从 0 到 1 实现浏览器端沙盒运行环境
Posted 腾讯技术工程
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了从 0 到 1 实现浏览器端沙盒运行环境相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

作者:easonruan,腾讯 CSIG 前端开发工程师
本文的浏览器端 Sandbox 沙盒运行环境,大家可以快速理解为类似 CodeSandbox 一样,所有页面代码编译都在前端完成(不依赖后端),并且具备实时热更新功能。
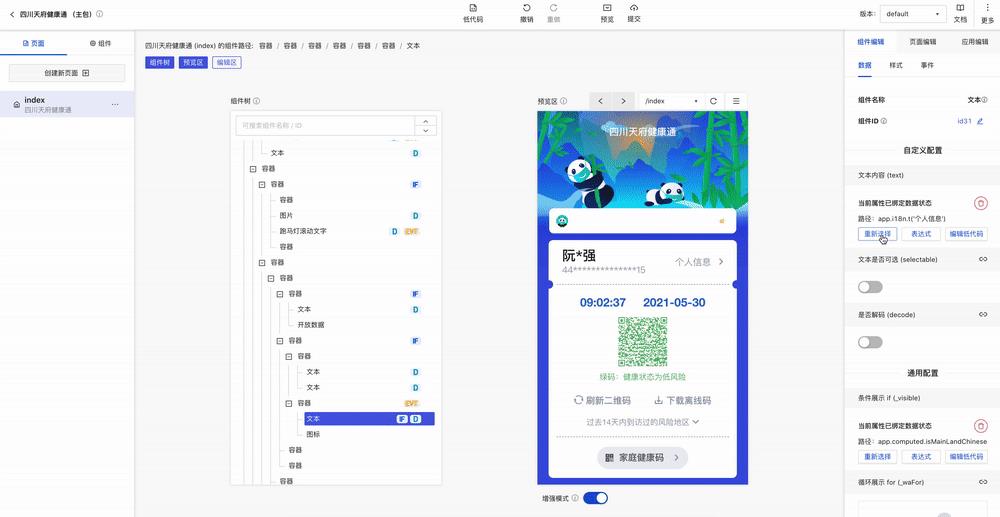
而本文终极目标就是实现这样的浏览器端 Sandbox 沙盒运行环境,可以轻松接入到大部分平台(尤其低代码平台),提升应用的预览速度和开发体验,效果如下:
为什么需要浏览器端 Sandbox 沙盒运行环境?
原因一:Demo 体验流程的转变:繁琐痛苦 → 快速便捷
如果你要体验 Ant Design 组件库里面 Tree 树组件的一个例子,并想修改部分参数查看效果,你需要做以下步骤:
Step1. 安装 Node.js (已安装可忽略)
Step2. 初始化 react 项目 npx create-react-app antd-tree-demo (必须)
Step3. 添加 Ant Design 并安装依赖 npm install (必须)
Step4. 修改项目代码为 Demo 例子代码 (必须)
Step5. 启动项目 npm start (必须)
而当有了浏览器端的前端 Sandbox 沙盒运行环境,只需一个步骤:
Step1. 点击打开一个链接
即可快速体验到 Demo,并且修改代码可实时看到效果。因此 Ant Design 组件库的每个组件例子都附带了 CodeSandbox 的链接:
原因二:低代码平台场景需要实时查看并调试当前应用的真实效果
用户在低代码平台开发时,如果应用实时预览的效果是与本地构建出来的效果是一致的,同时可以点击跳转到其他页面,查看整个业务流程的效果,那么整个开发体验都会有大幅度提升。
比如家庭健康码流程,包含 3 个页面:首页入口 → 健康码列表 → 健康码详情(详见开头视频动图)
第一个小目标:在浏览器上直接运行 React 源码文件渲染出 Hello, Sandbox!
源码如下:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
ReactDOM.render(
<div>Hello, Sandbox!</div>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
问题一:如何让源代码在浏览器上直接执行?
直接在浏览器上面执行可以吗?显然不行
原因 1:浏览器不支持直接 import NPM 模块 (目前支持加载服务端文件 '/xx/xx.jsx')
原因 2:浏览器无法识别 React 的 JSX 语法
虽然最新浏览器 (Chrome 67 版本开始) 已支持 ESM 模块的加载方式,但需要有以下两个前提条件:
条件 1:需要对源代码进行改造,改为相对或绝对路径,比如:
import React from 'react'改成import React from '/@module/react'条件 2:需要本地启动服务器端 Server,返回对应代码内容
当 import 其他文件时,比 import App from './App.jsx' ,因为 import 是系统关键词,我们无法直接模拟或者代理 import,此时浏览器会直接发起一个请求,
如果不依赖服务端,就必须另起一个 service worker 进行拦截。
而 service worker 的注册必须要加载单独的 js 文件(静态服务),无法将 sandbox 整套方案打包成一个 NPM 库来使用,更新迭代较为繁琐,不适用于我目前开发的低代码平台项目。
因此本文介绍的是更容易实现和管理的 CommonJS 格式规范,以 require 模块的形式来模拟执行环境。
问题二:如何将 ESM 格式转换成 CommonJS 格式?
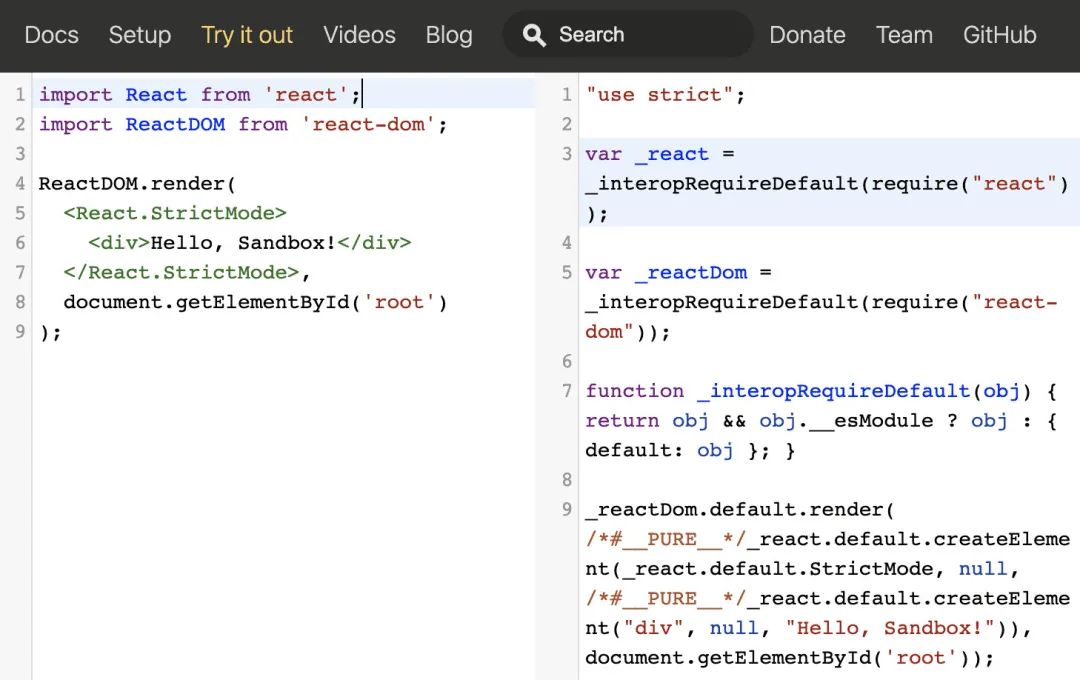
没错,就是 Babel,Babel 有在线转译的 Try it out 版本,大家可以点击 https://babeljs.io/repl 链接体验
其代码转换效果如下:
利用 @babel/plugin-transform-modules-commonjs 插件,将 ESM 语法转换成 CommonJS 格式规范
解决浏览器不支持直接 import NPM 模块的问题
利用 @babel/plugin-transform-react-jsx Babel 插件,将
<div />转换成React.createElement('div')函数解决浏览器无法直接识别 React JSX 语法的问题
有了思路,我们立刻开始执行:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- ① 依赖 -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@babel/standalone@7.13.12/babel.min.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<script>
const code = `
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
ReactDOM.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<div>Hello, Sandbox!</div>
</React.StrictMode>,
document.getElementById('root')
);`
// ② 转译
// 此时代码已转为 CJS 格式,import 变成了 require 函数
const transpiledCode = Babel.transform(code, {
plugins: [
['transform-modules-commonjs'],
['transform-react-jsx'],
]
}).code
// ③ 执行
eval(transpiledCode)
</script>
</body>
</html>
执行 Babel 转换后 CommonJS 规范的代码,发现吃了个闭门羹:

原来是 require 函数没有定义,因为 CommonJs 规范就是利用 require 来加载模块的,既然现在没有定义,那我们就定义一个
问题三:如何实现 require 函数?
因为 require 是要引入 react, react-dom 两个 NPM 依赖库的,所以实现 require 函数之前,先插入已打包为 UMD 规范的文件路径,以获取 React, ReactDom 全局变量。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- ① 依赖 -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@babel/standalone@7.13.12/babel.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@16.14.0/umd/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@16.14.0/umd/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<!-- 此时 react, react-dom 库已挂载到 window['React'], window['ReactDOM'] -->
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<script>
const externals = {
react: 'React',
'react-dom': 'ReactDOM'
}
function require(moduleName) {
return window[externals[moduleName]]
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
实现 require 函数也非常简单,需要拿哪个 NPM 依赖库,就直接把已加载到全局的库,返回回去即可。
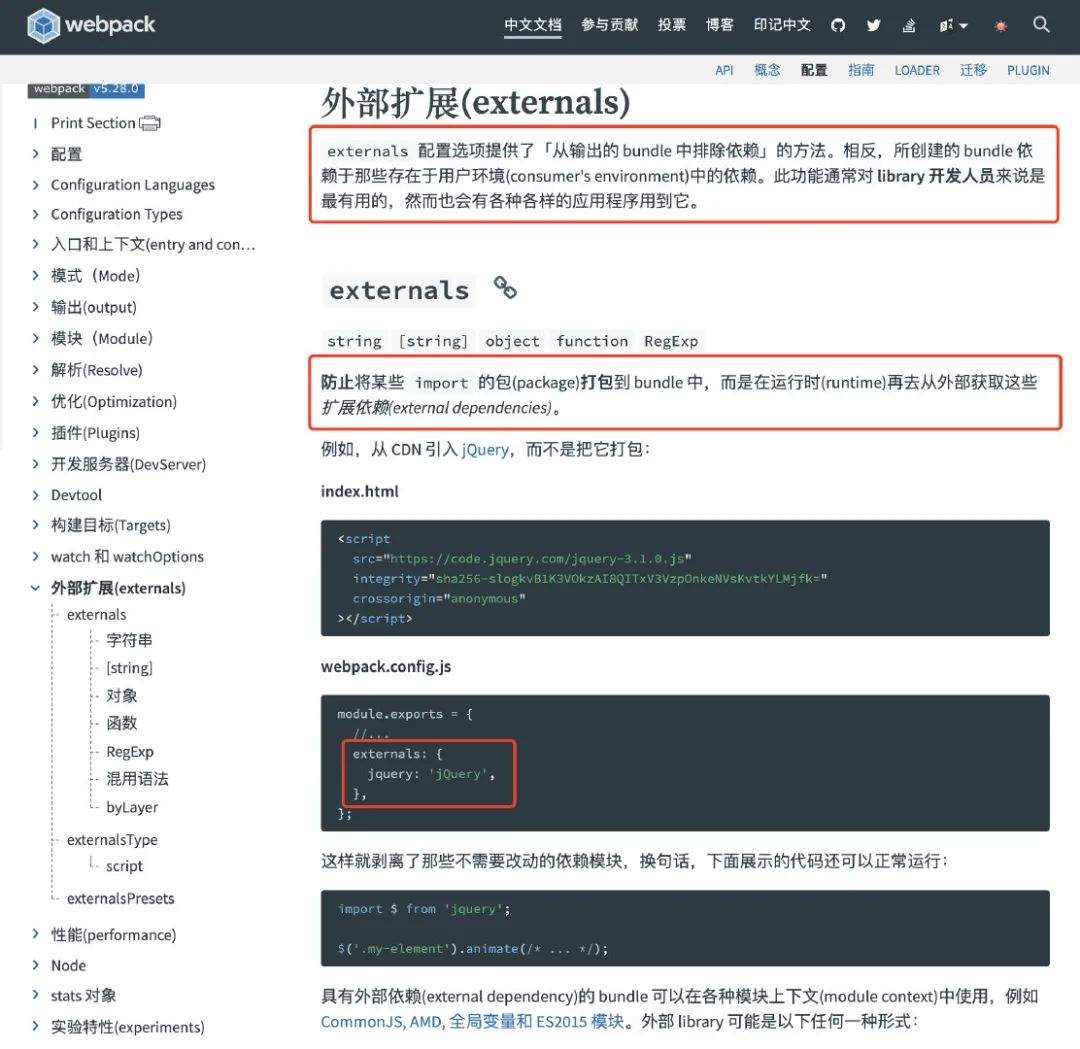
其中的 externals 是什么?
相信熟悉 webpack 的同学应该比较了解,简单来说就是配置哪些库是在运行时(runtime),再去外部(全局)获取这些扩展依赖。详情请点击
前期准备工作已经做完,我们将以下文件保存为 index.html ,然后本地打开看看效果
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<!-- ① 依赖 -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@babel/standalone@7.13.12/babel.min.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@16.14.0/umd/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@16.14.0/umd/react-dom.development.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<script>
const externals = {
react: 'React',
'react-dom': 'ReactDOM'
}
function require(moduleName) {
return window[externals[moduleName]]
}
const code = `
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
ReactDOM.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<div>Hello, Sandbox!</div>
</React.StrictMode>,
document.getElementById('root')
);`
// ② 转译
const transpiledCode = Babel.transform(code, {
plugins: [
['transform-modules-commonjs'],
['transform-react-jsx'],
]
}).code
// ③ 执行
eval(transpiledCode)
</script>
</body>
</html>
可以看到,第一个小目标已经完美完成!
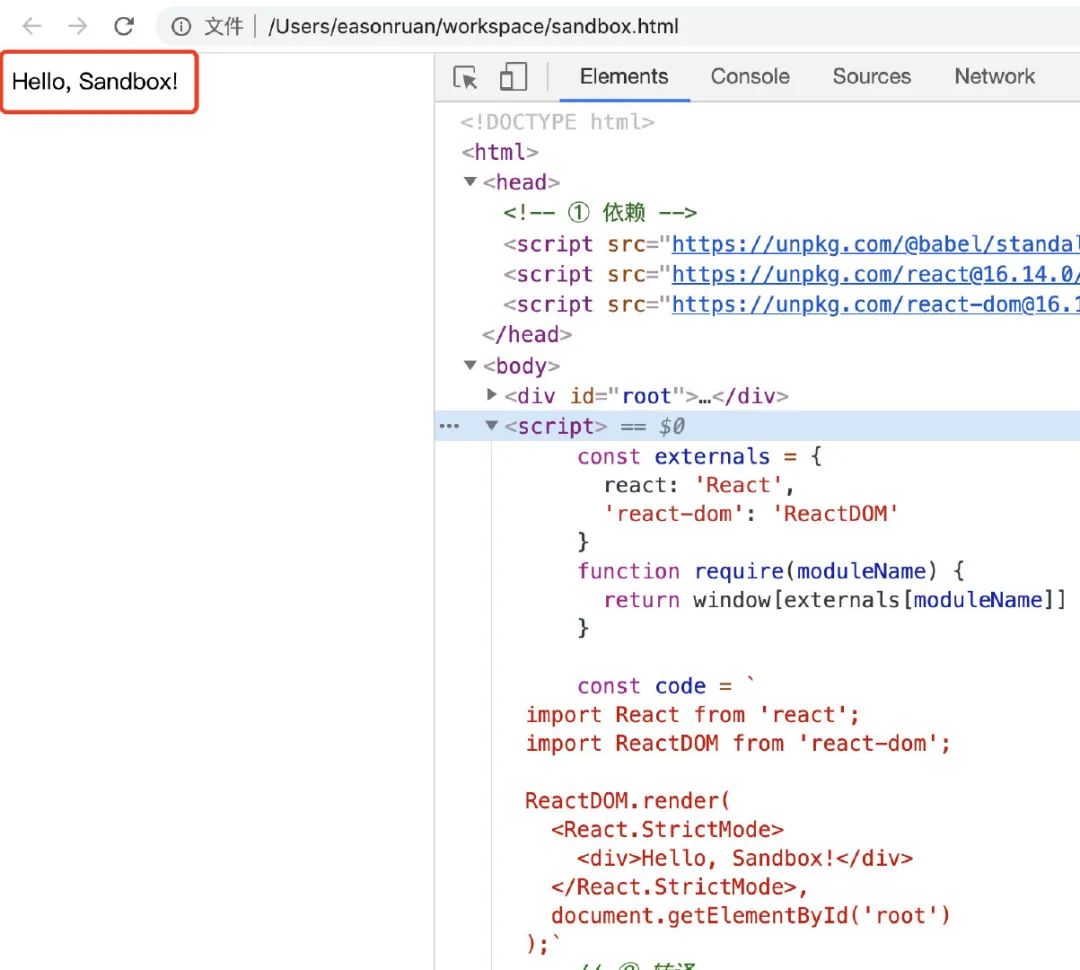
总结:Sandbox 核心方法论
经过上面简单例子的验证,不能发现,最小的例子都要不开以下三步,因此本文总结了浏览器端 Sandbox 沙盒的核心方法论:
Step1. 加载依赖
加载 Babel, React, ReactDOM
Step2. 转译模块
利用 Babel 将 ESM 转 CommonJS,转 JSX 语法
Step3. 执行代码
构造 CommonJS 环境,如 require 加载模块函数

所以看过本文的同学,其他知识点记不住没关系,将本文的 Sandbox 方法论三部曲记住就行,记住就已经算掌握一半浏览器端沙盒原理了。
重要的事情说三次:
Step1. 加载依赖,Step2. 转译模块,Step3. 执行代码
Step1. 加载依赖,Step2. 转译模块,Step3. 执行代码
Step1. 加载依赖,Step2. 转译模块,Step3. 执行代码
下面我们用 Vue 创建一个业务项目,让 Vue 中用 Sandbox 沙盒(Iframe 形式)来加载另一个 React 应用,同时验证上述 Sandbox 方法论。
第二个小目标:从 0 到 1 实现一个浏览器端的 Sandbox 沙盒运行环境
由于我目前研发的是 WeDa 低代码平台(专有版),因此暂时起名 WeSandbox 。
WeDa 低代码平台(专有版) 由于内网环境问题暂不放链接,后续合适时期将开放给公司内部体验,目前大家可以先体验 WeDa 公有云版本
第二个小目标最终效果其有以下特点:
可在 Vue 应用 Sandbox 里运行 React 代码
React useState 等功能均正常
修改 JSON 数据可热更新 React 组件(不丢失状态)
修改 CSS 数据可热更新样式
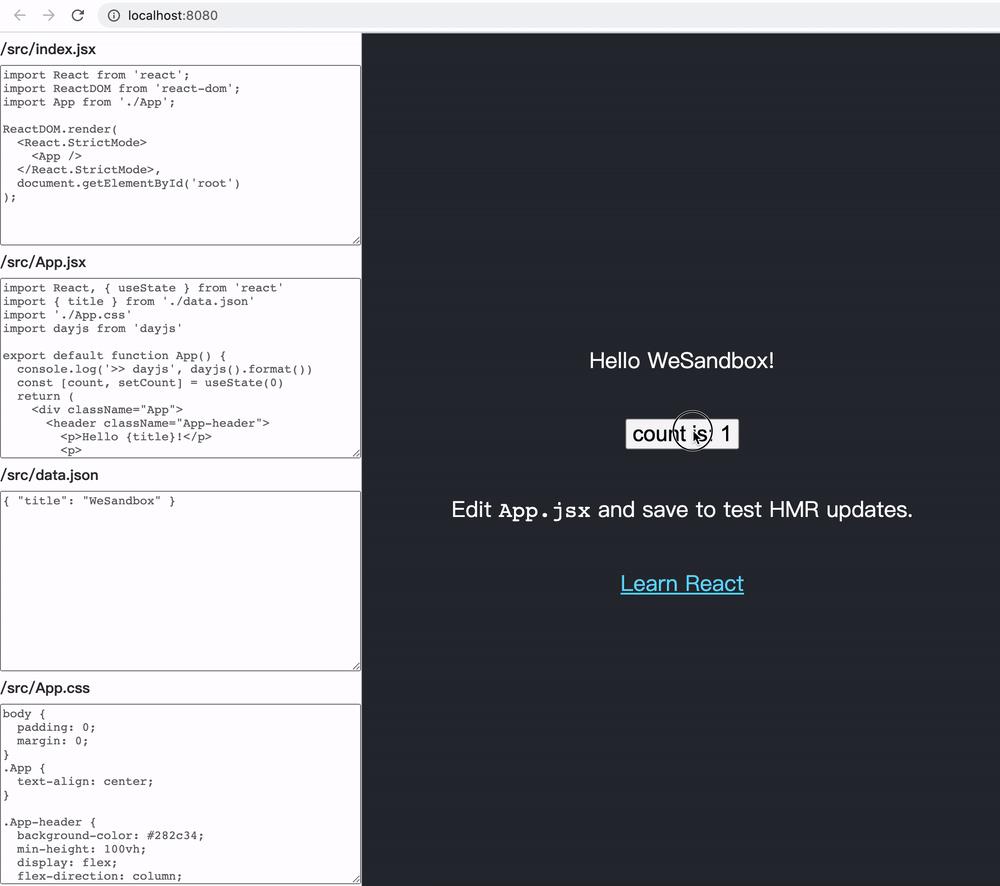
上图运行的是 Vue 应用,里面有个 iframe 承载着 WeSandbox 核心功能,其可以转译并运行 React 的代码。
Vue 应用代码
<template>
<div class="app-wrapper">
<div class="editor-wrapper">
<template v-for="item in Object.values(codeMap)">
<div class="file-name">{{item.path}}</div>
<textarea class="code-editor" @change="noticeSandboxUpdate" v-model="codeMap[item.path].code" />
</template>
</div>
<div class="sandbox-wrapper">
<iframe id="sandbox" @load="noticeSandboxUpdate" src="/sandbox.html" frameborder="0" />
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
data() {
return {
codeMap: {
'/src/index.js': {
code: `
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import App from './App';
ReactDOM.render(
<React.StrictMode>
<App />
</React.StrictMode>,
document.getElementById('root')
);`.trim(),
path: '/src/index.js'
},
'/src/App.jsx': {
code: `
import React, { useState } from 'react'
import { title } from './data.json'
import './App.css'
export default function App() {
const [count, setCount] = useState(0)
return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<p>Hello {title}!</p>
<p>
<button onClick={() => setCount((count) => count + 1)}>
count is: {count}
</button>
</p>
<p>
Edit <code>App.jsx</code> and save to test HMR updates.
</p>
<p>
<a
className="App-link"
href="https://reactjs.org"
target="_blank"
rel="noopener noreferrer"
>
Learn React
</a>
</p>
</header>
</div>
)
}
`.trim(),
path: '/src/App.jsx',
style: {
flex: 1
}
},
'/src/data.json': {
code: `{ "title": "Mini Sandbox - Json Data" }`,
path: '/src/data.json'
},
'/src/App.css': {
code: `
body {
padding: 0;
margin: 0;
}
.App {
text-align: center;
}
.App-header {
background-color: #282c34;
min-height: 100vh;
display: flex;
flex-direction: column;
align-items: center;
justify-content: center;
font-size: calc(10px + 2vmin);
color: white;
}
.App-link {
color: #61dafb;
}
button {
font-size: calc(10px + 2vmin);
}
`.trim(),
path: `/src/App.css`
}
}
}
},
methods: {
noticeSandboxUpdate() {
document.querySelector('#sandbox').contentWindow.postMessage({
codeMap: JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.codeMap)),
entry: '/src/index.js',
dependencies: {},
externals: {
react: 'React',
'react-dom': 'ReactDOM',
}
})
}
}
}
</script>
下面我们带着问题来一一查看部分功能的核心源码:
问题一:如何转译代码?
本文第一个小目标已经分析过,可以利用 Babel 进行转译,第二个小目标我们加个文件类型判断:
// Step2. 转译代码
function Transpile(packageInfo) {
const codeMap = packageInfo.codeMap
Object.keys(codeMap).map(path => {
const code = codeMap[path].code
// Babel Loader
if (/\\.jsx?$/.test(path)) {
codeMap[path].transpiledCode = Babel.transform(code, {
plugins: [
['transform-modules-commonjs'],
['transform-react-jsx'],
]
}).code
}
})
return codeMap
}
问题二:如何模拟 CommonJS 执行环境?
由于本文上部分只引入了 React,没有引入 js(x) 源代码文件,而源代码文件一般会利用 module.exports 导出该模块的值的,因此我们需要构造出 module 和 exports 来存储代码模块 eval 执行后的结果,其核心代码如下:
// transpiledCode 转译后的源代码
// require 自定义的获取模块函数,看下文
// module 是与当前源代码绑定的执行结果(一开始为空对象,eval执行后赋值)
function evaluateCode(transpiledCode, require, module) {
// #1. 构建 require, module, exports 当前函数的上下文全局数据
const allGlobals = {
require,
module,
exports: module.exports,
};
const allGlobalKeys = Object.keys(allGlobals).join(', ')
const allGlobalValues = Object.values(allGlobals);
try {
// #2. 源代码外面加一层函数,构建函数的入参为 require, module, exports
const newCode = `(function evaluate(` + allGlobalKeys + `) {` + transpiledCode + `\\n})`;
// #3. 利用 eval 执行此函数,并传入 require, module, exports
eval(newCode).apply(this, allGlobalValues);
return module.exports;
} catch (e) {
//
}
}
const defaultExternals = {
react: 'React',
'react-dom': 'ReactDOM',
}
function evaluateCodeModule(codeModule) {
codeModule.module = codeModule.module || getNewModule()
function require(moduleName) {
const extLib = window[defaultExternals[moduleName]]
if (extLib) {
return extLib
}
}
return evaluateCode(codeModule.transpiledCode, require, codeModule.module)
}
function getNewModule() {
const exports = {}
return {
exports,
}
}
至此,我们已经 CommonJS 必备三套件
require 获取依赖模块函数
module 存储模块执行结果
exports 存储模块执行结果
但演示例子的代码存在 import x from './x' 的写法,
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import App from './App';
ReactDOM.render(
<App />,
document.getElementById('root')
)
显然目前这么简单的 require 函数还是不够的。
问题三:如何处理 import x from './x' 引入其他代码模块文件?
核心思路:由于我们知道是哪个模块(知道模块路径 path)引用该代码文件的,因此我们可以结合引用者模块的代码绝对路径 + 引用相对路径 = 获取真正的代码绝对路径,比如:'./App.js' => '/src/App.js'
function require(moduleName) {
// #1 针对项目文件
if (/^[./]/.test(moduleName)) {
// 获取真正的代码路径,比如:'./App.js' => '/src/App.js'
const modulePath = resolveModulePath(moduleName, codeModule, moduleGraph)
const requiredModule = moduleGraph.getModule(modulePath)
if (requiredModule.module) {
return requiredModule.module.exports
}
requiredModule.module = getNewModule()
return evaluateCodeModule(requiredModule, moduleGraph)
}
// #2 针对外部(全局)依赖
// ...
}
// 获取真正的代码路径,比如:'./App.js' => '/src/App.js'
function resolveModulePath(moduleName, codeModule, moduleGraph) {
// #1 针对 /
let modulePath = moduleName
// #2 针对 .
if (moduleName.startsWith('.')) {
const currentDir = path.dirname(codeModule.path || codeModule.id)
modulePath = path.resolve(currentDir, moduleName)
}
if (moduleGraph.getModule(modulePath)) {
return modulePath
}
const FILE_EXTNAME = ['.js', '.jsx', '.css', '.json', '/index.js']
FILE_EXTNAME.some(ext => {
const withExtPath = `${modulePath}${ext}`
if (moduleGraph.getModule(withExtPath)) {
modulePath = withExtPath
return true
}
})
return modulePath
}
问题四:如何处理 JSON 代码模块?
此处先给 1 分钟读者思考一下,
好,估计你已经想出来了,没错,就是在 Sandbox 核心方法论 的 Step2. 转译代码 步骤添加一个简单的 JSON Loader 就行
// Step2. 转译代码
function Transpile(moduleGraph) {
const moduleMap = moduleGraph.moduleMap
moduleMap.forEach(codeModule => {
const code = codeModule.code
const path = codeModule.path
// Babel Loader
// ...
// JSON Loader
if (/\\.json$/.test(path)) {
codeModule.transpiledCode = `module.exports = ${code}`
}
})
}
问题五:如何处理 CSS 代码模块?
这个问题应该难不倒可以举一反三的你,我们直接看答案:
// Step2. 转译代码
function Transpile(moduleGraph) {
const moduleMap = moduleGraph.moduleMap
moduleMap.forEach(codeModule => {
const code = codeModule.code
const path = codeModule.path
// Babel Loader
// ...
// JSON Loader
// ...
// CSS Loader
if (/\\.css$/.test(path)) {
codeModule.transpiledCode = insertCss(path, code)
}
})
}
function insertCss(id, css) {
return `
function createStyleNode(id, content) {
var styleNode =
document.getElementById(id) || document.createElement('style');
styleNode.setAttribute('id', id);
styleNode.type = 'text/css';
if (styleNode.styleSheet) {
styleNode.styleSheet.cssText = content;
} else {
styleNode.innerHTML = '';
styleNode.appendChild(document.createTextNode(content));
}
document.head.appendChild(styleNode);
}
createStyleNode(
${JSON.stringify(id)},
${JSON.stringify(css)}
);
`
}
问题六:如何处理 Less 代码模块?
原理和上述一样,将 Less 文件转换成 css 文件之后再经过 CSS Loader 即可。
这是一道课外题,本文就不给出答案了,读者可以自行尝试。
问题七:如何实现热更新 React ?
这道是难题,但 React 官方有 react-refresh 标准答案,我们直接拿来抄。感兴趣的同学可以自行点击查看详情。
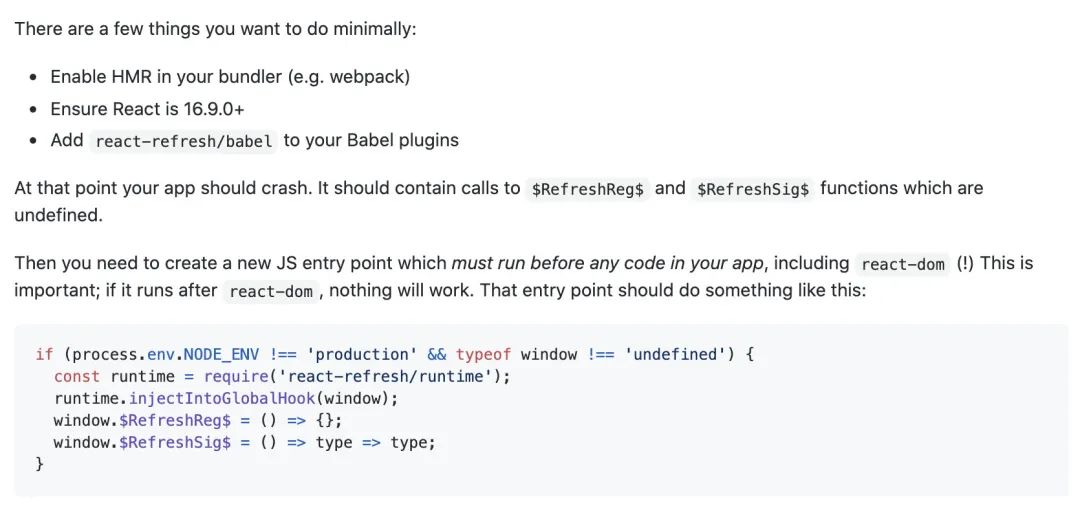
本文翻译并梳理下步骤以及重难点:
确保 React 版本是在
16.9.0+以上并且 React 必须是
development开发模式的版本(本人在此踩过坑)把
react-refresh/babel加到你的 Babel plugins 插件里面必须在加载
react-dom库之前加载以下代码:const runtime = require('react-refresh/runtime'); runtime.injectIntoGlobalHook(window); window.$RefreshReg$ = () => {}; window.$RefreshSig$ = () => type => type;然后在你 React 实际业务代码前后插入以下代码:
// BEFORE EVERY MODULE EXECUTES var prevRefreshReg = window.$RefreshReg$; var prevRefreshSig = window.$RefreshSig$; var RefreshRuntime = require('react-refresh/runtime'); window.$RefreshReg$ = (type, id) => { // Note module.id is webpack-specific, this may vary in other bundlers const fullId = module.id + ' ' + id; RefreshRuntime.register(type, fullId); } window.$RefreshSig$ = RefreshRuntime.createSignatureFunctionForTransform; try { // !!! // ... 你的 React 业务代码 ... // !!! } finally { window.$RefreshReg$ = prevRefreshReg; window.$RefreshSig$ = prevRefreshSig; }
而 Sandbox 中可以按以下步骤处理:
在 html 顶部引入 react-refresh-runtime, react-refresh-babel 两个库
<script src="./lib/react-refresh-runtime.js"></script> <script src="./lib/react-refresh-babel.js"></script> <script> ReactRefreshRuntime.injectIntoGlobalHook(window); window.$RefreshReg$ = () => {}; window.$RefreshSig$ = () => type => type; </script> <script src="https://unpkg.com/react@16.14.0/umd/react.development.js"></script> <script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@16.14.0/umd/react-dom.development.js"></script>在引入 react-dom 之前执行上述代码
确保 React 是 development 版本并且是
16.9.0+以上于引入 react-refresh-babel 库,已经存在全局对象
ReactFreshBabelPlugin,因此可以直接将其加到 Babel 插件列表里面然后在 Babel 返回结果前后加上官方指定代码
// Step2. 转译代码 function Transpile(moduleGraph) { const moduleMap = moduleGraph.moduleMap moduleMap.forEach(codeModule => { const code = codeModule.code const path = codeModule.path if (/\\.jsx?$/.test(path)) { codeModule.transpiledCode = getReactRefreshWrapperCode(babelTransform(code), path) } }) } function babelTransform(code) { return Babel.transform(code, { plugins: [ ['transform-modules-commonjs'], ['transform-react-jsx'], [ReactFreshBabelPlugin] ] }).code } function getReactRefreshWrapperCode(sourceCode, moduleId) { return ` // react refresh code before ${sourceCode} // react refresh code after ` }
至此,React 热更新的核心步骤已经完成,接下来就是收集代码已改变的模块列表,并重新执行该代码模块,即可达到热更新的效果。
问题八:如何实现模块互相引用的热更新?
简单来说就是,App.jsx 引用了 data.json 里面的数据,当 data.json 更新时,如何实现让 App.jsx 进行热更新?
答案是:收集模块依赖 (initiators 发起者) 。
我们可以在 require 函数引用模块的时候,收集当前模块是被谁引用过,称为initiators 发起者 ,然后等热更新执行模块时,先执行自身变化的代码模块,再执行该模块的 initiators 发起模块,即可达到互相引用热更新效果。
function evaluateCodeModule(codeModule, moduleGraph) {
codeModule.module = codeModule.module || getNewModule()
function require(moduleName) {
if (/^[./]/.test(moduleName)) {
const modulePath = resolveModulePath(moduleName, codeModule, moduleGraph)
const requiredModule = moduleGraph.getModule(modulePath)
if (requiredModule.module) {
return requiredModule.module.exports
}
requiredModule.module = getNewModule()
// 收集模块之间的依赖关系,以便热更新
requiredModule.initiators.add(codeModule)
return evaluateCodeModule(requiredModule, moduleGraph)
}
// ...
}
codeModule.isChanged = false
return evaluateCode(codeModule.transpiledCode, require, codeModule.module)
}
function StepThree_Evaluate(message, moduleGraph) {
const { entry } = message
// #1 从入口开始执行
const entryModule = moduleGraph.getModule(entry)
if (entryModule.isChanged) {
evaluateCodeModule(entryModule, moduleGraph)
return
}
// #2 热更新
const simpleHotModules = []
moduleGraph.moduleMap.forEach(codeModule => {
if (codeModule.isChanged) {
evaluateCodeModule(codeModule, moduleGraph)
codeModule.initiators.forEach(module => {
simpleHotModules.push(module)
})
}
})
simpleHotModules.forEach(module => {
evaluateCodeModule(module, moduleGraph)
})
}
问题九:如何获取 NPM 依赖包,dayjs 为例?
这个是难题,同学可以先主动思考下 ????,
如果要实现一个可用于生产环境的 WeSandbox,还有很多细节和问题需要考虑,
比如上面 NPM 依赖包、转译性能问题、如何便捷更新调试 等等
WeSandbox 即将用于 WeDa 低代码平台(专用版)生成环境
尽管 WeDa 低代码平台对于 Sandbox 的大部分已经攻克并实现,但本文篇幅有限,将在下一篇文章讲解,敬请期待~
下面 WeSandbox Mini 版仅仅是为了展示沙盒运行环境的核心思路,后续会给大家介绍正式版本。
我们再次回顾第二个小目标,其功能都已经实现:
[x] 可在 Vue 应用 Sandbox 里运行 React 代码
[x] React useState 等功能均正常
[x] 修改 JSON 数据可热更新 React 组件(不丢失状态)
[x] 修改 CSS 数据可热更新样式
如果本文对你有帮助,请帮顶,收藏,打赏,一键三连 ~ ????
最后,附上 WeSandbox Mini 版代码,共 280 行
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8"/>
<title>Mini Sandbox</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/@babel/standalone@7.13.12/babel.min.js"></script>
<script src="./lib/react-refresh-runtime.js"></script>
<script src="./lib/react-refresh-babel.js"></script>
<script>
ReactRefreshRuntime.injectIntoGlobalHook(window);
window.$RefreshReg$ = () => {};
window.$RefreshSig$ = () => type => type;
</script>
<!-- ① 加载依赖 -->
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react@16.14.0/umd/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/react-dom@16.14.0/umd/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<script src="./lib/path-browserify.js"></script>
<script>
class ModuleNode {
constructor(path) {
this.path = path
this.type = path.endsWith('css') ? 'css' : 'js'
this.initiators = new Set()
this.isChanged = true
this.module = null
this.transformResult = {
code: ''
}
}
}
class ModuleGraph {
moduleMap = new Map()
getModule(id) {
return this.moduleMap.get(id)
}
}
const globalModuleGraph = new ModuleGraph()
// 监听父级应用发送过来的消息
window.addEventListener('message', async (event) => {
const message = event.data
console.log('sandbox receive mes', message)
updateCodeModule(message, globalModuleGraph)
StepTwo_Transpile(globalModuleGraph)
StepThree_Evaluate(message, globalModuleGraph)
})
function updateCodeModule(message, moduleGraph) {
const { codeMap } = message
let finalFileMap = codeMap
Object.keys(finalFileMap).forEach(path => {
const codeFile = finalFileMap[path]
let module = moduleGraph.getModule(path)
if (!module) {
const newModule = new ModuleNode(path)
newModule.code = codeFile.code
newModule.isChanged = true
newModule.transpiledCode = codeFile.transpiledCode || null
moduleGraph.moduleMap.set(path, newModule)
return
}
if (module.code !== codeFile.code) {
module.code = codeFile.code
module.transpiledCode = null
module.module = null
module.isChanged = true
}
})
}
// ② 转译模块
function StepTwo_Transpile(moduleGraph) {
const moduleMap = moduleGraph.moduleMap
moduleMap.forEach(codeModule => {
const code = codeModule.code
if (/\\.jsx?$/.test(codeModule.path)) {
codeModule.transpiledCode = getReactRefreshWrapperCode(babelTransform(code), codeModule.path)
}
if (/\\.json$/.test(codeModule.path)) {
codeModule.transpiledCode = `module.exports = ${codeModule.code}`
}
if (/\\.css$/.test(codeModule.path)) {
codeModule.transpiledCode = insertCss(codeModule.path, codeModule.code)
}
})
}
function insertCss(id, css) {
return `
function createStyleNode(id, content) {
var styleNode =
document.getElementById(id) || document.createElement('style');
styleNode.setAttribute('id', id);
styleNode.type = 'text/css';
if (styleNode.styleSheet) {
styleNode.styleSheet.cssText = content;
} else {
styleNode.innerHTML = '';
styleNode.appendChild(document.createTextNode(content));
}
document.head.appendChild(styleNode);
}
createStyleNode(
${JSON.stringify(id)},
${JSON.stringify(css)}
);
`
}
function babelTransform(code) {
return Babel.transform(code, {
plugins: [
['transform-modules-commonjs'],
['transform-react-jsx'],
[ReactFreshBabelPlugin]
]
}).code
}
function getReactRefreshWrapperCode(sourceCode, moduleId) {
return `
var prevRefreshReg = window.$RefreshReg$,
prevRefreshSig = window.$RefreshSig$,
RefreshRuntime = require("react-refresh/runtime");
window.$RefreshReg$ = (type, id) => {
const s = ${JSON.stringify(moduleId)} + " " + id;
RefreshRuntime.register(type, s)
};
window.$RefreshSig$ = RefreshRuntime.createSignatureFunctionForTransform;
try {
${sourceCode}
} finally {
window.$RefreshReg$ = prevRefreshReg, window.$RefreshSig$ = prevRefreshSig
}
function debounce(func, wait, immediate) {
var timeout;
return function() {
var context = this, args = arguments;
var later = function() {
timeout = null;
if (!immediate) func.apply(context, args);
};
var callNow = immediate && !timeout;
clearTimeout(timeout);
timeout = setTimeout(later, wait);
if (callNow) func.apply(context, args);
};
};
const enqueueUpdate = debounce(RefreshRuntime.performReactRefresh, 30);
enqueueUpdate()
`;
}
// ③ 执行代码
function StepThree_Evaluate(message, moduleGraph) {
const { entry } = message
const entryModule = moduleGraph.getModule(entry)
if (entryModule.isChanged) {
evaluateCodeModule(entryModule, moduleGraph)
return
}
const simpleHotModules = []
moduleGraph.moduleMap.forEach(codeModule => {
if (codeModule.isChanged) {
evaluateCodeModule(codeModule, moduleGraph)
codeModule.initiators.forEach(module => {
simpleHotModules.push(module)
})
}
})
simpleHotModules.forEach(module => {
evaluateCodeModule(module, moduleGraph)
})
}
const defaultExternals = {
react: 'React',
'react-dom': 'ReactDOM',
'react-refresh/runtime': 'ReactRefreshRuntime'
}
function evaluateCodeModule(codeModule, moduleGraph) {
codeModule.module = codeModule.module || getNewModule()
function require(moduleName) {
// #1 针对项目文件
if (/^[./]/.test(moduleName)) {
// 获取真正的代码路径,比如:'./App.js' => '/src/App.js'
const modulePath = resolveModulePath(moduleName, codeModule, moduleGraph)
const requiredModule = moduleGraph.getModule(modulePath)
if (requiredModule.module) {
return requiredModule.module.exports
}
requiredModule.module = getNewModule()
requiredModule.initiators.add(codeModule)
return evaluateCodeModule(requiredModule, moduleGraph)
}
const extLib = window[moduleName] || window[defaultExternals[moduleName]]
if (extLib) {
return extLib
}
}
codeModule.isChanged = false
return evaluateCode(codeModule.transpiledCode, require, codeModule.module)
}
function resolveModulePath(moduleName, codeModule, moduleGraph) {
// #1 针对 /
let modulePath = moduleName
// #2 针对 .
if (moduleName.startsWith('.')) {
const currentDir = path.dirname(codeModule.path || codeModule.id)
modulePath = path.resolve(currentDir, moduleName)
}
if (moduleGraph.getModule(modulePath)) {
return modulePath
}
const FILE_EXTNAME = ['.js', '.jsx', '.css', '.json', '/index.js']
FILE_EXTNAME.some(ext => {
const withExtPath = `${modulePath}${ext}`
if (moduleGraph.getModule(withExtPath)) {
modulePath = withExtPath
return true
}
})
return modulePath
}
function getNewModule() {
const exports = {}
return {
exports,
}
}
function evaluateCode(code, require, module) {
const exports = module.exports
const allGlobals = {
require,
module,
exports,
};
const allGlobalKeys = Object.keys(allGlobals).join(', ')
const globalsValues = Object.values(allGlobals);
try {
const newCode = `(function evaluate(` + allGlobalKeys + `) {` + code + `\\n})`;
// @ts-ignore
eval(newCode).apply(allGlobals.window || this, globalsValues);
return module.exports;
} catch (e) {
let error = e;
if (typeof e === 'string') {
error = new Error(e);
}
error.isEvalError = true;
throw error;
}
}
</script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
</html>
视频号最新视频
以上是关于从 0 到 1 实现浏览器端沙盒运行环境的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章