Spring学习总结
Posted 我实在是想不出什么好听的昵称了啊
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了 Spring学习总结相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
Spring 框架概述
- pring 使创建 Java 企业应用程序变得容易。它提供了在企业环境中使用 Java 语言所需的一切,并支持 Groovy 和 Kotlin 作为 JVM 上的替代语言,并且可以根据应用程序的需求灵活地创建多种体系结构。从 Spring Framework 5.0 开始,Spring 需要 JDK 8(Java SE 8),并且已经为 JDK 9 提供了现成的支持。
- Spring 是分层的 Java SE/EE full-stack 轻量级开源框架,以 IoC(Inverse of Control,控制反转)和 AOP(Aspect Oriented Programming,面向切面编程)为内核,使用基本的 JavaBean 完成以前只可能由 EJB 完成的工作,取代了 EJB 臃肿和低效的开发模式。
- pring 是开源的。它拥有一个庞大而活跃的社区,可以根据各种实际用例提供持续的反馈。这帮助 Spring 在很长一段时间内成功地 Developing 了。
Spring优点
- 方便解耦,简化开发
Spring 就是一个大工厂,可以将所有对象的创建和依赖关系的维护交给 Spring 管理。 - 方便集成各大优秀框架
Spring 不排斥各种优秀的开源框架,其内部提供了对各种优秀框架(如 Struts2、Hibernate、MyBatis 等)的直接支持。 - 方便程序的测试
Spring 支持 JUnit4,可以通过注解方便地测试 Spring 程序。 - AOP 编程的支持
Spring 提供面向切面编程,可以方便地实现对程序进行权限拦截和运行监控等功能。 - 声明式事务的支持
只需要通过配置就可以完成对事务的管理,而无须手动编程。
Spring体系结构
Spring 框架采用分层架构,根据不同的功能被划分成了多个模块,这些模块大体可分为 Data Access/Integration、Web、AOP、Aspects、Messaging、Instrumentation、Core Container 和 Test,具体如下图所示:
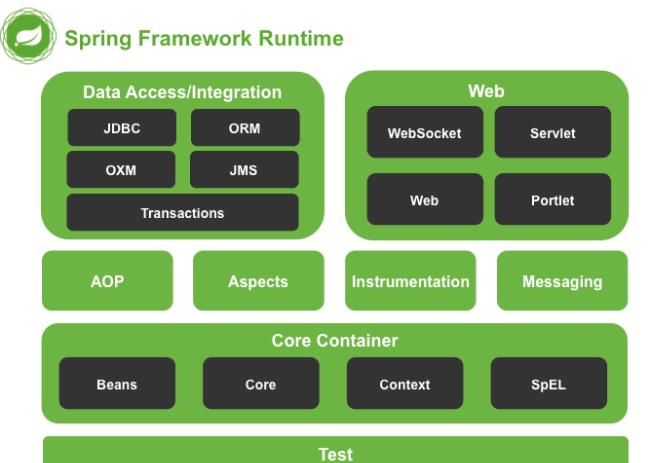
- Data Access/Integration(数据访问/集成)
数据访问/集成层包括 JDBC、ORM、OXM、JMS 和 Transactions 模块,具体介绍如下。
JDBC 模块:提供了一个 JDBC 的抽象层,大幅度减少了在开发过程中对数据库操作的编码。
ORM 模块:对流行的对象关系映射 API,包括 JPA、JDO、Hibernate 和 iBatis 提供了的集成层。
OXM 模块:提供了一个支持对象/XML 映射的抽象层实现,如 JAXB、Castor、XMLBeans、JiBX 和 XStream。
JMS 模块:指 Java 消息服务,包含的功能为生产和消费的信息。
Transactions 事务模块:支持编程和声明式事务管理实现特殊接口类,并为所有的 POJO。
- Web 模块
Spring 的 Web 层包括 Web、Servlet、Struts 和 Portlet 组件,具体介绍如下。
Web 模块:提供了基本的 Web 开发集成特性,例如多文件上传功能、使用的 Servlet 监听器的 IoC 容器初始化以及 Web 应用上下文。
Servlet模块:包括 Spring 模型—视图—控制器(MVC)实现 Web 应用程序。
Struts 模块:包含支持类内的 Spring 应用程序,集成了经典的 Struts Web 层。
Portlet 模块:提供了在 Portlet 环境中使用 MV C实现,类似 Web-Servlet 模块的功能。
- Core Container(核心容器)
Spring 的核心容器是其他模块建立的基础,由 Beans 模块、Core 核心模块、Context 上下文模块和 Expression Language 表达式语言模块组成,具体介绍如下。
Beans 模块:提供了 BeanFactory,是工厂模式的经典实现,Spring 将管理对象称为 Bean。
Core 核心模块:提供了 Spring 框架的基本组成部分,包括 IoC 和 DI 功能。
Context 上下文模块:建立在核心和 Beans 模块的基础之上,它是访问定义和配置任何对象的媒介。ApplicationContext 接口是上下文模块的焦点。
Expression Language 模块:是运行时查询和操作对象图的强大的表达式语言。
- 其他模块
Spring的其他模块还有 AOP、Aspects、Instrumentation 以及 Test 模块,具体介绍如下。
AOP 模块:提供了面向切面编程实现,允许定义方法拦截器和切入点,将代码按照功能进行分离,以降低耦合性。
Aspects 模块:提供与 AspectJ 的集成,是一个功能强大且成熟的面向切面编程(AOP)框架。
Instrumentation 模块:提供了类工具的支持和类加载器的实现,可以在特定的应用服务器中使用。
Test 模块:支持 Spring 组件,使用 JUnit 或 TestNG 框架的测试。
Spring拓展
Spring Boot与Spring Cloud
- Spring Boot 是 Spring 的一套快速配置脚手架,可以基于Spring Boot 快速开发单个微服务。
- Spring Cloud是基于Spring Boot实现的。
- Spring Boot专注于快速、方便集成的单个微服务个体,Spring Cloud关注全局的服务治理框架。
- Spring Boot使用了约束优于配置的理念,很多集成方案已经帮你选择好了,能不配置就不配置 , Spring Cloud很大的一部分是基于Spring Boot来实现,Spring Boot可以离开Spring Cloud独立使用开发项目,但是Spring Cloud离不开Spring Boot,属于依赖的关系。
- SpringBoot在SpringClound中起到了承上启下的作用,如果你要学习SpringCloud必须要学习SpringBoot。
Spring IoC 容器 (IoC 也称为依赖项注入(DI),或DI是实现IoC的一种方法)
IoC容器概述
- 控制反转是一种通过描述(XML或注解)并通过第三方去生产或获取特定对象的方式。在Spring中实现控制反转的是IoC容器,其实现方法是依赖注入。
- Spring容器在初始化时先读取配置文件,根据配置文件或元数据创建与组织对象存入容器中,程序使用时再从Ioc容器中取出需要的对象。
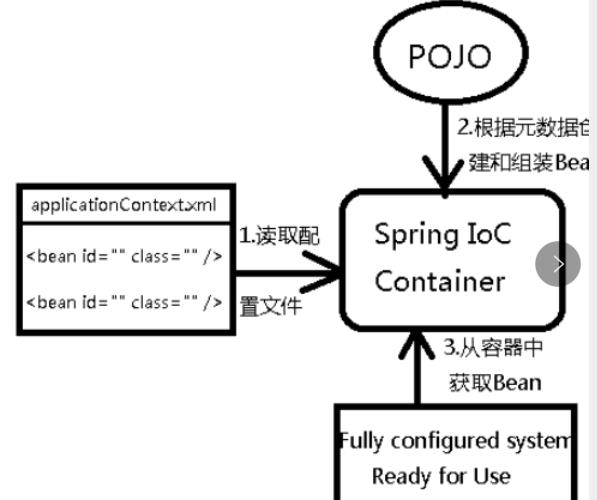
- Spring 提供了两种 IoC 容器,分别为 BeanFactory 和 ApplicationContext。
-
BeanFactory
beanFactory是一个Factory,用于管理bean的,有了一个Spring的beanFactory,我们就可以从spring中获取注册到其中的bean来使用。 -
ApplicationContext
ApplicationContext 是 BeanFactory 的子接口,也被称为应用上下文。该接口的全路径为:org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext,它不仅提供了 BeanFactory 的所有功能,还添加了对 i18n(国际化)、资源访问、事件传播等方面的良好支持。
ApplicationContext 接口有两个常用的实现类:ClassPathXmlApplicationContext和FileSystemXmlApplicationContext。
ClassPathXmlApplicationContext从类路径 ClassPath 中寻找指定的 XML 配置文件,找到并装载完成 ApplicationContext 的实例化工作,具体如下所示。ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation);configLocation 参数用于指定 Spring 配置文件的名称和位置,如 applicationContext.xml。FileSystemXmlApplicationContext从指定的文件系统路径中寻找指定的 XML 配置文件,找到并装载完成 ApplicationContext 的实例化工作,具体如下所示。ApplicationContext applicationContext = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext(String configLocation);它与 ClassPathXmlApplicationContext 的区别是:在读取 Spring 的配置文件时,FileSystemXmlApplicationContext 不再从类路径中读取配置文件,而是通过参数指定配置文件的位置,它可以获取类路径之外的资源,如“D:/workspaces/applicationContext.xml”。 -
BeanFactory 和 ApplicationContext区别:
BeanFactory在初始化容器时,并未实例化Bean,直到第一次访问某个Bean 时才实例目标Bean;而ApplicationContext 则在初始化应用上下文时就实例化所有单实例的Bean 。
在实际开发中,通常都选择使用 ApplicationContext,而只有在系统资源较少时,才考虑使用 BeanFactory。
(但是,它们都是通过 XML 配置文件加载 Bean 的。)
Spring入门程序
- 创建maven项目
- 在pom.xml导入jar包依赖
<dependencies>
<!--导入spring,maven依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>5.2.12.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<!--导入junit-->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>4.12</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
- 编写接口
package com.xxx.mapper;
/**
* @author shkstart
* @create 2021-06-11 15:50
*/
public interface UserMapper {
public void hello();
}
- 编写接口实现类
package com.xxx.mapper;/**
* @author shkstart
* @create 2021-06-11 15:50
*/
/**
*@program: springTest
*@description:
*@author: XieXianXin
*@create: 2021-06-11 15:50
*/
public class UserMapperImpl implements UserMapper{
@Override
public void hello() {
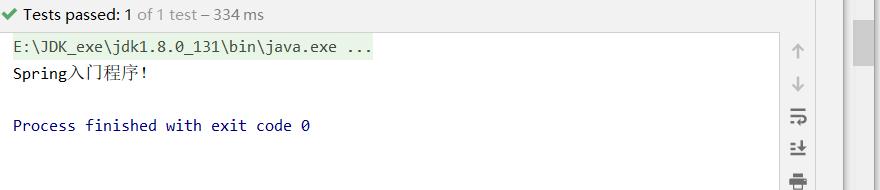
System.out.println("Spring入门程序!");
}
}
- 编写Spring核心配置文件applicationContext.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
使用Spring来创建对象,在Spring这些都称为Bean
类型 变量名 = new 类型();
Hello hello = new Hello();
id = 变量名
class = new 的对象
-->
<beans>
<bean id="hello" class="com.xxx.mapper.UserMapperImpl">
</bean>
</beans>
</beans>
- 测试
package com.xxx.mapper;/**
* @author shkstart
* @create 2021-06-11 15:57
*/
import org.junit.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
*@program: springTest
*@description:
*@author: XieXianXin
*@create: 2021-06-11 15:57
*/
public class helloTest {
@Test
public void helloTest1(){
// 1. 初始化Spring容器,加载配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 2. 通过容器获取userMapper实例
UserMapper hello = context.getBean("hello", UserMapper.class);
// 3.调用实例中的hello()方法
hello.hello();
}
}
- 测试结果
IoC创建对象的三种方式
编写实体类User:
public class User {
private String name;
// set方法
public void setName(String name) {
this.name=name;
}
public User() {
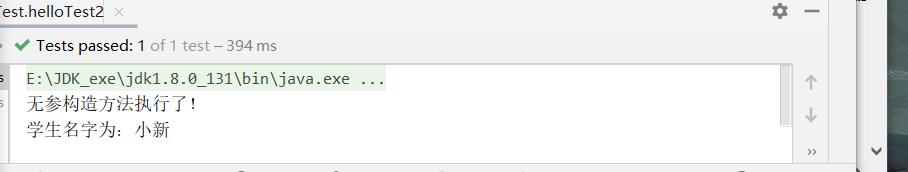
System.out.println("无参构造方法执行了!");
}
public void print(){
System.out.println("学生名字为:"+name);
}
}
编写Spring核心配置文件:
<!--无参构造,但是要有set方法-->
<bean id="user" class="com.xxx.pojo.User">
<property name="name" value="小新"/>
</bean>
测试以及结果:
@Test
public void helloTest2(){
// 1. 初始化Spring容器,加载配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 2. 通过容器获取userMapper实例
User user = context.getBean("user", User.class);
// 3.调用实例中的print()方法
user.print();
}
编写实体类User:
public class User {
private String name;
//get方法
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public User(String name) {
System.out.println("有参构造方法执行了!");
this.name = name;
}
public void print(){
System.out.println("学生名字为:"+name);
}
}
编写Spring核心配置文件:
<!--有参构造,但是要有get方法-->
<bean id="user" class="com.xxx.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg value="小新2" index="0"/>
</bean>
测试以及结果:
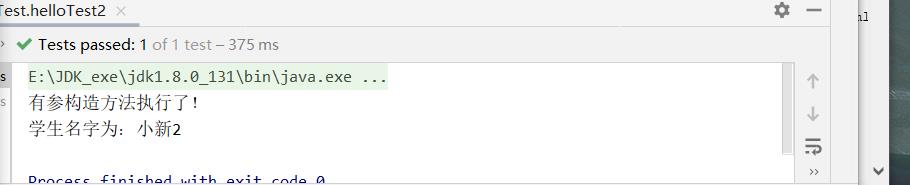
@Test
public void helloTest2(){
// 1. 初始化Spring容器,加载配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 2. 通过容器获取userMapper实例
User user = context.getBean("user", User.class);
// 3.调用实例中的print()方法
user.print();
}
 拓展:Spring核心配置文件有三种写法:
拓展:Spring核心配置文件有三种写法:
<!--有参构造,但是要有get方法-->
<bean id="user" class="com.xxx.pojo.User">
<constructor-arg index="0" value="小新-index属性(0开始,按顺序)"/>
<constructor-arg name="name" value="小新-name属性"/>
<constructor-arg type="java.lang.String" value="小新-参数类型"/>
</bean>
结果展示:



编写工厂类:
public class Factory {
//方法一,静态方法
public static User getStaticInstance(){
return new User("小新2——静态方法创建对象");
}
//方法二,实例方法
public User getInstance(){
return new User("小新3-实例方法创建对象");
}
}
编写Spring核心配置文件:
<!--工厂类创建对象-->
<!--创建工厂-->
<bean id="factory" class="com.xxx.mapper.Factory"/>
<!--静态方法对象-->
<bean id="staticFactory-user" class="com.xxx.mapper.Factory" factory-method="getStaticInstance"/>
<!--实例方法对象-->
<bean id="factory-user" factory-bean="factory" factory-method="getInstance"/>
测试以及结果:
静态方法:
@Test
public void helloTest4(){
// 1. 初始化Spring容器,加载配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 2. 通过容器获取userMapper实例
User user = context.getBean("staticFactory-user", User.class);
// 3.调用实例中的print()方法
user.print();
}
 实例方法:
实例方法:
@Test
public void helloTest3(){
// 1. 初始化Spring容器,加载配置文件
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("applicationContext.xml");
// 2. 通过容器获取userMapper实例
User user = context.getBean("factory-user", User.class);
// 3.调用实例中的print()方法
user.print();
}

Spring依赖注入(DI)和Bean的作用域
什么是依赖注入:Spring 容器在创建被调用者的实例时,会自动将调用者需要的对象实例注入给调用者,这样,调用者通过 Spring 容器获得被调用者实例。
依赖注入主要有两种实现方式,分别是属性 setter 注入和构造方法注入,其中setter注入要求重点掌握。
- 属性 setter 注入(重点展开讲解)
指 IoC 容器使用 setter 方法注入被依赖的实例。通过调用无参构造器或无参 static 工厂方法实例化 bean 后,调用该 bean 的 setter 方法,即可实现基于 setter 的 DI。 - 构造方法注入
指 IoC 容器使用构造方法注入被依赖的实例。基于构造器的 DI 通过调用带参数的构造方法实现,每个参数代表一个依赖。
属性 setter 注入讲解:
环境搭建:(创建一个Student和Book类):
Student
package com.xxx.pojo;/**
* @author shkstart
* @create 2021-06-11 17:45
*/
import java.util.*;
/**
*@program: Spring_study
*@description:
*@author: XieXianXin
*@create: 2021-06-11 17:45
*/
public class Student {
private String name;
private Book book;
private String[] course;
private List<String> hobbies;
private Map<String,String> card;
private Set<String> fruit;
private String marriage;
private Properties info;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, Book book, String[] course, List<String> hobbies, Map<String, String> card, Set<String> fruit, String marriage, Properties info) {
this.name = name;
this.book = book;
this.course = course;
this.hobbies = hobbies;
this.card = card;
this.fruit = fruit;
this.marriage = marriage;
this.info = info;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\\'' +
", book=" + book +
", course=" + Arrays.toString(course) +
", hobbies=" + hobbies +
", card=" + card +
", fruit=" + fruit +
", marriage='" + marriage + '\\'' +
", info=" + info +
'}';
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public Book getBook() {
return book;
}
public void setBook(Book book) {
this.book = book;
}
public String[] getCourse() {
return course;
}
public void setCourse(String[] course) {
this.course = course;
}
public List<String> getHobbies() {
return hobbies;
}
public void setHobbies(List<String> hobbies) {
this.hobbies = hobbies;
}
public Map<String, String> getCard() {
return card;
}
public void setCard(Map<String, String> card) {
this.card = card;
}
public Set<String> getFruit() {
return fruit;
}
public void setFruit(Set<String> fruit) {
this.fruit = fruit;
}
public String getMarriage() {
return marriage;
}
public void setMarriage(String marriage) {
this.marriage = marriage;
}
public Properties getInfo() {
return info;
}
public void setInfo(Properties info) {
this.info = info;
}
}
Book
package com.xxx.pojo;/**
* @author shkstart
* @create 2021-06-11 17:45
*/
/**
*@program: Spring_study
*@description:
*@author: XieXianXin
*@create: 2021-06-11 17:45
*/
public class Book {<以上是关于 Spring学习总结的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章