springIOC原理——自己实现一下不就懂了嘛
Posted 小王子jvm
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了springIOC原理——自己实现一下不就懂了嘛相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
使用Spring
只需要引入对应的依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>5.2.0.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
maven自动依赖几个核心包:
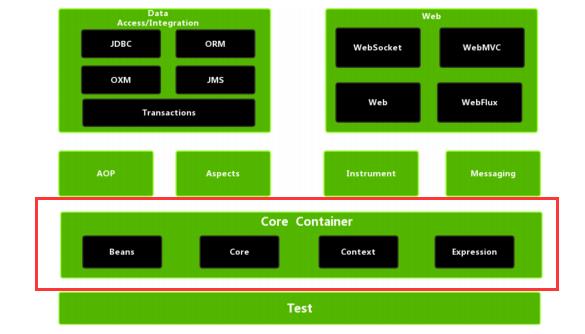
测试
//DAO 层
public interface UserDao {
void add();
}
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
public void add() {
System.out.println("UserDao...");
}
}
//service 层
public interface UserService {
void add();
}
public class UserServiceImpl implements UserService {
private UserDao userDao;
private String username;
private String password;
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public void setUserDao(UserDao userDao) {
this.userDao = userDao;
}
public void add() {
userDao.add();
System.out.println("UserService实现类"+username+"=="+password);
}
}
使用xml配置文件方式,配置如下:
<beans >
<!--创建userService,依赖注入dao-->
<bean id="userService" class="com.sheep.service.impl.UserServiceImpl">
<property name="userDao" ref="userDao"/>
<property name="username" value="sheep"/>
<property name="password" value="123456"/>
</bean>
<!--dao相关的bean-->
<bean id="userDao" class="com.sheep.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"/>
</beans>
然后就是controller,用一个main模拟:
public class MainController {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//创建IOC容器,加载配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring-ioc.xml");
//获取相应的bean
UserService userService = context.getBean("userService", UserService.class);
userService.add();
}
}
经过测试是可以正常输出内容的。
相关IOC接口源码
Spring中Bean的创建是典型的工厂模式,这一系列的Bean工厂,即IoC容器,为开发者管理对象之间 的依赖关系提供了很多便利和基础服务,在Spring中有许多IoC容器的实现供用户选择。
最顶层接口是一个BeanFactory,定义了IoC容器的基本功能规范。它的实现有很多。每个接口都有它的使用场合,主要是为了区分在Spring内部操作过程中对象的传递和转化,对对象的 数据访问所做的限制。
在BeanFactory里只对IoC容器的基本行为做了定义,根本不关心你的Bean是如何定义及怎样加载 的。正如我们只关心能从工厂里得到什么产品,不关心工厂是怎么生产这些产品的。 BeanFactory有一个很重要的子接口,就是ApplicationContext接口,该接口主要来规范容器中 的bean对象是非延时加载,即在创建容器对象的时候就对象bean进行初始化,并存储到一个容器中。

要知道工厂是如何产生对象的,我们需要看具体的IoC容器实现,Spring提供了许多IoC容器实现,比如:
- ClasspathXmlApplicationContext : 根据类路径加载xml配置文件,并创建IOC容器对象。
FileSystemXmlApplicationContext:根据系统路径加载xml配置文件,并创建IOC容器对象。- AnnotationConfigApplicationContext :加载注解类配置,并创建IOC容器。
BeanDefinition解析
Spring IoC容器管理我们定义的各种Bean对象及其相互关系,而Bean对象在Spring实现中是以 BeanDefinition来描述的,如下面配置文件:
<bean id="userDao" class="com.sheep.dao.impl.UserDaoImpl"></bean>
bean标签还有很多属性:
scope、init-method、destory-method等。
解析id,class这些东西然后封装成一个BeanDefinition,被没有什么特别。
BeanDefinitionReader解析
Bean的解析过程非常复杂,功能被分得很细,因为这里需要被扩展的地方很多,必须保证足够的灵活 性,以应对可能的变化。Bean的解析主要就是对Spring配置文件的解析。这个解析过程主要通过 BeanDefinitionReader来完成,看看Spring中BeanDefinitionReader的类结构图,如下图所示。

总之这个接口就是规范解析配置的规范,比如像解析xml,就有对应的实现做这个事情。
BeanDefinitionRegistry解析
BeanDefinitionReader用来解析bean定义,并封装BeanDefinition对象,而我们定义的配置文 件中定义了很多bean标签,所以就有一个问题,解析的BeanDefinition对象存储到哪儿?答案就是 BeanDefinition的注册中心,而该注册中心顶层接口就是BeanDefinitionRegistry。
也没有什么特别的,这个接口只不过定义的怎么注册,实现类都会有一个map集合来保存解析出来的东西。

从上面类图可以看到BeanDefinitionRegistry接口的子实现类主要有以下几个: (所谓的注册就是保存解析的东西,这里就是解析出来的东西就是BeanDefinition)
-
DefaultListableBeanFactory 在该类中定义了如下代码,就是用来注册bean
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256); -
SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry 在该类中定义了如下代码,就是用来注册bean:
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(64);
创建容器的过程
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext对Bean配置资源的载入是从refresh()方法开始的。
refresh()方法是一个模板方法,规定了 IoC 容器的启动流程,有些逻辑要交给其子类实现。它对 Bean 配置资源进行载入,ClassPathXmlApplicationContext通过调用其父类 AbstractApplicationContext的refresh()方法启动整个IoC容器对Bean定义的载入过程。
自定义SpringIOC
整个工程的结构如下:
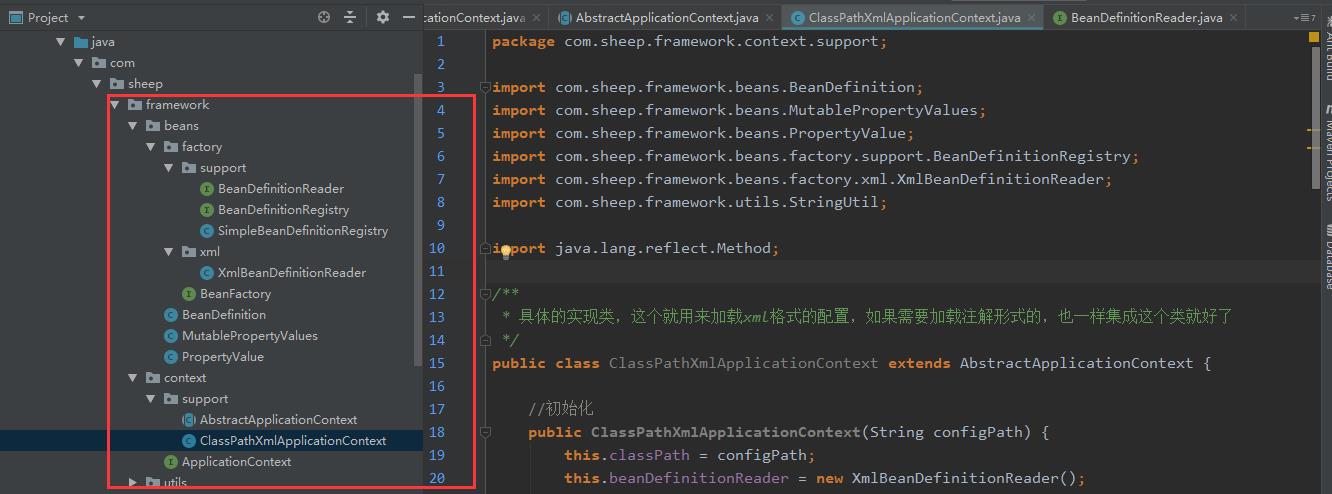
定义bean相关的pojo类
PropertyValue类
用于封装bean的属性,体现到上面的配置文件就是封装bean标签的子标签property标签数据。
/**
* 每一bean可能会引用其他bean,这个用来封装被引用的bean解析后的属性
* @Description: 封装被引用的bean解析后的属性
* name : 引用的名字,也就是放在容器中的key
* ref : 引用类型
* value : 基本类型的引用
*/
public class PropertyValue {
private String name;
private String ref;
private String value;
public PropertyValue() {
}
public PropertyValue(String name, String ref, String value) {
this.name = name;
this.ref = ref;
this.value = value;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getRef() {
return ref;
}
public void setRef(String ref) {
this.ref = ref;
}
public String getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(String value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
MutablePropertyValues类
一个bean标签可以有多个property子标签,所以再定义一个MutablePropertyValues类,用来存 储并管理多个PropertyValue对象。
/**
* 一个bean标签可以有多个property子标签,所以再定义一个MutablePropertyValues类,用来存
* 储并管理多个PropertyValue对象。
*/
public class MutablePropertyValues implements Iterable<PropertyValue> {
//用一个list集合保存
private final List<PropertyValue> propertyValueList;
public MutablePropertyValues() {
propertyValueList = new ArrayList<PropertyValue>();
}
public MutablePropertyValues(List<PropertyValue> propertyValueList) {
this.propertyValueList = (propertyValueList != null ?
propertyValueList : new ArrayList<PropertyValue>());
}
//获取所有的PropertyValue,并以数组的形式返回
public PropertyValue[] getPropertyValues(){
return (PropertyValue[]) propertyValueList.toArray();
}
//通过propertyName获取对应的PropertyValue
public PropertyValue getPropertyValue(String propertyName){
for (PropertyValue propertyValue : propertyValueList) {
if (propertyName.equals(propertyValue.getName())){
return propertyValue;
}
}
return null;
}
//迭代器模式,用于遍历
public Iterator<PropertyValue> iterator() {
return propertyValueList.iterator();
}
//判断是否为空
public boolean isEmpty(){
return this.propertyValueList.isEmpty();
}
//是否已有这个封装的对象
public boolean contains(String propertyName) {
return getPropertyValue(propertyName) != null;
}
//添加一个propertyValue到容器中,存在的化进行覆盖
public MutablePropertyValues addPropertyValue(PropertyValue propertyValue){
for (int i = 0; i < propertyValueList.size(); i++) {
PropertyValue tmp = this.propertyValueList.get(i);
if (tmp.getName().equals(propertyValue.getName())){
//存在就覆盖
propertyValueList.set(i,new PropertyValue(propertyValue.getName(),
propertyValue.getRef(),propertyValue.getValue()));
}
}
this.propertyValueList.add(propertyValue);
return this;
}
}
BeanDefinition类
BeanDefinition类用来封装bean信息的,主要包含id(即bean对象的名称)、class(需要交由 spring管理的类的全类名)及子标签property数据。
/**
* 解析出来的Bean的配置属性
*/
public class BeanDefinition {
private String id;
private String className;
private MutablePropertyValues propertyValues;
public BeanDefinition() {
propertyValues = new MutablePropertyValues();
}
public String getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getClassName() {
return className;
}
public void setClassName(String className) {
this.className = className;
}
public MutablePropertyValues getPropertyValues() {
return propertyValues;
}
public void setPropertyValues(MutablePropertyValues propertyValues) {
this.propertyValues = propertyValues;
}
}
定义注册表相关类
BeanDefinitionRegistry接口
BeanDefinitionRegistry接口定义了注册表的相关操作,定义如下功能:
- 注册BeanDefinition对象到注册表中
- 从注册表中删除指定名称的BeanDefinition对象
- 根据名称从注册表中获取BeanDefinition对象
- 判断注册表中是否包含指定名称的BeanDefinition对象
- 获取注册表中BeanDefinition对象的个数
- 获取注册表中所有的BeanDefinition的名称
/**
* 用于注册保存BeanDefinition
*/
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistry {
void registryBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition);
void removeBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws Exception;
BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws Exception;
boolean containsBeanDefinition(String beanName);
int getBeanDefinitionCount();
String[] getBeanDefinitionsName();
}
SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry类
该类实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,定义了Map集合作为注册表容器。
public class SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry implements BeanDefinitionRegistry {
//既然是需要保存,就需要用到map
private final Map<String,BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String, BeanDefinition>();
//注册这个BeanDefinition到表中
public void registryBeanDefinition(String beanName, BeanDefinition beanDefinition) {
beanDefinitionMap.put(beanName,beanDefinition);
}
//删除
public void removeBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws Exception {
beanDefinitionMap.remove(beanName);
}
//获取这个beanDefinition
public BeanDefinition getBeanDefinition(String beanName) throws Exception {
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = beanDefinitionMap.get(beanName);
return beanDefinition;
}
public boolean containsBeanDefinition(String beanName) {
return beanDefinitionMap.containsKey(beanName);
}
public int getBeanDefinitionCount() {
return beanDefinitionMap.size();
}
public String[] getBeanDefinitionsName() {
return beanDefinitionMap.keySet().toArray(new String[0]);
}
}
定义解析器相关类
BeanDefinitionReader接口
BeanDefinitionReader是用来解析配置文件并在注册表中注册bean的信息。定义了两个规范:
- 获取注册表的功能,让外界可以通过该对象获取注册表对象。
- 加载配置文件,并注册bean数据。
/**
* 解析xml并在封装成BeanDefinition的规范接口
*/
public interface BeanDefinitionReader {
BeanDefinitionRegistry getBeanDefinitionRegistry();
void loadBeanDefinitions(String classPath) throws Exception;
}
XmlBeanDefinitionReader类
既然要解析xml文件,解析的包是必不可少的:
<dependency>
<groupId>dom4j</groupId>
<artifactId>dom4j</artifactId>
<version>1.6.1</version>
</dependency>
XmlBeanDefinitionReader类是专门用来解析xml配置文件的。该类实现 BeanDefinitionReader接口并实现接口中的两个功能。
public class XmlBeanDefinitionReader implements BeanDefinitionReader {
private BeanDefinitionRegistry registry;
public XmlBeanDefinitionReader() {
this.registry = new SimpleBeanDefinitionRegistry();
}
public BeanDefinitionRegistry getBeanDefinitionRegistry() {
return registry;
}
/**
* 加载配置文件,并解析成对应的BeanDefinition
* @param classPath
* @throws Exception
*/
public void loadBeanDefinitions(String classPath) throws Exception {
//从类路径下加载
InputStream is = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream(classPath);
//利用dom4j解析配置文件
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
Document document = saxReader.read(is);
Element rootElement = document.getRootElement(); //也就是Beans标签
parseBean(rootElement); //解析这个根节点并封装
}
/**
* 利用dom4j进行解析
* @param rootElement
*/
private void parseBean(Element rootElement) {
//获取所有的标签,这里只有bean标签
List<Element> elements = rootElement.elements();
for (Element element : elements) {
//遍历这些标签,逐个解析
String id = element.attributeValue("id");
String className = element.attributeValue("class");
//封装这些参数
BeanDefinition beanDefinition = new BeanDefinition();
beanDefinition.setId(id);
beanDefinition.setClassName(className);
//然后继续解析可能会有的引用依赖,也就是property
List<Element> list = element.elements("property");
MutablePropertyValues propertyValues = new MutablePropertyValues();
//逐个解析
for (Element element1 : list) {
String name = element1.attributeValue("name");
String ref = element1.attributeValue("ref");
String value = element1.attributeValue("value");
PropertyValue propertyValue = new PropertyValue(name, ref, value);
propertyValues.addPropertyValue(propertyValue);
}
//将所有的依赖全部注入相应的bean
beanDefinition.setPropertyValues(propertyValues);
registry.registryBeanDefinition(id,beanDefinition);
}
}
}
IOC容器相关类
BeanFactory接口
在该接口中定义IOC容器的统一规范即获取bean对象。
/**
* IOC容器的顶级接口,规范怎么获取生产获取Bean,这就是一个典型的工厂模式
*/
public interface BeanFactory {
Object getBean(String name) throws Exception;
<T> T getBean(String name,Class<? extends T> clazz) throws Exception;
}
ApplicationContext接口
该接口的所以的子实现类对bean对象的创建都是非延时的,所以在该接口中定义 refresh() 方法, 该方法主要完成以下两个功能:
- 加载配置文件。
- 根据注册表中的BeanDefinition对象封装的数据进行bean对象的创建。
public interface ApplicationContext extends BeanFactory {
void refresh() throws Exception