnlyOpt = ReadOnlyOption.ReadOnlySafe;
}
switch (readOnlyOpt) {
case ReadOnlySafe:
final List<PeerId> peers = this.conf.getConf().getPeers();
Requires.requireTrue(peers != null && !peers.isEmpty(), "Empty peers");
final ReadIndexHeartbeatResponseClosure heartbeatDone = new ReadIndexHeartbeatResponseClosure(closure,
respBuilder, quorum, peers.size());
// 向其他follower发送心跳,确认自己任然是leader
for (final PeerId peer : peers) {
if (peer.equals(this.serverId)) {
continue;
}
this.replicatorGroup.sendHeartbeat(peer, heartbeatDone);
}
break;
case ReadOnlyLeaseBased:
respBuilder.setSuccess(true);
closure.setResponse(respBuilder.build());
closure.run(Status.OK());
break;
}
}
针对一致性读,有ReadIndex和LeaseRead两种可选方案,默认使用ReadIndex方案。
ReadIndex(ReadOnlySafe):需要向其他Follower发送心跳,确认当前节点任然是leader;
LeaseRead(ReadOnlyLeaseBased):为了减少发送心跳rpc请求的次数,每次leader向follower发送心跳,会更新一个时间戳,如果这个读请求在心跳超时时间之内,可以认为当前节点仍然是leader。
private boolean checkLeaderLease(final long monotonicNowMs) {
// 当前时间 - 上次心跳时间 < 心跳超时时间 * 0.9 = 0.9s
return monotonicNowMs - this.lastLeaderTimestamp < this.options.getLeaderLeaseTimeoutMs();
}
心跳请求响应回调ReadIndexHeartbeatResponseClosure,这是第四个回调,当leader收到大部分follower响应心跳后,认为自己仍然是leader,执行第三个回调的run方法。
private class ReadIndexHeartbeatResponseClosure extends RpcResponseClosureAdapter<AppendEntriesResponse> {
@Override
public synchronized void run(final Status status) {
if (this.isDone) {
return;
}
if (status.isOk() && getResponse().getSuccess()) {
this.ackSuccess++;
} else {
this.ackFailures++;
}
// Include leader self vote yes.
if (this.ackSuccess + 1 >= this.quorum) {
this.respBuilder.setSuccess(true);
this.closure.setResponse(this.respBuilder.build());
this.closure.run(Status.OK());
this.isDone = true;
} else if (this.ackFailures >= this.failPeersThreshold) {
this.respBuilder.setSuccess(false);
this.closure.setResponse(this.respBuilder.build());
this.closure.run(Status.OK());
this.isDone = true;
}
}
}
ReadIndexResponseClosure是第三个回调,这是段公用逻辑,无论当前节点是leader还是follower,当ReadIndex处理完毕,都会调用这个方法。这里会判断如果readIndex达到applyIndex,即可响应第二个回调;如果readIndex未达到applyIndex,会放入一个等待队列,等到日志复制到readIndex了才会执行第二个回调。这里第二个回调就是用户代码传入NodeImpl#readIndex方法的回调ReadIndexClosure。此时用户即可从状态机中读取value返回了。
class ReadIndexResponseClosure extends RpcResponseClosureAdapter<ReadIndexResponse> {
final List<ReadIndexState> states;
final ReadIndexRequest request;
/**
* 当一致性读返回时,客户端节点处理回调状态
*/
@Override
public void run(final Status status) {
// 1. 如果失败,响应读失败
if (!status.isOk()) {
notifyFail(status);
return;
}
final ReadIndexResponse readIndexResponse = getResponse();
if (!readIndexResponse.getSuccess()) {
notifyFail(new Status(-1, "Fail to run ReadIndex task, maybe the leader stepped down."));
return;
}
// 2. 设置ReadIndexStatus
final ReadIndexStatus readIndexStatus = new ReadIndexStatus(this.states, this.request,
readIndexResponse.getIndex());
for (final ReadIndexState state : this.states) {
state.setIndex(readIndexResponse.getIndex());
}
boolean doUnlock = true;
ReadOnlyServiceImpl.this.lock.lock();
try {
// 3. 如果当前节点的applyIndex大于等于ReadIndexResponse的current commit index,执行用户的Closure回调,可以读取当前节点状态机中的数据
if (readIndexStatus.isApplied(ReadOnlyServiceImpl.this.fsmCaller.getLastAppliedIndex())) {
ReadOnlyServiceImpl.this.lock.unlock();
doUnlock = false;
notifySuccess(readIndexStatus);
} else {
// 4. 如果applyIndex小于current commit index,放入队列,等待applyIndex
ReadOnlyServiceImpl.this.pendingNotifyStatus
.computeIfAbsent(readIndexStatus.getIndex(), k -> new ArrayList<>(10)) //
.add(readIndexStatus);
}
} finally {
if (doUnlock) {
ReadOnlyServiceImpl.this.lock.unlock();
}
}
}
}
当前节点是Follower
当前节点是follower,会将readIndex请求转发到Leader节点上。
// NodeImpl
private void readFollower(final ReadIndexRequest request, final RpcResponseClosure<ReadIndexResponse> closure) {
if (this.leaderId == null || this.leaderId.isEmpty()) {
closure.run(new Status(RaftError.EPERM, "No leader at term %d.", this.currTerm));
return;
}
// send request to leader.
final ReadIndexRequest newRequest = ReadIndexRequest.newBuilder() //
.mergeFrom(request) //
.setPeerId(this.leaderId.toString()) //
.build();
this.rpcService.readIndex(this.leaderId.getEndpoint(), newRequest, -1, closure);
}
Leader通过ReadIndexRequestProcessor处理ReadIndexRequest,仍然调用NodeImpl(RaftServerService的实现类)的handleReadIndexRequest方法处理ReadIndexRequest请求,和节点是leader的情况完全一致。
public class ReadIndexRequestProcessor extends NodeRequestProcessor<ReadIndexRequest> {
@Override
public Message processRequest0(final RaftServerService service, final ReadIndexRequest request,
final RpcRequestClosure done) {
service.handleReadIndexRequest(request, new RpcResponseClosureAdapter<RpcRequests.ReadIndexResponse>() {
@Override
public void run(final Status status) {
if (getResponse() != null) {
// 1. 如果response不为null,响应客户端成功
done.sendResponse(getResponse());
} else {
// 2. 如果response是null,返回原始status
done.run(status);
}
}
});
return null;
}
}
总结
使用sofa-jraft,需要用户实现StateMachine接口,用于保存数据和读取数据。创建RaftGroupService,通过RaftGroupService的start方法启动Raft服务,得到NodeImpl。
public class CounterServer {
private RaftGroupService raftGroupService; // raft服务
private Node node; // 当前节点
private CounterStateMachine fsm; // 状态机
}
从用户代码角度看raft写。用户需要创建一个Task,其中data是需要写入的数据,done是task处理完成后的回调函数Closure。最后将Task通过Node#apply(Task)方法提交到JRaft框架。
final Task task = new Task();
// 把请求入参序列化为ByteBuffer
task.setData(ByteBuffer.wrap(SerializerManager.getSerializer(SerializerManager.Hessian2).serialize(op)));
// 把外部传入的closure放到Task的done成员变量里
task.setDone(closure);
// 将Task提交到当前Node处理,托管给JRaft框架
this.counterServer.getNode().apply(task);
当JRaft框架处理完毕后,会调用用户的StateMachine的onApply方法,将需要应用的日志通过迭代器Iterator的方式批量给到用户来处理。Iterator中每个元素都持有一个Closure,是当时提交task时传入的,用户处理完成后需要调用Closure的run方法进行回调。
从sofa-jraft框架的角度看raft写。大致流程:
Task提交Leader->数据写内存->内存落盘->commit
Leader->Replicator日志复制->Follower->数据写内存->内存落盘->响应Leader->commit
Leader的BallotBox投票箱处理commit->超半数quorum节点commit->提交ApplyTask->调用用户StateMachine的onApply方法
Leader的Replicator日志复制->Follower->Follower投票箱发现committedIndex超过applyIndex->Follower提交ApplyTask->调用用户StateMachine的onApply方法
从用户角度看raft一致性读。用户可以请求leader节点,也可以请求follower节点,都支持一致性读。通过NodeImpl的readIndex方法执行一致性读,传入ReadIndexClosure回调函数。当JRaft框架处理完毕后,会回调ReadIndexClosure的run方法。如果status成功,代表readIndex小于等于applyIndex,可以从用户本地状态机获取值;如果status失败,可以考虑当当前节点为leader节点时,执行普通raft流程,降级为和写操作一样的流程。
this.counterServer.getNode().readIndex(BytesUtil.EMPTY_BYTES, new ReadIndexClosure() {
@Override
public void run(Status status, long index, byte[] reqCtx) {
// 保证readIndex(commitIndex) <= applyIndex后,获取状态机中的值
if(status.isOk()){
closure.success(getValue());
closure.run(Status.OK());
return;
}
// 失败处理
CounterServiceImpl.this.readIndexExecutor.execute(() -> {
// 如果当前节点是Leader,提交task到Raft集群,如果成功了,会回调CounterStateMachine的onApply方法响应
if(isLeader()){
applyOperation(CounterOperation.createGet(), closure);
}else {
// 如果当前节点不是Leader,响应失败
handlerNotLeaderError(closure);
}
});
}
});
从框架角度看raft一致性读。如果用户请求的是follower,会将请求转发至leader。leader针对一致性读,有ReadIndex和LeaseRead两种可选方案,默认使用ReadIndex方案。
ReadIndex(ReadOnlySafe):需要向其他Follower发送心跳,确认当前节点任然是leader;
LeaseRead(ReadOnlyLeaseBased):为了减少发送心跳rpc请求的次数,每次leader向follower发送心跳,会更新一个时间戳,如果这个读请求在心跳超时时间之内,可以认为当前节点仍然是leader。
以上是关于Nacos源码Sofa-JRaft的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章