common clk framework
Posted Linux学习之路
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了common clk framework相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
文章目录
1. 概述
2. mux、gate、divider注册过程分析
内核将硬件上的gate\\mux\\divider都抽象成一个时钟结构,它们既是时钟的消费者(root clk除外),也是时钟的生产者,软件上用父子关系来描述它们之间的联系,这也就是为什么将一个时钟注册进内核时,比如要指明它父时钟名字的原因。
include/linux/clk-provider.h 中定义了 common clk framework 的时钟注册API,这里以 Mux、gate、divider为例,分析注册过程
clk_hw_register_mux
struct clk_hw *clk_hw_register_mux(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char * const *parent_names, u8 num_parents,
unsigned long flags,
void __iomem *reg, u8 shift, u8 width,
u8 clk_mux_flags, spinlock_t *lock)
{
u32 mask = BIT(width) - 1;
return clk_hw_register_mux_table(dev, name, parent_names, num_parents,
flags, reg, shift, mask, clk_mux_flags,
NULL, lock);
}
对于一个 mux ,它最重要的参数就是父时钟的信息,因此需要提供父时钟的名字以及个数,同时,当设置父时钟时,内核还需要设置soc的寄存器,那么参数中就需要寄存器地址、偏移值等信息。
clk_hw_register_mux_table
struct clk_hw *clk_hw_register_mux_table(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char * const *parent_names, u8 num_parents,
unsigned long flags,
void __iomem *reg, u8 shift, u32 mask,
u8 clk_mux_flags, u32 *table, spinlock_t *lock)
{
struct clk_mux *mux;
struct clk_hw *hw;
struct clk_init_data init;
u8 width = 0;
int ret;
/* allocate the mux */
mux = kzalloc(sizeof(*mux), GFP_KERNEL);
/* 填充 clk_init_data 放入 clk_hw */
init.name = name;
if (clk_mux_flags & CLK_MUX_READ_ONLY)
init.ops = &clk_mux_ro_ops;
else
init.ops = &clk_mux_ops;
init.flags = flags | CLK_IS_BASIC;
init.parent_names = parent_names;
init.num_parents = num_parents;
/* mux操作需要的寄存器参数 */
mux->reg = reg;
mux->shift = shift;
mux->mask = mask;
mux->flags = clk_mux_flags;
mux->lock = lock;
mux->table = table;
mux->hw.init = &init;
hw = &mux->hw;
/* 注册 clk_hw 稍后分析 */
ret = clk_hw_register(dev, hw);
return hw;
}
值得注意的是:clk_mux_ops
const struct clk_ops clk_mux_ops = {
.get_parent = clk_mux_get_parent,
.set_parent = clk_mux_set_parent,
.determine_rate = __clk_mux_determine_rate,
};
clk_mux_get_parent读寄存器获取当前的父时钟返回索引
static u8 clk_mux_get_parent(struct clk_hw *hw)
{
struct clk_mux *mux = to_clk_mux(hw);
int num_parents = clk_hw_get_num_parents(hw);
u32 val;
/*
* FIXME need a mux-specific flag to determine if val is bitwise or numeric
* e.g. sys_clkin_ck's clksel field is 3 bits wide, but ranges from 0x1
* to 0x7 (index starts at one)
* OTOH, pmd_trace_clk_mux_ck uses a separate bit for each clock, so
* val = 0x4 really means "bit 2, index starts at bit 0"
*/
val = clk_readl(mux->reg) >> mux->shift;
val &= mux->mask;
if (mux->table) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < num_parents; i++)
if (mux->table[i] == val)
return i;
return -EINVAL;
}
if (val && (mux->flags & CLK_MUX_INDEX_BIT))
val = ffs(val) - 1;
if (val && (mux->flags & CLK_MUX_INDEX_ONE))
val--;
if (val >= num_parents)
return -EINVAL;
return val;
}
clk_mux_set_parent与clk_mux_get_parent相反
static int clk_mux_set_parent(struct clk_hw *hw, u8 index)
{
struct clk_mux *mux = to_clk_mux(hw);
u32 val;
unsigned long flags = 0;
if (mux->table) {
index = mux->table[index];
} else {
if (mux->flags & CLK_MUX_INDEX_BIT)
index = 1 << index;
if (mux->flags & CLK_MUX_INDEX_ONE)
index++;
}
if (mux->lock)
spin_lock_irqsave(mux->lock, flags);
else
__acquire(mux->lock);
if (mux->flags & CLK_MUX_HIWORD_MASK) {
val = mux->mask << (mux->shift + 16);
} else {
val = clk_readl(mux->reg);
val &= ~(mux->mask << mux->shift);
}
val |= index << mux->shift;
clk_writel(val, mux->reg);
if (mux->lock)
spin_unlock_irqrestore(mux->lock, flags);
else
__release(mux->lock);
return 0;
}
__clk_mux_determine_rate 针对给出的时钟频率,找到最优的父时钟索引
/*
* Helper for finding best parent to provide a given frequency. This can be used
* directly as a determine_rate callback (e.g. for a mux), or from a more
* complex clock that may combine a mux with other operations.
*/
int __clk_mux_determine_rate(struct clk_hw *hw,
struct clk_rate_request *req)
{
return clk_mux_determine_rate_flags(hw, req, 0);
}
如果hw->core->flags指定了CLK_SET_RATE_NO_REPARENT,那么就使用当前的父时钟计算出一个最接近的clk频率
如果没有指定,那么就使用所有的父时钟都计算一遍,挑一个最优的父时钟,得到一个最优的clk频率
static int
clk_mux_determine_rate_flags(struct clk_hw *hw, struct clk_rate_request *req,
unsigned long flags)
{
struct clk_core *core = hw->core, *parent, *best_parent = NULL;
int i, num_parents, ret;
unsigned long best = 0;
struct clk_rate_request parent_req = *req;
/* if NO_REPARENT flag set, pass through to current parent */
if (core->flags & CLK_SET_RATE_NO_REPARENT) {
parent = core->parent;
if (core->flags & CLK_SET_RATE_PARENT) {
ret = __clk_determine_rate(parent ? parent->hw : NULL,
&parent_req);
if (ret)
return ret;
best = parent_req.rate;
} else if (parent) {
best = clk_core_get_rate_nolock(parent);
} else {
best = clk_core_get_rate_nolock(core);
}
goto out;
}
/* find the parent that can provide the fastest rate <= rate */
num_parents = core->num_parents;
for (i = 0; i < num_parents; i++) {
parent = clk_core_get_parent_by_index(core, i);
if (!parent)
continue;
if (core->flags & CLK_SET_RATE_PARENT) {
parent_req = *req;
ret = __clk_determine_rate(parent->hw, &parent_req);
if (ret)
continue;
} else {
parent_req.rate = clk_core_get_rate_nolock(parent);
}
if (mux_is_better_rate(req->rate, parent_req.rate,
best, flags)) {
best_parent = parent;
best = parent_req.rate;
}
}
if (!best_parent)
return -EINVAL;
out:
if (best_parent)
req->best_parent_hw = best_parent->hw;
req->best_parent_rate = best;
req->rate = best;
return 0;
}
clk_hw_register_gate
/**
* clk_hw_register_gate - register a gate clock with the clock framework
* @dev: device that is registering this clock
* @name: name of this clock
* @parent_name: name of this clock's parent
* @flags: framework-specific flags for this clock
* @reg: register address to control gating of this clock
* @bit_idx: which bit in the register controls gating of this clock
* @clk_gate_flags: gate-specific flags for this clock
* @lock: shared register lock for this clock
*/
struct clk_hw *clk_hw_register_gate(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char *parent_name, unsigned long flags,
void __iomem *reg, u8 bit_idx,
u8 clk_gate_flags, spinlock_t *lock)
{
struct clk_gate *gate;
struct clk_hw *hw;
struct clk_init_data init;
int ret;
/* allocate the gate */
gate = kzalloc(sizeof(*gate), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!gate)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
init.name = name;
init.ops = &clk_gate_ops;
init.flags = flags | CLK_IS_BASIC;
init.parent_names = parent_name ? &parent_name : NULL;
init.num_parents = parent_name ? 1 : 0;
/* struct clk_gate assignments */
gate->reg = reg;
gate->bit_idx = bit_idx;
gate->flags = clk_gate_flags;
gate->lock = lock;
gate->hw.init = &init;
hw = &gate->hw;
ret = clk_hw_register(dev, hw);
if (ret) {
kfree(gate);
hw = ERR_PTR(ret);
}
return hw;
}
与前面mux的注册过程如出一辙,值得注意的是clk_gate_ops
clk_gate_ops
const struct clk_ops clk_gate_ops = {
.enable = clk_gate_enable,
.disable = clk_gate_disable,
.is_enabled = clk_gate_is_enabled,
};
在使用时钟时,我们经常用 clk_enable 操作,其实就是对这个 gate 进行控制,具体如何控制的还得分析代码
static int clk_gate_enable(struct clk_hw *hw)
{
clk_gate_endisable(hw, 1);
return 0;
}
static void clk_gate_disable(struct clk_hw *hw)
{
clk_gate_endisable(hw, 0);
}
static void clk_gate_endisable(struct clk_hw *hw, int enable)
{
struct clk_gate *gate = to_clk_gate(hw);
int set = gate->flags & CLK_GATE_SET_TO_DISABLE ? 1 : 0;
unsigned long uninitialized_var(flags);
u32 reg;
set ^= enable;
if (gate->lock)
spin_lock_irqsave(gate->lock, flags);
else
__acquire(gate->lock);
if (gate->flags & CLK_GATE_HIWORD_MASK) {
reg = BIT(gate->bit_idx + 16);
if (set)
reg |= BIT(gate->bit_idx);
} else {
reg = clk_readl(gate->reg);
if (set)
reg |= BIT(gate->bit_idx);
else
reg &= ~BIT(gate->bit_idx);
}
clk_writel(reg, gate->reg);
if (gate->lock)
spin_unlock_irqrestore(gate->lock, flags);
else
__release(gate->lock);
}
还是具体的操作 gate 相关寄存器,但是这不是一个完成的 clk_enable 过程,后面分析 clk_enable 时再论
clk_hw_register_divider
/**
* clk_hw_register_divider - register a divider clock with the clock framework
* @dev: device registering this clock
* @name: name of this clock
* @parent_name: name of clock's parent
* @flags: framework-specific flags
* @reg: register address to adjust divider
* @shift: number of bits to shift the bitfield
* @width: width of the bitfield
* @clk_divider_flags: divider-specific flags for this clock
* @lock: shared register lock for this clock
*/
struct clk_hw *clk_hw_register_divider(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char *parent_name, unsigned long flags,
void __iomem *reg, u8 shift, u8 width,
u8 clk_divider_flags, spinlock_t *lock)
{
return _register_divider(dev, name, parent_name, flags, reg, shift,
width, clk_divider_flags, NULL, lock);
}
static struct clk_hw *_register_divider(struct device *dev, const char *name,
const char *parent_name, unsigned long flags,
void __iomem *reg, u8 shift, u8 width,
u8 clk_divider_flags, const struct clk_div_table *table,
spinlock_t *lock)
{
struct clk_divider *div;
struct clk_hw *hw;
struct clk_init_data init;
int ret;
/* allocate the divider */
div = kzalloc(sizeof(*div), GFP_KERNEL);
init.name = name;
if (clk_divider_flags & CLK_DIVIDER_READ_ONLY)
init.ops = &clk_divider_ro_ops;
else
init.ops = &clk_divider_ops;
init.flags = flags | CLK_IS_BASIC;
init.parent_names = (parent_name ? &parent_name: NULL);
init.num_parents = (parent_name ? 1 : 0);
/* struct clk_divider assignments */
div->reg = reg;
div->shift = shift;
div->width = width;
div->flags = clk_divider_flags;
div->lock = lock;
div->hw.init = &init;
div->table = table;
/* register the clock */
hw = &div->hw;
ret = clk_hw_register(dev, hw);
return hw;
}
值得注意的是 clk_divider_ops
clk_divider_ops
const struct clk_ops clk_divider_ops = {
.recalc_rate = clk_divider_recalc_rate,
.round_rate = clk_divider_round_rate,
.set_rate = clk_divider_set_rate,
};
clk_divider_recalc_rate
重新起算当前时钟的频率
clk_divider_round_rate
根据父时钟以及request_rate返回一个最接近的时钟频率
clk_divider_set_rate
设置时钟频率
clk_register
struct clk *clk_register(struct device *dev, struct clk_hw *hw)
{
int i, ret;
struct clk_core *core;
core = kzalloc(sizeof(*core), GFP_KERNEL);
core->name = kstrdup_const(hw->init->name, GFP_KERNEL);
core->ops = hw->init->ops;
if (dev && pm_runtime_enabled(dev))
core->dev = dev;
if (dev && dev->driver)
core->owner = dev->driver->owner;
core->hw = hw;
core->flags = hw->init->flags;
core->num_parents = hw->init->num_parents;
core->min_rate = 0;
core->max_rate = ULONG_MAX;
hw->core = core;
/* allocate local copy in case parent_names is __initdata */
core->parent_names = kcalloc(core->num_parents, sizeof(char *),GFP_KERNEL);
/* copy each string name in case parent_names is __initdata */
for (i = 0; i < core->num_parents; i++) {
core->parent_names[i] = kstrdup_const(hw->init->parent_names[i],
GFP_KERNEL);
if (!core->parent_names[i]) {
ret = -ENOMEM;
goto fail_parent_names_copy;
}
}
/* avoid unnecessary string look-ups of clk_core's possible parents. */
core->parents = kcalloc(core->num_parents, sizeof(*core->parents), GFP_KERNEL);
INIT_HLIST_HEAD(&core->clks);
hw->clk = __clk_create_clk(hw, NULL, NULL);
ret = __clk_core_init(core);
if (!ret)
return hw->clk;
主要工作用前面填充的 clk_init_data 来初始化 clk_core
struct clk_core *core;
- core->name = kstrdup_const(hw->init->name, GFP_KERNEL);
- core->ops = hw->init->ops;
- core->hw = hw;
- core->flags = hw->init->flags;
- core->num_parents = hw->init->num_parents;
- core->min_rate = 0;
- core->max_rate = ULONG_MAX;
- core->parent_names = hw->init->parent_names;
- core->parents 分配内存
- __clk_create_clk
- __clk_core_init
__clk_create_clk 分配一个clk结构挂入clk_core的clks链表
struct clk *__clk_create_clk(struct clk_hw *hw, const char *dev_id,
const char *con_id)
{
struct clk *clk;
/* This is to allow this function to be chained to others */
if (IS_ERR_OR_NULL(hw))
return ERR_CAST(hw);
clk = kzalloc(sizeof(*clk), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!clk)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
clk->core = hw->core;
clk->dev_id = dev_id;//null
clk->con_id = kstrdup_const(con_id, GFP_KERNEL);//null
clk->max_rate = ULONG_MAX;
clk_prepare_lock();
hlist_add_head(&clk->clks_node, &hw->core->clks);
clk_prepare_unlock();
return clk;
}
全局链表
static HLIST_HEAD(clk_root_list);
static HLIST_HEAD(clk_orphan_list);
static LIST_HEAD(clk_notifier_list);
__clk_core_init
static int __clk_core_init(struct clk_core *core)
{
int i, ret;
struct clk_core *orphan;
struct hlist_node *tmp2;
unsigned long rate;
if (!core)
return -EINVAL;
clk_prepare_lock();
ret = clk_pm_runtime_get(core);
if (ret)
goto unlock;
/* 1. 从 clk_root_list 和 clk_orphan_list 查找是否有同名的clk */
if (clk_core_lookup(core->name)) {
pr_debug("%s: clk %s already initialized\\n", __func__, core->name);
ret = -EEXIST;
goto out;
}
/* 2. 对 ops 进行必要的检查 */
if (core->ops->set_rate &&
!((core->ops->round_rate || core->ops->determine_rate) &&
core->ops->recalc_rate)) {
pr_err("%s: %s must implement .round_rate or .determine_rate in addition to .recalc_rate\\n",
__func__, core->name);
ret = -EINVAL;
goto out;
}
if (core->ops->set_parent && !core->ops->get_parent) {
pr_err("%s: %s must implement .get_parent & .set_parent\\n",
__func__, core->name);
ret = -EINVAL;
goto out;
}
if (core->num_parents > 1 && !core->ops->get_parent) {
pr_err("%s: %s must implement .get_parent as it has multi parents\\n",
__func__, core->name);
ret = -EINVAL;
goto out;
}
if (core->ops->set_rate_and_parent &&
!(core->ops->set_parent && core->ops->set_rate)) {
pr_err("%s: %s must implement .set_parent & .set_rate\\n",
__func__, core->name);
ret = -EINVAL;
goto out;
}
/* throw a WARN if any entries in parent_names are NULL */
for (i = 0; i < core->num_parents; i++)
WARN(!core->parent_names[i],
"%s: invalid NULL in %s's .parent_names\\n",
__func__, core->name);
/* 3. 从clk_root_list 和 clk_orphan_list 查找当前的 parent clk_core */
core->parent = __clk_init_parent(core);
/* 4. 根据 parent 不同的状态进行分别处理 */
if (core->parent) {//如果parent已经被初始化过了,把core挂入parent->children链表
hlist_add_head(&core->child_node,
&core->parent->children);
core->orphan = core->parent->orphan;
} else if (!core->num_parents) {//如果parent没被初始化过且没有父时钟,挂入clk_root_list
hlist_add_head(&core->child_node, &clk_root_list);
core->orphan = false;
} else {//parent没被初始化过,且有Parent,挂入clk_orphan_list
hlist_add_head(&core->child_node, &clk_orphan_list);
core->orphan = true;
}
/*
* Set clk's accuracy. The preferred method is to use
* .recalc_accuracy. For simple clocks and lazy developers the default
* fallback is to use the parent's accuracy. If a clock doesn't have a
* parent (or is orphaned) then accuracy is set to zero (perfect
* clock).
*/
if (core->ops->recalc_accuracy)
core->accuracy = core->ops->recalc_accuracy(core->hw,
__clk_get_accuracy(core->parent));
else if (core->parent)
core->accuracy = core->parent->accuracy;
else
core->accuracy = 0;
/*
* Set clk's phase.
* Since a phase is by definition relative to its parent, just
* query the current clock phase, or just assume it's in phase.
*/
if (core->ops->get_phase)
core->phase = core->ops->get_phase(core->hw);
else
core->phase = 0;
/* 5. 计算时钟频率 */
/*
* Set clk's rate. The preferred method is to use .recalc_rate. For
* simple clocks and lazy developers the default fallback is to use the
* parent's rate. If a clock doesn't have a parent (or is orphaned)
* then rate is set to zero.
*/
if (core->ops->recalc_rate)
rate = core->ops->recalc_rate(core->hw,
clk_core_get_rate_nolock(core->parent));
else if (core->parent)
rate = core->parent->rate;
else
rate = 0;
core->rate = core->req_rate = rate;
/*
* Enable CLK_IS_CRITICAL clocks so newly added critical clocks
* don't get accidentally disabled when walking the orphan tree and
* reparenting clocks
*/
if (core->flags & CLK_IS_CRITICAL) {
unsigned long flags;
clk_core_prepare(core);
flags = clk_enable_lock();
clk_core_enable(core);
clk_enable_unlock(flags);
}
/* 6. 遍历孤儿时钟树查找新的父子关系 */
/*
* walk the list of orphan clocks and reparent any that newly finds a
* parent.
*/
hlist_for_each_entry_safe(orphan, tmp2, &clk_orphan_list, child_node) {
struct clk_core *parent = __clk_init_parent(orphan);
/*
* We need to use __clk_set_parent_before() and _after() to
* to properly migrate any prepare/enable count of the orphan
* clock. This is important for CLK_IS_CRITICAL clocks, which
* are enabled during init but might not have a parent yet.
*/
if (parent) {
/* update the clk tree topology */
__clk_set_parent_before(orphan, parent);
__clk_set_parent_after(orphan, parent, NULL);
__clk_recalc_accuracies(orphan);
__clk_recalc_rates(orphan, 0);
}
}
/*
* optional platform-specific magic
*
* The .init callback is not used by any of the basic clock types, but
* exists for weird hardware that must perform initialization magic.
* Please consider other ways of solving initialization problems before
* using this callback, as its use is discouraged.
*/
if (core->ops->init)
core->ops->init(core->hw);
kref_init(&core->ref);
out:
clk_pm_runtime_put(core);
unlock:
clk_prepare_unlock();
if (!ret)
clk_debug_register(core);
return ret;
}
__clk_init_parent
static struct clk_core *__clk_init_parent(struct clk_core *core)
{
u8 index = 0;
if (core->num_parents > 1 && core->ops->get_parent)
index = core->ops->get_parent(core->hw);//clk_mux_get_parent 读寄存器,查找目前的 parent
return clk_core_get_parent_by_index(core, index);
}
3. 4412 audio clk 的注册过程
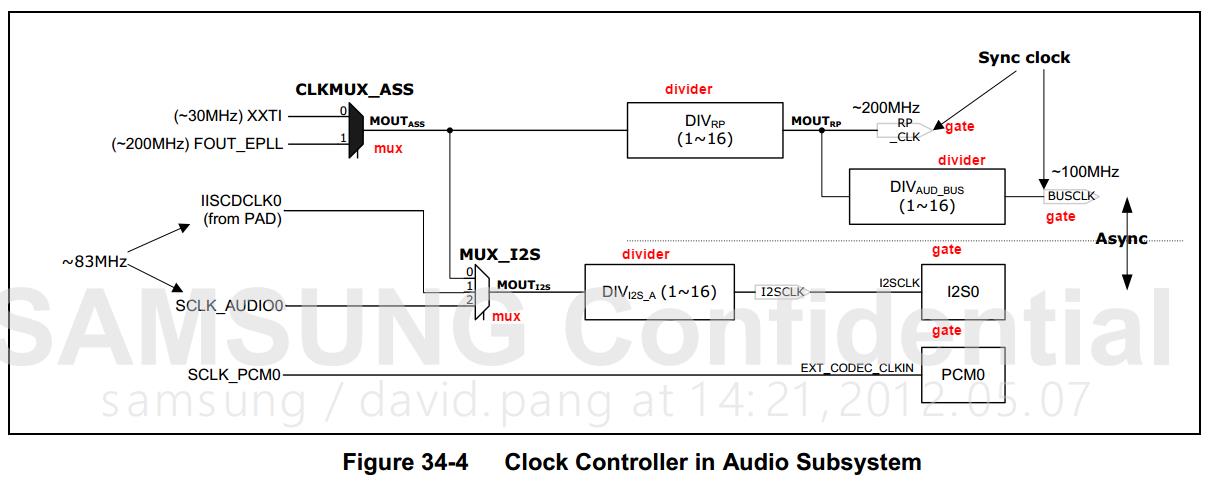
设备树
clock_audss: clock-controller@3810000 {
compatible = "samsung,exynos4210-audss-clock";
reg = <0x03810000 0x0C>;
#clock-cells = <1>;
clocks = <&clock CLK_FIN_PLL>, <&clock CLK_FOUT_EPLL>,
<&clock CLK_SCLK_AUDIO0>, <&clock CLK_SCLK_AUDIO0>;
clock-names = "pll_ref", "pll_in", "sclk_audio", "sclk_pcm_in";
};
4412 audio部分的时钟被单独抽取出来作为一个 clk_provider 注册进内核,这部分的内容比较少,比较适合分析学习,下面的代码就是将上图中的gate\\mux\\divider分别注册进内核
对应的驱动代码
clk_table[EXYNOS_MOUT_AUDSS] = clk_hw_register_mux(dev, "mout_audss",
mout_audss_p, ARRAY_SIZE(mout_audss_p),
CLK_SET_RATE_NO_REPARENT | CLK_SET_RATE_PARENT,
reg_base + ASS_CLK_SRC, 0, 1, 0, &lock);
cdclk = devm_clk_get(dev, "cdclk");
sclk_audio = devm_clk_get(dev, "sclk_audio");
if (!IS_ERR(cdclk))
mout_i2s_p[1] = __clk_get_name(cdclk);
if (!IS_ERR(sclk_audio))
mout_i2s_p[2] = __clk_get_name(sclk_audio);
clk_table[EXYNOS_MOUT_I2S] = clk_hw_register_mux(dev, "mout_i2s",
mout_i2s_p, ARRAY_SIZE(mout_i2s_p),
CLK_SET_RATE_NO_REPARENT,
reg_base + ASS_CLK_SRC, 2, 2, 0, &lock);
clk_table[EXYNOS_DOUT_SRP] = clk_hw_register_divider(dev, "dout_srp",
"mout_audss", CLK_SET_RATE_PARENT,
reg_base + ASS_CLK_DIV, 0, 4, 0, &lock);
clk_table[EXYNOS_DOUT_AUD_BUS] = clk_hw_register_divider(dev,
"dout_aud_bus", "dout_srp", CLK_SET_RATE_PARENT,
reg_base + ASS_CLK_DIV, 4, 4, 0, &lock);
clk_table[EXYNOS_DOUT_I2S] = clk_hw_register_divider(dev, "dout_i2s",
"mout_i2s", 0, reg_base + ASS_CLK_DIV, 8, 4, 0,
&lock);
clk_table[EXYNOS_SRP_CLK] = clk_hw_register_gate(dev, "srp_clk",
"dout_srp", CLK_SET_RATE_PARENT,
reg_base + ASS_CLK_GATE, 0, 0, &lock);
clk_table[EXYNOS_I2S_BUS] = clk_hw_register_gate(dev, "i2s_bus",
"dout_aud_bus", CLK_SET_RATE_PARENT,
reg_base + ASS_CLK_GATE, 2, 0, &lock);
clk_table[EXYNOS_SCLK_I2S] = clk_hw_register_gate(dev, "sclk_i2s",
"dout_i2s", CLK_SET_RATE_PARENT,
reg_base + ASS_CLK_GATE, 3, 0, &lock);
clk_table[EXYNOS_PCM_BUS] = clk_hw_register_gate(dev, "pcm_bus",
"sclk_pcm", CLK_SET_RATE_PARENT,
reg_base + ASS_CLK_GATE, 4, 0, &lock);
for (i = 0; i < clk_data->num; i++) {
if (IS_ERR(clk_table[i])) {
dev_err(dev, "failed to register clock %d\\n", i);
ret = PTR_ERR(clk_table[i]);
goto unregister;
}
}
ret = of_clk_add_hw_provider(dev->of_node, of_clk_hw_onecell_get,
clk_data);
上述这段代码已经将 4412 audio 相关的时钟注册进内核,我们可以根据我们的需求去设置时钟路径和时钟频率,那么必须要通过代码来实现吗?比如我想让MountAss的父时钟来自Epll如何操作?其实在设备树中声明一下即可。
&clock_audss {
assigned-clocks = <&clock_audss EXYNOS_MOUT_AUDSS>,
<&clock_audss EXYNOS_MOUT_I2S>,
<&clock_audss EXYNOS_DOUT_SRP>,
<&clock_audss EXYNOS_DOUT_AUD_BUS>;
assigned-clock-parents = <&clock CLK_FOUT_EPLL>,
<&clock_audss EXYNOS_MOUT_AUDSS>;
assigned-clock-rates = <0>, <0>, <96000000>, <48000000>;
};
上述设备树中,声明了4个时钟,并且设置EXYNOS_MOUT_AUDSS的父时钟为CLK_FOUT_EPLL,EXYNOS_MOUT_I2S的父时钟为EXYNOS_MOUT_AUDSS
同时还设置了相应的时钟频率,那么这些是如何实现的?
of_clk_add_hw_provider
int of_clk_add_hw_provider(struct device_node *np,
struct clk_hw *(*get)(struct of_phandle_args *clkspec,
void *data),
void *data)
{
struct of_clk_provider *cp;
int ret;
cp = kzalloc(sizeof(*cp), GFP_KERNEL);
if (!cp)
return -ENOMEM;
cp->node = of_node_get(np);
cp->data = data;
cp->get_hw = get;
mutex_lock(&of_clk_mutex);
list_add(&cp->link, &of_clk_providers);
mutex_unlock(&of_clk_mutex);
pr_debug("Added clk_hw provider from %pOF\\n", np);
ret = of_clk_set_defaults(np, true);
if (ret < 0)
of_clk_del_provider(np);
return ret;
}
首先,它会将我们之前注册的那一堆东西填充到一个of_clk_provider中,挂入of_clk_providers链表
然后,of_clk_set_defaults 这里面就会根据设备树中的assigned-xxx的信息进行设置parents,rate
4. 时钟的使用过程分析
clk_get
在使用一个clk之前,我们首先需要获取到这个clk,使用clk_get或者devm_clk_get,在旧的内核中,我们经常将第一个参数置为NULL,现在在新的时代,已经不推荐这种用法。第一个参数置为NULL的情况下,会走clk_get_sys去一个clocks链表中寻找clk,但是我们在前面分析的注册过程中并没有涉及到这个链表,老的内核中才会将clk注册到这里。推荐的做法是指定dev,从设备树中获取。
struct clk *clk_get(struct device *dev, const char *con_id)
{
const char *dev_id = dev ? dev_name(dev) : NULL;
struct clk *clk;
if (dev) {
clk = __of_clk_get_by_name(dev->of_node, dev_id, con_id);
if (!IS_ERR(clk) || PTR_ERR(clk) == -EPROBE_DEFER)
return clk;
}
return clk_get_sys(dev_id, con_id);
}
如果 con_id 不为空的话,会从设备树中的"clock-names"属性中寻找对应的clk,如果为空,取第一个clk
static struct clk *__of_clk_get_by_name(struct device_node *np,
const char *dev_id,
const char *name)
{
struct clk *clk = ERR_PTR(-ENOENT);
/* Walk up the tree of devices looking for a clock that matches */
while (np) {
int index = 0;
/*
* For named clocks, first look up the name in the
* "clock-names" property. If it cannot be found, then
* index will be an error code, and of_clk_get() will fail.
*/
if (name)
index = of_property_match_string(np, "clock-names", name);
clk = __of_clk_get(np, index, dev_id, name);
if (!IS_ERR(clk)) {
break;
} else if (name && index >= 0) {
if (PTR_ERR(clk) != -EPROBE_DEFER)
pr_err("ERROR: could not get clock %pOF:%s(%i)\\n",
np, name ? name : "", index);
return clk;
}
/*
* No matching clock found on this node. If the parent node
* has a "clock-ranges" property, then we can try one of its
* clocks.
*/
np = np->parent;
if (np && !of_get_property(np, "clock-ranges", NULL))
break;
}
return clk;
}
不通过设备树,我们真的就没法获取到common clk framework注册的clk了吗?有一个api可以使用
struct clk *__clk_lookup(const char *name)
{
struct clk_core *core = clk_core_lookup(name);
return !core ? NULL : core->hw->clk;
}
static struct clk_core *clk_core_lookup(const char *name)
{
struct clk_core *root_clk;
struct clk_core *ret;
if (!name)
return NULL;
/* search the 'proper' clk tree first */
hlist_for_each_entry(root_clk, &clk_root_list, child_node) {
ret = __clk_lookup_subtree(name, root_clk);
if (ret)
return ret;
}
/* if not found, then search the orphan tree */
hlist_for_each_entry(root_clk, &clk_orphan_list, child_node) {
ret = __clk_lookup_subtree(name, root_clk);
if (ret)
return ret;
}
return NULL;
}
那么有没有办法将新的common clk framework和旧内核联系起来?
/**
* clk_hw_register_clkdev - register one clock lookup for a struct clk_hw
* @hw: struct clk_hw to associate with all clk_lookups
* @con_id: connection ID string on device
* @dev_id: format string describing device name
*
* con_id or dev_id may be NULL as a wildcard, just as in the rest of
* clkdev.
*
* To make things easier for mass registration, we detect error clk_hws
* from a previous clk_hw_register_*() call, and return the error code for
* those. This is to permit this function to be called immediately
* after clk_hw_register_*().
*/
int clk_hw_register_clkdev(struct clk_hw *hw, const char *con_id,
const char *dev_id)
{
struct clk_lookup *cl;
if (IS_ERR(hw))
return PTR_ERR(hw);
/*
* Since dev_id can be NULL, and NULL is handled specially, we must
* pass it as either a NULL format string, or with "%s".
*/
if (dev_id)
cl = __clk_register_clkdev(hw, con_id, "%s", dev_id);
else
cl = __clk_register_clkdev(hw, con_id, NULL);
return cl ? 0 : -ENOMEM;
}
使用这个api就可以将clk注册到clocks链表中,使用旧的方式来获取时钟了,但是有设备树的情况下,不推荐这么用
clk_enable
int clk_enable(struct clk *clk)
{
if (!clk)
return 0;
return clk_core_enable_lock(clk->core);
}
static int clk_core_enable(struct clk_core *core)
{
int ret = 0;
lockdep_assert_held(&enable_lock);
if (!core)
return 0;
if (WARN_ON(core->prepare_count == 0))
return -ESHUTDOWN;
if (core->enable_count == 0) {
ret = clk_core_enable(core->parent);
if (ret)
return ret;
trace_clk_enable_rcuidle(core);
if (core->ops->enable)
ret = core->ops->enable(core->hw);
trace_clk_enable_complete_rcuidle(core);
if (ret) {
clk_core_disable(core->parent);
return ret;
}
}
core->enable_count++;
return 0;
}
clk_core_enable(core->parent) 会递归调用,一路向上调用 core->ops->enable(core->hw),当然只有 gate 才有这个ops,可见enable时钟的过程就是打开这个clk与root clk之间所有的gate。
clk_get_rate
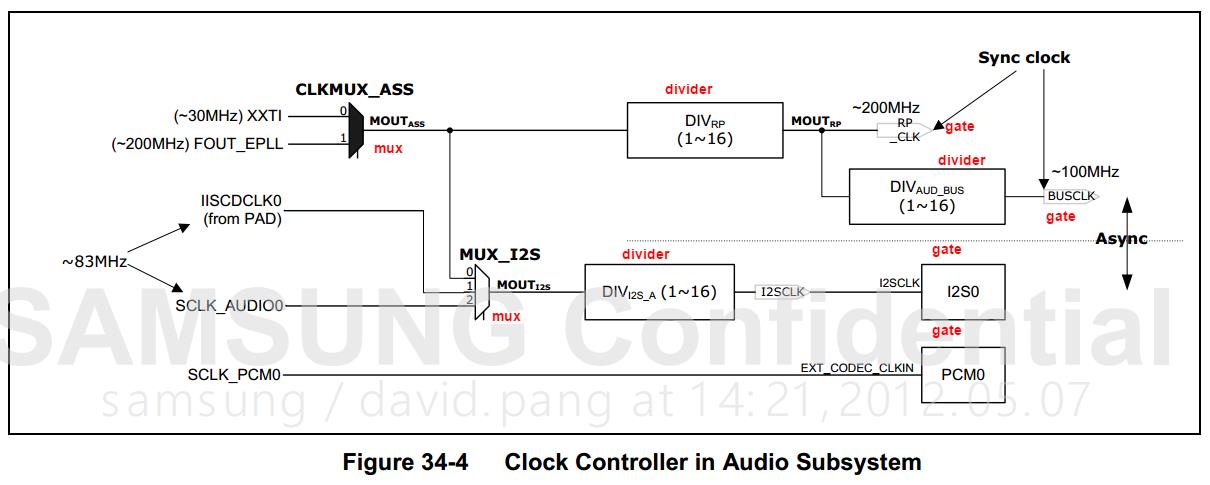
再来看看这个图,mux、gate、divider的输入时钟和输出时钟频率分别是什么呢?对于Mux和gate,输入时钟和输出时钟都等于它的父时钟频率,divider的输入时钟频率等于父时钟的频率,输出频率等于它分频之后的频率。
static unsigned long clk_core_get_rate(struct clk_core *core)
{
unsigned long rate;
clk_prepare_lock();
if (core && (core->flags & CLK_GET_RATE_NOCACHE))
__clk_recalc_rates(core, 0);
rate = clk_core_get_rate_nolock(core);
clk_prepare_unlock();
return rate;
}
clk_core_get_rate_nolock 从变量中获取,我们就不看了,来看一下它重新计算频率的过程
static void __clk_recalc_rates(struct clk_core *core, unsigned long msg)
{
unsigned long old_rate;
unsigned long parent_rate = 0;
struct clk_core *child;
lockdep_assert_held(&prepare_lock);
old_rate = core->rate;
if (core->parent)
parent_rate = core->parent->rate;
/* 传入父时钟频率,用来计算自己的频率 */
core->rate = clk_recalc(core, parent_rate);
/*
* ignore NOTIFY_STOP and NOTIFY_BAD return values for POST_RATE_CHANGE
* & ABORT_RATE_CHANGE notifiers
*/
if (core->notifier_count && msg)
__clk_notify(core, msg, old_rate, core->rate);
hlist_for_each_entry(child, &core->children, child_node)
__clk_recalc_rates(child, msg);
}
对于divider才有recalc_rate方法,其余mux gate都直接rate=parent_rate
static unsigned long clk_recalc(struct clk_core *core,
unsigned long parent_rate)
{
unsigned long rate = parent_rate;
if (core->ops->recalc_rate && !clk_pm_runtime_get(core)) {
rate = core->ops->recalc_rate(core->hw, parent_rate);
clk_pm_runtime_put(core);
}
return rate;
}
clk_set_rate
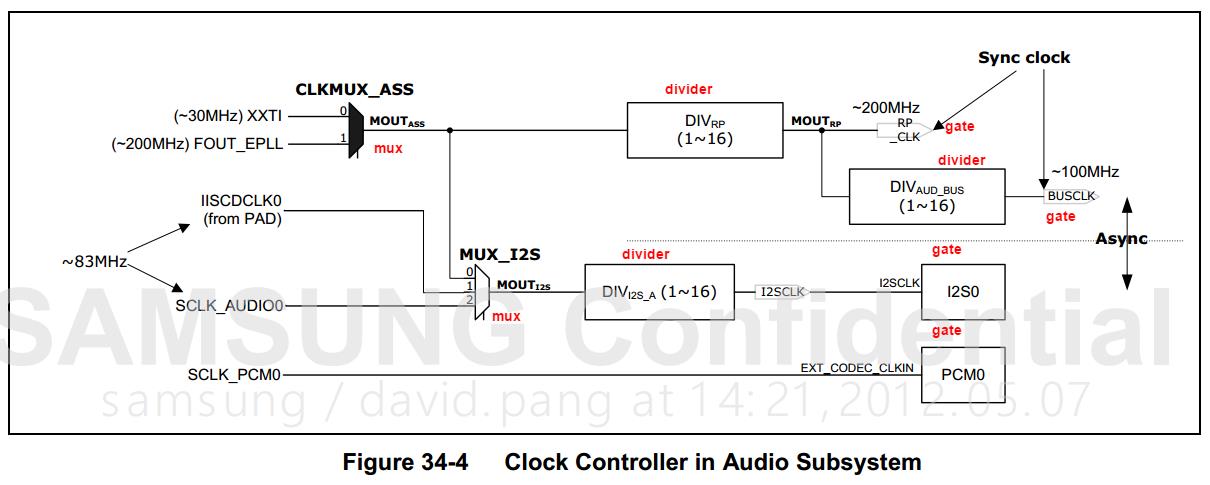
设置时钟频率是一个有意思的过程,首先来分析一下,对于gate,它的输出频率是固定的等于父时钟频率,我想设置它的频率能行吗?它自己是没法改变频率了,但是它可以考虑改变一下父时钟的频率,比如图中的I2S0它的父时钟是个divider它的时钟频率还是比较容易改变的。对于mux,它的输出时钟也是固定的,等于父时钟频率,但是它有多个父时钟,如果能行可以考虑换个父时钟
这部分的实现代码是个递归的过程,算法比较复杂,首先留意几个flag
clk_table[EXYNOS_MOUT_AUDSS] = clk_hw_register_mux(dev, "mout_audss",
mout_audss_p, ARRAY_SIZE(mout_audss_p),
CLK_SET_RATE_NO_REPARENT | CLK_SET_RATE_PARENT,
reg_base + ASS_CLK_SRC, 0, 1, 0, &lock);
clk_table[EXYNOS_MOUT_I2S] = clk_hw_register_mux(dev, "mout_i2s",
mout_i2s_p, ARRAY_SIZE(mout_i2s_p),
CLK_SET_RATE_NO_REPARENT,
reg_base + ASS_CLK_SRC, 2, 2, 0, &lock);
clk_table[EXYNOS_DOUT_SRP] = clk_hw_register_divider(dev, "dout_srp",
"mout_audss", CLK_SET_RATE_PARENT,
reg_base + ASS_CLK_DIV, 0, 4, 0, &lock);
CLK_SET_RATE_NO_REPARENT 设置时钟的时候不要重新选择父时钟(mux),默认是会去重新选择父时钟的,除非你加上这个flag禁止这样做
CLK_SET_RATE_PARENT 设置时钟的时候去改变它的父时钟(mux gate divider均可用),默认是不允许改变父时钟的,除非你加上这个flag
结合实例分析这个过程
clk_set_rate(I2S0, 67M)
clk_core_set_rate_nolock
top = clk_calc_new_rates(I2S0, 67M);
top = clk_calc_new_rates(i2sclk, 67M);
ret = core->ops->round_rate(i2sclk, 67M, &best_parent_rate); clk_divider_round_rate
ret == 96M
待测试官方的epll是不是动态的
clk_set_parent
static int clk_core_set_parent(struct clk_core *core, struct clk_core *parent)
{
int ret = 0;
int p_index = 0;
unsigned long p_rate = 0;
if (!core)
return 0;
/* prevent racing with updates to the clock topology */
clk_prepare_lock();
/* 如果要设置的父时钟与当前父时钟相同,就不需要操作了,除了mux都返回吧 */
if (core->parent == parent)
goto out;
/* 如果有多个父时钟又没有set_parent接口,出错返回 */
if ((core->num_parents > 1) && (!core->ops->set_parent)) {
ret = -ENOSYS;
goto out;
}
/* 如果这个时钟设置了 CLK_SET_PARENT_GATE 且它已经 prepare 过了出错返回 */
if ((core->flags & CLK_SET_PARENT_GATE) && core->prepare_count) {
ret = -EBUSY;
goto out;
}
/* try finding the new parent index */
if (parent) {
p_index = clk_fetch_parent_index(core, parent);
if (p_index < 0) {
pr_debug("%s: clk %s can not be parent of clk %s\\n",
__func__, parent->name, core->name);
ret = p_index;
goto out;
}
p_rate = parent->rate;
}
/* propagate PRE_RATE_CHANGE notifications */
ret = __clk_speculate_rates(core, p_rate);
/* abort if a driver objects */
if (ret & NOTIFY_STOP_MASK)
goto out;
/* 真正的设置父时钟操作 */
ret = __clk_set_parent(core, parent, p_index);
/* propagate rate an accuracy recalculation accordingly */
if (ret) {
__clk_recalc_rates(core, ABORT_RATE_CHANGE);
} else {
__clk_recalc_rates(core, POST_RATE_CHANGE);
__clk_recalc_accuracies(core);
}
out:
clk_prepare_unlock();
return ret;
}
static int __clk_set_parent(struct clk_core *core, struct clk_core *parent,
u8 p_index)
{
unsigned long flags;
int ret = 0;
struct clk_core *old_parent;
/* 1. 准备工作父子时钟的链表操作 */
old_parent = __clk_set_parent_before(core, parent);
trace_clk_set_parent(core, parent);
/* 2. 设置调用Mux的set_parent设置寄存器 */
if (parent && core->ops->set_parent)
ret = core->ops->set_parent(core->hw, p_index);
trace_clk_set_parent_complete(core, parent);
/* 3. 如果前面失败了,还原回去 */
if (ret) {
flags = clk_enable_lock();
clk_reparent(core, old_parent);
clk_enable_unlock(flags);
__clk_set_parent_after(core, old_parent, parent);
return ret;
}
/* 4. 善后工作 */
__clk_set_parent_after(core, parent, old_parent);
return 0;
}
static struct clk_core *__clk_set_parent_before(struct clk_core *core,
struct clk_core *parent)
{
unsigned long flags;
struct clk_core *old_parent = core->parent;
/* enable old_parent & parent if CLK_OPS_PARENT_ENABLE is set */
if (core->flags & CLK_OPS_PARENT_ENABLE) {
clk_core_prepare_enable(old_parent);
clk_core_prepare_enable(parent);
}
/* migrate prepare count if > 0 */
if (core->prepare_count) {
clk_core_prepare_enable(parent);
clk_core_enable_lock(core);
}
/* update the clk tree topology */
flags = clk_enable_lock();
clk_reparent(core, parent);
clk_enable_unlock(flags);
return old_parent;
}
static void __clk_set_parent_after(struct clk_core *core,
struct clk_core *parent,
struct clk_core *old_parent)
{
/*
* Finish the migration of prepare state and undo the changes done
* for preventing a race with clk_enable().
*/
if (core->prepare_count) {
clk_core_disable_lock(core);
clk_core_disable_unprepare(old_parent);
}
/* re-balance ref counting if CLK_OPS_PARENT_ENABLE is set */
if (core->flags & CLK_OPS_PARENT_ENABLE) {
clk_core_disable_unprepare(parent);
clk_core_disable_unprepare(old_parent);
}
}
以上是关于common clk framework的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章