LeetCode﹝并查集ி﹞连通分量个数(套用模板一直爽)
Posted 白鳯
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了LeetCode﹝并查集ி﹞连通分量个数(套用模板一直爽)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
【LeetCode】﹝并查集ி﹞连通分量个数(套用模板一直爽)
文章目录
模板(使用路径压缩的加权quick-union算法)
详细并查集的知识见往期博客 高级数据结构(Ⅰ)并查集(Union-Find)
class UF{
int N;
int count;
int[] id;
int[] sz;
UF(int N){
this.N = N;
count = N;
id = new int[N];
sz = new int[N];
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
id[i] = i;
sz[i] = 1;
}
}
public int getCount() {
return count;
}
public void union(int p, int q) {
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if(pRoot != qRoot) {
if(sz[pRoot] < sz[qRoot]) {
id[pRoot] = id[qRoot];
sz[qRoot] += sz[pRoot];
}else {
id[qRoot] = id[pRoot];
sz[pRoot] += sz[qRoot];
}
count--;
}
}
private int find(int p) {
if(p == id[p]) return p;
id[p] = find(id[p]);
return id[p];
}
}
连通网络的操作次数★★
【题目】用以太网线缆将 n 台计算机连接成一个网络,计算机的编号从 0 到 n-1。线缆用 connections 表示,其中 connections[i] = [a, b] 连接了计算机 a 和 b。
网络中的任何一台计算机都可以通过网络直接或者间接访问同一个网络中其他任意一台计算机。
给你这个计算机网络的初始布线 connections,你可以拔开任意两台直连计算机之间的线缆,并用它连接一对未直连的计算机。请你计算并返回使所有计算机都连通所需的最少操作次数。如果不可能,则返回 -1 。
提示:
1 <= n <= 10^51 <= connections.length <= min(n*(n-1)/2, 10^5)connections[i].length == 20 <= connections[i][0], connections[i][1] < nconnections[i][0] != connections[i][1]- 没有重复的连接。
- 两台计算机不会通过多条线缆连接。
【示例】
示例1:
输入:n = 4, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,2]]
输出:1
解释:拔下计算机 1 和 2 之间的线缆,并将它插到计算机 1 和 3 上。
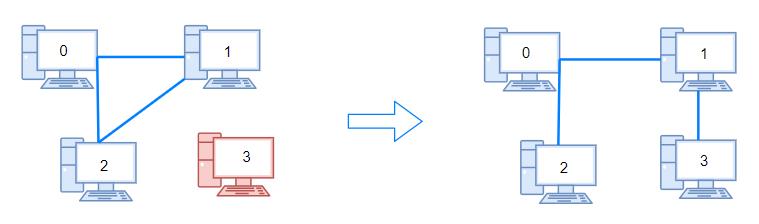
示例2:
输入:n = 6, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[0,3],[1,2]]
输出:-1
解释:线缆数量不足。
【解题思路】
利用并查集求出多余的缆线数量和连通分量的个数(java耗时6ms)
class Solution {
public int makeConnected(int n, int[][] connections) {
UF uf = new UF(n);
int ress = 0;
for (int[] connection : connections) {
int t = uf.union(connection[0], connection[1]);
if (t == -1) {
ress++;
}
}
return ress >= uf.getCount() - 1 ? uf.getCount() - 1 : -1;
}
class UF {
int N;
int count;
int[] id;
int[] sz;
private UF (int n) {
N = n;
count = n;
id = new int[N];
sz = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
id[i] = i;
sz[i] = 1;
}
}
public int getCount () {
return count;
}
public int union (int p, int q) {
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if (pRoot != qRoot) {
if (sz[pRoot] < sz[qRoot]) {
id[pRoot] = qRoot;
sz[qRoot] += sz[pRoot];
} else {
id[qRoot] = pRoot;
sz[pRoot] += sz[qRoot];
}
count--;
return 1;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
private int find (int p) {
if (p == id[p]) {
return p;
}
id[p] = find(id[p]);
return id[p];
}
}
}
模板因题测试而异,如测试数据量较大,适合用上述模板,若测试数据量较小,使用如下简单版本的并查集
(java耗时3ms)
class Solution {
public int makeConnected(int n, int[][] connections) {
int[] id = new int[n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
id[i] = i;
}
int cons = n, ress = 0;
for (int[] e : connections) {
int p1 = find(id, e[0]);
int p2 = find(id, e[1]);
if (p1 == p2) {
ress++;
} else {
cons--;
id[p1] = p2;
}
}
return ress + 1 >= cons ? cons - 1 : -1;
}
private int find(int[] id, int p) {
if (p == id[p]) return p;
id[p] = find(id, id[p]);
return id[p];
}
}
省份数量★★
【题目】有 n 个城市,其中一些彼此相连,另一些没有相连。如果城市 a 与城市 b 直接相连,且城市 b 与城市 c 直接相连,那么城市 a 与城市 c 间接相连。
省份 是一组直接或间接相连的城市,组内不含其他没有相连的城市。
给你一个 n x n 的矩阵 isConnected ,其中 isConnected[i][j] = 1 表示第 i 个城市和第 j 个城市直接相连,而 isConnected[i][j] = 0 表示二者不直接相连。
返回矩阵中 省份 的数量。
提示:
1 <= n <= 200n == isConnected.lengthn == isConnected[i].lengthisConnected[i][j] 为 1 或 0isConnected[i][i] == 1isConnected[i][j] == isConnected[j][i]
【示例】
输入:isConnected = [[1,1,0],[1,1,0],[0,0,1]]
输出:2
-----------------------------------------------------
输入:isConnected = [[1,0,0],[0,1,0],[0,0,1]]
输出:3
【解题思路】
class Solution {
int[] id;
int count = 0;
public int findCircleNum(int[][] M) {
if (M == null || M.length == 0 || M[0].length == 0) return 0;
count = M.length;
id = new int[M.length];
for (int i = 0; i < M.length; i++) id[i] = i;
for (int i = 0; i < M.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < M.length; j++) {
if (M[i][j] == 1) union(i, j);
}
}
return count;
}
private int find(int p) {
if (p == id[p]) return p;
id[p] = find(id[p]);
return id[p];
}
private void union(int p, int q) {
int pid = find(p);
int qid = find(q);
if (pid == qid) return;
id[pid] = qid;
count--;
}
}
岛屿数量★★
【题目】给你一个由 ‘1’(陆地)和 ‘0’(水)组成的的二维网格,请你计算网格中岛屿的数量。
岛屿总是被水包围,并且每座岛屿只能由水平方向和/或竖直方向上相邻的陆地连接形成。
此外,你可以假设该网格的四条边均被水包围。
提示:
m == grid.lengthn == grid[i].length1 <= m, n <= 300grid[i][j] 的值为 '0' 或 '1'
【示例】
输入:grid = [
["1","1","1","1","0"],
["1","1","0","1","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","0","0","0"]
]
输出:1
------------------------------------------------
输入:grid = [
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["1","1","0","0","0"],
["0","0","1","0","0"],
["0","0","0","1","1"]
]
输出:3
【解题思路】
方法一:并查集,只考虑右边和下边即可
class Solution {
int[] id;
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
if (grid == null || grid.length == 0 || grid[0].length == 0) {
return 0;
}
int R = grid.length, C = grid[0].length;
int count = R * C;
id = new int[R * C];
for (int i = 0; i < id.length; i++) id[i] = i;
for (int i = 0; i < R; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < C; j++) {
char c = grid[i][j];
int k = i * C + j;
if (c == '0') {
count--;
} else {
if (j < C - 1 && grid[i][j + 1] == '1') {
count += union(k, k + 1);
}
if (i < R - 1 && grid[i + 1][j] == '1') {
count += union(k, k + C);
}
}
}
}
return count;
}
private int find(int p) {
if (p == id[p]) {
return p;
}
id[p] = find(id[p]);
return id[p];
}
private int union(int p, int q) {
int pRoot = find(p);
int qRoot = find(q);
if (pRoot != qRoot) {
id[pRoot] = qRoot;
return -1;
} else {
return 0;
}
}
}
方法二:dfs,下沉与它连接的所有岛屿
class Solution {
public int numIslands(char[][] grid) {
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < grid.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < grid[i].length; j++) {
if (grid[i][j] == '1') {
sinkLand(grid, i, j);
count++;
}
}
}
return count;
}
public void sinkLand(char[][] grid, int r, int c){
if (r < 0 || r >= grid.length || c < 0 || c >= grid[0].length || grid[r][c] == '0') {
return;
}
grid[r][c] = '0';
sinkLand(grid,以上是关于LeetCode﹝并查集ி﹞连通分量个数(套用模板一直爽)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章