吴恩达机器学习作业neural network _python实现
Posted 挂科难
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了吴恩达机器学习作业neural network _python实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
手写字体识别:
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import scipy.io as scio
import matplotlib
import scipy.optimize as opt
path = 'ex3data1.mat'
def sigmoid(z):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
def cost(theta, X, y, learningRate):
theta = np.mat(theta)
X = np.mat(X)
y = np.mat(y)
first = np.multiply(-y, np.log(sigmoid(X * theta.T)))
second = np.multiply((1 - y), np.log(1 - sigmoid(X * theta.T)))
reg = (learningRate / (2 * len(X))) * np.sum(np.power(theta[:,1:theta.shape[1]], 2))
return np.sum(first - second) / len(X) + reg
def gradient(theta, X, y, learningRate):
theta = np.mat(theta)
X = np.mat(X)
y = np.mat(y)
error = sigmoid(X * theta.T) - y
grad = ((X.T * error) / len(X)).T + ((learningRate / len(X)) * theta)
# intercept gradient is not regularized,截距梯度不是正则化的
grad[0, 0] = np.sum(np.multiply(error, X[:, 0])) / len(X)
return np.array(grad).ravel()
def plot_an_image(image):
# """#绘图函数
# image : (400,)
# """
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(1, 1))
ax.matshow(image.reshape((20, 20)), cmap=matplotlib.cm.binary)#这是一个把矩阵或者数组绘制成图像的函数
plt.xticks(np.array([])) # just get rid of ticks
plt.yticks(np.array([]))
def plot_100_image(X):
""" sample 100 image and show them
assume the image is square
X : (5000, 400)
"""
size = int(np.sqrt(X.shape[1]))#X.shape is 400
# sample 100 image, reshape, reorg it
sample_idx = np.random.choice(np.arange(X.shape[0]), 100) # 100*400
#np.arange(X.shape[0]),X.shape[0] is 5000,在产生0-4999一个列表。随机选100个
sample_images = X[sample_idx, :]
fig, ax_array = plt.subplots(nrows=10, ncols=10, sharey=True, sharex=True, figsize=(8, 8))
for r in range(10):
for c in range(10):
ax_array[r, c].matshow(sample_images[10 * r + c].reshape((size, size)),
cmap=matplotlib.cm.binary)
plt.xticks(np.array([]))
plt.yticks(np.array([]))
#绘图函数,画100张图片
def one_vs_all(X, y, num_labels, learning_rate):
row = X.shape[0] # row 本列为5000
column = X.shape[1] # column 本列为 400
all_theta = np.zeros((num_labels, column + 1))
# 在截距项的开头插入一列1
X = np.insert(X, 0, values=np.ones(row), axis=1)
for i in range(1, num_labels + 1): # i 从1到10
theta = np.zeros(column + 1) # 401
y_i = np.array([1 if label == i else 0 for label in y]) # 向量化标签
y_i = np.reshape(y_i, (row, 1)) # 5000行,1列,训练一个模型的theta,利用for循环训练了10个
# minimize the objective function
fmin = opt.minimize(fun=cost, x0=theta, args=(X, y_i, learning_rate), method='TNC', jac=gradient)
all_theta[i - 1, :] = fmin.x # 将训练好的数据模型放到all_theta中,共有10个
return all_theta
def predict_all(X, all_theta):
rows = X.shape[0]
# same as before, insert ones to match the shape
X = np.insert(X, 0, values=np.ones(rows), axis=1)
# convert to matrices
X = np.mat(X)
all_theta = np.mat(all_theta)
# compute the class probability for each class on each training instance
h = sigmoid(X * all_theta.T) #X 401行,all_theta.T有401列
# create array of the index with the maximum probability
h_argmax = np.argmax(h, axis=1)
# because our array was zero-indexed we need to add one for the true label prediction
h_argmax = h_argmax + 1
return h_argmax
'''
#查看数据
X = data['X']
y = data['y']
pick_one = np.random.randint(0, 5000)#返回0~5000中任意一个整数
plot_an_image(X[pick_one, :])
plt.show()
print('this should be {}'.format(y[pick_one]))#在该标签中1~9,为数字1~9,0的标签是10
plot_100_image(X)
plt.show()
'''
data = scio.loadmat('ex3data1.mat')
row = data['X'].shape[0] # 5000行,
column = data['X'].shape[1] # 400列
all_theta = np.zeros((10, column + 1))
all_theta = one_vs_all(data['X'], data['y'], 10, 1)
y_pred = predict_all(data['X'], all_theta)
correct = [1 if a == b else 0 for (a, b) in zip(y_pred, data['y'])] # 预测正确输出为1
accuracy = (sum(map(int, correct)) / float(len(correct)))
print ('accuracy = {0}%'.format(accuracy * 100))
scio.savemat('theta.mat', {'results': all_theta}) # 保存all_theta,
最终准确率达到了94.46%,本着严谨的态度,又自己写了20个数测试了一下。思路(已实现):先将上述代码中的all_theta保存,用自带画图软件写一个数字,保存本地后压缩成20*20像素,和训练集中的像素保持一致,再将图片转化为灰度图像,旋转垂直镜像后转为矩阵与保存的all_theta相乘,带入sigmoid函数,np.argmax得出结果。
手写体用数字0 ~ 9命名,微软雅黑用0_ ~ 9_ 命名。结果只能说不是很理想。。。可能参数有点过拟合。(最多才对了6个,手写的对了四个。这结果实在不敢恭维)
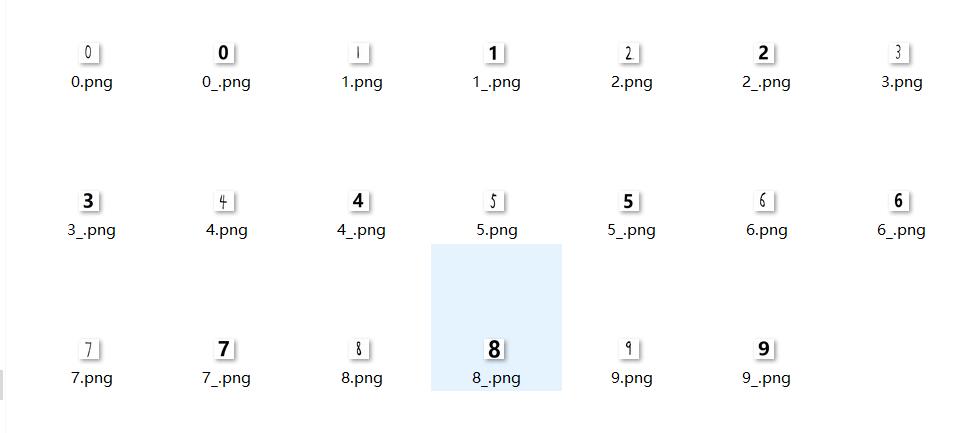
测试:
from PIL import Image
import numpy as np
import scipy.io as scio
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib
import cv2
def produceImage(file_in, width, height, file_out):
image = Image.open(file_in)
resized_image = image.resize((width, height), Image.ANTIALIAS)
resized_image.save(file_out)
def sigmoid(z):
return 1 / (1 + np.exp(-z))
def plot_an_image(image):
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(1, 1))
ax.matshow(image.reshape((20, 20)), cmap=matplotlib.cm.binary) # 这是一个把矩阵或者数组绘制成图像的函数
plt.xticks(np.array([])) # just get rid of ticks
plt.yticks(np.array([]))
for i in range(10):
filename = 'image/'+str(i)+'.png'
im = 255 - np.array(Image.open(filename).convert('L'))
if im.shape != (20, 20):
produceImage(filename, 20, 20, filename)
im = 255 - np.array(Image.open(filename).convert('L').rotate(90))
im = cv2.flip(im, 0, dst=None) # 垂直镜像
im = im.ravel()
im = im.astype(float) / 255.0
all_theta = scio.loadmat('theta.mat')
all_theta = all_theta['results']
im = np.mat(im)
im2 = np.insert(im, 0, values=np.ones(1), axis=1)
answer = sigmoid(im2 * all_theta.T)
print(" i think this should be " + str(np.argmax(answer) + 1))
plot_an_image(im)
plt.show()
以上是关于吴恩达机器学习作业neural network _python实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章