iOS网络请求缓存-URLCache
Posted 想名真难
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了iOS网络请求缓存-URLCache相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
浅谈ios网络请求缓存
在读过一些开源项目(比如:SDWebImage)之后了解到,大多都是采用的本地存文件的方式进行缓存。当然如何去造这个轮子不是今天想讲的重点。那么今天的想说的重点是什么呢?
URLCache类
没错URLCache类才是今天要谈的重点。URLCache是Apple为开发者已经准备好了的网络请求缓存类,并且提供的是内存以及磁盘的综合缓存机制。
实践是检验真理的唯一标准
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplicationLaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
print("URLCache's disk capacity is \\(URLCache.shared.diskCapacity) bytes")
print("URLCache's disk usage capacity is \\(URLCache.shared.currentDiskUsage) bytes")
print("URLCache's memory capacity is \\(URLCache.shared.memoryCapacity) bytes")
print("URLCache's memory usage capacity is \\(URLCache.shared.currentMemoryUsage) bytes")
return true
}也就是说在我们不去设置URLCache的缓存空间的时候,系统默认在内存上分配约512KB的空间,在磁盘上分配约10M的空间。
如何使用上缓存
1.配置缓存空间
项目中如果你觉得系统默认分配的缓存空间不够的时候我们可以手动去配置URLCache的缓存空间,以及数据缓存的位置。
func application(_ application: UIApplication, didFinishLaunchingWithOptions launchOptions: [UIApplicationLaunchOptionsKey: Any]?) -> Bool {
URLCache.shared.diskCapacity = 1024 * 1024 * 5
URLCache.shared.memoryCapacity = 1024 * 1024 * 30
print("URLCache's disk capacity is \\(URLCache.shared.diskCapacity) bytes")
print("URLCache's disk usage capacity is \\(URLCache.shared.currentDiskUsage) bytes")
print("URLCache's memory capacity is \\(URLCache.shared.memoryCapacity) bytes")
print("URLCache's memory usage capacity is \\(URLCache.shared.currentMemoryUsage) bytes")
print("\\(URLCache.shared)")
return true
}
这个时候磁盘缓存空间就变成了30M内存缓存空间就变成了5M
URLCache's disk capacity is 31457280 bytes
URLCache's disk usage capacity is 86016 bytes
URLCache's memory capacity is 5242880 bytes
URLCache's memory usage capacity is 0 bytes
当然你也可以自己去设计缓存管理器let urlCache = URLCache.init(memoryCapacity: Int, diskCapacity: Int, diskPath: String?)
2.缓存策略
HTTP定义了与服务器交互不同的方法,最基本的四种分别是:GET,POST,PUT,DELETE对应的分别是:查,改,增,删。我想现在大家应该都能明白,GET一般用于获取资源,POST一般用于更新资源信息。因此从Http规范来看URLCache只会对你的GET进行缓存,事实上也是如此。
当然如果大家想对Http的交互有更加深入的了解,可以参考Http对Method Definitions的说明文档Method Definitions
那我们先来看看有哪些缓存策略
- useProtocolCachePolicy 使用协议中的缓存策略缓存
- reloadIgnoringLocalCacheData 不使用缓存
- reloadIgnoringLocalAndRemoteCacheData 没有实现
- returnCacheDataElseLoad 使用缓存,没有缓存在加载
- returnCacheDataDontLoad 使用缓存,即使没有也不加载
- reloadRevalidatingCacheData 没有实现
除了第一点useProtocolCachePolicy,其它的从字面上都比较好理解,使用协议中的缓存策略缓存 就让我不是很明白,因此硬着头皮有去看了看Http协议
Caching in HTTP,服务器在返回的相应头中会有一个这样的字段Cache-Control: max-age或者是Cache-Control: s- maxage通过Cache-Control来指定缓存策略maxage表示过期时间。对协议一脸懵逼的我,只好用print去看看这个里面都是些什么了。
func loadData() -> Void {
// http://img15.3lian.com/2015/f2/50/d/71.jpg
// http://pic63.nipic.com/file/20150407/20689804_142523239491_2.jpg
// https://ss0.bdstatic.com/94oJfD_bAAcT8t7mm9GUKT-xh_/timg?image&quality=100&size=b4000_4000&sec=1481818074&di=6cd852a0ba3b2379b06399f0981c3d1f&src=http://pic1.win4000.com/wallpaper/3/581bfb16b6726.jpg
let imgUrl = URL.init(string: "http://img15.3lian.com/2015/f2/50/d/71.jpg")
let request = URLRequest.init(url: imgUrl!)
DispatchQueue.global().async {
let dataTask = URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: request) { (data, respose, erroe) in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
print((respose as? HTTPURLResponse)?.allHeaderFields ?? "respose is nil")
self.imgV.frame = CGRect.init(x: 20, y: 400, width: self.view.frame.size.width-40, height: 200)
self.imgV.image = UIImage.init(data: data!)
self.view .addSubview(self.imgV)
}
}
dataTask.resume()
}
let path = NSSearchPathForDirectoriesInDomains(FileManager.SearchPathDirectory.cachesDirectory, FileManager.SearchPathDomainMask.userDomainMask, true).first
print("caches directory is \\(path)")
}
我找了三个连接试验了一下发现两个里面都有Cache-Control字段,其中一个没有。在查阅一些资料发现Cache-Control常见取字有
- public
- private(default)
- no-cache
- max-age
- must-revalidate
当然大家如果想进一步了解可以参考Cache-Control。
AnyHashable("Cache-Control"): max-age=315360000
AnyHashable("Cache-Control"): no-cache
此时我想大家都能明白所谓使用协议中的缓存策略缓存,就是根据响应头中的Cache-Control来设置缓存。
说到这里不得不提一下,我们可以有时候会踩这样的坑,调试过程中服务器将URL对用的内容换了,我们不停的请求数据但是内容一直没有更新,因此这个时候应该考虑清理一下缓存。
既然都走到这里了我们就一探究竟吧URLCache类到底是如何进行缓存的,刚才我用了三个URL分别请求。这个时候我打开沙盒中有没有发生什么变化,我们会发现有多了几个文件
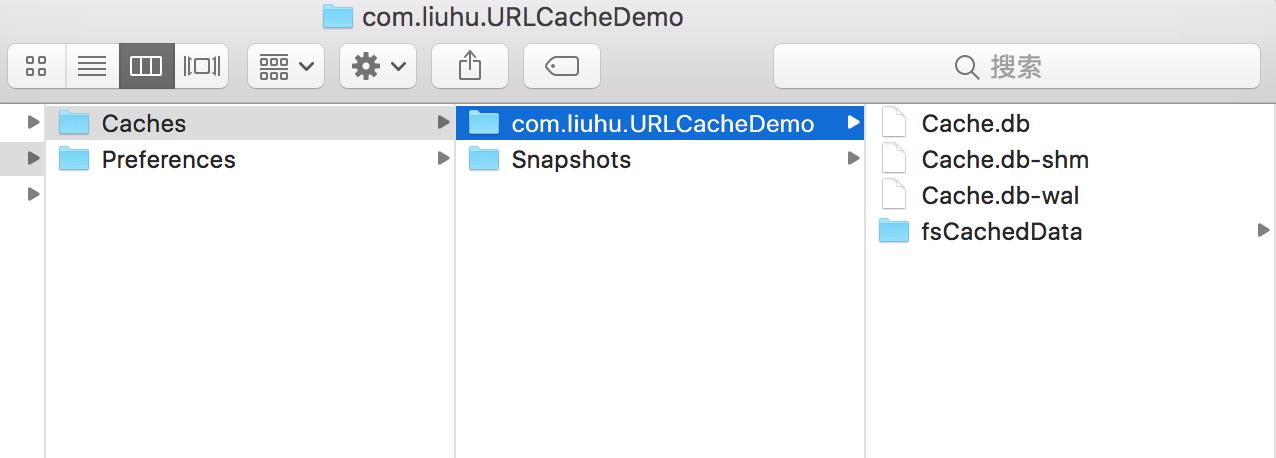
打开fsCacheData会发现下载下来的几张图片。我们还发现有一个Cache.db的数据库。
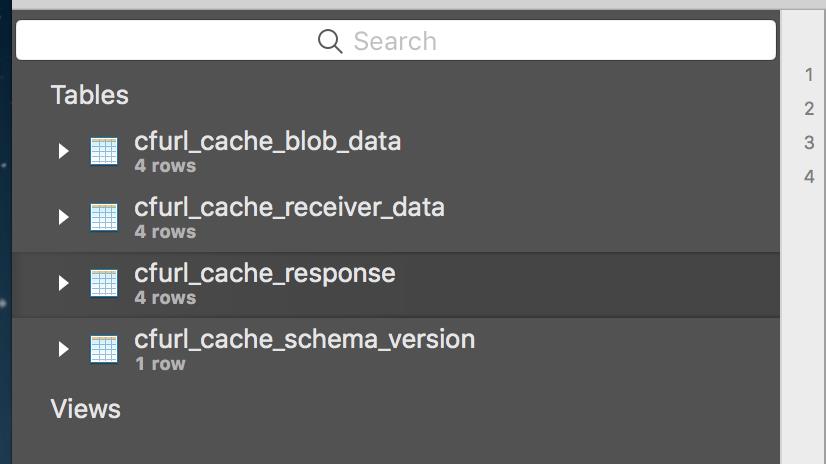
这说明磁盘上的数据记录是存在数据库中,因此查询上的性能是不用担心的。我们主要看一下cfurl_cache_response表里面的数据
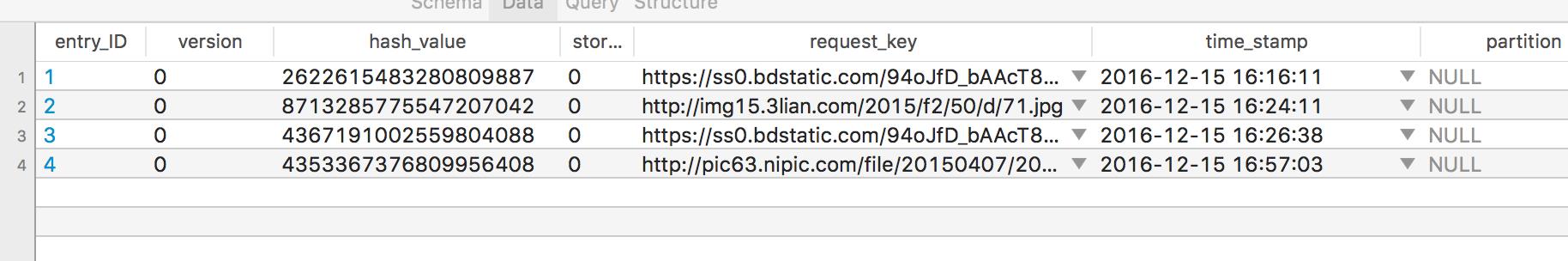
发现里面有一个request_key的key通过里面的value可以断定response是通过URL+Parameters为key存储的。在断网,有网不同环境下试验,发现Cache-Control为no-cache的时候,NSURLCache也会进行缓存,但是并不使用缓存的数据。
3.自定义缓存
你觉得服务器给你默认的缓存策略不合理的时候,你依然可以使用NSURLCache来自己定义搞一套属于自己的缓存。即使协议是忽略缓存我们也可以通过下面的方法读取缓存
let imgUrl = URL.init(string: "http://img15.3lian.com/2015/f2/50/d/71.jpg")
var request = URLRequest.init(url: imgUrl!)
request.cachePolicy = URLRequest.CachePolicy.reloadIgnoringLocalCacheData
let respose = URLCache.shared.cachedResponse(for: request);
cachedResponse保存了上次请求的响应头和数据。
这里还有一些其他的方法来管理缓存
- URLCache.shared.removeAllCachedResponses()
- URLCache.shared.removeCachedResponse(for: URLRequest)
- URLCache.shared.removeCachedResponse(for: URLSessionDataTask)
- URLCache.shared.storeCachedResponse(CachedURLResponse, for: URLRequest)
- URLCache.shared.storeCachedResponse(CachedURLResponse, for: URLSessionDataTask)
通过这些方法我们可以灵活的控制缓存了。服务器的文件存贮,大多采用资源变动后就重新生成一个链接的做法。而且如果你的文件存储采用的是第三方的服务,比如七牛、青云等服务,则一定是如此。这种做法虽然是推荐做法,但同时也不排除不同文件使用同一个链接。那么如果服务端的file更改了,本地已经有了缓存。如何更新缓存?这种情况下需要借助ETag或Last-Modified判断缓存是否有效。
Last-Modifie And ETag
Last-Modified资源最后修改的时间戳,往往与缓存时间进行对比来判断缓存是否过期。在浏览器第一次请求某一个URL时,服务器端的返回状态会是200,内容是你请求的资源,同时有一个Last-Modified的属性标记此文件在服务期端最后被修改的时间,格式类似这样:Last-Modified: Fri, 12 May 2006 18:53:33 GMT
客户端第二次请求此URL时,根据 HTTP 协议的规定,浏览器会向服务器传送If-Modified-Since报头,询问该时间之后文件是否有被修改过,格式类似这样:If-Modified-Since: Fri, 12 May 2006 18:53:33 GMT
如果服务器端的资源没有变化,则自动返回304状态码Not Changed,内容为空,这样就节省了传输数据量。当服务器端代码发生改变或者重启服务器时,则重新发出资源,返回和第一次请求时类似。从而保证不向客户端重复发出资源,也保证当服务器有变化时,客户端能够得到最新的资源。先看下面的伪代码
if ETagFromServer != ETagOnClient || LastModifiedFromServer != LastModifiedOnClient
GetDataFromServer
else
GetDataFromURLCache
在这里我们最好不要使用>,<,>=,<=因为当服务端对资源文件,废除其新版,回滚启用旧版本,此时会出现LastModifiedFromServer <= LastModifiedOnClient但我们依然要更新本地缓存
func getDataCompareLastModified() -> Void {
let imgUrl = URL.init(string: "https://ss0.bdstatic.com/94oJfD_bAAcT8t7mm9GUKT-xh_/timg?image&quality=100&size=b4000_4000&sec=1481818074&di=6cd852a0ba3b2379b06399f0981c3d1f&src=http://pic1.win4000.com/wallpaper/3/581bfb16b6726.jpg")
var request = URLRequest.init(url: imgUrl!, cachePolicy: URLRequest.CachePolicy.reloadIgnoringCacheData, timeoutInterval: 30)
let cachedRespose = URLCache.shared.cachedResponse(for: request);
let lastModified = (cachedRespose?.response as? HTTPURLResponse)?.allHeaderFields["Last-Modified"]
if lastModified != nil {
request.setValue(lastModified as? String, forHTTPHeaderField: "If-Modified-Since")
}
DispatchQueue.global().async {
let dataTask = URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: request) { (data, respose, erroe) in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
let httpRespose = respose as? HTTPURLResponse
if httpRespose?.statusCode == 304 { //Not Modified
let data = URLCache.shared.cachedResponse(for: request)?.data
self.imgV.frame = CGRect.init(x: 20, y: 400, width: self.view.frame.size.width-40, height: 200)
self.view.addSubview(self.imgV);
self.imgV.image = UIImage.init(data: data!)
} else {
self.imgV.frame = CGRect.init(x: 20, y: 400, width: self.view.frame.size.width-40, height: 200)
self.view.addSubview(self.imgV);
self.imgV.image = UIImage.init(data: data!)
}
}
}
dataTask.resume()
}
}
当然在HTTP规范里面Etag表示被请求变量的实体值(其实是一个hash值)用于唯一标记资源。服务器单独负责判断Etag是什么含义,并在HTTP响应头中将其传送到客户端,以下是服务端返回的格式:Etag:"50b1c1d4f775c61:df3"客户端的查询跟新格式是这样的:If-None-Match: W/"50b1c1d4f775c61:df3"其中If-None-Match与响应头的Etag相对应,可以判断本地缓存数据是否发生变化。如果Etag没有改变,则返回304,data为空。与Last-Modified一样。
func getDataCompareETag() -> Void {
let imgUrl = URL.init(string: "https://ss0.bdstatic.com/94oJfD_bAAcT8t7mm9GUKT-xh_/timg?image&quality=100&size=b4000_4000&sec=1481818074&di=6cd852a0ba3b2379b06399f0981c3d1f&src=http://pic1.win4000.com/wallpaper/3/581bfb16b6726.jpg")
var request = URLRequest.init(url: imgUrl!, cachePolicy: URLRequest.CachePolicy.reloadIgnoringCacheData, timeoutInterval: 30)
let cachedRespose = URLCache.shared.cachedResponse(for: request);
let eTag = (cachedRespose?.response as? HTTPURLResponse)?.allHeaderFields["ETag"]
if eTag != nil {
request.setValue(eTag as? String, forHTTPHeaderField: "If-Modified-Since")
}
DispatchQueue.global().async {
let dataTask = URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: request) { (data, respose, erroe) in
DispatchQueue.main.async {
let httpRespose = respose as? HTTPURLResponse
if httpRespose?.statusCode == 304 { //Not Modified
let data = URLCache.shared.cachedResponse(for: request)?.data
self.imgV.frame = CGRect.init(x: 20, y: 400, width: self.view.frame.size.width-40, height: 200)
self.view.addSubview(self.imgV);
self.imgV.image = UIImage.init(data: data!)
} else {
self.imgV.frame = CGRect.init(x: 20, y: 400, width: self.view.frame.size.width-40, height: 200)
self.view.addSubview(self.imgV);
self.imgV.image = UIImage.init(data: data!)
}
}
}
dataTask.resume()
}
}
服务器端如果修改了资源Etag值会立即改变,因此在断点下载的时候Etag是非常有用的一个参数。
以上是关于iOS网络请求缓存-URLCache的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章
VSCode自定义代码片段14——Vue的axios网络请求封装