C++数据结构——顺序队列(基本代码实现与案例)
Posted eyes++
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了C++数据结构——顺序队列(基本代码实现与案例)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一:顺序队列的基本概念
顺序队列的结构(会出现假溢出现象):
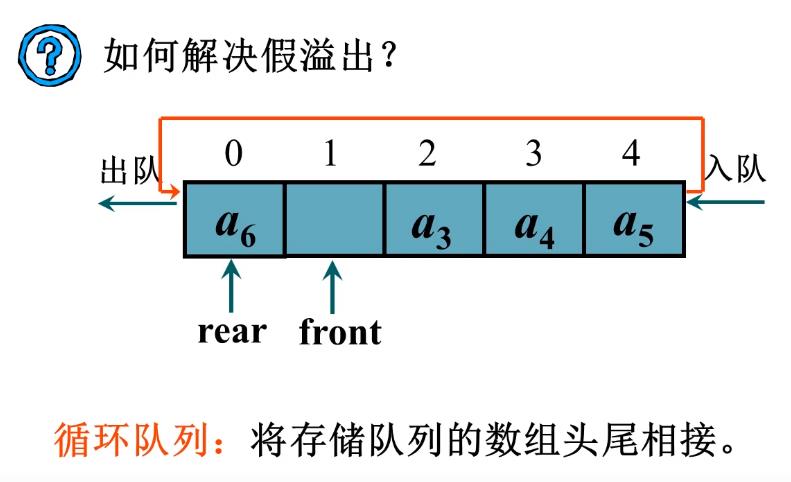
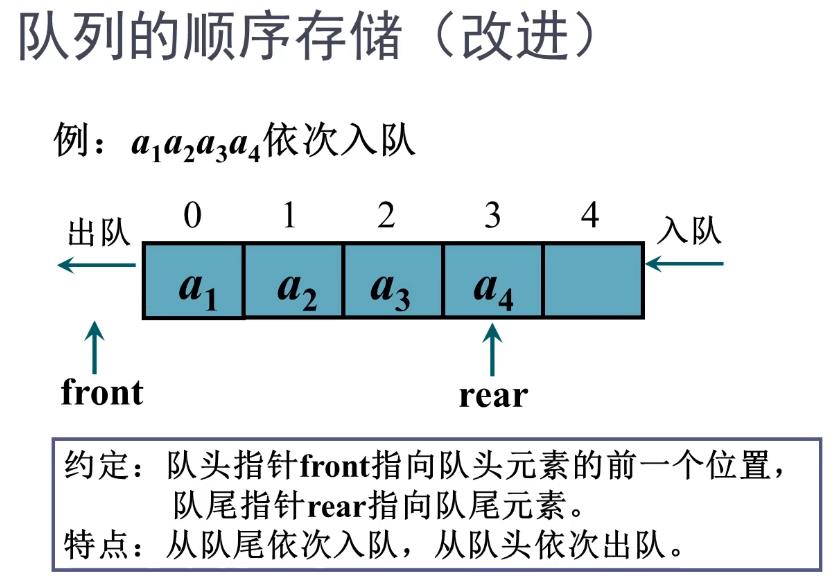 循环队列的结构:
循环队列的结构:
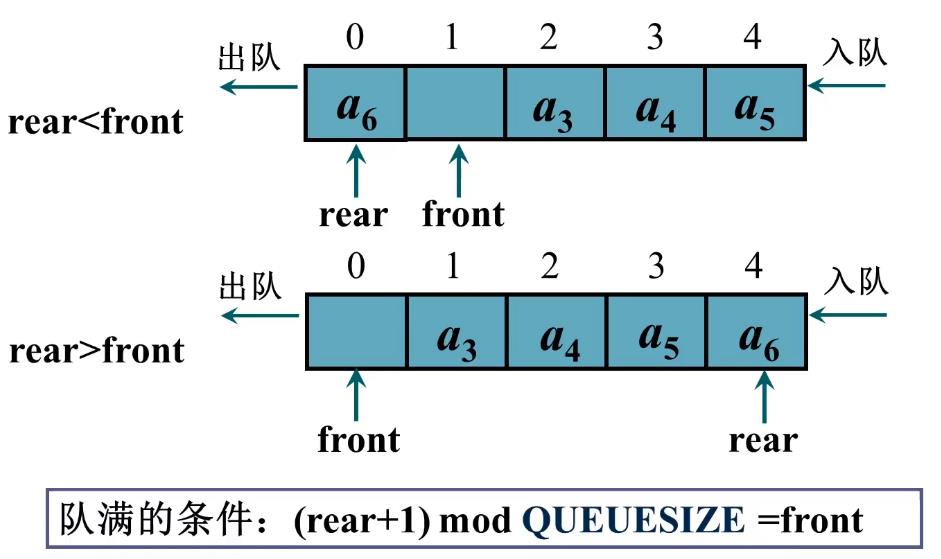
队满判断:

循环队列的基本代码实现:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
enum error_code{
success,overflow,underflow
};
class queue{
public:
queue(int len);
bool empty()const;
bool full()const;
int getCount()const;
error_code get_front(int &x)const;
error_code append(const int x);
error_code serve();
private:
int count, maxlen;
int front, rear;
int *data = new int[maxlen];
};
queue::queue(int len){
count = 0;
maxlen = len;
front = rear = 0;
}
bool queue::empty()const{
return count == 0;
//等价于 return front == rear
}
bool queue::full()const{
if(count == maxlen - 1) return true;
return false;
//等价于 return(rear + 1) % maxlen == front;
}
int queue::getCount()const{
return count;
}
error_code queue::get_front(int &x)const{
if(empty()) return underflow;
x = data[(front + 1) % maxlen];
return success;
}
error_code queue::append(const int x){
if(full()) return overflow;
rear = ( rear + 1 ) % maxlen;
data[rear] = x;
count ++;
return success;
}
error_code queue::serve(){
if(empty()) return underflow;
front = ( front + 1 ) % maxlen;
count --;
return success;
}
bool ReferenceError(error_code a){
if(a == overflow){
cout << "overflow!" << endl;
return false;
}
if(a == underflow){
cout << "underflow!" << endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
int len, front;
cin >> len;
queue q(len); //初始化类,输入循环队列最大长度
for(int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
q.append(i);
for(int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
q.serve();
ReferenceError(q.get_front(front));
cout << front << endl;
cout << q.getCount() << endl;
return 0;
}
二:顺序队列的使用
- 案例一(周末舞会):周末舞会上,男士们和女士们进入舞厅时,各自排成一队,跳舞开始时,依次从男队和女队的对头上各出一人配成舞伴,规定每个舞曲只能有一对跳舞者,若两队初始人数不相同,则较长的那一队中未配对者等待下一轮舞曲,现用程序模拟舞伴配对问题。
- 案例二(杨辉三角):用队列计算并打印杨辉三角前n行。
- 案例三(酒桌文化):n个人围成一个圆桌,按照顺时针的顺序1, 2,…, n进行编号,某一个人开始报一个数字,然后顺时针的下一个人会报数+1,当某个人报的数字含有一或是七的倍数时,这个人退出游戏,其他人接着报数,直到剩下一个人。输入n, m, t,其中m代表开始报数的人的编号,t表示开始报数的人报出的数字是t,然后接下来有n行,是这n个人的名字,求最后一个人的名字。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
enum error_code{
success,overflow,underflow
};
class queue{
public:
queue(int len);
bool empty()const;
bool full()const;
int getCount()const;
error_code get_front(int &x)const;
error_code append(const int x);
error_code serve();
private:
int count, maxlen;
int front, rear;
int *data = new int[maxlen];
};
queue::queue(int len){
count = 0;
maxlen = len;
front = rear = 0;
}
bool queue::empty()const{
return count == 0;
//等价于 return front == rear
}
bool queue::full()const{
if(count == maxlen - 1) return true;
return false;
//等价于 return(rear + 1) % maxlen == front;
}
int queue::getCount()const{
return count;
}
error_code queue::get_front(int &x)const{
if(empty()) return underflow;
x = data[(front + 1) % maxlen];
return success;
}
error_code queue::append(const int x){
if(full()) return overflow;
rear = ( rear + 1 ) % maxlen;
data[rear] = x;
count ++;
return success;
}
error_code queue::serve(){
if(empty()) return underflow;
front = ( front + 1 ) % maxlen;
count --;
return success;
}
bool ReferenceError(error_code a){
if(a == overflow){
cout << "overflow!" << endl;
return false;
}
if(a == underflow){
cout << "underflow!" << endl;
return false;
}
return true;
}
// 周末舞会
void danceInWeek()
{
cout << "周末舞会问题!" << endl;
// 初始化题目条件(m: 男士人数 n:女士人数 k:舞曲数)
int m, n, k;
cin >> m >> n >> k;
// 初始化队列结构
queue q1(20), q2(20);
int front1, front2;
for(int i = 0; i < m; i++)
ReferenceError(q1.append(i));
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++)
ReferenceError(q2.append(i));
// 开始计算
while(k--)
{
ReferenceError(q1.get_front(front1));
ReferenceError(q2.get_front(front2));
cout << front1 << " 与 " << front2 << "一起跳舞" << endl;
ReferenceError(q1.serve());
ReferenceError(q2.serve());
ReferenceError(q1.append(front1));
ReferenceError(q2.append(front2));
}
}
// 杨辉三角
void YHtriangle()
{
cout << "杨辉三角问题!" << endl;
// 初始化题目条件
int n;
cin >> n;
// 初始化队列结构
queue q(150);
int s1, front;
// 开始计算
cout << 1 << endl;
ReferenceError(q.append(1));
for(int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
{
s1 = 0;
for(int j = 1; j <= i - 1; j++)
{
ReferenceError(q.get_front(front));
ReferenceError(q.serve());
cout << s1 + front << " ";
ReferenceError(q.append(s1 + front));
s1 = front;
}
cout << 1 << endl;
ReferenceError(q.append(1));
}
}
// 酒桌游戏
bool isSeven(int n) // 判断是否含有 7
{
int k;
while(n != 0)
{
k = n % 10;
if(k == 7)
return true;
n /= 10;
}
return false;
}
void drinkingGame()
{
cout << "酒桌游戏问题!" << endl;
// 初始化题目条件
int n, m, t;
cin >> n >> m >> t;
// 初始化队列结构
queue q(n + 2);
int front;
// 开始计算
for(int i = 0; i < n; i++) // 给人添加编号
ReferenceError(q.append((m + i) % n));
for(int i = 0; q.getCount() != 1; i++)
{
ReferenceError(q.get_front(front));
cout << "本次报数人:" << front << " " << "报数:" << t + i << " ";
if((t + i) % 7 == 0 || isSeven(t + i))
{
ReferenceError(q.serve());
cout << "出队!!" << " " << "剩余人数:" << q.getCount() << endl;
}
else
{
ReferenceError(q.append(front));
ReferenceError(q.serve());
cout << "回队尾!!" << " " << "剩余人数:" << q.getCount() << endl;
}
}
ReferenceError(q.get_front(front));
cout << "最后一个人是:" << front << endl;
}
int main()
{
// 周末舞会
danceInWeek();
// 杨辉三角
YHtriangle();
// 酒桌游戏
drinkingGame();
return 0;
}
以上是关于C++数据结构——顺序队列(基本代码实现与案例)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章