多线程学习 线程通信
Posted *^O^*—*^O^*
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了多线程学习 线程通信相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
线程通信
多线程执行程序代码指令,表现为并发并行,如果涉及共享变量的操作,使用加锁保证线程安全,保证线程是一个一个依次执行,但不保证线程的执行顺序
线程通信,就是让线程等待,或者通知等待线程恢复,让多个线程之间满足一定的执行
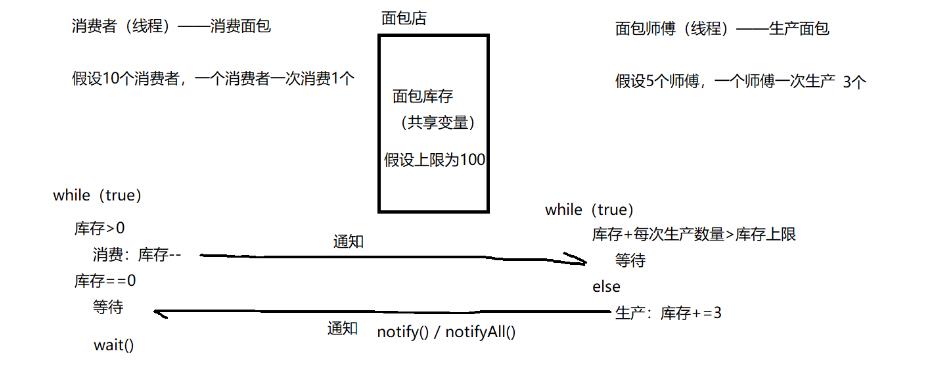
示例:生产者和消费者模型

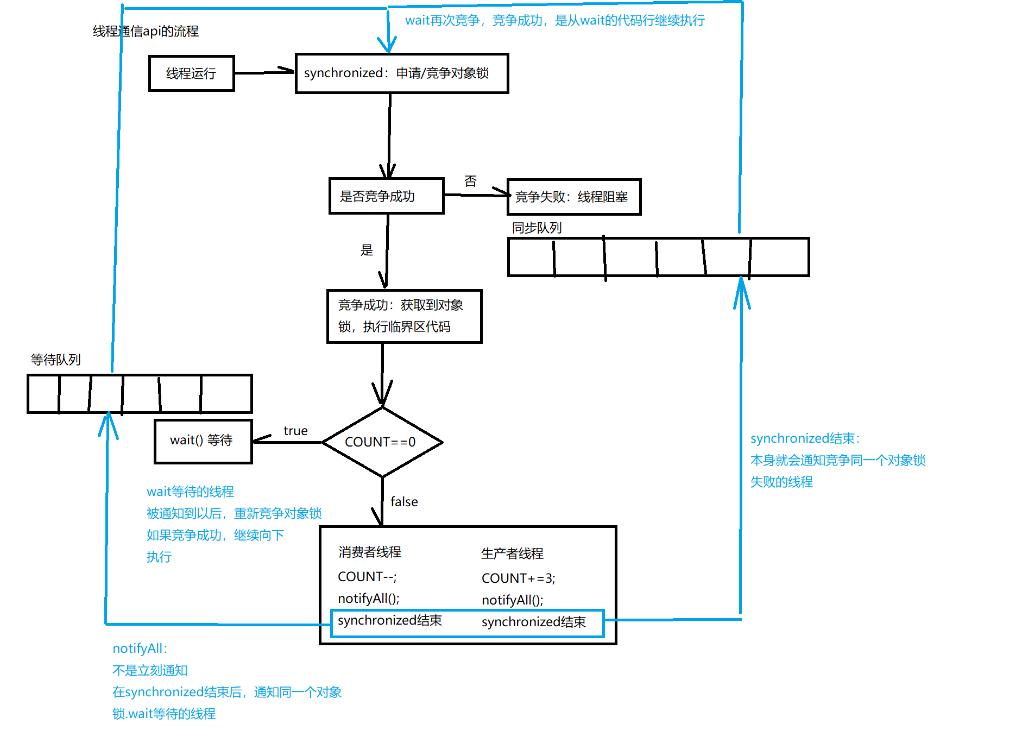
当前线程(运行态,以获取对象锁),调用wait马上释放对象锁,等待其他线程调用notify/notifyAll会再次竞争对象锁
//10个消费着,不停的消费,每次每个消费1个
//5个生产者。不停的生产,每次每个生产3个
//库存上限100
public class BreadShop {
private static int COUNT;
public static void main(String[] args){
for (int i =0;i<10;i++){
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true){
//消费着之间,消费者和生产者之间们都是用库存(共享变量)
synchronized (BreadShop.class){
while(COUNT==0) BreadShop.class.wait();
COUNT--;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"消费,库存"+COUNT);
BreadShop.class.notifyAll();
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"消费者["+i+"]").start();
}
for (int i =0;i<5;i++){
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while (true){
//消费着之间,消费者和生产者之间们都是用库存(共享变量)
synchronized (BreadShop.class){
while(COUNT+3>100) BreadShop.class.wait();
COUNT+=3;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"生产,库存"+COUNT);
BreadShop.class.notifyAll();
}
Thread.sleep(1000);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"生产者["+i+"]").start();
}
}
}
阻塞队列
生产者消费模型,基于阻塞队列来实现,可以解耦
消费者:不用关心生产者如何生产,只需要从阻塞队列,取任务,来执行
生产者:不用关心消费者如何消费,只需要把任务提交到阻塞队列
public class MyBlockingQueue<E> {
private Object[] elements;//循环数组的方式
private int putIndex;//存放元素的索引
private int takeIndex;//取元素的索引
private int size;//存放的元素数量
public MyBlockingQueue(int capacity){//容量
elements = new Object[capacity];
}
//存放元素
public synchronized void put(E e){
try {
while(size==elements.length)
wait();
elements[putIndex] = e;
size++;
//循环数组的方式,存取的索引需要考虑超过数组长度的情况
putIndex = (putIndex+1) % elements.length;
notifyAll();
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
ie.printStackTrace();
}
}
//取元素
public synchronized E take(){
try {
while (size == 0) wait();
E e = (E) elements[takeIndex];
size--;
takeIndex = (takeIndex+1) % elements.length;
notifyAll();
return e;
} catch (InterruptedException ie) {
ie.printStackTrace();
throw new RuntimeException("被中断了", ie);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyBlockingQueue<Integer> queue = new MyBlockingQueue<>(10);
//生产者存放元素
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while(true) {
queue.put(3);
System.out.println("生产了3个面包");
Thread.sleep(300);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
//消费者取元素
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
new Thread(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
while(true) {
Integer n = queue.take();
System.out.println("消费了" + n + "个面包");
Thread.sleep(300);
}
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}).start();
}
}
}
以上是关于多线程学习 线程通信的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章