HarmonyOS之深入解析自定义组件与布局的实现
Posted Forever_wj
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了HarmonyOS之深入解析自定义组件与布局的实现相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、概述
- HarmonyOS 提供了一套复杂且强大的 Java UI 框架,其中 Component 提供内容显示,是界面中所有组件的基类。ComponentContainer 作为容器容纳 Component 或 ComponentContainer 对象,并对它们进行布局。
- Java UI 框架也提供了一部分 Component 和 ComponentContainer 的具体子类,即常用的组件(比如:Text、Button、Image 等)和常用的布局(比如:DirectionalLayout、DependentLayout 等)。如果现有的组件和布局无法满足设计需求,例如仿遥控器的圆盘按钮、可滑动的环形控制器等,可以通过自定义组件和自定义布局来实现。
- 自定义组件是由开发者定义的具有一定特性的组件,通过扩展 Component 或其子类实现,可以精确控制屏幕元素的外观,也可响应用户的点击、触摸、长按等操作。
- 自定义布局是由开发者定义的具有特定布局规则的容器类组件,通过扩展 ComponentContainer 或其子类实现,可以将各子组件摆放到指定的位置,也可响应用户的滑动、拖拽等事件。
二、自定义组件
- 当 Java UI 框架提供的组件无法满足设计需求时,可以创建自定义组件,根据设计需求添加绘制任务,并定义组件的属性及事件响应,完成组件的自定义。
① 常用接口
- Component 类相关接口如下表所示:
| 接口名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| setEstimateSizeListener | 设置测量组件的侦听器 |
| onEstimateSize | 测量组件的大小以确定宽度和高度 |
| setEstimatedSize | 将测量的宽度和高度设置给组件 |
| EstimateSpec.getChildSizeWithMode | 基于指定的大小和模式为子组件创建度量规范 |
| EstimateSpec.getSize | 从提供的度量规范中提取大小 |
| EstimateSpec.getMode | 获取该组件的显示模式 |
| addDrawTask | 添加绘制任务 |
| onDraw | 通过绘制任务更新组件时调用 |
② 如何实现自定义组件
- 以自定义圆环组件为例:在屏幕中绘制蓝色圆环,并实现点击变化圆环颜色的功能,自定义圆环组件如下所示:
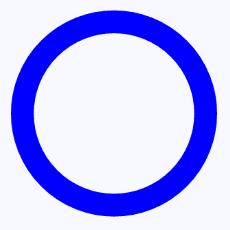
- 创建自定义组件的类,并继承 Component 或其子类,添加构造方法。示例代码如下:
public class CustomComponent extends Component{
public CustomComponent(Context context) {
super(context);
}
}
- 实现 Component.EstimateSizeListener 接口,在 onEstimateSize 方法中进行组件测量,并通过 setEstimatedSize 方法将测量的宽度和高度设置给组件。示例代码如下:
public class CustomComponent extends Component implements Component.EstimateSizeListener {
public CustomComponent(Context context) {
super(context);
...
// 设置测量组件的侦听器
setEstimateSizeListener(this);
}
...
@Override
public boolean onEstimateSize(int widthEstimateConfig, int heightEstimateConfig) {
int width = Component.EstimateSpec.getSize(widthEstimateConfig);
int height = Component.EstimateSpec.getSize(heightEstimateConfig);
setEstimatedSize(
Component.EstimateSpec.getChildSizeWithMode(width, width, Component.EstimateSpec.NOT_EXCEED),
Component.EstimateSpec.getChildSizeWithMode(height, height, Component.EstimateSpec.NOT_EXCEED));
return true;
}
}
- 需要注意:
-
- 自定义组件测量出的大小需通过 setEstimatedSize 设置给组件,并且必须返回 true 使测量值生效。
-
- setEstimatedSize 方法的入参携带模式信息,可使用 Component.EstimateSpec.getChildSizeWithMode 方法进行拼接。
- 测量模式:测量组件的宽高需要携带模式信息,不同测量模式下的测量结果也不相同,需要根据实际需求选择适合的测量模式。测量模式信息如下表所示:
| 模式 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| UNCONSTRAINT | 父组件对子组件没有约束,表示子组件可以任意大小 |
| PRECISE | 父组件已确定子组件的大小 |
| NOT_EXCEED | 已为子组件确定了最大大小,子组件不能超过指定大小 |
- 实现 Component.DrawTask 接口,在 onDraw 方法中执行绘制任务,该方法提供的画布 Canvas,可以精确控制屏幕元素的外观。在执行绘制任务之前,需要定义画笔 Paint。示例代码如下:
public class CustomComponent extends Component implements Component.DrawTask,Component.EstimateSizeListener {
// 圆环宽度
private static final float CIRCLE_STROKE_WIDTH = 100f;
// 绘制圆环的画笔
private Paint circlePaint;
public CustomComponent(Context context) {
super(context);
// 初始化画笔
initPaint();
// 添加绘制任务
addDrawTask(this);
}
private void initPaint(){
circlePaint = new Paint();
circlePaint.setColor(Color.BLUE);
circlePaint.setStrokeWidth(CIRCLE_STROKE_WIDTH);
circlePaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE_STYLE);
}
@Override
public void onDraw(Component component, Canvas canvas) {
// 在界面中绘制一个圆心坐标为(500,500),半径为400的圆
canvas.drawCircle(500,500,400,circlePaint);
}
...
}
- 实现 Component.TouchEventListener 或其他事件的接口,使组件可响应用户输入。示例代码如下:
public class CustomComponent extends Component implements Component.DrawTask, Component.EstimateSizeListener, Component.TouchEventListener {
...
public CustomComponent(Context context) {
...
// 设置TouchEvent响应事件
setTouchEventListener(this);
}
...
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(Component component, TouchEvent touchEvent) {
switch (touchEvent.getAction()) {
case TouchEvent.PRIMARY_POINT_DOWN:
circlePaint.setColor(Color.GREEN);
invalidate();
break;
case TouchEvent.PRIMARY_POINT_UP:
circlePaint.setColor(Color.YELLOW);
invalidate();
break;
}
return false;
}
}
- 需要注意:
-
- 需要更新 UI 显示时,可调用 invalidate() 方法。
-
- 示例中展示 TouchEventListener 为响应触摸事件,除此之外还可实现 ClickedListener 响应点击事件、LongClickedListener 响应长按事件等。
- 在 onStart() 方法中,将自定义组件添加至 UI 界面中:
@Override
protected void onStart(Intent intent) {
super.onStart(intent);
DirectionalLayout.LayoutConfig config = new DirectionalLayout.LayoutConfig(
DirectionalLayout.LayoutConfig.MATCH_PARENT, DirectionalLayout.LayoutConfig.MATCH_PARENT);
myLayout.setLayoutConfig(config);
CustomComponent customComponent = new CustomComponent(this);
DirectionalLayout.LayoutConfig layoutConfig = new DirectionalLayout.LayoutConfig(1080, 1000);
customComponent.setLayoutConfig(layoutConfig);
myLayout.addComponent(customComponent);
super.setUIContent(myLayout);
}
③ 场景示例
- 利用自定义组件,绘制环形进度控制器,可通过滑动改变当前进度,也可响应进度的改变,UI 显示的样式也可通过设置属性进行调整。自定义环形进度控制器如下所示:
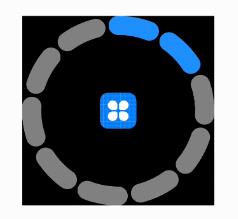
- 示例代码如下:
public class CustomControlBar extends Component implements Component.DrawTask,
Component.EstimateSizeListener, Component.TouchEventListener {
private final static float CIRCLE_ANGLE = 360.0f;
private final static int DEF_UNFILL_COLOR = 0xFF808080;
private final static int DEF_FILL_COLOR = 0xFF1E90FF;
// 圆环轨道颜色
private Color unFillColor;
// 圆环覆盖颜色
private Color fillColor;
// 圆环宽度
private int circleWidth;
// 画笔
private Paint paint;
// 个数
private int count;
// 当前进度
private int currentCount;
// 间隙值
private int splitSize;
// 内圆的正切方形
private RectFloat centerRectFloat;
// 中心绘制的图片
private PixelMap image;
// 原点坐标
private Point centerPoint;
// 进度改变的事件响应
private ProgressChangeListener listener;
public CustomControlBar(Context context) {
super(context);
paint = new Paint();
initData();
setEstimateSizeListener(this);
setTouchEventListener(this);
addDrawTask(this);
}
// 初始化属性值
private void initData() {
unFillColor = new Color(DEF_UNFILL_COLOR);
fillColor = new Color(DEF_FILL_COLOR);
count = 10;
currentCount = 2;
splitSize = 15;
circleWidth = 60;
centerRectFloat = new RectFloat();
image = Utils.createPixelMapByResId(ResourceTable.Media_icon, getContext()).get();
listener = null;
}
@Override
public boolean onEstimateSize(int widthEstimateConfig, int heightEstimateConfig) {
int width = Component.EstimateSpec.getSize(widthEstimateConfig);
int height = Component.EstimateSpec.getSize(heightEstimateConfig);
setEstimatedSize(
Component.EstimateSpec.getChildSizeWithMode(width, width, Component.EstimateSpec.PRECISE),
Component.EstimateSpec.getChildSizeWithMode(height, height, Component.EstimateSpec.PRECISE)
);
return true;
}
@Override
public void onDraw(Component component, Canvas canvas) {
paint.setAntiAlias(true);
paint.setStrokeWidth(circleWidth);
paint.setStrokeCap(Paint.StrokeCap.ROUND_CAP);
paint.setStyle(Paint.Style.STROKE_STYLE);
int width = getWidth();
int center = width / 2;
centerPoint = new Point(center, center);
int radius = center - circleWidth / 2;
drawCount(canvas, center, radius);
int inRadius = center - circleWidth;
double length = inRadius - Math.sqrt(2) * 1.0f / 2 * inRadius;
centerRectFloat.left = (float) (length + circleWidth);
centerRectFloat.top = (float) (length + circleWidth);
centerRectFloat.bottom = (float) (centerRectFloat.left + Math.sqrt(2) * inRadius);
centerRectFloat.right = (float) (centerRectFloat.left + Math.sqrt(2) * inRadius);
// 如果图片比较小,那么根据图片的尺寸放置到正中心
Size imageSize = image.getImageInfo().size;
if (imageSize.width < Math.sqrt(2) * inRadius) {
centerRectFloat.left = (float) (centerRectFloat.left + Math.sqrt(2) * inRadius * 1.0f / 2 - imageSize.width * 1.0f / 2);
centerRectFloat.top = (float) (centerRectFloat.top + Math.sqrt(2) * inRadius * 1.0f / 2 - imageSize.height * 1.0f / 2);
centerRectFloat.right = centerRectFloat.left + imageSize.width;
centerRectFloat.bottom = centerRectFloat.top + imageSize.height;
}
canvas.drawPixelMapHolderRect(new PixelMapHolder(image), centerRectFloat, paint);
}
private void drawCount(Canvas canvas, int centre, int radius) {
float itemSize = (CIRCLE_ANGLE - count * splitSize) / count;
RectFloat oval = new RectFloat(centre - radius, centre - radius, centre + radius, centre + radius);
paint.setColor(unFillColor);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
Arc arc = new Arc((i * (itemSize + splitSize)) - 90, itemSize, false);
canvas.drawArc(oval, arc, paint);
}
paint.setColor(fillColor);
for (int i = 0; i < currentCount; i++) {
Arc arc = new Arc((i * (itemSize + splitSize)) - 90, itemSize, false);
canvas.drawArc(oval, arc, paint);
}
}
@Override
public boolean onTouchEvent(Component component, TouchEvent touchEvent) {
switch (touchEvent.getAction()) {
case TouchEvent.PRIMARY_POINT_DOWN:
case TouchEvent.POINT_MOVE: {
this.getContentPositionX();
MmiPoint absPoint = touchEvent.getPointerPosition(touchEvent.getIndex());
Point point = new Point(absPoint.getX() - getContentPositionX(),
absPoint.getY() - getContentPositionY());
double angle = calcRotationAngleInDegrees(centerPoint, point);
double multiple = angle / (CIRCLE_ANGLE / count);
if ((multiple - (int) multiple) > 0.4) {
currentCount = (int) multiple + 1;
} else {
currentCount = (int) multiple;
}
if (listener != null) {
listener.onProgressChangeListener(currentCount);
}
invalidate();
break;
}
}
return false;
}
public interface ProgressChangeListener {
void onProgressChangeListener(int Progress);
}
// 计算centerPt到targetPt的夹角,单位为度。返回范围为[0, 360),顺时针旋转。
private double calcRotationAngleInDegrees(Point centerPt, Point targetPt) {
double theta = Math.atan2(targetPt.getPointY()
- centerPt.getPointY(), targetPt.getPointX()
- centerPt.getPointX());
theta += Math.PI / 2.0;
double angle = Math.toDegrees(theta);
if (angle < 0) {
angle += CIRCLE_ANGLE;
}
return angle;
}
public Color getUnFillColor() {
return unFillColor;
}
public CustomControlBar setUnFillColor(Color unFillColor) {
this.unFillColor = unFillColor;
return this;
}
public Color getFillColor() {
return fillColor;
}
public CustomControlBar setFillColor(Color fillColor) {
this.fillColor = fillColor;
return this;
}
public int getCircleWidth() {
return circleWidth;
}
public CustomControlBar setCircleWidth(int circleWidth) {
this.circleWidth = circleWidth;
return this;
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public CustomControlBar setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
return this;
}
public int getCurrentCount() {
return currentCount;
}
public CustomControlBar setCurrentCount(int currentCount) {
this.currentCount = currentCount;
return this;
}
public int getSplitSize() {
return splitSize;
}
public CustomControlBar setSplitSize(int splitSize) {
this.splitSize = splitSize;
return this;
}
public PixelMap getImage() {
return image;
}
public CustomControlBar setImage(PixelMap image) {
this.image = image;
return this;
}
public void build() {
invalidate();
}
public void setProgressChangerListener(ProgressChangeListener listener) {
this.listener = listener;
}
}
- 在绘制图片时使用到 Utils 工具类:
public class Utils {
private static final HiLogLabel TAG = new HiLogLabel(3, 0xD001100, "Utils");
private static byte[] readResource(Resource resource) {
final int bufferSize = 1024;
final int ioEnd = -1;
byte[] byteArray;
byte[] buffer = new byte[bufferSize];
try (ByteArrayOutputStream output = new ByteArrayOutputStream()) {
while (true) {
int readLen = resource.read(buffer, 0, bufferSize);
if (readLen == ioEnd) {
HiLog.error(TAG, "readResource finish");
byteArray = output.toByteArray();
break;
}
output.write(buffer, 0, readLen);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
HiLog.debug(TAG, "readResource failed " + e.getLocalizedMessage());
return new byte[0];
}
HiLog.debug(TAG, "readResource len: " + byteArray.length);
return byteArray;
}
/**
* Creates a {@code PixelMap} object based on the image resource ID.
* <p>
* This method only loads local image resources. If the image file does not exist or the loading fails,
* {@code null} is returned.
*
* @param resourceId Indicates the image resource ID.
* @param slice Indicates the Context.
* @return Returns the image.
*/
public static Optional<PixelMap> createPixelMapByResId(int resourceId, Context slice) {
ResourceManager manager = slice.getResourceManager();
if (manager == null) {
return Optional.empty();
}
try (Resource resource = manager.getResource(resourceId)) {
if (resource == null) {
return Optional.empty();
}
ImageSource.SourceOptions srcOpts = new ImageSource.SourceOptions();
srcOpts.formatHint = "image/png";
ImageSource imageSource = ImageSource.create(readResource(resource), srcOpts);
if (imageSource == null) {
return Optional.empty();
}
ImageSource.DecodingOptions decodingOpts = new ImageSource.DecodingOptions();
decodingOpts.desiredSize = new Size(0, 0);
decodingOpts.desiredRegion = new Rect(0, 0, 0, 0);
decodingOpts.desiredPixelFormat = PixelFormat.ARGB_8888;
return Optional.of(imageSource.createPixelmap(decodingOpts));
} catch (NotExistException | IOException e) {
return Optional.empty();
}
}
}
- 在 onStart() 方法里将此组件添加到界面中,并可自由设置其事件响应、颜色、大小等属性:
@Override
protected void onStart(Intent intent) {
super.onStart(intent);
DirectionalLayout.LayoutConfig config = new DirectionalLayout.LayoutConfig(
DirectionalLayout.LayoutConfig.MATCH_PARENT, DirectionalLayout.LayoutConfig.MATCH_PARENT);
myLayout.setLayoutConfig(config);
// 在此创建自定义组件,并可设置其属性
CustomControlBar controlBar = new CustomControlBar(this);
controlBar.setClickable(true);
DirectionalLayout.LayoutConfig layoutConfig = new DirectionalLayout.LayoutConfig(
600, 600);
controlBar.setLayoutConfig(layoutConfig);
ShapeElement element = new ShapeElement();
element.setRgbColor(new RgbColor(0, 0, 0));
controlBar.setBackground(element);
// 将此组件添加至布局,并在界面中显示
myLayout.addComponent(controlBar);
super.setUIContent(myLayout);
}
三、自定义布局
- 当 Java UI 框架提供的布局无法满足设计需求时,可以创建自定义布局,根据需求自定义布局规则。
① 常用接口
- Component 类相关接口如下表所示:
| 接口名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| setEstimateSizeListener | 设置测量组件的侦听器 |
| onEstimateSize | 测量组件的大小以确定宽度和高度 |
| setEstimatedSize | 将测量的宽度和高度设置给组件 |
| EstimateSpec.getChildSizeWithMode | 基于指定的大小和模式为子组件创建度量规范 |
| EstimateSpec.getSize | 从提供的度量规范中提取大小 |
| EstimateSpec.getMode | 获取该组件的显示模式 |
| arrange | 相对于容器组件设置组件的位置和大小 |
- ComponentContainer 类相关接口如下表所示:
| 接口名 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| setArrangeListener | 设置容器组件布局子组件的侦听器 |
| onArrange | 通知容器组件在布局时设置子组件的位置和大小 |
② 如何实现自定义布局
- 使用自定义布局,将各子组件摆放到指定的位置。自定义布局的使用效果如下所示:

- 创建自定义布局的类,并继承 ComponentContainer,添加构造方法:
public class CustomLayout extends ComponentContainer {
public CustomLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
}
- 实现 ComponentContainer.EstimateSizeListener 接口,在 onEstimateSize 方法中进行测量:
public class CustomLayout extends ComponentContainer
implements ComponentContainer.EstimateSizeListener {
...
public CustomLayout(Context context) {
...
setEstimateSizeListener(this);
}
@Override
public boolean onEstimateSize(int widthEstimatedConfig, int heightEstimatedConfig) {
// 通知子组件进行测量
measureChildren(widthEstimatedConfig, heightEstimatedConfig);
int width = Component.EstimateSpec.getSize(widthEstimatedConfig);
// 关联子组件的索引与其布局数据
for (int idx = 0; idx < getChildCount(); idx++) {
Component childView = getComponentAt(idx);
addChild(childView, idx, width);
}
setEstimatedSize(
Component.EstimateSpec.getChildSizeWithMode(maxWidth, widthEstimatedConfig, 0),
Component.EstimateSpec.getChildSizeWithMode(maxHeight, heightEstimatedConfig, 0));
return true;
}
private void measureChildren(int widthEstimatedConfig, int heightEstimatedConfig) {
for (int idx = 0; idx < getChildCount(); idx++) {
Component childView = getComponentAt(idx);
if (childView != null) {
measureChild(childView, widthEstimatedConfig, heightEstimatedConfig);
}
}
}
private void measureChild(Component child, int parentWidthMeasureSpec, int parentHeightMeasureSpec) {
ComponentContainer.LayoutConfig lc = child.getLayoutConfig();
int childWidthMeasureSpec = EstimateSpec.getChildSizeWithMode(
lc.width, parentWidthMeasureSpec, EstimateSpec.UNCONSTRAINT);
int childHeightMeasureSpec = EstimateSpec.getChildSizeWithMode(
lc.height, parentHeightMeasureSpec, EstimateSpec.UNCONSTRAINT);
child.estimateSize(childWidthMeasureSpec, childHeightMeasureSpec);
}
}
- 需要注意:
-
- 容器类组件在自定义测量过程不仅要测量自身,也要递归的通知各子组件进行测量。
-
- 测量出的大小需通过 setEstimatedSize 设置给组件,并且必须返回 true 使测量值生效。
- 测量时,需要确定每个子组件大小和位置的数据,并保存这些数据:
private int xx = 0;
private int yy = 0;
private int maxWidth = 0;
private int maxHeight = 0;
private int lastHeight = 0;
// 子组件索引与其布局数据的集合
private final Map<Integer, Layout> axis = new HashMap<>();
private static class Layout {
int positionX = 0;
int positionY = 0;
int width = 0;
int height = 0;
}
...
private void invalidateValues() {
xx = 0;
yy = 0;
maxWidth = 0;
maxHeight = 0;
axis.clear();
}
private void addChild(Component component, int id, int layoutWidth) {
Layout layout = new Layout();
layout.positionX = xx + component.getMarginLeft();
layout.positionY = yy + component.getMarginTop();
layout.width = component.getEstimatedWidth();
layout.height = component.getEstimatedHeight();
if ((xx + layout.width) > layoutWidth) {
xx = 0;
yy += lastHeight;
lastHeight = 0;
layout.positionX = xx + component.getMarginLeft();
layout.positionY = yy + component.getMarginTop();
}
axis.put(id, layout);
lastHeight = Math.max(lastHeight, layout.height + component.getMarginBottom());
xx += layout.width + component.getMarginRight();
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, layout.positionX + layout.width);
maxHeight = Math.max(maxHeight, layout.positionY + layout.height);
}
- 在 onStart 方法中添加此布局,在布局中添加若干子组件,并在界面中显示:
@Override
protected void onStart(Intent intent) {
super.onStart(intent);
DirectionalLayout.LayoutConfig config = new DirectionalLayout.LayoutConfig(
DirectionalLayout.LayoutConfig.MATCH_PARENT, DirectionalLayout.LayoutConfig.MATCH_PARENT);
myLayout.setLayoutConfig(config);
CustomLayout customLayout = new CustomLayout(this);
for (int idx = 0; idx < 15; idx++) {
customLayout.addComponent(getComponent(idx + 1));
}
ShapeElement shapeElement = new ShapeElement();
shapeElement.setRgbColor(COLOR_LAYOUT_BG);
customLayout.setBackground(shapeElement);
LayoutConfig layoutConfig = new LayoutConfig(LayoutConfig.MATCH_PARENT,
LayoutConfig.MATCH_CONTENT);
customLayout.setLayoutConfig(layoutConfig);
myLayout.addComponent(customLayout);
super.setUIContent(myLayout);
}
// 创建子组件
private Component getComponent(int idx) {
Button button = new Button(getContext());
ShapeElement shapeElement = new ShapeElement();
shapeElement.setRgbColor(COLOR_BTN_BG);
button.setBackground(shapeElement);
button.setTextColor(Color.WHITE);
LayoutConfig layoutConfig = new LayoutConfig(300, 100);
if (idx == 1) {
layoutConfig = new LayoutConfig(1080, 200);
button.setText("1080 * 200");
} else if (idx == 6) {
layoutConfig = new LayoutConfig(500, 100);
button.setText("500 * 100");
} else if (idx == 8) {
layoutConfig = new LayoutConfig(600, 600);
button.setText("600 * 600");
} else {
button.setText("Item" + idx);
}
layoutConfig.setMargins(10, 10, 10, 10);
button.setLayoutConfig(layoutConfig);
return button;
}
以上是关于HarmonyOS之深入解析自定义组件与布局的实现的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章