SpringBoot-配置文件与自动配置
Posted 滑稽404#
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了SpringBoot-配置文件与自动配置相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、配置文件注入
1、properties和yaml例子
server.port=8080
server:
port: 8080
2、实体类
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
public class Person {
private String name;
private String sex;
private Integer age;
private Cat cat;
private Map<String,Object> map;
private List<Object> lists;
}
3、对应yaml
person:
name: zhangsan
sex: 男
age: 18
cat: {name: 小橘,color: 橘黄色}
map: {key: 123}
lists:
-1
-2
-3
4、绑定注解
@Component//只有组件才能被boot扫描,才会绑定
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
//告诉本类与yaml或properties(application)中前缀为person的元素进行绑定
5、测试
@SpringBootTest
class Springboot02YamlApplicationTests {
//将组件中的person注入person
@Autowired
Person person;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(person);
}
}
5、yaml换成properties
person.name=张三
person.sex=男
...
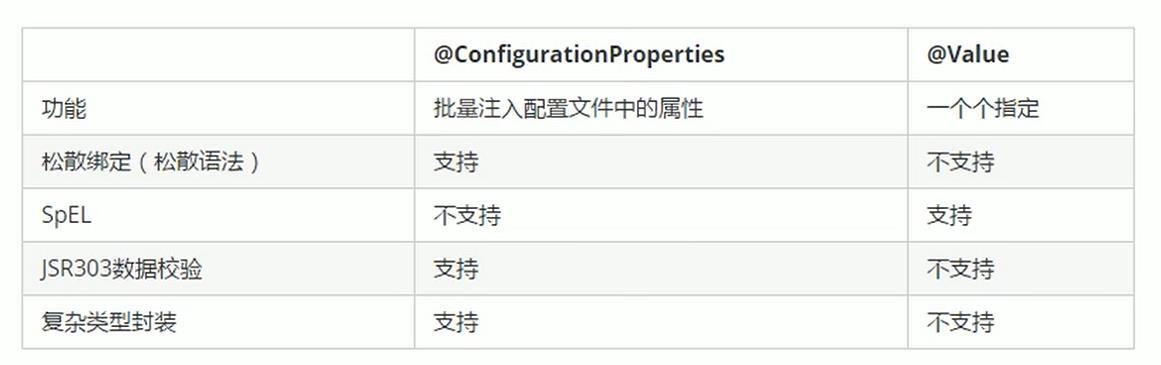
6、@ConfigurationProperties与@Value区别
@Component
public class Person {
@Value("${person.name}")
private String name;
@Value("#{1+1}")
private String sex;
@Value必须一一指定,${xxx}从配置文件、环境变量中获取值,#{xxx}为spring表达式
而且@Value不支持引用类型、map等复杂属性的绑定
6、@PropertySource
加载指定配置文件
person.properties:
person.name=李四 person.sex=女 person.age=18 person.cat.name=小橘 person.cat.color=橘黄色 person.map.k1=v1 person.map.k2=v2
(1)与@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “person”)搭配使用
通过指定配置文件对属性进行注入
@PropertySource(value={"classpath:person.properties"})
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "person")
class Person{
}
(2)与@Value搭配
通过指定配置文件对属性一一注入
@PropertySource(value={"classpath:person.properties"})
class Person{
@Value("${person.name}")
private String name;
}
7、@ImportSource
加载指定spring配置文件,假如你写了一个beans.xml
就需要在Spring主程序里加入这个注解才会加载这个配置文件
自己写的配置文件程序并不会自动识别,想让配置文件生效就得在配置类上加上这个注解
<bean id="helloService" class="com.chime.service.HelloService"></bean>
@ImportResource(locations = {"classpath:beans.xml"})
@SpringBootApplication
public class Springboot02YamlApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Springboot02YamlApplication.class, args);
}
}
@Autowired
ApplicationContext ioc;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(ioc.containsBean("helloService"));
}
但是SpringBoot并不推荐使用配置文件
而是用注解+配置类替代了(纯注解开发)
8、配置类代替配置文件
@Configuration//声明该类是配置类
public class MyAppConfig {
/*
<bean id="helloService" class="com.chime.service.HelloService"></bean>
*/
//@Bean注解将方法返回值添加到容器中,组件默认id是方法名
@Bean
public HelloService helloService(){
return new HelloService();
}
}
@Bean注解将方法返回值添加到容器中,组件默认id是方法名
二、配置文件占位符
yaml和properties都支持
#person.name=张三${random.value}
person.sex=男
person.age=${random.int}
person.cat.name=${person.name:张三}_小橘
person.cat.color=橘黄色
person.map.k1=v1
person.map.k2=v2
1、随机数
使用${random.xxx}会随机类型值拼接
字段
2、可以使用占位符获取元素
person.cat.name=${person.name}_小橘
若配置文件中有person.name则拼接成xxx_小橘,没有就原封不动${person.name}_小橘
使用以下方法就不会出现这种问题
${person.name:默认值}:若没有该元素,就会拼接默认值
person.cat.name=${person.name:张三}_小橘
三、多环境Profiles配置
1、properties
SpringBoot可以通过 application-{profiles}.properties 文件格式编写多种环境的配置
程序默认使用application.properties配置
在默认配置文件中可使用
spring.profiles.active={profile}
更改配置环境
- application.properties
server.port=8081
spring.profiles.active=dev//激活环境,不激活就使用默认
- application-dev.properties
server.port=8083
- application-prod.properties
server.port=8085
2、yaml
而yaml则不用写这么多配置文件,直接利用语言文档分割的特性使用—来分割文档块
server:
port: 8081
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
---
server:
port: 8083
spring:
profiles: dev
---
server:
port: 8085
spring:
profiles: prod
3、激活指定profile
- 通过spring.profiles.active=xxx配置文件指定激活
- 项目打包后,通过命令行指定
java -jar xxx.jar --spring.profiles.active=dev
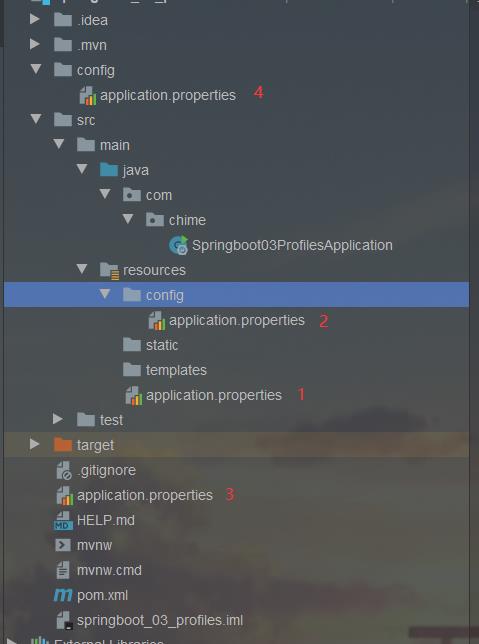
四、配置文件加载位置
1、优先级
-file:./config/
-file:./
-classpath:/config/
-classpath:/
以上是优先级由低到高的顺序,如果存在相同属性,则优先级高的覆盖优先级低的,如果不存在的则互补
如在其中配置文件中添加
server.servlet.context-path=/boot
加载所有文件,然后覆盖互补形成最后的配置环境
2、打包后命令行
只会打包classpath底下的配置文件,file底下的两配置位置并不会被打包
java -jar xxx.jar --spring.config.location=G:\\path\\application.properties
可通过–spring.config.location=xxx来获取指定地址的配置文件,一般用于开发后的更改配置
五、外部配置加载顺序
- 命令行参数
java -jar xxx.jar --server.port=8085 --server.servlet.context-path=boot5
参数需用--声明,参数之间需用空格隔开
-
来自java:comp/env的JNDI属性
-
Java系统属性(System.getProperties())
-
操作系统环境变量
-
RandomValuePropertySource配置的random.*属性值
由jar包外向jar包内进行寻找;(.properties>.yml)
使用命令行运行jar包后会先找该jar包外的配置文件(优先级比下面的都高)
优先加载带profile
-
jar包外部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
-
jar包内部的application-{profile}.properties或application.yml(带spring.profile)配置文件
-
–spring.config.location=C:/application.properties(它在这里)
再来加载不带profile
-
jar包外部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
-
jar包内部的application.properties或application.yml(不带spring.profile)配置文件
-
@Configuration注解类上的@PropertySource
-
通过SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties指定的默认属性
六、自动配置原理
启动SpringBoot程序的时候,会自动加载自动配置类
@SpringBootApplication注解由@EnableAutoConfiguration组成
1、概述
-
@EnableAutoConfiguration通过AutoConfigurationImportSelector类去加载自动配置类
-
其中的selectImports()方法通过SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames()扫描所有具有
“META-INF/spring.factories”
的jar包 -
SpringBoot通过@SpringBootApplication注解去获取所有jar包下的/META-INF/spring.factories中的自动配置类,
将这些组件添加到容器中 -
每一个AutoConfiguration类都对应着一个封装了配置属性的Properties类
2、例子
如配置server.port=8080对应着
@EnableConfigurationProperties(ServerProperties.class)
ServletWebServerFactoryAutoConfiguration{
}
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "server", ignoreUnknownFields = true)
public class ServerProperties {
/**
* Server HTTP port.
*/
private Integer port;
}
Properties类中中则有相应自动对应配置属性
@ConfigurationProperties注解与全局配置文件中对应的属性进行绑定的。
3、配置类生效
SpringBooy虽然在启动的时候加载了所有自动配置类
但是因为自动配置类拥有@Conditional注解,所以不是所有自动配置类都会生效的
如:
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "spring.aop", name = "auto", havingValue = "true", matchIfMissing = true)
public class AopAutoConfiguration {
@ConditionalOnClass(Advice.class)
static class AspectJAutoProxyingConfiguration {
}
}
aop自动配置类,因为没有包含Advice切面类,并不会生效,将组件添加到容器中
各种各样的自动配置类也有各种生效条件,所以并不是所有自动配置类都会生效
&如何知道哪些自动配置类生效
启动debug=true配置,会显示自动配置日志
============================
CONDITIONS EVALUATION REPORT
============================
Positive matches(自动配置类启用的):
-----------------
AopAutoConfiguration matched:
- @ConditionalOnProperty (spring.aop.auto=true) matched (OnPropertyCondition)
AopAutoConfiguration.ClassProxyingConfiguration matched:
- @ConditionalOnMissingClass did not find unwanted class 'org.aspectj.weaver.Advice' (OnClassCondition)
- @ConditionalOnProperty (spring.aop.proxy-target-class=true) matched (OnPropertyCondition)
Negative matches(自动配置类未启用或没有满足生效条件的):
-----------------
ActiveMQAutoConfiguration:
Did not match:
- @ConditionalOnClass did not find required class 'javax.jms.ConnectionFactory' (OnClassCondition)
AopAutoConfiguration.AspectJAutoProxyingConfiguration:
Did not match:
- @ConditionalOnClass did not find required class 'org.aspectj.weaver.Advice' (OnClassCondition)
ArtemisAutoConfiguration:
Did not match:
- @ConditionalOnClass did not find required class 'javax.jms.ConnectionFactory' (OnClassCondition)
Exclusions:
-----------
None
Unconditional classes(没有生效条件的类):
----------------------
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.ConfigurationPropertiesAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.LifecycleAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.context.PropertyPlaceholderAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.availability.ApplicationAvailabilityAutoConfiguration
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.info.ProjectInfoAutoConfiguration
以上是关于SpringBoot-配置文件与自动配置的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章