精选力扣500题 第35题 LeetCode 94. 二叉树的中序遍历c++ / java 详细题解
Posted 林深时不见鹿
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了精选力扣500题 第35题 LeetCode 94. 二叉树的中序遍历c++ / java 详细题解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
1、题目
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它的 中序 遍历。
示例 1:

输入:root = [1,null,2,3]
输出:[1,3,2]
示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:[]
示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:[1]
示例 4:

输入:root = [1,2]
输出:[2,1]
示例 5:
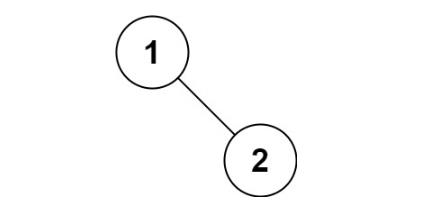
输入:root = [1,null,2]
输出:[1,2]
提示:
- 树中节点数目在范围
[0, 100]内 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
进阶: 递归算法很简单,你可以通过迭代算法完成吗?
2、思路1
(递归)
在处理每个节点时,要按照 左子树 => 根节点 => 右子树的顺序进行遍历二叉树。
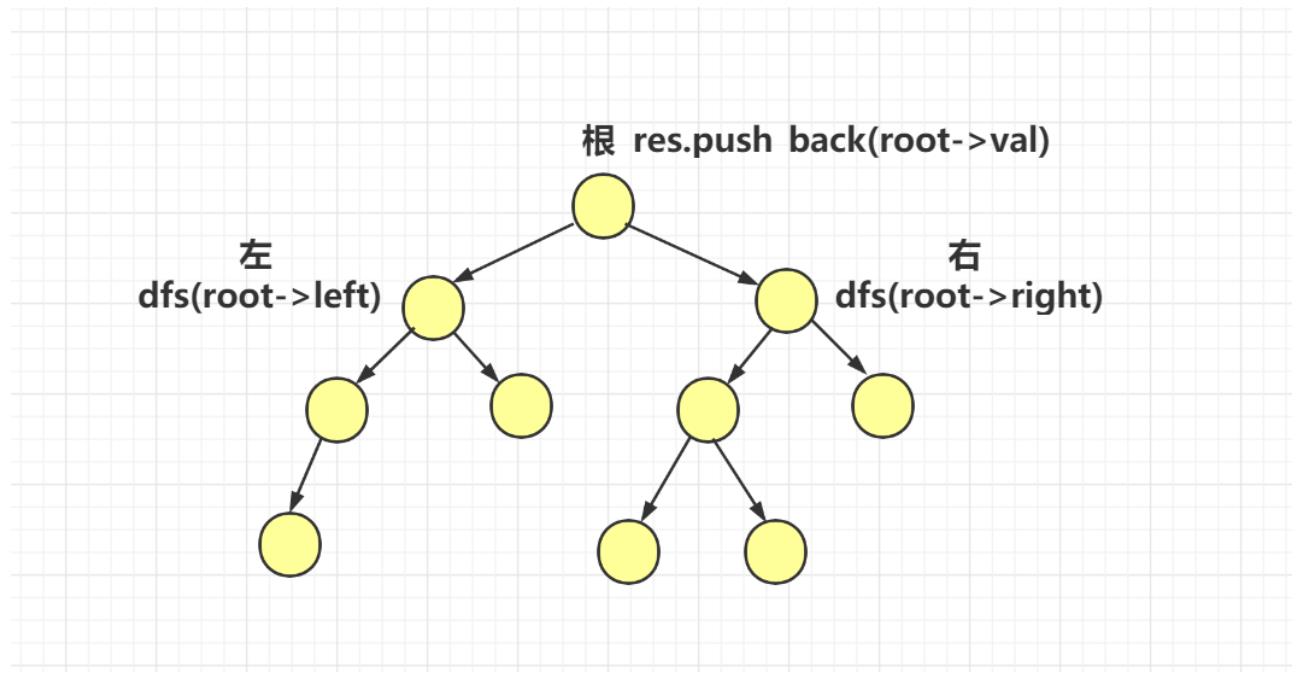
3、c++代码1
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> res; //记录答案
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode * root)
{
if(!root) return ;
dfs(root->left); //递归左子树
res.push_back(root->val); //将当前节点插入到答案序列里面
dfs(root->right); //递归右子树
}
};
4、java代码1
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
static List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<Integer>();
static void dfs(TreeNode root)
{
if(root != null)
{
dfs(root.left);
ans.add(root.val);
dfs(root.right);
}
}
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
ans.clear();
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
}
5、思路2
(迭代)
对于二叉树中的当前节点:
- 1、如果当前节点有左子树的话,将其压入栈中。
- 2、如果当前点的左儿子还有左子树,继续将左儿子压入栈中,直到最后一个节点没有左子树为止。
在递归处理左子树之前,先要保存当前节点,将其压入栈中,这个过程是可以迭代的。处理完当前节点以后,对于栈中元素:
- 1、取出栈顶元素,此时栈顶元素就是中序遍历下一个要遍历的节点,我们将其存入答案中。
- 2、如果当前栈顶元素有右子树,同上述步骤一样递归处理右子树。
- 3、如果当前栈顶元素没有右子树并且此时栈不为空,那么后继节点就是当前的栈顶元素 ,将其存入答案中。
6、c++代码2
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> inorderTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
vector<int> res;
stack<TreeNode*> stk;
while (root || stk.size()) {
while (root) {
stk.push(root);
root = root->left;
}
root = stk.top();
stk.pop();
res.push_back(root->val);
root = root->right;
}
return res;
}
};
7、java代码2
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public List<Integer> inorderTraversal(TreeNode root) {
List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<Integer>();
Stack<TreeNode> stk = new Stack<TreeNode>();
TreeNode p = root;
while(p != null || !stk.isEmpty())//说明还有元素能放进栈中 和 栈中有元素未访问
{
while(p != null)
{
stk.add(p);
p = p.left;
}
p = stk.pop();
ans.add(p.val);
p = p.right;
}
return ans;
}
}
原题链接: 94. 二叉树的中序遍历

以上是关于精选力扣500题 第35题 LeetCode 94. 二叉树的中序遍历c++ / java 详细题解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章