贪心算法——模拟机器人行走(LeetCode874)
Posted AI 菌
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了贪心算法——模拟机器人行走(LeetCode874)相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、模拟机器人行走
题目如下:


题目来源:力扣(LeetCode)
原题链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/walking-robot-simulation
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
二、题目解析
对于题目中的实例2,机器人的行走路线如下图所示:
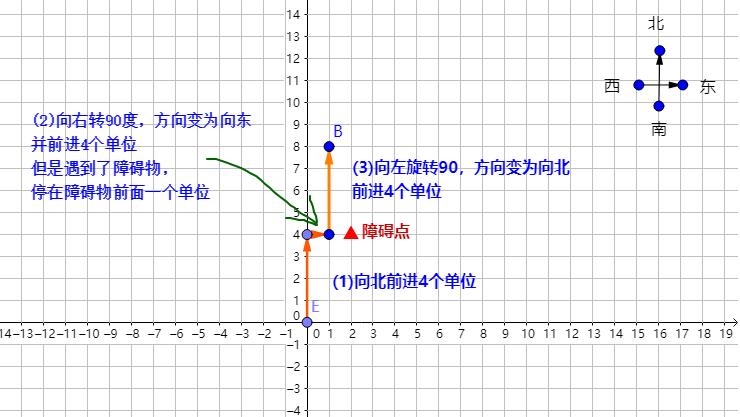
对于本题,情况稍微有点复杂,所以我们可以分以下三个步骤由简向繁,逐步完成。
步骤1:假设没有障碍物,模拟机器人行走
C++解法:
class Solution {
public:
int robotSim(vector<int>& commands, vector<vector<int>>& obstacles) {
int n = commands.size();
int grad = 0; //方向向北
int x=0, y=0; //初始化点坐标
int dis_max=0; //最远点距离
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i)
{
if(commands[i]==-2)
grad += 3; //向左转90度,即向右转270度,加3。
else if(commands[i]==-1)
grad += 1; //向右转90度,加1
else //否则,就是正常移动
{
grad = grad % 4;
if(grad==0) //向北移动commands[i]
y += commands[i];
else if(grad==1) //向东移动commands[i]
x += commands[i];
else if(grad==2) //向南移动commands[i]
y -= commands[i];
else //向西移动commands[i]
x -= commands[i];
int dis = pow(x,2)+pow(y,2);
dis_max = max(dis_max, dis);
}
}
return dis_max;
}
};
步骤2:当有障碍物时,模拟机器人行走
C++解法:
class Solution {
public:
int robotSim(vector<int>& commands, vector<vector<int>>& obstacles) {
int n = commands.size();
int m = obstacles.size();
int grad = 0; //方向向北
int x=0, y=0; //初始化点坐标
int dis_max=0; //最远点距离
set<pair<int, int>> obstacleSet;
for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
obstacleSet.insert(make_pair(obstacles[i][0], obstacles[i][1]));
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i)
{
if(commands[i]==-2)
grad += 3; //向左转90度,即向右转270度,加3。
else if(commands[i]==-1)
grad += 1; //向右转90度,加1
else //否则,就是正常移动
{
grad = grad % 4;
if(grad==0) //向北移动commands[i]
{
for(int j=0; j<commands[i]; ++j)
{
y += 1;
if(obstacleSet.find(make_pair(x, y)) != obstacleSet.end()) //(x,y)是障碍点
{
y -= 1;
break;
}
}
}
else if(grad==1) //向东移动commands[i]
{
for(int j=0; j<commands[i]; ++j)
{
x += 1;
if(obstacleSet.find(make_pair(x, y)) != obstacleSet.end())
{
x -= 1;
break;
}
}
}
else if(grad==2) //向南移动commands[i]
{
for(int j=0; j<commands[i]; ++j)
{
y -= 1;
if(obstacleSet.find(make_pair(x, y)) != obstacleSet.end())
{
y += 1;
break;
}
}
}
else //向西移动commands[i]
{
for(int j=0; j<commands[i]; ++j)
{
x -= 1;
if(obstacleSet.find(make_pair(x, y)) != obstacleSet.end())
{
x += 1;
break;
}
}
}
int dis = pow(x,2)+pow(y,2);
dis_max = max(dis_max, dis);
}
}
return dis_max;
}
};
提交结果:
步骤3:进一步优化
C++解法:
class Solution {
public:
int robotSim(vector<int>& commands, vector<vector<int>>& obstacles) {
int n = commands.size();
int m = obstacles.size();
int grad = 0; //方向向北
int x=0, y=0; //初始化点坐标
int dis_max=0; //最远点距离
int grad_x[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
int grad_y[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
set<pair<int, int>> obstacleSet;
for(int i=0; i<m; i++)
obstacleSet.insert(make_pair(obstacles[i][0], obstacles[i][1]));
for(int i=0; i<n; ++i)
{
if(commands[i]==-2)
grad += 3; //向左转90度,即向右转270度,加3。
else if(commands[i]==-1)
grad += 1; //向右转90度,加1
else //否则,就是正常移动
{
grad = grad % 4;
for(int j=0; j<commands[i]; ++j)
{
x += grad_x[grad];
y += grad_y[grad];
if(obstacleSet.find(make_pair(x, y)) != obstacleSet.end())
{
x -= grad_x[grad];
y -= grad_y[grad];
break;
}
}
int dis = pow(x,2)+pow(y,2);
dis_max = max(dis_max, dis);
}
}
return dis_max;
}
};
提交结果:
以上是关于贪心算法——模拟机器人行走(LeetCode874)的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章