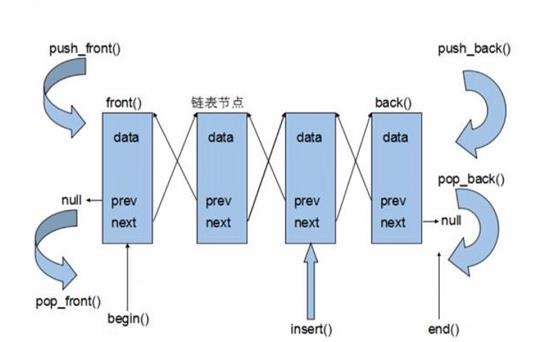
[C++STL]list容器用法介绍
Posted Wecccccccc
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了[C++STL]list容器用法介绍相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。




代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
void printList(const list<int>&L)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
list<int>L1;
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
printList(L1);
list<int>L2(L1.begin(), L1.end());
printList(L2);
list<int>L3(L2);
printList(L3);
list<int>L4(10, 100);
printList(L4);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
测试结果:

代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
void printList(const list<int>&L)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
list<int>L1;
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
printList(L1);
//赋值
list<int>L2;
L2 = L1;
printList(L2);
list<int>L3;
L3.assign(L2.begin(), L2.end());
printList(L3);
list<int>L4;
L4.assign(10, 100);
printList(L4);
}
//交换
void test02()
{
list<int>L1;
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
list<int>L2;
L2.assign(10, 100);
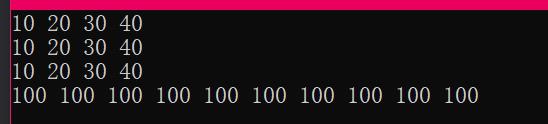
cout << "交换前" << endl;
printList(L1);
printList(L2);
cout << endl;
L1.swap(L2);
cout << "交换后" << endl;
printList(L1);
printList(L2);
}
int main()
{
test01();
test02();
return 0;
}
测试结果:

代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
void printList(const list<int>&L)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
list<int>L1;
L1.push_back(10);
L1.push_back(20);
L1.push_back(30);
L1.push_back(40);
if (L1.empty())
{
cout << "L1 empty" << endl;
}
else
{
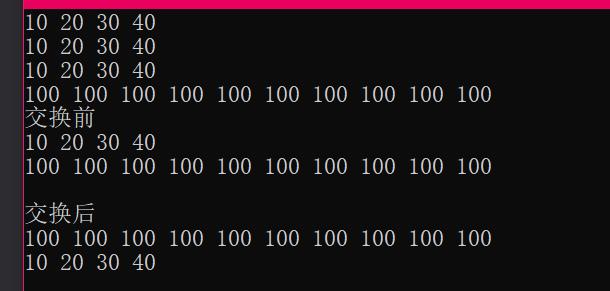
cout << "L1 no empty" << endl;
cout << "L1 capacity = " << L1.size() << endl;
}
L1.resize(10);
printList(L1);
L1.resize(2);
printList(L1);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
测试结果:
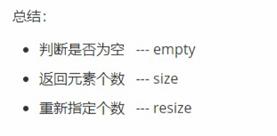
总结:

代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
void printList(const list<int>&L)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
list<int>l;
l.push_back(10);
l.push_back(20);
l.push_back(30);
l.push_front(100);
l.push_front(200);
l.push_front(300);
printList(l);
l.pop_back();
printList(l);
l.pop_front();
printList(l);
list<int>::iterator it = l.begin();
l.insert(++it, 1000);
printList(l);
it = l.begin();
l.erase(++it);
printList(l);
l.push_back(10000);
l.push_back(10000);
l.push_back(10000);
printList(l);
l.remove(10000);
printList(l);
l.clear();
printList(l);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
测试结果:
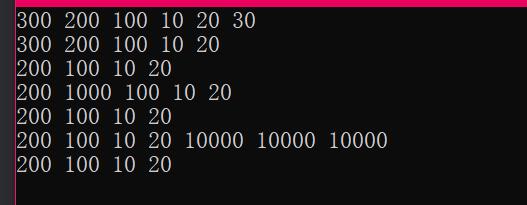
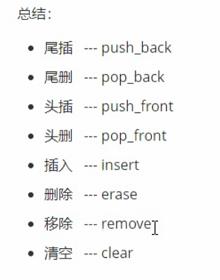
总结:

代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
void printList(const list<int>&L)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test01()
{
list<int>l1;
l1.push_back(10);
l1.push_back(20);
l1.push_back(30);
l1.push_back(40);
//cout<<l1.at(0)<<endl;//错误,不支持at访问数据
//cout<<l1[0]<<endl;//错误,不支持[]方式访问数据
cout << "front elem = " << l1.front() << endl;
cout << "back elem = " << l1.back() << endl;
//list容器的迭代器是双向迭代器,不支持随机访问
list<int>::iterator it = l1.begin();
//it = it+1;//错误,不可以跳跃访问,即便是+1
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
测试结果:
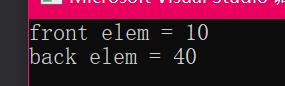
总结:


代码如下:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <list>
using namespace std;
void printList(const list<int>&L)
{
for (list<int>::const_iterator it = L.begin(); it != L.end(); it++)
{
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
bool cmp(int a, int b)
{
return a > b;
}
void test01()
{
list<int>l;
l.push_back(90);
l.push_back(30);
l.push_back(20);
l.push_back(70);
printList(l);
l.reverse();
printList(l);
l.sort();
printList(l);
l.sort(cmp);
printList(l);
}
int main()
{
test01();
return 0;
}
测试结果:
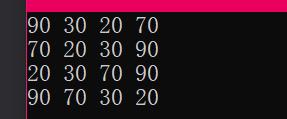
总结:
反转 — reverse
排序 — sort(成员函数)
以上是关于[C++STL]list容器用法介绍的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章