JDK1.8 Thread类说明
Posted zhujm320
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了JDK1.8 Thread类说明相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
简介
Thread Java线程类,用于线程相关操作,是并发和多线程的基础。本文将对Thread源码和日常使用的函数进行解读。在对线程的使用有基本的了解后,再来阅读它的源码,有助于加深对线程的理解;如有小伙伴对线程的使用不是很清楚的话,请参考《Java开启线程的4种方式》。
线程是操作系统中的概念,也是系统调度的基本单元。对于线程的创建,通常通过系统的API来进行创建,Thread的线程创建也是通过系统API来进行创建,Thread只是对系统线程的一个包装。
构造函数
初始化线程
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,
long stackSize) {
init(g, target, name, stackSize, null, true);
}参数说明
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ThreadGroup g | 线程组 |
| Runnable target | 线程启动后,线程中回调run的目标对象 |
| String name | 线程名 |
| long stackSize | 线程栈大小 |
调用6参得初始化线程函数
private void init(ThreadGroup g, Runnable target, String name,
long stackSize, AccessControlContext acc,
boolean inheritThreadLocals)参数说明
| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ThreadGroup g | 线程组 |
| Runnable target | 线程回调run方法 |
| String name | 线程名字 |
| long stackSize | 线程堆栈大小 |
| AccessControlContext acc | 上下文 |
| boolean inheritThreadLocals | 是否继承ThreadLocals的值 |
无参构造函数
public Thread() {
init(null, null, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0);
}带一个参数构造函数
public Thread(Runnable target) {
init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0);
}| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Runnable target | 线程回调后的目标对象 |
public Thread(String name) {
init(null, null, name, 0);
}| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| String name | 线程名 |
带两个参数的构造函数
Thread(Runnable target, AccessControlContext acc) {
init(null, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0, acc, false);
}| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| Runnable target | 线程回调后的目标对象 |
| AccessControlContext acc | 系统资源访问决策类 |
public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target) {
init(group, target, "Thread-" + nextThreadNum(), 0);
}| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ThreadGroup group | 线程组 |
| Runnable target | 线程回调后的目标对象 |
public Thread(ThreadGroup group, String name) {
init(group, null, name, 0);
}| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ThreadGroup group | 线程组 |
| String name | 线程名 |
带三个参数的构造函数
public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name) {
init(group, target, name, 0);
}| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ThreadGroup group | 线程组 |
| Runnable target | 线程回调后的目标对象 |
| String name | 线程名 |
带四个参数的构造函数
public Thread(ThreadGroup group, Runnable target, String name,
long stackSize) {
init(group, target, name, stackSize);
}| 参数 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| ThreadGroup group | 线程组 |
| Runnable target | 线程回调后的目标对象 |
| String name | 线程名 |
| long stackSize | 线程堆栈大小 |
从以上看,Thread构造函数都是通过调用init函数进行初始化。
线程启动函数
通过调用Thread类的start()函数,线程正式启动,并且会调用run方法,此时run方法就是在线程中执行。
public synchronized void start() {
/**
* This method is not invoked for the main method thread or "system"
* group threads created/set up by the VM. Any new functionality added
* to this method in the future may have to also be added to the VM.
*
* A zero status value corresponds to state "NEW".
*/
if (threadStatus != 0)
throw new IllegalThreadStateException();
/* Notify the group that this thread is about to be started
* so that it can be added to the group's list of threads
* and the group's unstarted count can be decremented. */
group.add(this);
boolean started = false;
try {
start0();
started = true;
} finally {
try {
if (!started) {
group.threadStartFailed(this);
}
} catch (Throwable ignore) {
/* do nothing. If start0 threw a Throwable then
it will be passed up the call stack */
}
}
}
private native void start0();start方法只能调用一次,多次调用会包异常,start方法通过jni方法start0启动线程,由于Thread类只是对系统线程的一个封装,通过start0启动系统线程,启动线程启动后,通过jni回调run方法。
线程运行run方法
@Override
public void run() {
if (target != null) {
target.run();
}
}线程真正运行的地方,系统线程启动后,回调run方法,所以说在start后,run方法是在线程中执行。
Native方法
//获取当前运行线程对象
public static native Thread currentThread();
//线程礼让, 让出自己的cpu,让别人执行
public static native void yield();
//线程休眠 单位毫秒
public static native void sleep(long millis) throws InterruptedException;
//线程启动的真正方法
private native void start0();
//线程是否活着
public final native boolean isAlive();
//设置线程优先级
private native void setPriority0(int newPriority);
//停止线程
private native void stop0(Object o);
//暂停线程
private native void suspend0();
//唤醒线程
private native void resume0();
//中断线程
private native void interrupt0();
//设置线程名字
private native void setNativeName(String name);线程退出
private void exit() {
if (group != null) {
group.threadTerminated(this);
group = null;
}
/* Aggressively null out all reference fields: see bug 4006245 */
target = null;
/* Speed the release of some of these resources */
threadLocals = null;
inheritableThreadLocals = null;
inheritedAccessControlContext = null;
blocker = null;
uncaughtExceptionHandler = null;
}线程退出函数,调用该函数后,线程不一定会真正退出,如果在run方法中执行如下代码:
public void run(){
while(true){
....
}
}这样线程就无法退出了
线程中断通知
public void interrupt() {
if (this != Thread.currentThread())
checkAccess();
synchronized (blockerLock) {
Interruptible b = blocker;
if (b != null) {
interrupt0(); // Just to set the interrupt flag
b.interrupt(this);
return;
}
}
interrupt0();
}给真正运行的线程发送中断通知,以便该线程在执行时,能够收到该中断
public void run(){
while(true){
try{
...
}catch(Exception e){
...
}
}
}在run方法中进行异常捕获,当线程发起中断通知时,以便在线程中能收到。如果在run方法中没有去捕获异常的话,那么即使调用interrupt(),线程也是无法得到中断通知。
public static boolean interrupted() {
return currentThread().isInterrupted(true);
}测试该线程是否已经进行中断,重置当前线程的中断状态。
public boolean isInterrupted() {
return isInterrupted(false);
}判断该线程是否中断,不会清楚线程中断状态
设置线程优先级
public final void setPriority(int newPriority) {
ThreadGroup g;
checkAccess();
if (newPriority > MAX_PRIORITY || newPriority < MIN_PRIORITY) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
if((g = getThreadGroup()) != null) {
if (newPriority > g.getMaxPriority()) {
newPriority = g.getMaxPriority();
}
setPriority0(priority = newPriority);
}
}线程优先级从小到大分为1-10个等级,默认优先级为5
获取线程优先级
public final int getPriority() {
return priority;
}设置线程名字
public final synchronized void setName(String name) {
checkAccess();
if (name == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("name cannot be null");
}
this.name = name;
if (threadStatus != 0) {
setNativeName(name);
}
}给线程设置一个名字
获取线程名字
public final String getName() {
return name;
}join方法(停止当前线程执行另外一个线程,另外一个线程结束后再执行本线程)
public final synchronized void join(long millis)
throws InterruptedException {
long base = System.currentTimeMillis();
long now = 0;
if (millis < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
if (millis == 0) {
while (isAlive()) {
wait(0);
}
} else {
while (isAlive()) {
long delay = millis - now;
if (delay <= 0) {
break;
}
wait(delay);
now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base;
}
}
}
/**
* Waits at most {@code millis} milliseconds plus
* {@code nanos} nanoseconds for this thread to die.
*
* <p> This implementation uses a loop of {@code this.wait} calls
* conditioned on {@code this.isAlive}. As a thread terminates the
* {@code this.notifyAll} method is invoked. It is recommended that
* applications not use {@code wait}, {@code notify}, or
* {@code notifyAll} on {@code Thread} instances.
*
* @param millis
* the time to wait in milliseconds
*
* @param nanos
* {@code 0-999999} additional nanoseconds to wait
*
* @throws IllegalArgumentException
* if the value of {@code millis} is negative, or the value
* of {@code nanos} is not in the range {@code 0-999999}
*
* @throws InterruptedException
* if any thread has interrupted the current thread. The
* <i>interrupted status</i> of the current thread is
* cleared when this exception is thrown.
*/
public final synchronized void join(long millis, int nanos)
throws InterruptedException {
if (millis < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
if (nanos < 0 || nanos > 999999) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"nanosecond timeout value out of range");
}
if (nanos >= 500000 || (nanos != 0 && millis == 0)) {
millis++;
}
join(millis);
}
/**
* Waits for this thread to die.
*
* <p> An invocation of this method behaves in exactly the same
* way as the invocation
*
* <blockquote>
* {@linkplain #join(long) join}{@code (0)}
* </blockquote>
*
* @throws InterruptedException
* if any thread has interrupted the current thread. The
* <i>interrupted status</i> of the current thread is
* cleared when this exception is thrown.
*/
public final void join() throws InterruptedException {
join(0);
}执行流程图如下:
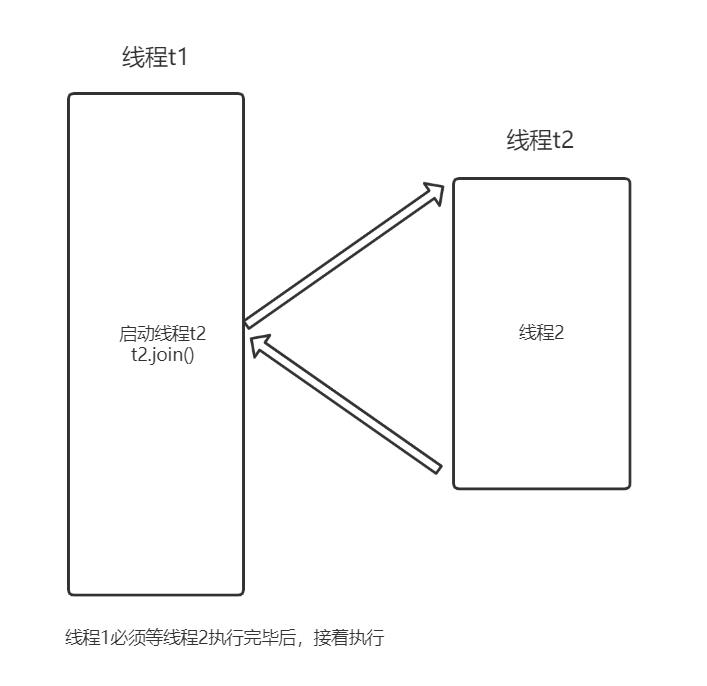
join方法中,有下面这段
public final synchronized void join(long millis)
throws InterruptedException {
long base = System.currentTimeMillis();
long now = 0;
if (millis < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("timeout value is negative");
}
if (millis == 0) {
while (isAlive()) { //判断线程是否活着
wait(0); //调用者线程等待
}
} else {
while (isAlive()) {
long delay = millis - now;
if (delay <= 0) {
break;
}
wait(delay);
now = System.currentTimeMillis() - base;
}
}
}也就是说在哪一个线程中调用了join方法,那么它就等待,直到join对象的那个线程退出,例子如下:
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("t1 start...");
Thread t2 = new Thread(()->{
System.out.println("t2 start...");
try{
Thread.sleep(2000);
}catch (Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("t2 end...");
});
t2.start();
try {
t2.join();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("t1 end...");
});
t1.start();
}
执行结果:
t1 start...
t2 start...
t2 end...
t1 end...在线程t1中启动线程t2,然后调用t2.join方法,那么t2.join是在t1线程中执行的,t1将阻塞直到t2运行结束。
获取类加载器
public ClassLoader getContextClassLoader() {
if (contextClassLoader == null)
return null;
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
ClassLoader.checkClassLoaderPermission(contextClassLoader,
Reflection.getCallerClass());
}
return contextClassLoader;
}类加载器用来加载一些class文件
设置类加载器
public void setContextClassLoader(ClassLoader cl) {
SecurityManager sm = System.getSecurityManager();
if (sm != null) {
sm.checkPermission(new RuntimePermission("setContextClassLoader"));
}
contextClassLoader = cl;
}获取线程ID
public long getId() {
return tid;
}线程状态
public enum State {
/**
* NEW状态: 并没有调用start方法
*/
NEW,
/**
* 可执行状态: 调用start方法
*/
RUNNABLE,
/**
* 阻塞状态,在run中调用了wait或者synchronized方法导致了阻塞
*/
BLOCKED,
/**
* 等待状态: 调用Object.wait()后的状态
*/
WAITING,
/**
* 等待超时状态: 调用Object.wait(timeOut), timeOut结束后的状态
*/
TIMED_WAITING,
/**
* 结束状态: 线程结束状态
*/
TERMINATED;
}状态切换图:
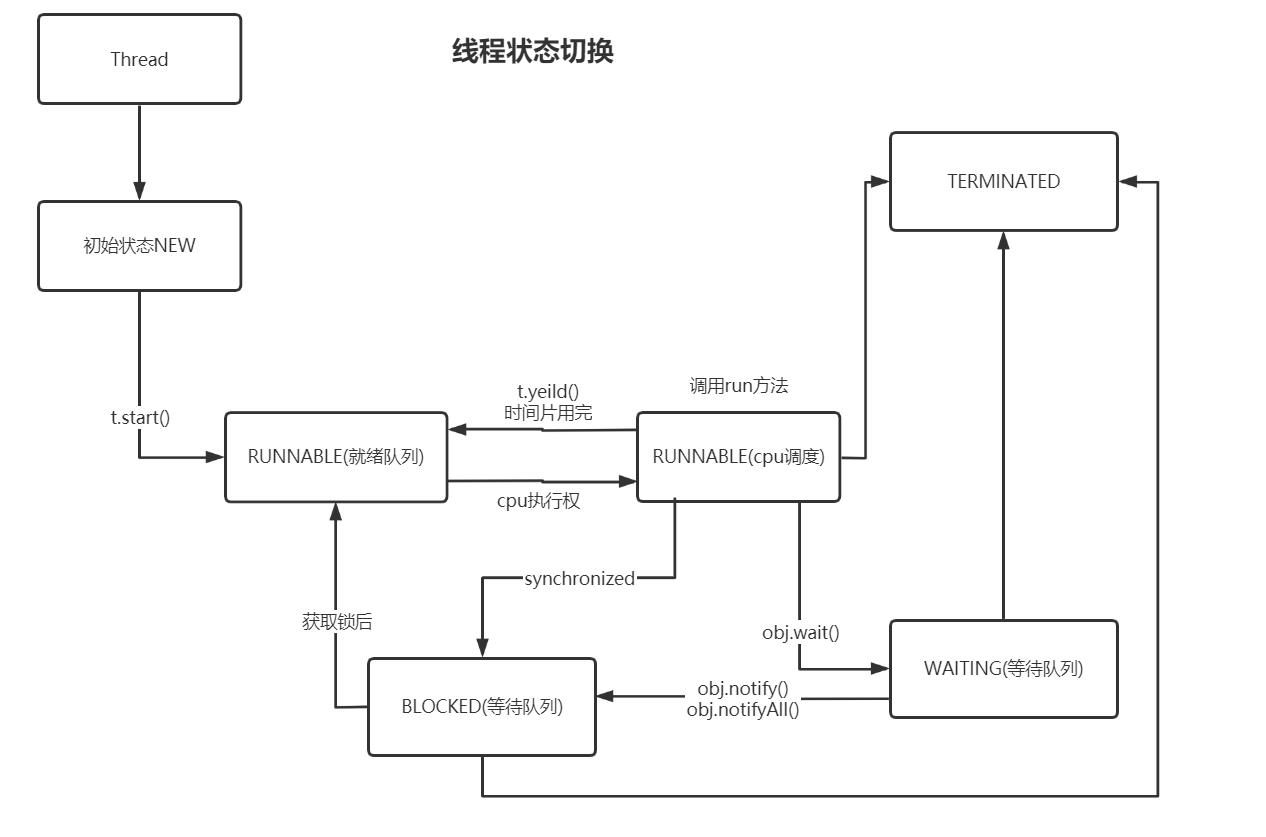
以上是关于JDK1.8 Thread类说明的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章