还没有女朋友的朋友们,你们有福了,学会CycleGAN把男朋友变成女朋友
Posted 盼小辉丶
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了还没有女朋友的朋友们,你们有福了,学会CycleGAN把男朋友变成女朋友相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
还没有女朋友的朋友们,你们有福了,学会CycleGAN把男朋友变成女朋友
前言
事情的起因是这样的,室友在经历的4年的找女朋友之旅后,终于放弃了,而我为了让他的青春不留遗憾,只能使用 CycleGAN 把下铺壮汉变成萌妹了。
转眼又到了毕业季,还在为没有女朋友而着急么?还在为没有谈一场青春的恋爱而遗憾么?还没有女朋友的朋友们,你们有福了!!!没有女朋友,还能没有男朋友么?学会 CycleGAN ,把男朋友变成女朋友,赶快学起来吧。
效果展示
在学习之前,大家肯定想先知道CycleGAN模型进行男女性别转换的效果如何,所以先让大家看看模型训练的效果.
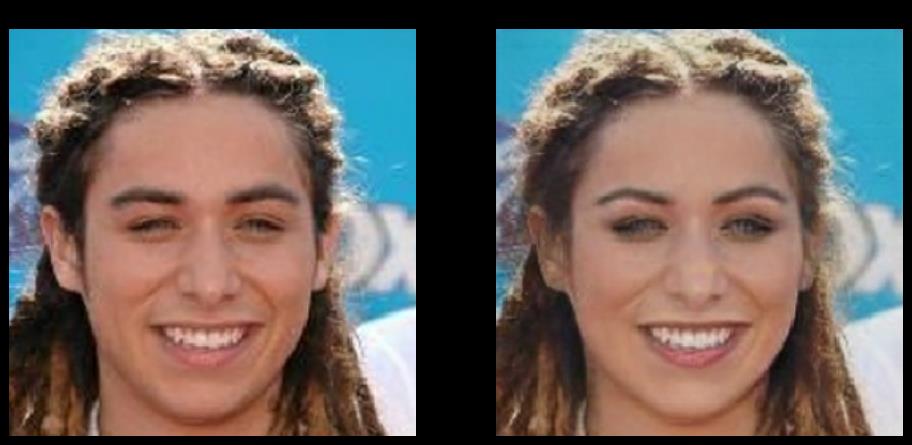
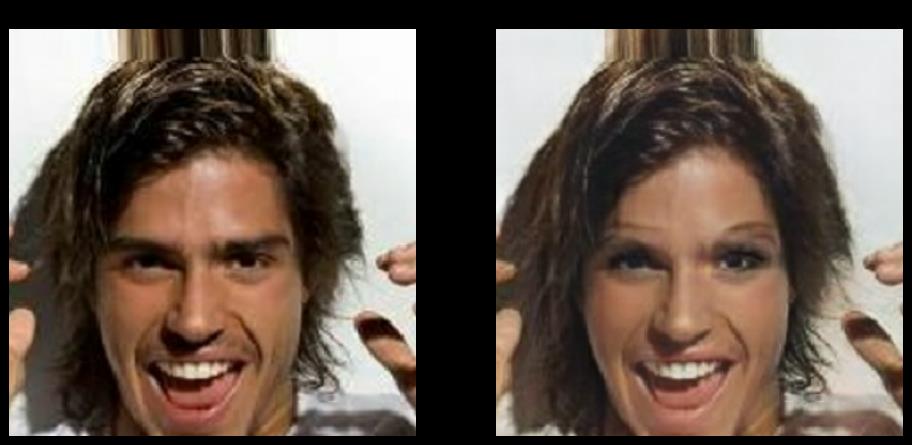
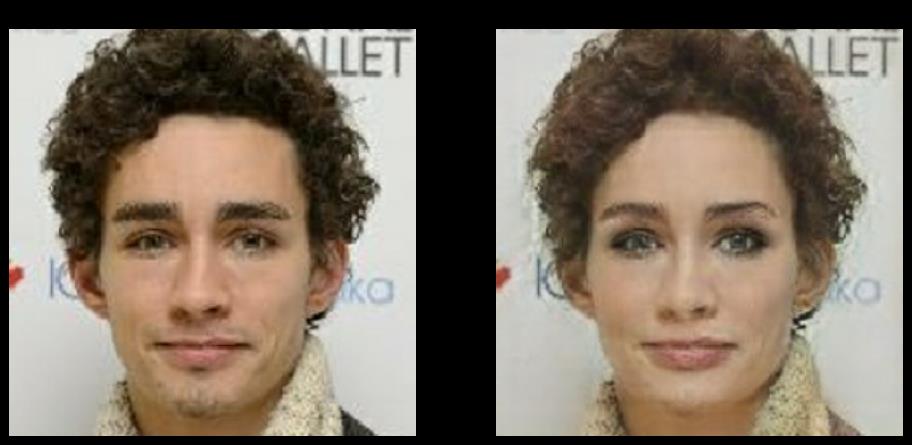
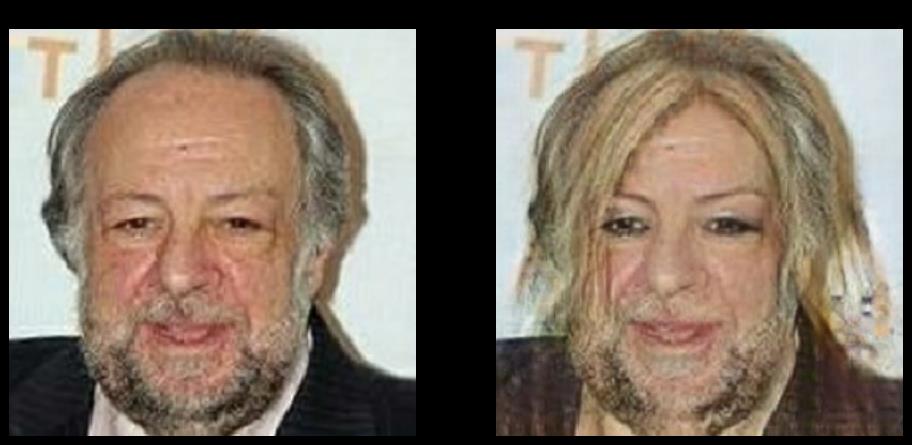




效果这么惊人,还不快学起来???
使用 CycleGAN 进行不成对的图像转换
CycleGAN 可以使用两个生成器和两个鉴别器训练不成对(unpaired)的图像。
本文主要以实战为主,如果想要了解 CycleGAN 背后的具体原理,请参考 CycleGAN 原理与实现(采用tensorflow2.x实现).
不成对的数据集
CycleGAN 的一个重要贡献是,改变了pix2pix需要成对的训练数据集的缺点。某些情况下,我们可以很容易地创建成对数据集,如彩色的图像对应的灰度图像数据集,完成成对数据集的构建,从而用于训练灰度图像上色的深度学习模型。但是,更多数的情况下,无法创建成对的数据集,例如从男性到女性的图像转换。
这便是 CycleGAN 的优势所在,因为它不需要成对的数据, CycleGAN 可以训练不成对的数据集!
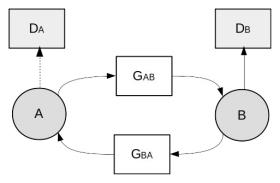
CycleGAN模型
简单看下CycleGAN的体系架构:
数据集
数据集取自 Celeb A ,可以自行构建数据集,也可以使用此数据集,提取码:nql9。
数据加载与预处理
# 导入必要库
import tensorflow as tf
import os
import time
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
import tensorflow_datasets as tfds
AUTOTUNE = tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE
# 定义超参数
BUFFER_SIZE = 128
BATCH_SIZE = 1
IMG_WIDTH = 256
IMG_HEIGHT = 256
OUTPUT_CHANNELS = 3
LAMBDA = 10
EPOCHS = 100
"""
# 数据预处理函数
"""
def random_crop(image):
cropped_image = tf.image.random_crop(image, size=[IMG_HEIGHT, IMG_WIDTH, 3])
return cropped_image
# normalizing the images to [-1, 1]
def normalize(image):
image = tf.cast(image, tf.float32)
image = (image / 127.5) - 1
return image
def random_jitter(image):
# resizing to 286 x 286 x 3
image = tf.image.resize(image, [286, 286], method=tf.image.ResizeMethod.NEAREST_NEIGHBOR)
# randomly cropping to 256 x 256 x 3
image = random_crop(image)
# random mirroring
image = tf.image.random_flip_left_right(image)
return image
def preprocess_image_train(image):
image = random_jitter(image)
image = normalize(image)
return image
def preprocess_image_test(image):
image = normalize(image)
return image
def load(image_file):
image = tf.io.read_file(image_file)
image = tf.image.decode_jpeg(image)
input_image = tf.cast(image, tf.float32)
return input_image
def load_image_train(image_file):
image = load(image_file)
image = preprocess_image_train(image)
return image
def load_image_test(image_file):
image = load(image_file)
image = preprocess_image_test(image)
return image
# 加载男性图片,构建训练数据集
train_man = tf.data.Dataset.list_files('./man2woman/trainA/*.jpg')
train_man = train_man.map(load_image_train, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE)
train_man = train_man.shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE)
train_man = train_man.batch(BATCH_SIZE, drop_remainder=True)
# 加载女性图片,构建训练数据集
train_woman = tf.data.Dataset.list_files('./man2woman/trainB/*.jpg')
train_woman = train_woman.map(load_image_train, num_parallel_calls=tf.data.experimental.AUTOTUNE)
train_woman = train_woman.shuffle(BUFFER_SIZE)
train_woman = train_woman.batch(BATCH_SIZE, drop_remainder=True)
模型构建
在 CycleGAN 中,使用实例归一化代替批归一化,但在 tensorflow 中,未包含实例归一化层,因此需要自行实现。
class InstanceNormalization(tf.keras.layers.Layer):
"""Instance Normalization Layer."""
def __init__(self, epsilon=1e-5):
super(InstanceNormalization, self).__init__()
self.epsilon = epsilon
def build(self, input_shape):
self.scale = self.add_weight(
name='scale',
shape=input_shape[-1:],
initializer=tf.random_normal_initializer(1., 0.02),
trainable=True)
self.offset = self.add_weight(
name='offset',
shape=input_shape[-1:],
initializer='zeros',
trainable=True)
def call(self, x):
mean, variance = tf.nn.moments(x, axes=[1, 2], keepdims=True)
inv = tf.math.rsqrt(variance + self.epsilon)
normalized = (x - mean) * inv
return self.scale * normalized + self.offset
为了减少代码量,定义上采样块和下采样块:
# 下采样块
def downsample(filters, size, norm_type='batchnorm', apply_norm=True):
initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.02)
result = tf.keras.Sequential()
result.add(
tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(filters, size, strides=2, padding='same',
kernel_initializer=initializer, use_bias=False))
if apply_norm:
if norm_type.lower() == 'batchnorm':
result.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization())
elif norm_type.lower() == 'instancenorm':
result.add(InstanceNormalization())
result.add(tf.keras.layers.LeakyReLU())
return result
# 上采样快
def upsample(filters, size, norm_type='batchnorm', apply_dropout=False):
initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.02)
result = tf.keras.Sequential()
result.add(
tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(filters, size, strides=2,
padding='same',
kernel_initializer=initializer,
use_bias=False))
if norm_type.lower() == 'batchnorm':
result.add(tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization())
elif norm_type.lower() == 'instancenorm':
result.add(InstanceNormalization())
if apply_dropout:
result.add(tf.keras.layers.Dropout(0.5))
result.add(tf.keras.layers.ReLU())
return result
接下来构建生成器:
def unet_generator(output_channels, norm_type='batchnorm'):
down_stack = [
downsample(64, 4, norm_type, apply_norm=False),
downsample(128, 4, norm_type),
downsample(256, 4, norm_type),
downsample(512, 4, norm_type),
downsample(512, 4, norm_type),
downsample(512, 4, norm_type),
downsample(512, 4, norm_type),
downsample(512, 4, norm_type),
]
up_stack = [
upsample(512, 4, norm_type, apply_dropout=True),
upsample(512, 4, norm_type, apply_dropout=True),
upsample(512, 4, norm_type, apply_dropout=True),
upsample(512, 4, norm_type),
upsample(256, 4, norm_type),
upsample(128, 4, norm_type),
upsample(64, 4, norm_type),
]
initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.02)
last = tf.keras.layers.Conv2DTranspose(
output_channels, 4, strides=2,
padding='same', kernel_initializer=initializer,
activation='tanh') # (bs, 256, 256, 3)
concat = tf.keras.layers.Concatenate()
inputs = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[None, None, 3])
x = inputs
# Downsampling through the model
skips = []
for down in down_stack:
x = down(x)
skips.append(x)
skips = reversed(skips[:-1])
# Upsampling and establishing the skip connections
for up, skip in zip(up_stack, skips):
x = up(x)
x = concat([x, skip])
x = last(x)
return tf.keras.Model(inputs=inputs, outputs=x)
构建鉴别器:
def discriminator(norm_type='batchnorm', target=True):
initializer = tf.random_normal_initializer(0., 0.02)
inp = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[None, None, 3], name='input_image')
x = inp
if target:
tar = tf.keras.layers.Input(shape=[None, None, 3], name='target_image')
x = tf.keras.layers.concatenate([inp, tar]) # (bs, 256, 256, channels*2)
down1 = downsample(64, 4, norm_type, False)(x) # (bs, 128, 128, 64)
down2 = downsample(128, 4, norm_type)(down1) # (bs, 64, 64, 128)
down3 = downsample(256, 4, norm_type)(down2) # (bs, 32, 32, 256)
zero_pad1 = tf.keras.layers.ZeroPadding2D()(down3) # (bs, 34, 34, 256)
conv = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(
512, 4, strides=1, kernel_initializer=initializer,
use_bias=False)(zero_pad1) # (bs, 31, 31, 512)
if norm_type.lower() == 'batchnorm':
norm1 = tf.keras.layers.BatchNormalization()(conv)
elif norm_type.lower() == 'instancenorm':
norm1 = InstanceNormalization()(conv)
leaky_relu = tf.keras.layers.LeakyReLU()(norm1)
zero_pad2 = tf.keras.layers.ZeroPadding2D()(leaky_relu) # (bs, 33, 33, 512)
last = tf.keras.layers.Conv2D(
1, 4, strides=1,
kernel_initializer=initializer)(zero_pad2) # (bs, 30, 30, 1)
if target:
return tf.keras.Model(inputs=[inp, tar], outputs=last)
else:
return tf.keras.Model(inputs=inp, outputs=last)
实例化生成器与鉴别器:
generator_g = unet_generator(OUTPUT_CHANNELS, norm_type='instancenorm')
generator_f = unet_generator(OUTPUT_CHANNELS, norm_type='instancenorm')
discriminator_x = discriminator(norm_type='instancenorm', target=False)
discriminator_y = discriminator(norm_type='instancenorm', target=False)
损失函数与优化器的定义:
loss_obj = tf.keras.losses.BinaryCrossentropy(from_logits=True)
# 鉴别器损失
def discriminator_loss(real, generated):
real_loss = loss_obj(tf.ones_like(real), real)
generated_loss = loss_obj(tf.zeros_like(generated), generated)
total_disc_loss = real_loss + generated_loss
return total_disc_loss * 0.5
# 生成器损失
def generator_loss(generated):
return loss_obj(tf.ones_like(generated), generated)
# 循环一致性损失
def calc_cycle_loss(real_image, cycled_image):
loss1 = tf.reduce_mean(tf.abs(real_image - cycled_image))
return LAMBDA * loss1
# identity loss
def identity_loss(real_image, same_image):
loss = tf.reduce_mean(tf.abs(real_image - same_image))
return LAMBDA * 0.5 * loss
# 优化器
generator_g_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(2e-4, beta_1=0.5)
generator_f_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(2e-4, beta_1=0.5)
discriminator_x_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(2e-4, beta_1=0.5)
discriminator_y_optimizer = tf.keras.optimizers.Adam(2e-4, beta_1=0.5)
训练结果可视化函数
创建 generate_images 函数用于在训练过程中查看模型效果.
def generate_images(model, test_input):
prediction = model(test_input)
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
display_list = [test_input[0], prediction[0]]
title = ['Input Image', 'Predicted Image']
for i in range(2):
plt.subplot(1, 2, i+1)
plt.title(title[i])
# getting the pixel values between [0, 1] to plot it.
plt.imshow(display_list[i] * 0.5 + 0.5)
plt.axis('off')
# plt.show()
plt.savefig('results/{}.png'.format(int(time.time())))
训练步骤
首先需要定义训练函数:
@tf.function
def train_step(real_x, real_y):
with tf.GradientTape(persistent=True) as tape:
# Generator G translates X -> Y
# Generator F translates Y -> X.
fake_y = generator_g(real_x, training=True)
cycled_x = generator_f(fake_y, training=True)
fake_x = generator_f(real_y, training=True)
cycled_y = generator_g(fake_x, training=True)
# same_x and same_y are used for identity loss.
same_x = generator_f(real_x, training=True)
same_y = generator_g(real_y, training=True)
disc_real_x = discriminator_x(real_x, training=True)
disc_real_y = discriminator_y(real_y, training=True)
disc_fake_x = discriminator_x(fake_x, training=True)
disc_fake_y = discriminator_y(fake_y, training=True)
# calculate the loss
gen_g_loss = generator_loss(disc_fake_y)
gen_f_loss = generator_loss(disc_fake_x)
total_cycle_loss = calc_cycle_loss(r以上是关于还没有女朋友的朋友们,你们有福了,学会CycleGAN把男朋友变成女朋友的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章