0x00 基本算法
Posted 幽殇默
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了0x00 基本算法相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
目录
位运算
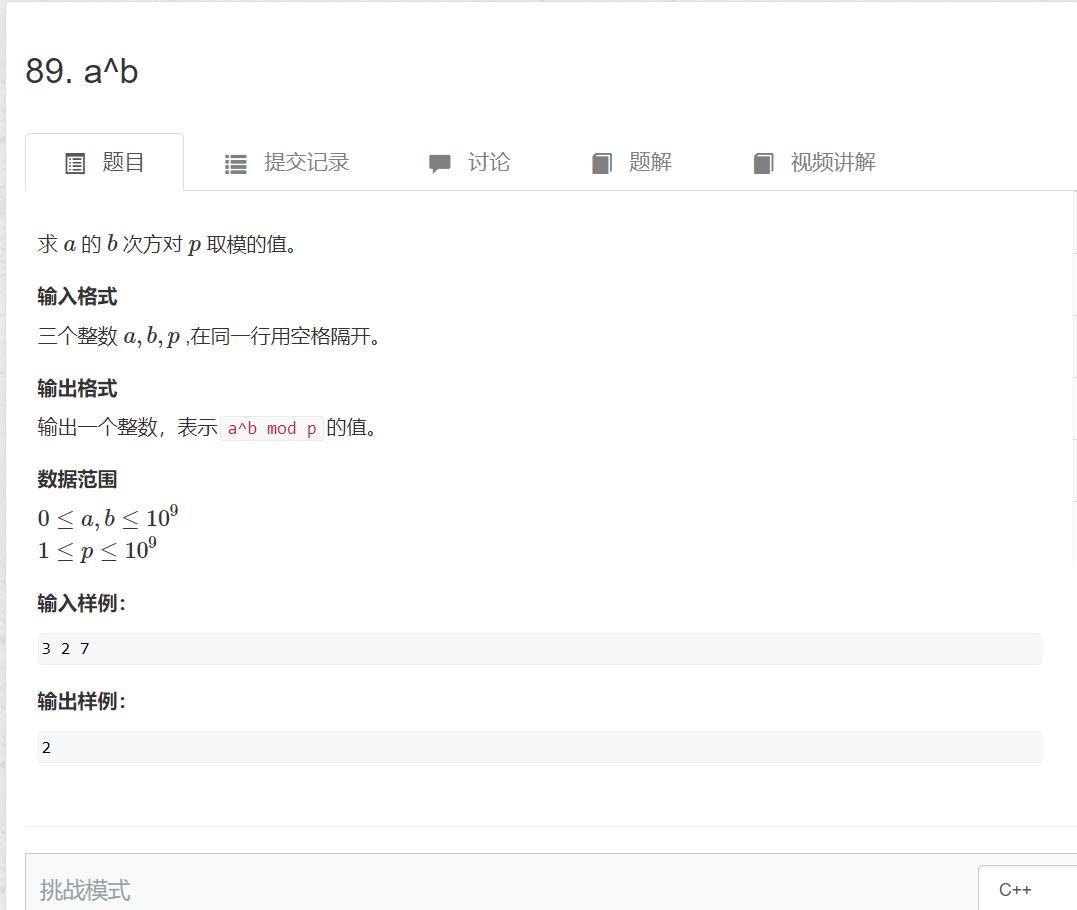
89. a^b
考察的知识点: 二进制快速幂
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
LL a,b,p;
LL quick_mi(LL a,LL b,LL p)
{
LL res=1;
while(b)
{
if(b&1) res=res*a%p;
a=a*a%p;
b>>=1;
}
return res%p;//这里取模 排除 b=0的特殊情况
}
int main(void)
{
cin>>a>>b>>p;
cout<<quick_mi(a,b,p);
return 0;
}
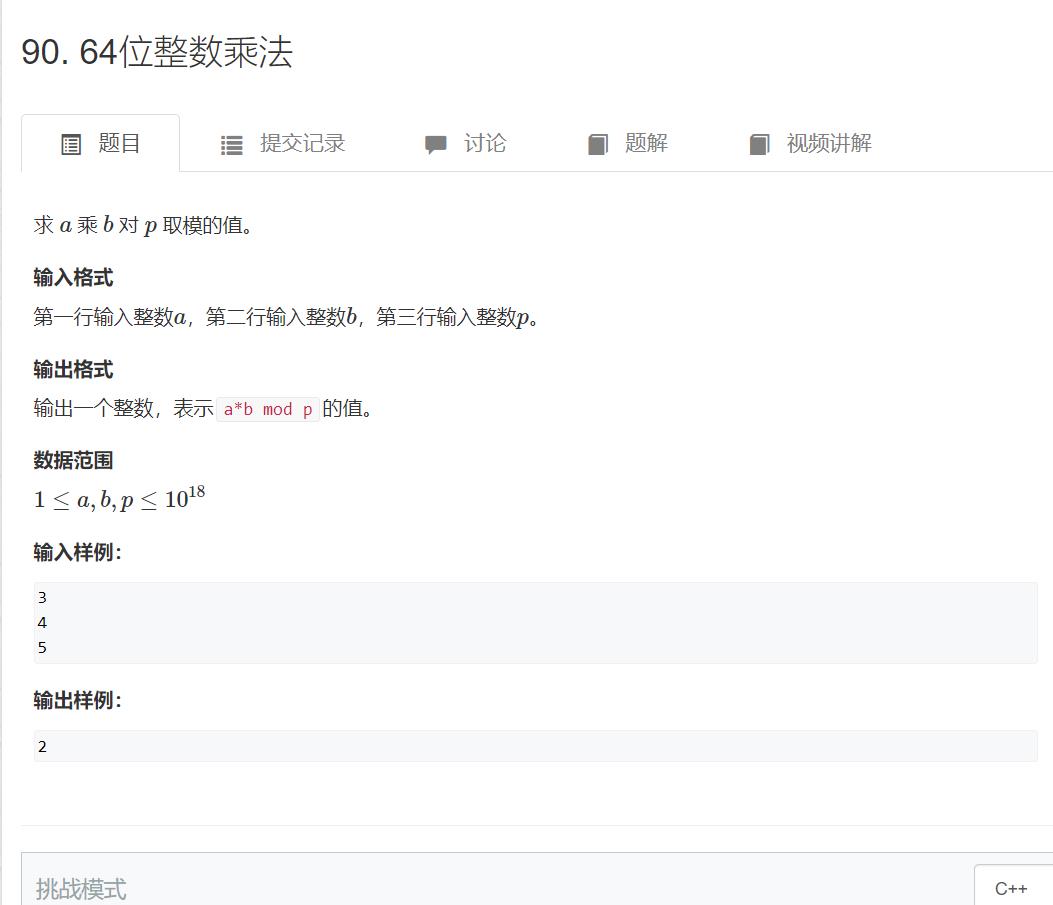
90. 64位整数乘法
考察的知识点:还是二进制快速幂和上面的题的思路几乎一样,不过这里是加法而已。
因为 a*b 等于 b个a相加
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
typedef long long int LL;
LL a,b,p;
LL f(LL a,LL b, LL p)
{
LL res=0;
while(b)
{
if(b&1) res=(res+a)%p;
a=a*2%p;
b=b>>1;
}
return res%p;
}
int main(void)
{
cin>>a>>b>>p;
cout<<f(a,b,p);
return 0;
}
__128int写法
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
void scan(__int128 &x)//输入
{
x = 0;
int f = 1;
char ch;
if((ch = getchar()) == '-') f = -f;
else x = x*10 + ch-'0';
while((ch = getchar()) >= '0' && ch <= '9')
x = x*10 + ch-'0';
x *= f;
}
void _print(__int128 x)
{
if(x > 9) _print(x/10);
putchar(x%10 + '0');
}
void print(__int128 x)//输出
{
if(x < 0)
{
x = -x;
putchar('-');
}
_print(x);
}
int main()
{
__int128 a,b,p;
scan(a); scan(b); scan(p);
print(a%p*b%p%p);
return 0;
}
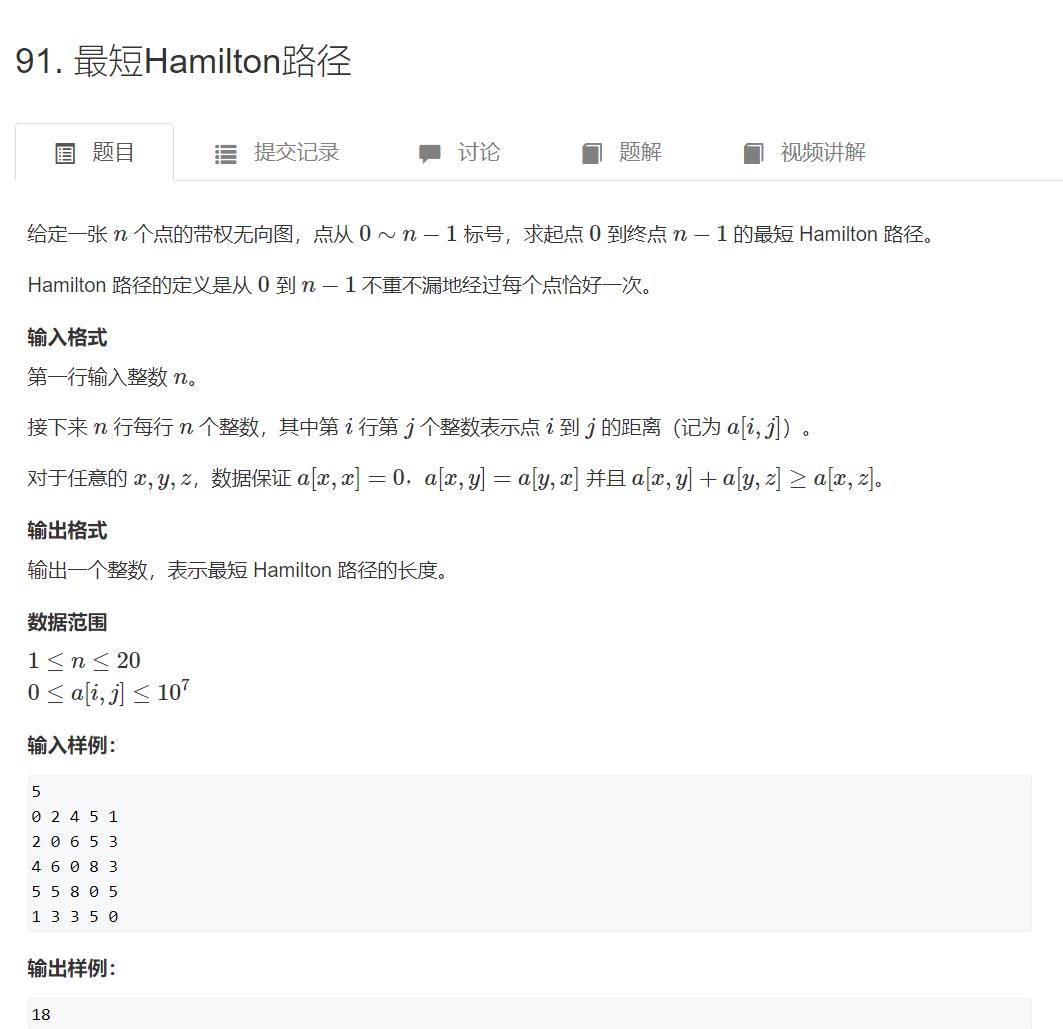
91. 最短Hamilton路径 【二进制 / 状态压缩DP】
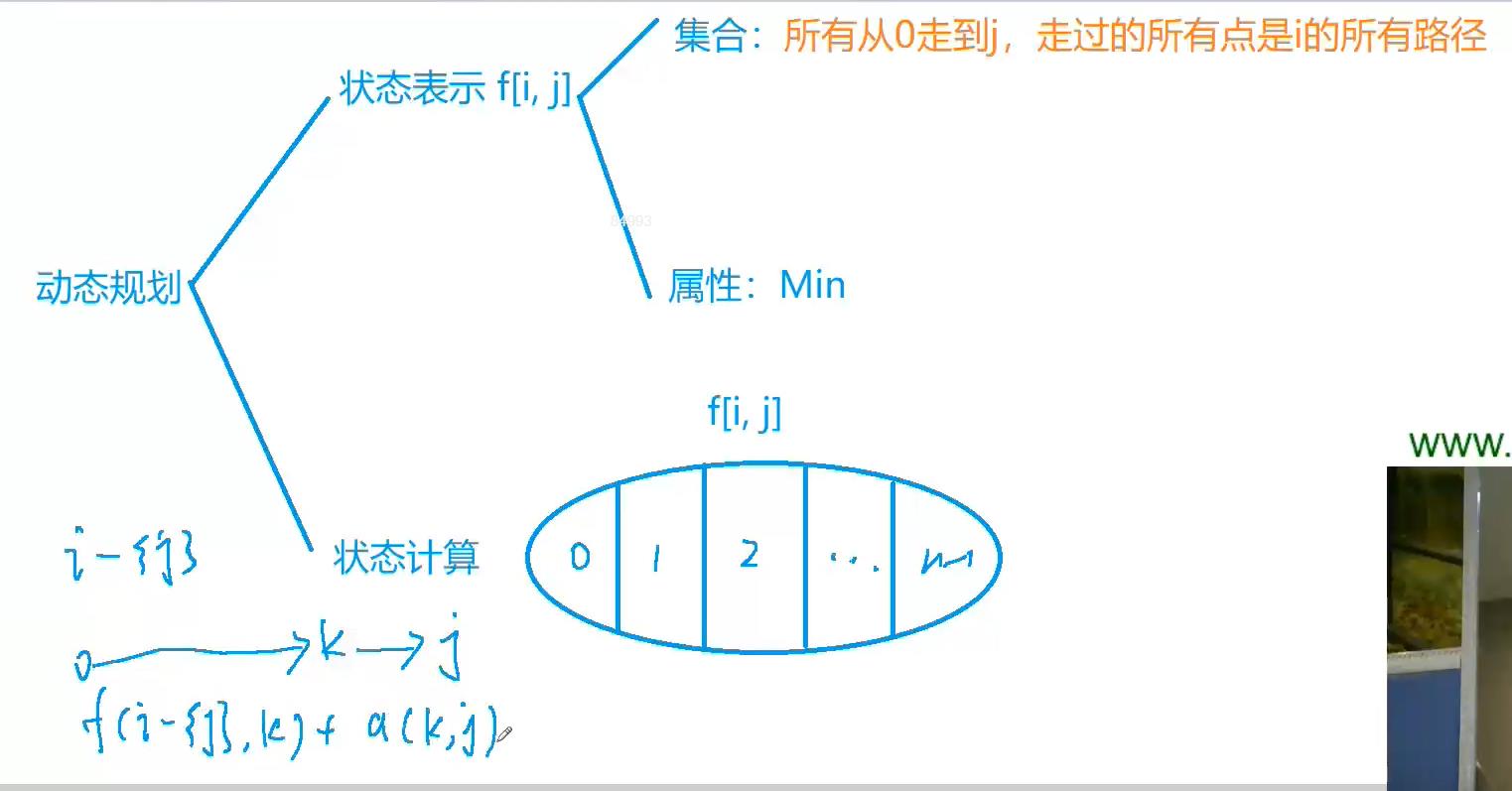
状态表示f[i][j] i表示走过的点的集合,用二进制表示 ,1代表该点走过了 0代表还没有走过 j表示当前状态的终点的点
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N=20,M=1<<20;
int f[M][N],w[N][N];
int n;
int main(void)
{
int n; cin>>n;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
cin>>w[i][j];
memset(f,0x3f,sizeof f);
f[1][0]=0;//当前在起点距离为0
for(int i=0;i<(1<<n);i++)//走的点的集合
{
for(int j=0;j<n;j++)
{
if(i>>j & 1 )//集合中含有j,是一种合法的状态。 因为j的含义是终点,所以i的集合中一定得有
{
for(int k=0;k<n;k++)//看一下上一个结点k 是否存在
{
if( (i-(1<<j))>>k & 1)//除掉j这个点,看剩余的集合中是否有k
{
f[i][j]=min(f[i][j],f[i-(1<<j)][k]+w[k][j]);//从当前状态和从k转移到j的状态中选一个小的
}
}
}
}
}
cout<<f[ (1<<n)-1][n-1]<<endl;
return 0;
}
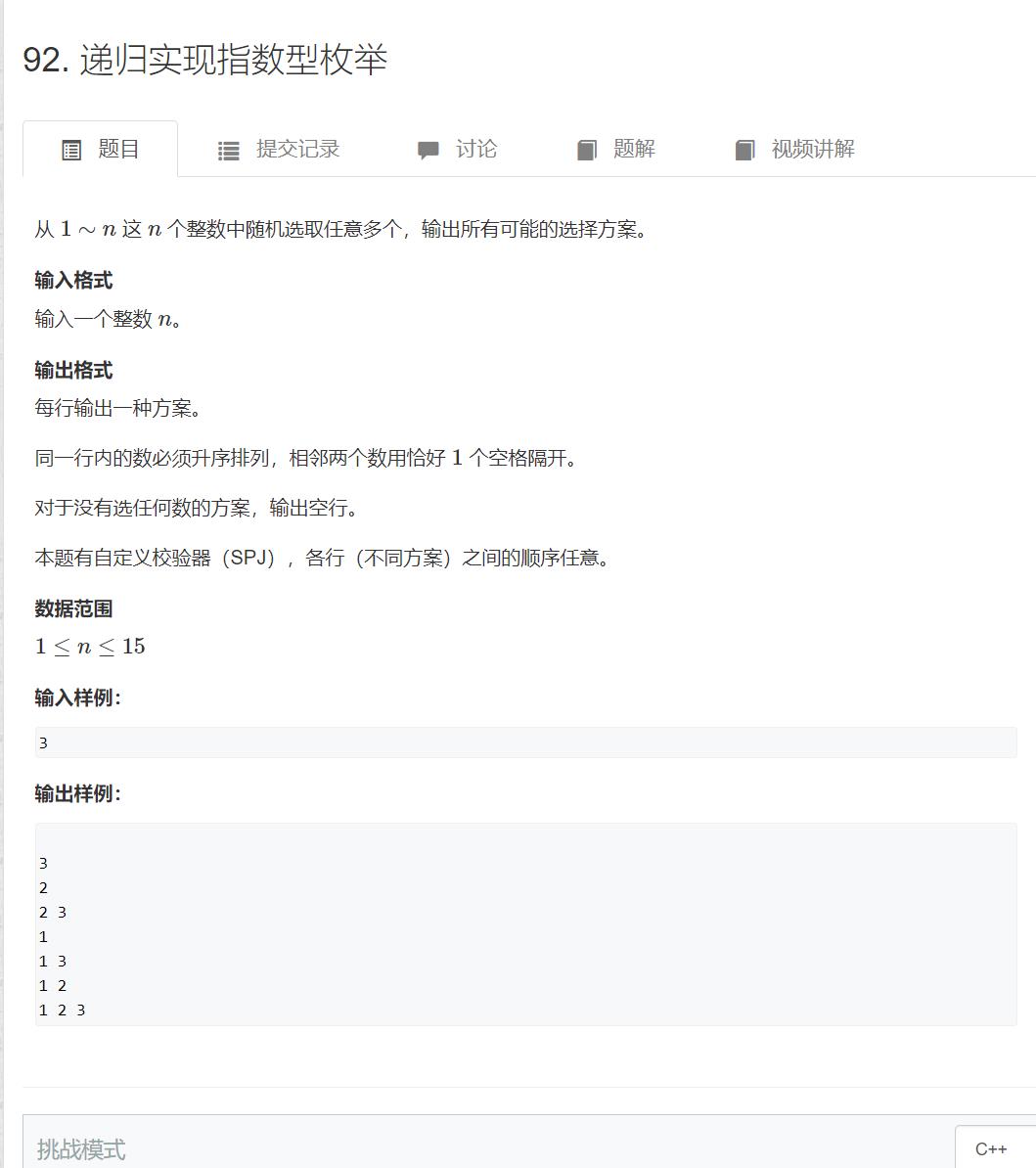
递推与递归
92. 递归实现指数型枚举
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int n;
int a[30];
void dfs(int index)
{
if(index==n+1)
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(a[i]) cout<<i<<" ";
cout<<endl;
return ;
}
a[index]=1;
dfs(index+1);
a[index]=0;
dfs(index+1);
}
int main(void)
{
cin>>n;
dfs(1);
return 0;
}
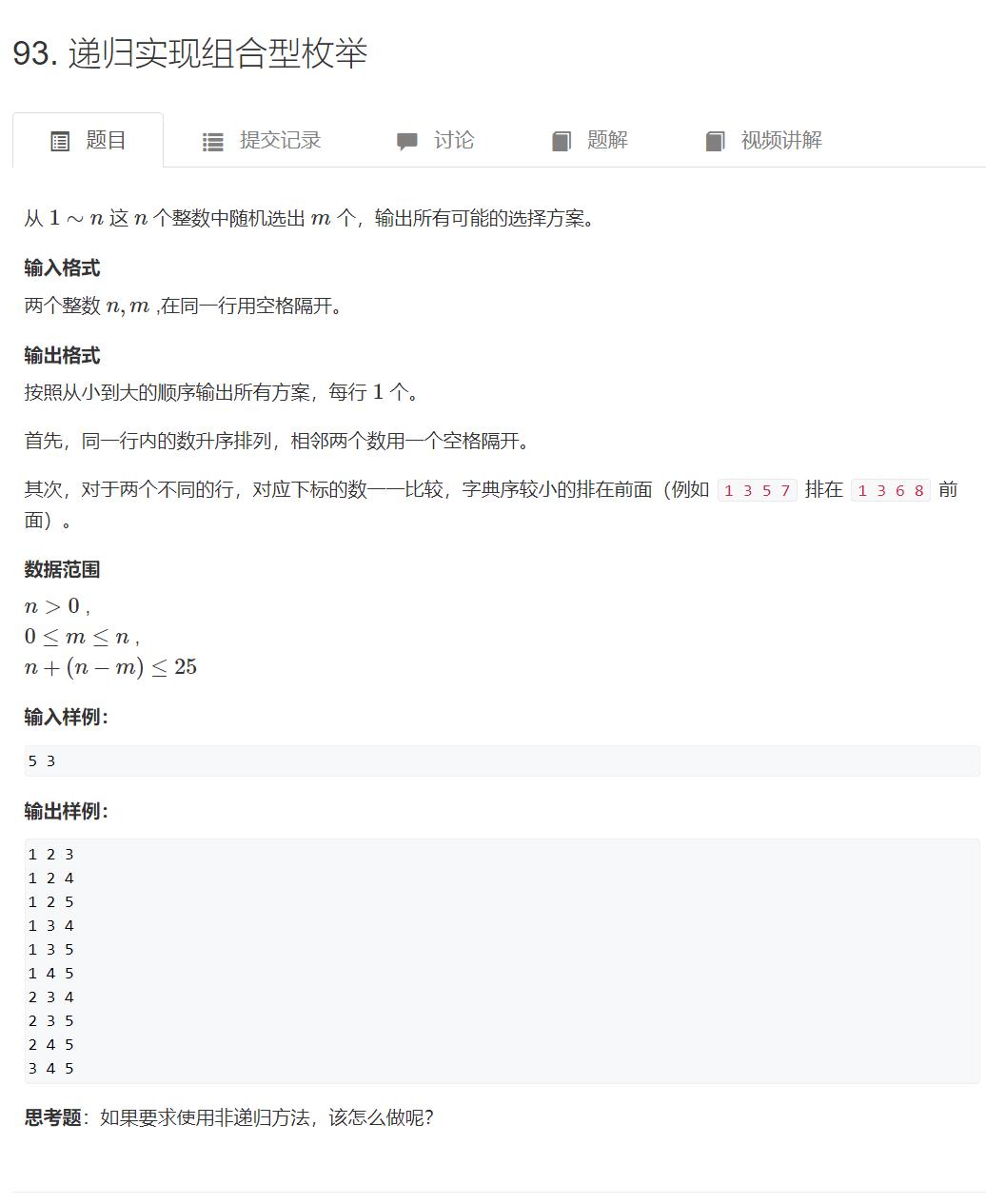
93. 递归实现组合型枚举
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int a[50];
bool st[50];
int n,k;
void dfs(int index,int start)
{
if(index==k+1)
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
if(st[i]) cout<<i<<" ";
cout<<endl;
return ;
}
for(int i=start;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!st[i])
{
st[i]=true;
dfs(index+1,i);
st[i]=false;
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
cin>>n>>k;
dfs(1,1);
return 0;
}
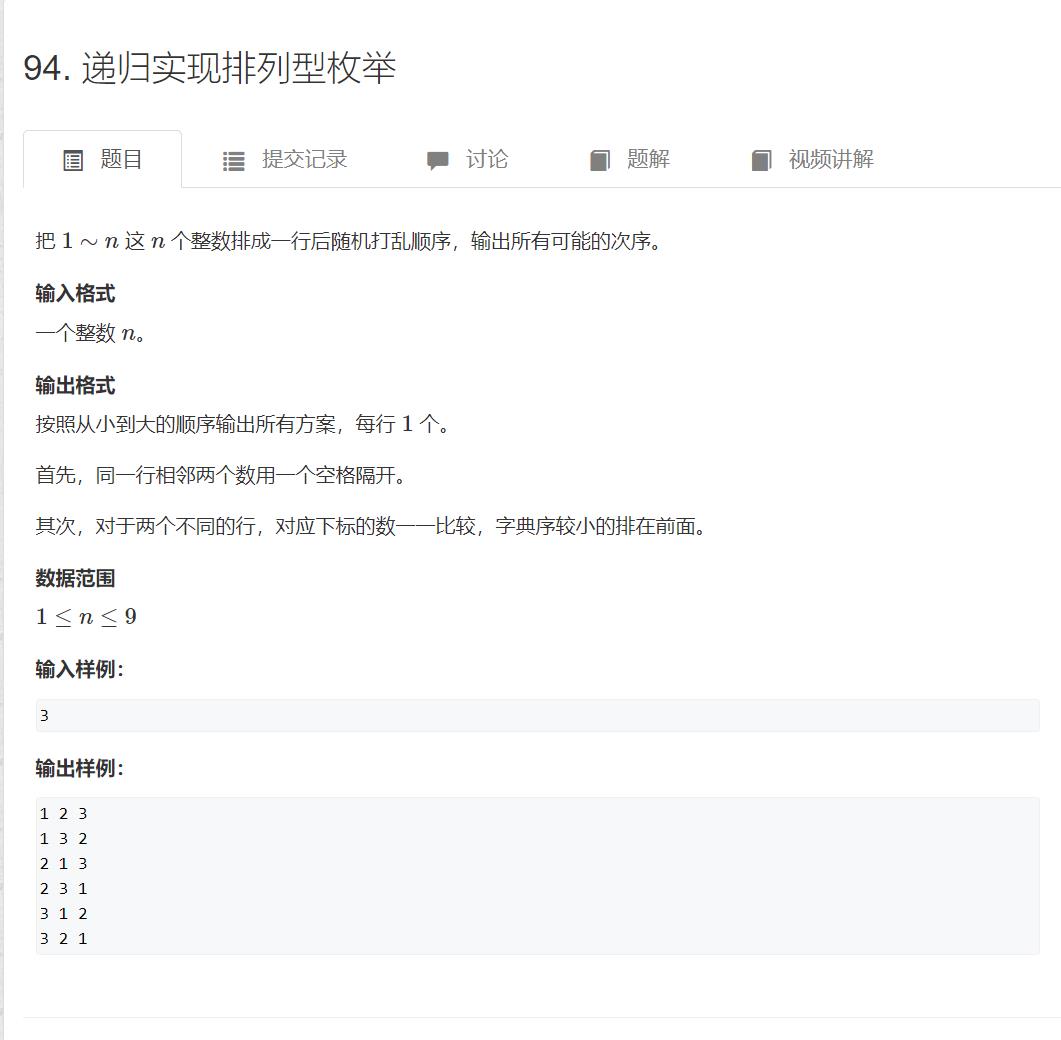
94. 递归实现排列型枚举
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int a[50];
bool st[50];
int n;
void dfs(int index)
{
if(index==n+1)
{
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cout<<a[i]<<" ";
cout<<endl;
return;
}
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
if(!st[i])
{
a[index]=i;
st[i]=true;
dfs(index+1);
st[i]=false;
}
}
}
int main(void)
{
cin>>n;
dfs(1);
return 0;
}
以上是关于0x00 基本算法的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章