打怪升级之小白的大数据之旅(七十三)<Flume高级>
Posted GaryLea
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了打怪升级之小白的大数据之旅(七十三)<Flume高级>相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
打怪升级之小白的大数据之旅(七十三)
Flume高级
上次回顾
上一章介绍了Flume的内部原理,本章就Flume的扩展知识进行讲解,本章的重点就是了解并学会使用Flume的自定义组件
自定义组件
在上一章介绍了内部原理,所以下面我们就可以根据内部原理来制定自定义的组件,例如上一章说的Channel选择器中的多路复用,就是需要搭配自定义拦截器Interceptor来使用
自定义 Interceptor
在实际开发中,自定义拦截器算是我们比较常用的手段,它可以配合channel选择器来将我们的日志信息分类存储,下面就通过案例来模拟实现此功能
案例需求:
- 使用Flume采集服务器本地日志
- 需要按照日志类型的不同,将不同种类的日志发往不同的分析系统
案例分析:
- 实际的开发中,一台服务器产生的日志类型可能有很多种,不同类型的日志可能需要发送到不同的分析系统
- 此时会用到Flume拓扑结构中的Multiplexing(多路复用)
- Multiplexing的原理是,根据event中Header的某个key的值,将不同的event发送到不同的Channel中,所以我们需要自定义一个Interceptor,为不同类型的event的Header中的key赋予不同的值
- 在该案例中,我们以端口数据模拟日志,以hello和非hello信息模拟不同类型的日志,我们需要自定义interceptor来对日志内容进行区分,将其分别发往不同的分析系统(Channel)
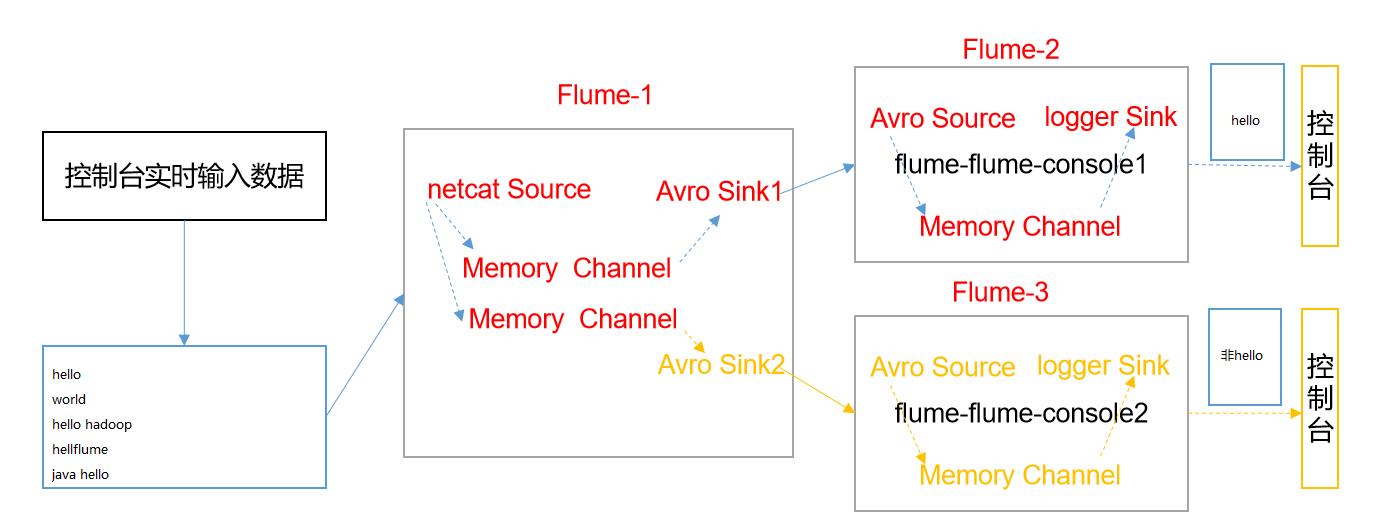
案例实现:
- 既然是自定义拦截器,那么我们就需要写Java代码了,创建一个Maven工程,然后导入依赖:
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.flume</groupId>
<artifactId>flume-ng-core</artifactId>
<version>1.9.0</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- 自定义拦截器类
package com.company.myinterceptor;
import org.apache.flume.Context;
import org.apache.flume.Event;
import org.apache.flume.interceptor.Interceptor;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
public class MyInterceptor implements Interceptor {
// 声明存储事件集合
private List<Event> addHeaderEvents;
// 初始化拦截器
@Override
public void initialize() {
// 初始化集合
addHeaderEvents = new ArrayList<>();
}
// 处理单个事件
@Override
public Event intercept(Event event) {
// 获取事件的头信息
Map<String, String> headers = event.getHeaders();
// 获取事件的body信息
String eventBody = new String(event.getBody());
if (eventBody.contains("hello")){
headers.put("type","hello");
}else {
headers.put("type","other");
}
return event;
}
// 批量处理事件
@Override
public List<Event> intercept(List<Event> events) {
// 清空集合
addHeaderEvents.clear();
// 遍历events,对每个event添加头信息
for (Event event : events) {
// 添加头信息
addHeaderEvents.add(intercept(event));
}
// 返回events
return addHeaderEvents;
}
// 关闭资源
@Override
public void close() {
}
// 拦截器类的构造方法
public static class MyBuilder implements Interceptor.Builder{
@Override
public Interceptor build() {
return new MyInterceptor();
}
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
}
}
}
将写好的拦截器类打包,改个名字,放到flume中
名字改为 myInterceptor.jar
放到 /opt/module/flume/lib文件夹下
配置flume文件:先在hadoop102, hadoop103,hadoop104.创建一个文件夹,存储配置文件
mkdir /opt/module/flume/job/group4
Flume1
vim /opt/module/flume/job/group4/flume1-netcat.conf
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1 k2
a1.channels = c1 c2
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444
a1.sources.r1.interceptors = i1
a1.sources.r1.interceptors.i1.type = com.company.myinterceptor.MyInterceptor$MyBuilder
a1.sources.r1.selector.type = multiplexing
a1.sources.r1.selector.header = type
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.hello = c1
a1.sources.r1.selector.mapping.other= c2
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = avro
a1.sinks.k1.hostname = hadoop103
a1.sinks.k1.port = 4141
a1.sinks.k2.type=avro
a1.sinks.k2.hostname = hadoop104
a1.sinks.k2.port = 4142
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c2.type = memory
a1.channels.c2.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c2.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1 c2
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a1.sinks.k2.channel = c2
Flume2
# Name the components on this agent
a2.sources = r1
a2.sinks = k1
a2.channels = c1
a2.sources.r1.type = avro
a2.sources.r1.bind = hadoop103
a2.sources.r1.port = 4141
a2.sinks.k1.type = logger
a2.channels.c1.type = memory
a2.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a2.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a2.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a2.sources.r1.channels = c1
Flume3
# Name the components on this agent
a3.sources = r1
a3.sinks = k1
a3.channels = c1
a3.sources.r1.type = avro
a3.sources.r1.bind = hadoop104
a3.sources.r1.port = 4142
a3.sinks.k1.type = logger
a3.channels.c1.type = memory
a3.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a3.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
a3.sinks.k1.channel = c1
a3.sources.r1.channels = c1
运行Flume
# flume3
flume-ng agent -n a3 -c /opt/module/flume/conf/ -f /opt/module/flume/job/group4/flume3-console2.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
# flume2
flume-ng agent -n a2 -c /opt/module/flume/conf/ -f /opt/module/flume/job/group4/flume2-console1.conf -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
# flume1
flume-ng agent -c /opt/module/flume/conf/ -f /opt/module/flume/job/group4/flume1-netcat.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
测试数据
# 模拟数据产生,利用natcat向44444端口发送数据
nc localhost 44444
hello
hello world
hive
flume
自定义source
官方提供的Source有很多,如exec source 、avro source、Taildir source等,如果官方提供的source不能满足我们的需求,我们就可以根据需求自定义source(目前为止,我还没有遇到官方案例解决不了的需求)
自定义source的说明文档: https://flume.apache.org/FlumeDeveloperGuide.html#source
自定义source案例实现
案例需求:
- 使用flume接收数据,并给每条数据添加前缀,输出到控制台
- 前缀可从flume配置文件中配置
需求分析:
- 因为配置Flume主要是通过配置文件来完成相应的数据传输,所以为了进行自定义Source,就需要知道实现该Source的类是什么,具体实现方法是什么
- 通过源码分析,Source的实现底层是抽象类AbstractSource和Configurable与PollableSource接口
- 它的主要方法是:
- configure(Context context)//初始化context(读取配置文件内容)
- process()//获取数据封装成event并写入channel,这个方法将被循环调用
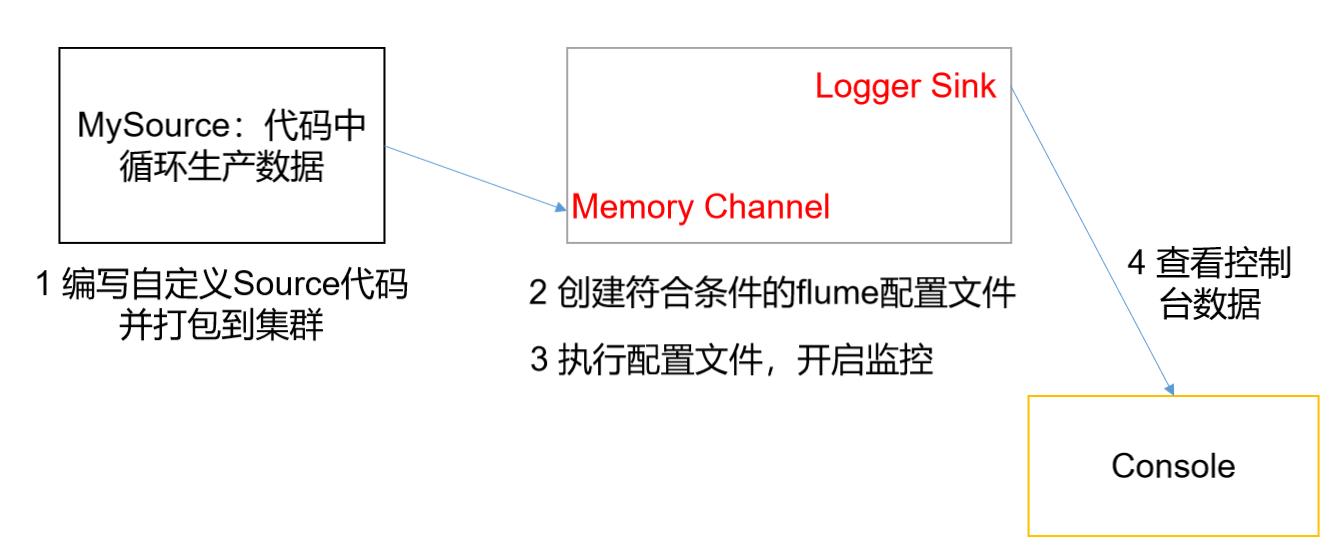
案例实现
- 第一步还是创建maven工程并且导入依赖
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.flume</groupId> <artifactId>flume-ng-core</artifactId> <version>1.9.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
Mysource具体代码
package com.company;
import org.apache.flume.Context;
import org.apache.flume.EventDeliveryException;
import org.apache.flume.PollableSource;
import org.apache.flume.conf.Configurable;
import org.apache.flume.event.SimpleEvent;
import org.apache.flume.source.AbstractSource;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class MySource extends AbstractSource implements Configurable, PollableSource {
//定义配置文件将来要读取的字段
private Long delay;
private String field;
//初始化配置信息
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
delay = context.getLong("delay");
field = context.getString("field", "Hello!");
}
@Override
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
try {
//创建事件头信息
HashMap<String, String> hearderMap = new HashMap<>();
//创建事件
SimpleEvent event = new SimpleEvent();
//循环封装事件
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
//给事件设置头信息
event.setHeaders(hearderMap);
//给事件设置内容
event.setBody((field + i).getBytes());
//将事件写入channel
getChannelProcessor().processEvent(event);
Thread.sleep(delay);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return Status.BACKOFF;
}
return Status.READY;
}
@Override
public long getBackOffSleepIncrement() {
return 0;
}
@Override
public long getMaxBackOffSleepInterval() {
return 0;
}
}
将写好的Source类打包,改个名字,放到flume中
名字改为 mySource.jar
放到 /opt/module/flume/lib文件夹下
配置flume文件:先在hadoop102, hadoop103,hadoop104.创建一个文件夹,存储配置文件
mkdir /opt/module/flume/job/group5
这个需求比较简单,直接一个flume即可
vim /opt/module/flume/job/group5/mysource.conf
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = com.company.source.MySource
a1.sources.r1.delay = 1000
#a1.sources.r1.field = atguigu
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = logger
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
运行flume
flume-ng agent -c /opt/module/flume/conf/ -f /opt/module/flume/job/group4/mysource.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
自定义sink
自定义sink也是一样,当根据业务需要时,就需要自定义sink来满足我们的需求,比如使用sink将数据写入到mysql中(后面会介绍sqoop,它专门用于写入数据库)
自定义sink的说明文档地址: https://flume.apache.org/FlumeDeveloperGuide.html#sink
自定义Sink案例实现
案例需求
- 使用flume接收数据,并在Sink端给每条数据添加前缀和后缀,输出到控制台
- 前后缀可在flume任务配置文件中配置
需求分析:
- 同样的,我们需要了解Sink的实现方法,通过源码可以知道,自定义Sink需要继承AbstractSink类并实现Configurable接口
- 主要实现的方法是:
- configure(Context context)//初始化context(读取配置文件内容)
- process()//从Channel读取获取数据(event),这个方法将被循环调用
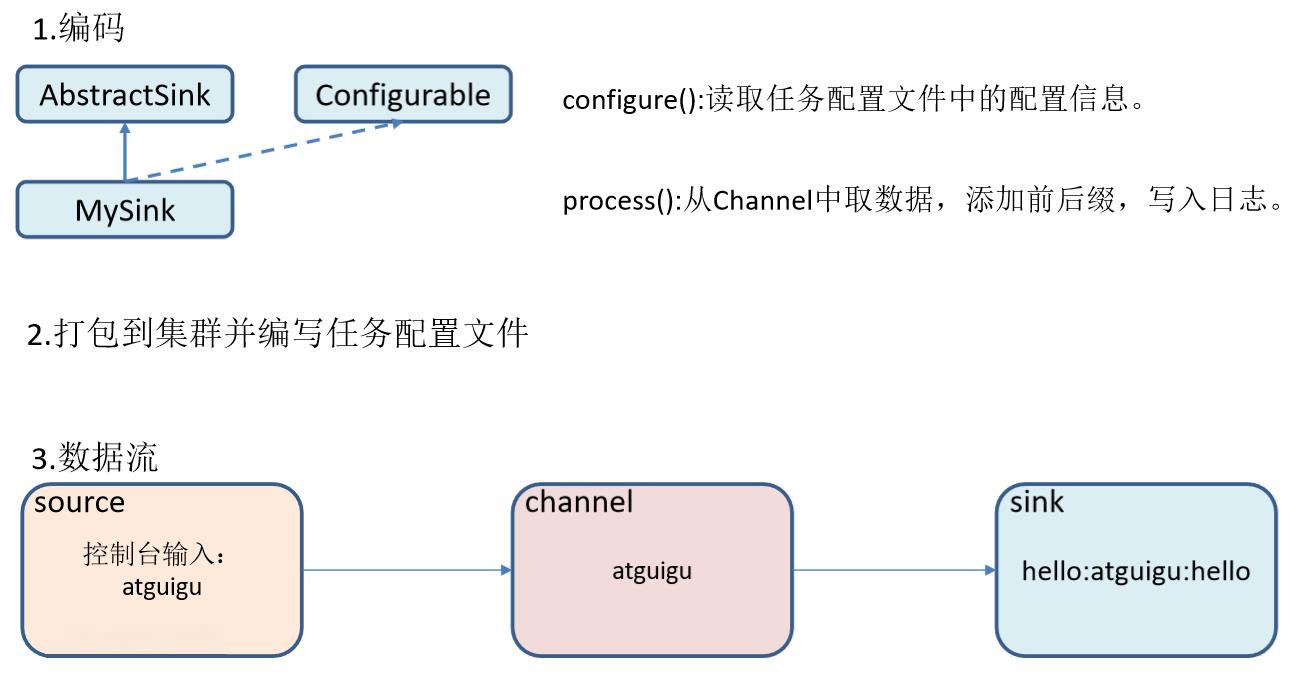
案例实现
- 第一步还是创建maven工程并且导入依赖
<dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.flume</groupId> <artifactId>flume-ng-core</artifactId> <version>1.9.0</version> </dependency> </dependencies>
mysink具体代码
package com.company;
import org.apache.flume.*;
import org.apache.flume.conf.Configurable;
import org.apache.flume.sink.AbstractSink;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
public class MySink extends AbstractSink implements Configurable {
//创建Logger对象
private static final Logger LOG = LoggerFactory.getLogger(AbstractSink.class);
private String prefix;
private String suffix;
@Override
public Status process() throws EventDeliveryException {
//声明返回值状态信息
Status status;
//获取当前Sink绑定的Channel
Channel ch = getChannel();
//获取事务
Transaction txn = ch.getTransaction();
//声明事件
Event event;
//开启事务
txn.begin();
//读取Channel中的事件,直到读取到事件结束循环
while (true) {
event = ch.take();
if (event != null) {
break;
}
}
try {
//处理事件(打印)
LOG.info(prefix + new String(event.getBody()) + suffix);
//事务提交
txn.commit();
status = Status.READY;
} catch (Exception e) {
//遇到异常,事务回滚
txn.rollback();
status = Status.BACKOFF;
} finally {
//关闭事务
txn.close();
}
return status;
}
@Override
public void configure(Context context) {
//读取配置文件内容,有默认值
prefix = context.getString("prefix", "hello:");
//读取配置文件内容,无默认值
suffix = context.getString("suffix");
}
}
将写好的Sink类打包,改个名字,放到flume中
名字改为 mySink.jar
放到 /opt/module/flume/lib文件夹下
配置flume文件:先在hadoop102, hadoop103,hadoop104.创建一个文件夹,存储配置文件
mkdir /opt/module/flume/job/group6
这个需求比较简单,直接一个flume即可
vim /opt/module/flume/job/group5/mysink.conf
# Name the components on this agent
a1.sources = r1
a1.sinks = k1
a1.channels = c1
# Describe/configure the source
a1.sources.r1.type = netcat
a1.sources.r1.bind = localhost
a1.sources.r1.port = 44444
# Describe the sink
a1.sinks.k1.type = com.atguigu.MySink
#a1.sinks.k1.prefix = atguigu:
a1.sinks.k1.suffix = :atguigu
# Use a channel which buffers events in memory
a1.channels.c1.type = memory
a1.channels.c1.capacity = 1000
a1.channels.c1.transactionCapacity = 100
# Bind the source and sink to the channel
a1.sources.r1.channels = c1
a1.sinks.k1.channel = c1
运行flume
flume-ng agent -c /opt/module/flume/conf/ -f /opt/module/flume/job/group4/mysink.conf -n a1 -Dflume.root.logger=INFO,console
使用Ganglia监控Flume
Ganglia可以让我们通过web页面,很方便地监控我们Flume的运行状态
Ganglia由gmond、gmetad和gweb三部分组成
- gmond(Ganglia Monitoring Daemon)是一种轻量级服务,安装在每台需要收集指标数据的节点主机上。使用gmond,你可以很容易收集很多系统指标数据,如CPU、内存、磁盘、网络和活跃进程的数据等。
- gmetad(Ganglia Meta Daemon)整合所有信息,并将其以RRD格式存储至磁盘的服务
- gweb(Ganglia Web)Ganglia可视化工具,gweb是一种利用浏览器显示gmetad所存储数据的php前端。在Web界面中以图表方式展现集群的运行状态下收集的多种不同指标数据
Ganglia安装与部署
第一步: 三台节点安装epel源
sudo yum install -y epel-release
第二步: 在102安装web,meta和monitor
sudo yum -y install ganglia-gmetad ganglia-web ganglia-gmond
第三步: 在103、104安装monitor
sudo yum -y install ganglia-gmond
第四步:修改hadoop102的 ganglia 配置文件
sudo vim /etc/httpd/conf.d/ganglia.conf
<Location /ganglia>
Require ip 192.168.5.1
Require all granted
</Location>
第五步:修改hadoop102的 gmetad 配置文件
sudo vim /etc/ganglia/gmetad.conf
data_source "hadoop102" hadoop102
第六步:修改hadoop102的 gmond 配置文件
sudo vim /etc/ganglia/gmond.conf
cluster {
name = "hadoop102"
owner = "unspecified"
latlong = "unspecified"
url = "unspecified"
}
udp_send_channel {
#bind_hostname = yes # Highly recommended, soon to be default.
# This option tells gmond to use a source address
# that resolves to the machine's hostname. Without
# this, the metrics may appear to come from any
# interface and the DNS names associated with
# those IPs will be used to create the RRDs.
# mcast_join = 239.2.11.71
host = hadoop102
port = 8649
ttl = 1
}
udp_recv_channel {
# mcast_join = 239.2.11.71
port = 8649
bind = 0.0.0.0
retry_bind = true
}
第七步:同步修改后的文件
xsync /etc/httpd
xsync /etc/ganglia
第八步:修改hadoop selinux 配置文件
sudo vim 以上是关于打怪升级之小白的大数据之旅(七十三)<Flume高级>的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章