机器学习可视化的4大Python库
Posted 小白玩转Python
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了机器学习可视化的4大Python库相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
引言
随着人工智能如火如荼的发展,人们需要对模型的预测以及它们的工作原理进行解释。
幸运的是,Python提供了越来越多的库来解决此问题。下面是四个流行的解释机器学习模型的图书馆的快速指南。
Yellowbrick
这个是Python库和scikit-learn包的扩展,为机器学习提供了可视化。如果你习惯使用scikit-learn,那么yellowbrick的流程你会感觉很熟悉。
Yellowbrick提供了模型选择、特征重要性确定和模型性能分析。
首先使用pip进行安装:
pip install yellowbrick为了演示一些功能,我们将使用一个名为葡萄酒识别的scikit-learn数据集。这个具有13个特性和3个目标类的数据集是直接从scikit-learn库加载的。在下面的代码中,我们导入数据集并将其转换为对象DataFrame。分类器无需预先处理即可使用信息。
import pandas as pdfrom sklearn import datasetswine_data = datasets.load_wine()df_wine = pd.DataFrame(wine_data.data,columns=wine_data.feature_names)df_wine['target'] = pd.Series(wine_data.target)
使用scikit-learn将数据集进一步划分为验证集和训练集:
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_splitX = df_wine.drop(['target'], axis=1)y = df_wine['target']X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2)
下一步,使用Yellowbricks可视化工具查看数据集中特征之间的相关性。
from yellowbrick.features import Rank2Dimport matplotlib.pyplot as pltvisualizer = Rank2D(algorithm="pearson", size=(1080, 720))visualizer.fit_transform(X_train)visualizer.poof()
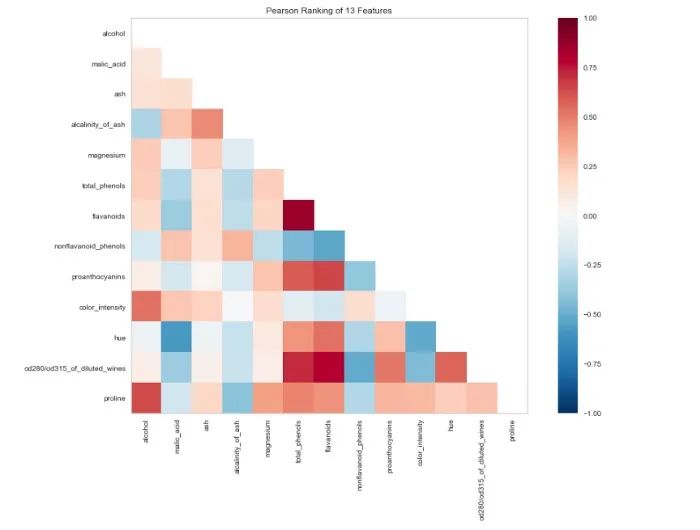
现在,我们调整RandomForestClassifier并使用另一个渲染器评估性能:
from yellowbrick.classifier import ClassificationReportfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifiermodel = RandomForestClassifier()visualizer = ClassificationReport(model, size=(1080, 720))visualizer.fit(X_train, y_train)visualizer.score(X_test, y_test)visualizer.poof()
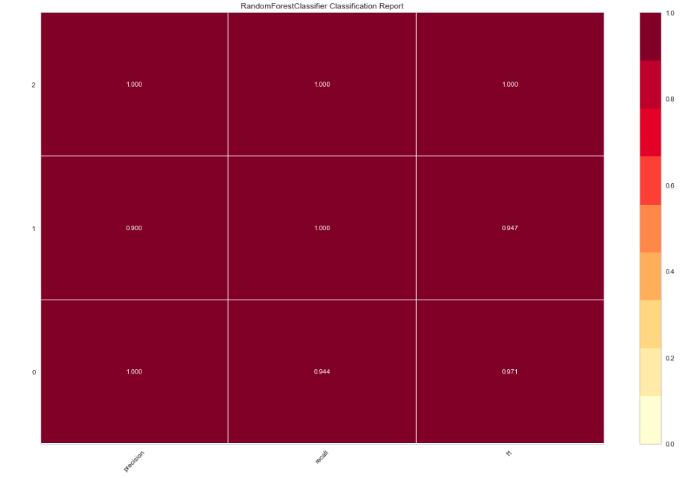
ELI5
ELI5是另一个可视化库,可用于调试机器学习模型并解释所作的预测。与最常见的Python机器学习工具一起使用,例如scikit-learn,XGBoost和Keras。
使用ELI5来测试上面讨论的模型特性的重要性:
import eli5eli5.show_weights(model, feature_names = X.columns.tolist())
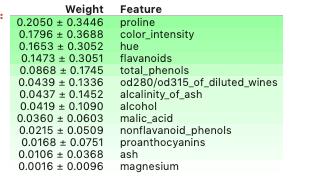
默认情况下,方法show_weightsuses使用gains计算权重,并且在需要其他类型时,添加一个参数Important_type。
并且还使用show_prediction测试单个预测的基础。
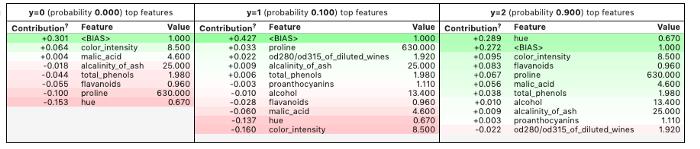
LIME
LIME代表独立于模型的解释。解释机器学习算法做出的预测。Lime支持解释来自多个分类器的单元预测,并且还可以直接与scikit-learn交互。
让我们用Lime解释我们之前训练的模型的预测。
通过 pip 安装库:
pip install lime首先,让我们创建一个解释器。为此,我们从模型中使用的特性名称和目标变量中的类名称中获取训练数据集作为数组。
import lime.lime_tabularexplainer = lime.lime_tabular.LimeTabularExplainer(X_train.values,feature_names=X_train.columns.values.tolist(),class_names=y_train.unique())
然后,我们创建一个lambda函数,该函数采用模型来预测数据样本。
predict_fn = lambda x: model.predict_proba(x).astype(float)使用解释器解释取样样本的预测。你会看到下面的结果。 Lime创建了可视化效果,显示特征如何促成一个特定的预测。
exp = explainer.explain_instance(X_test.values[0], predict_fn, num_features=6)exp.show_in_notebook(show_all=False)

MLxtend
在这个库中,你会发现很多支持机器学习的功能。它包括叠加和表决分类器、模型评估、特征提取以及设计和制图。
让我们转向 MLxtend 来比较投票分类器和组合分类器的判定界限。
通过pip安装库:
pip install mlxtend然后导入必要的库
from mlxtend.plotting import plot_decision_regionsfrom mlxtend.classifier import EnsembleVoteClassifierimport matplotlib.gridspec as gridspecimport itertoolsfrom sklearn import model_selectionfrom sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegressionfrom sklearn.naive_bayes import GaussianNBfrom sklearn.ensemble import RandomForestClassifier
以下可视化只能同时使用两个功能,因此首先让我们创建一个具有属性proline和color_intensity的数组。选择这些特征的原因是,与上述使用ELI5测试的那些特征相比,它们的权重最大。
X_train_ml = X_train[['proline', 'color_intensity']].valuesy_train_ml = y_train.values
然后我们创建分类器,将它们与训练数据进行匹配,并使用MLxtend获得决策边界的可视化。结果在代码的下面。
clf1 = LogisticRegression(random_state=1)clf2 = RandomForestClassifier(random_state=1)clf3 = GaussianNB()eclf = EnsembleVoteClassifier(clfs=[clf1, clf2, clf3], weights=[1,1,1])value=1.5width=0.75gs = gridspec.GridSpec(2,2)fig = plt.figure(figsize=(10,8))labels = ['Logistic Regression', 'Random Forest', 'Naive Bayes', 'Ensemble']for clf, lab, grd in zip([clf1, clf2, clf3, eclf],labels,itertools.product([0, 1], repeat=2)):clf.fit(X_train_ml, y_train_ml)ax = plt.subplot(gs[grd[0], grd[1]])fig = plot_decision_regions(X=X_train_ml, y=y_train_ml, clf=clf)plt.title(lab)
总结
用好上面这4个可视化的python库,将会大大提高机器学习的可解释性,加强我们对机器学习的认识。
以上是关于机器学习可视化的4大Python库的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章