[C++STL]仿函数用法介绍
Posted Wecccccccc
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了[C++STL]仿函数用法介绍相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。

代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
//函数对象在使用时,可以像普通函数那样调用,可以有参数,可以有返回值
class MyAdd
{
public:
int operator()(int a, int b)
{
return a + b;
}
};
void test01()
{
MyAdd myAdd;
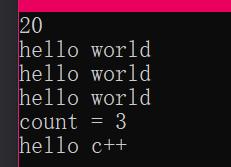
cout << myAdd(10, 10) << endl;
}
//函数对象可以有自己的状态
class MyPrint
{
public:
MyPrint()
{
count = 0;
}
void operator()(string test)
{
cout << test << endl;
count++;
}
int count = 0;
};
void test02()
{
MyPrint myPrint;
myPrint("hello world");
myPrint("hello world");
myPrint("hello world");
cout << "count = " << myPrint.count << endl;
}
//函数对象可以作为参数传递
void doPrint(MyPrint &mp, string test)
{
mp(test);
}
void test03()
{
MyPrint myPrint;
doPrint(myPrint, "hello c++");
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
test03();
return 0;
}
测试结果:
总结:


一元谓词
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
struct GreaterFive {
bool operator()(int a)
{
return a > 5;
}
};
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
v.push_back(i);
}
vector<int>::iterator it = find_if(v.begin(), v.end(), GreaterFive());
if (it == v.end())
{
cout << "no find" << endl;
}
else
{
cout << "find" << *it << endl;
}
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
测试结果:

总结:

二元谓词
代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class cmp
{
public:
bool operator()(int a, int b)
{
return a > b;
}
};
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(30);
v.push_back(50);
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
cout << "---------------------------------------" << endl;
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), cmp());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main() {
test01();
return 0;
}
测试结果:

总结:



代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
negate<int> n;
cout << n(50) << endl;
}
void test02()
{
plus<int>p;
cout << p(10, 20) << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
return 0;
}
测试结果:

总结:


代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
class cmp
{
public:
bool operator()(int a, int b)
{
return a > b;
}
};
void test01()
{
vector<int>v;
v.push_back(10);
v.push_back(20);
v.push_back(50);
v.push_back(40);
v.push_back(90);
v.push_back(70);
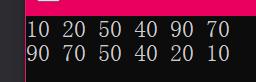
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
sort(v.begin(), v.end(), greater<int>());
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
测试结果:
总结:


代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <functional>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
void test01()
{
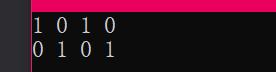
vector<bool> v;
v.push_back(true);
v.push_back(false);
v.push_back(true);
v.push_back(false);
for (vector<bool>::iterator it = v.begin(); it != v.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector<bool> v2;
v2.resize(v.size());
transform(v.begin(), v.end(), v2.begin(), logical_not<bool>());
for (vector<bool>::iterator it = v2.begin(); it != v2.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
测试结果:
总结:

以上是关于[C++STL]仿函数用法介绍的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章