基于K-means聚类算法实现无线传感器网络分簇路由协议
Posted 博主QQ2449341593
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了基于K-means聚类算法实现无线传感器网络分簇路由协议相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
一、算法设计

二、仿真分析
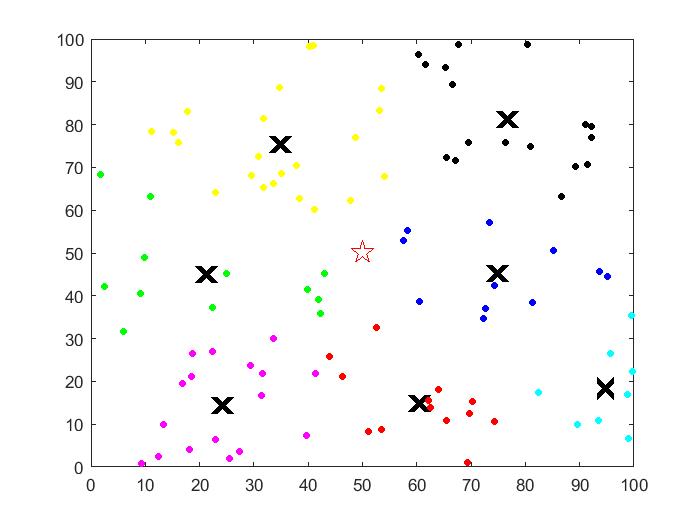
图1 K-means分簇
如图1所示,使用MATLAB R2018b进行了100个节点的仿真,黑色十字表示选择到的簇头节点,每个颜色代表簇。可见,网络的拓扑结构合理,簇头节点位置在族的中心,这样节约了簇内节点信息汇集的传输成本。
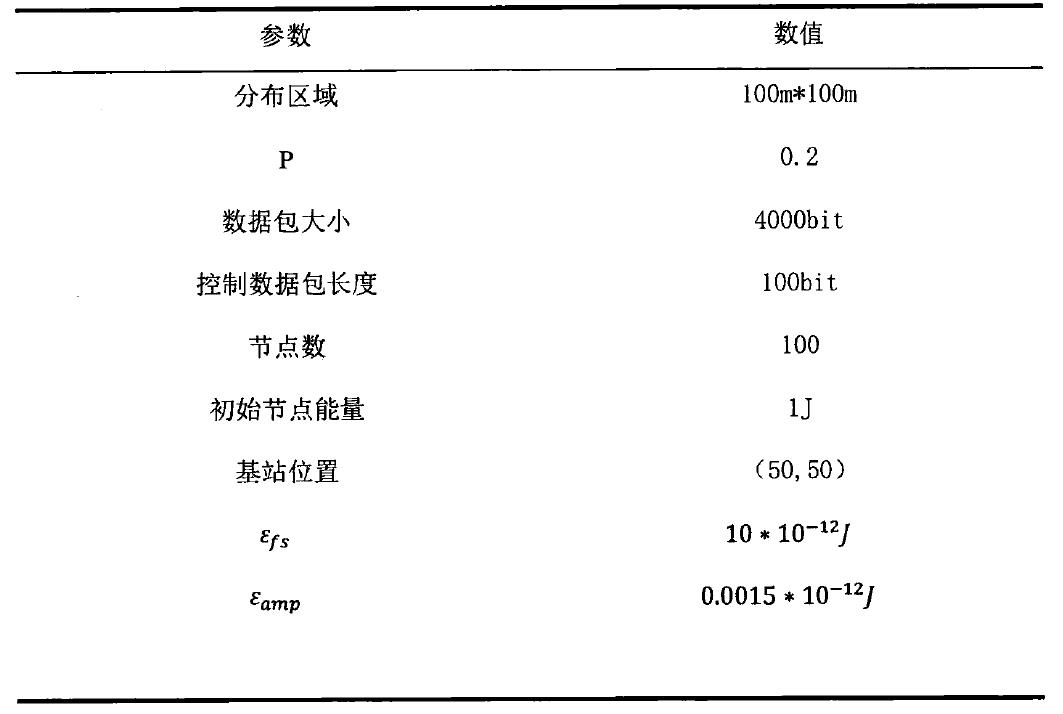
对于仿真中节点的参数设定则如表1所示:
表1 仿真参数
存活节点与轮数的关系如图2所示: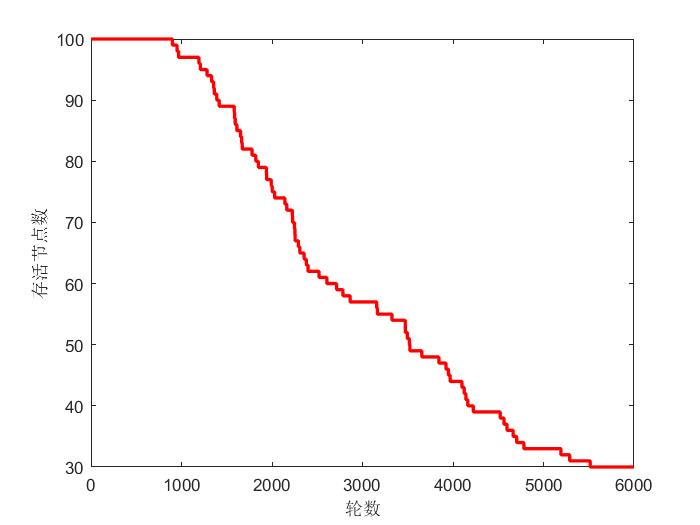
图2 存活节点与轮数的关系
系统剩余总能量与轮数的关系如图3所示: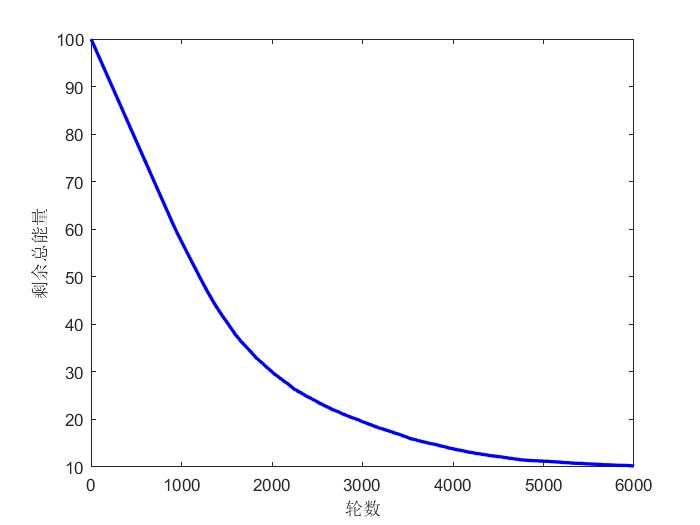
图3 系统剩余总能量与轮数的关系
系统消耗总能量与轮数的关系如图4所示: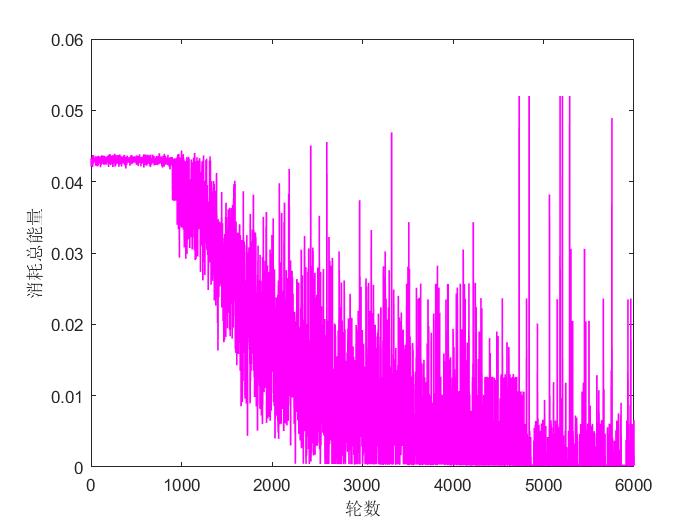
图3 系统剩余总能量与轮数的关系
代码如下:
%% 清空环境变量
close all;
clear;
clc;
%% % 网络建立参数
%% 网络参数
xm = 100;
ym = 100; % 区域范围
n = 100; % 节点总个数
sinkx = 50;
sinky = 50; % 基站位置
p = 0.2; % 簇头选择概率
%% 能量参数
Eo = 1; % 初始能量(单位:焦耳J)
% 所需的能量(发射器和接收器)
Eelec = 50*10^(-9);
Efs = 10*10^(-12);
Eamp = 0.0015*10^(-12);
d0 = sqrt(Efs/Eamp);
EDA = 5*10^(-9); % 数据聚合能量
packetLength = 4000; % 数据包大小
ctrPacketLength = 100; % 控制数据包大小
rmax = 7000; % 最大循环轮数
%% % Creation of the Wireless Sensor Network
%% 画出WSN
figure
for i = 1:n
Node(i).id = i; % 节点的ID
Node(i).x = rand(1,1)*xm; % 节点X坐标
Node(i).y = rand(1,1)*ym; % 节点Y坐标
Node(i).E = Eo; % 节点当前能量 (初始值为Eo)
Node(i).cond = 1; % 节点的当前状态:存活 1;死亡 0
Node(i).dts = sqrt((Node(i).x-sinkx)^2+(Node(i).y-sinky)^2); % 节点到基站的距离
Node(i).role = 0; % 节点的角色:普通节点 0;簇头节点 1
Node(i).CH = 0; % 簇头节点:-1 自己是簇头
Node(i).G = 0; % 候选集标志
plot(Node(i).x, Node(i).y, 'ob', sinkx, sinky, '*r');
hold on;
title 'Wireless Sensor Network';
xlabel '(m)';
ylabel '(m)';
X(i, :) = [Node(i).x, Node(i).y];
end
alive = zeros(rmax, 1); % 每轮存活节点数
re = zeros(rmax, 1); % 每轮节点总能量
ce = zeros(rmax, 1); % 每轮节点消耗总能量
%% % 迭代
for r = 1:rmax
if mod(r, round(1/p)) == 0
for i = 1:n
Node(i).G=0;
end
end
for i = 1:n
if Node(i).cond ~= 0
Node(i).type = 'N';
Node(i).role = 0;
re(r) = re(r)+Node(i).E;
alive(r) = alive(r)+1;
end
end
f = 0;
if alive(r) == 0
break;
end
%% 簇头选举
k = 0; % 质心个数
% 确定质心个数
for i = 1:n
if Node(i).role == 0 && Node(i).cond ~= 0
temp_rand = rand;
if Node(i).G <= 0 && temp_rand < p/(1-p*mod(r,round(1/p)))
k = k + 1;
Node(i).G = 1;
end
end
end
%%% k-means聚类
center = zeros(k, 2);
Idx = zeros(n, 1);
% 随机选择k个质心
for i = 1:k
center(i, :) = rand(1, 2)*xm;
end
while 1
distance = zeros(1, k); % 最小距离矩阵
num = zeros(1, k); % 聚类簇数矩阵
new_center = zeros(k, 2); % 聚类中心矩阵
for i = 1:n
for j = 1:k
distance(j) = norm(X(i, :)-center(j, :)); % 计算到每个簇的距离
end
[~, min_index] = min(distance); % 求最小的距离
Idx(i) = min_index; % 划分所有对象点到最近的聚类中心
end
q = 0;
for i = 1:k
for j = 1:n
if Idx(j) == i
new_center(i, :) = new_center(i, :)+X(j, :);
num(i) = num(i)+1;
end
end
if num(i) > 0
new_center(i, :) = new_center(i, :)/num(i); % 求均值,即新的聚类中心
else
new_center(i, :) = center(i, :);
end
if norm(new_center(i, :)-center(i, :)) < 0.1 % 检查集群中心是否已收敛。如果是则终止。
q = q+1;
end
end
if q >= k
break;
else
center = new_center;
end
end
% figure;
% plot(sinkx, sinky, 'rp', 'MarkerSize', 14)
% hold on
% plot(center(:, 1), center(:, 2), 'kx', 'MarkerSize', 14, 'LineWidth', 4)
% hold on
% plot(X(Idx==1,1),X(Idx==1,2),'r.','MarkerSize',14)
% hold on
% plot(X(Idx==2,1),X(Idx==2,2),'b.','MarkerSize',14)
% hold on
% plot(X(Idx==3,1),X(Idx==3,2),'g.','MarkerSize',14)
% hold on
% plot(X(Idx==4,1),X(Idx==4,2),'k.','MarkerSize',14)
% hold on
% plot(X(Idx==5,1),X(Idx==5,2),'y.','MarkerSize',14)
% hold on
% plot(X(Idx==6,1),X(Idx==6,2),'c.','MarkerSize',14)
% hold on
% plot(X(Idx==7,1),X(Idx==7,2),'m.','MarkerSize',14)
% hold on
% 找出离质心最近的节点作为簇头
if k ~= 0
for i = 1:k
len = sqrt((X(Idx==i, 1)-center(i, 1)).^2+(X(Idx==i, 2)-center(i, 2)).^2);
if ~isempty(len)
[~, min_index] = min(len);
count = 0;
for j = 1:n
if Idx(j) == i
count = count + 1;
end
if count == min_index
min_index = j;
break;
end
end
if Node(min_index).E > 0
Node(min_index).role = 1;
Node(min_index).CH = -1;
% 簇头广播
distanceBroad = sqrt(xm*xm+ym*ym);
if distanceBroad > d0
Node(min_index).E = Node(min_index).E- (Eelec*ctrPacketLength + Eamp*ctrPacketLength*distanceBroad^4);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength + Eamp*ctrPacketLength*distanceBroad^4;
else
Node(min_index).E = Node(min_index).E- (Eelec*ctrPacketLength + Efs*ctrPacketLength*distanceBroad^2);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength + Efs*ctrPacketLength*distanceBroad^2;
end
% 簇头自己发送数据包能量消耗
if Node(min_index).dts > d0
Node(min_index).E = Node(min_index).E- ((Eelec+EDA)*packetLength+Eamp*packetLength*Node(i).dts^4);
ce(r) = ce(r)+(Eelec+EDA)*packetLength+Eamp*packetLength*Node(i).dts^4;
else
Node(min_index).E = Node(min_index).E- ((Eelec+EDA)*packetLength+Efs*packetLength*Node(i).dts^2);
ce(r) = ce(r)+(Eelec+EDA)*packetLength+Efs*packetLength*Node(i).dts^2;
end
for j = 1:n
if Idx(j) == i && min_index ~= j
% 普通节点接收簇头发来的广播的消耗
Node(j).E = Node(j).E - Eelec*ctrPacketLength;
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength;
% 普通节点向簇头发送加入簇的控制消息,并发送数据给簇头
dist = sqrt((Node(j).x-Node(min_index).x)^2+(Node(j).y-Node(min_index).y)^2);
if dist < d0
Node(j).E = Node(j).E - (Eelec*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)+Efs*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)*dist^2);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)+Efs*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)*dist^2;
else
Node(j).E = Node(j).E - (Eelec*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)+Eamp*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)*dist^4);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)+Eamp*(ctrPacketLength+packetLength)*dist^4;
end
Node(j).CH = min_index;
% 簇头接收簇成员数据包消耗能量,接收加入消息和确认加入消息
Node(min_index).E = Node(min_index).E - (Eelec+EDA)*packetLength; %接受簇成员发来的数据包
Node(min_index).E = Node(min_index).E - Eelec*ctrPacketLength; %接收加入消息
ce(r) = ce(r)+(Eelec+EDA)*packetLength+Eelec*ctrPacketLength;
if dist > d0 % 簇头向簇成员发送确认加入的消息
Node(min_index).E = Node(min_index).E - (Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Eamp*ctrPacketLength*dist^4);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Eamp*ctrPacketLength*dist^4;
else
Node(min_index).E = Node(min_index).E - (Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Efs*ctrPacketLength*dist^2);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Efs*ctrPacketLength*dist^2;
end
end
end
else % 此质心所在的簇成员直接发送数据包到基站
for j = 1:n
if Node(j).E > 0
if Idx(j) == i && min_index ~= j
if Node(j).dts > d0 % 簇头向簇成员发送确认加入的消息
Node(j).E = Node(j).E - (Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Eamp*ctrPacketLength*Node(j).dts^4);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Eamp*ctrPacketLength*Node(j).dts^4;
else
Node(j).E = Node(j).E - (Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Efs*ctrPacketLength*Node(j).dts^2);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Efs*ctrPacketLength*Node(j).dts^2;
end
end
end
end
end
end
end
else % 无质心,直接发送数据包到基站
for i = 1:n
if Node(i).E > 0
if Node(j).dts > d0 % 簇头向簇成员发送确认加入的消息
Node(j).E = Node(j).E - (Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Eamp*ctrPacketLength*Node(j).dts^4);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Eamp*ctrPacketLength*Node(j).dts^4;
else
Node(j).E = Node(j).E - (Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Efs*ctrPacketLength*Node(j).dts^2);
ce(r) = ce(r)+Eelec*ctrPacketLength+Efs*ctrPacketLength*Node(j).dts^2;
end
end
end
end
% % 画出分簇图
% figure;
% for i = 1:n
% if Node(i).role == 1
% plot(Node(i).x, Node(i).y, '*');
% hold on
% else
% plot(Node(i).x, Node(i).y, 'o');
% hold on
% plot([Node(Node(i).CH).x; Node(i).x], [Node(Node(i).CH).y; Node(i).y]);
% hold on
% end
% end
for i = 1:n
if Node(i).E <= 0
Node(i).cond = 0;
end
end
end
%% 绘图显示
figure;
plot(1:rmax, alive, 'r', 'LineWidth', 2);
xlabel '轮数'; ylabel '存活节点数';
figure;
plot(1:rmax, re, 'b', 'LineWidth', 2);
xlabel '轮数'; ylabel '剩余总能量';
figure;
plot(1:rmax, ce, 'm', 'LineWidth', 1);
xlabel '轮数'; ylabel '消耗总能量';
三、参考文献
[1] 王家深. 无线传感器路由协议优化研究[D].海南大学,2019.
[2] nineships. K-means算法的matlab实现. CSDN博客.
以上是关于基于K-means聚类算法实现无线传感器网络分簇路由协议的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章