你们要的Android计算器,今天它来了!
Posted 振华OPPO
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了你们要的Android计算器,今天它来了!相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
项目目录
一、项目概述
本次项目主要实现了简单的计算器功能,包括加减乘除基本运算,还有小数点和清零功能。可以算得上是很好的android界面和按钮点击事件学习实例。刚用模拟器显示hello world的同学或者完全没有接触过Android的同学都可以直接上手。
二、开发环境
Android版本相对之前调整了一下,现在是4.2.1,当然版本不影响,代码语法并不会变,只是gradle变了而已。到时候导入我项目的时候改下gradle路径就可以了。
如果遇到问题,可以参考这两篇经验:
快速解决Android项目的Gradle报错问题
如何导入gradle版本不同的Android项目
三、详细设计
1、布局设计
在讲布局前我们先介绍GridLayout(网格布局),来说下它的优点:
| 1、可以自己设置布局中组件的排列方式 |
|---|
| 2、可以自定义网格布局有多少行,多少列 |
|---|
| 3、可以直接设置组件位于某行某列 |
|---|
| 4、可以设置组件横跨几行或者几列 |
|---|
下面我们看下计算器的layout代码:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<GridLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity"
android:orientation="vertical">
<GridLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="top">
<!--输入的文本框-->
<EditText
android:id="@+id/result"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:hint="请输入数字"
android:textSize="30dp"/>
</GridLayout>
<GridLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:rowCount="5"
android:columnCount="4"
android:layout_gravity="center|top">
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn1"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_columnSpan="1"
android:text="1" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn2"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:text="2" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn3"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:text="3" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/divide"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:text="/" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn4"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:text="4" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn5"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:text="5" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn6"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:text="6" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/multi"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:text="*" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn7"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:text="7"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn8"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:text="8" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn9"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:text="9" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/sub"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:text="—" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/btn0"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:text="0" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/point"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_columnSpan="1"
android:text="." />
<Button
android:id="@+id/clean"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:text="del" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/plus"
android:layout_width="90dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:layout_rowSpan="1"
android:text="+" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/equ"
android:layout_width="390dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:layout_columnSpan="4"
android:layout_margin="5dp"
android:text="="
android:textSize="30dp"/>
</GridLayout>
</GridLayout>
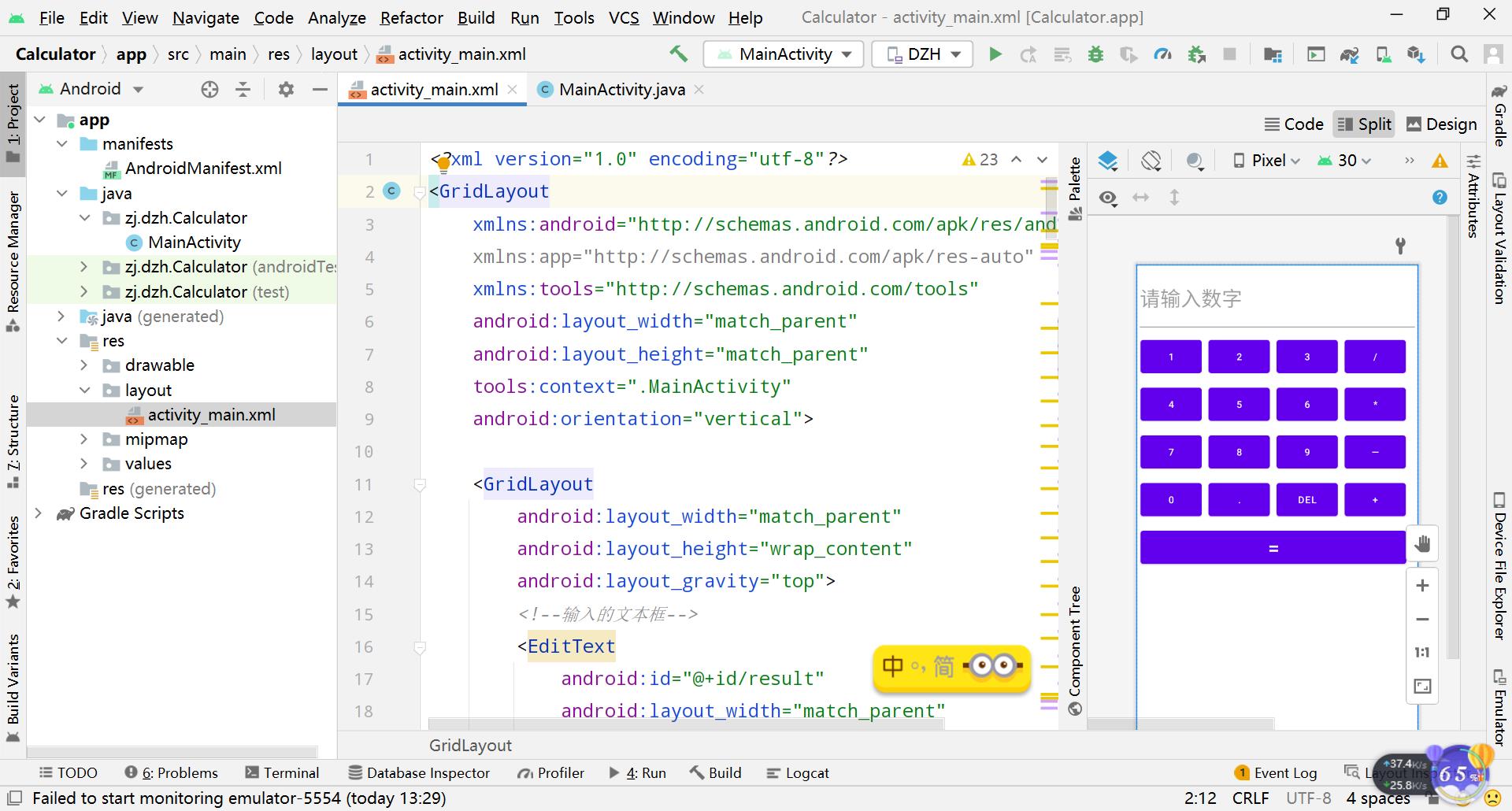
代码很简单,每个Button设置了id,其中“=”按钮横跨一行,其他的都是直接添加的,默认每个组件都是占一行一列。
另外还有一点要注意的:我们通过android:layout_rowSpan与android:layout_columnSpan设置了组件横跨多行或者多列的话;如果你要让组件填满横越过的行或列的话,需要添加下面这个属性: android:layout_gravity = “fill”。就像这个计算器显示数字的部分(result输入框)。
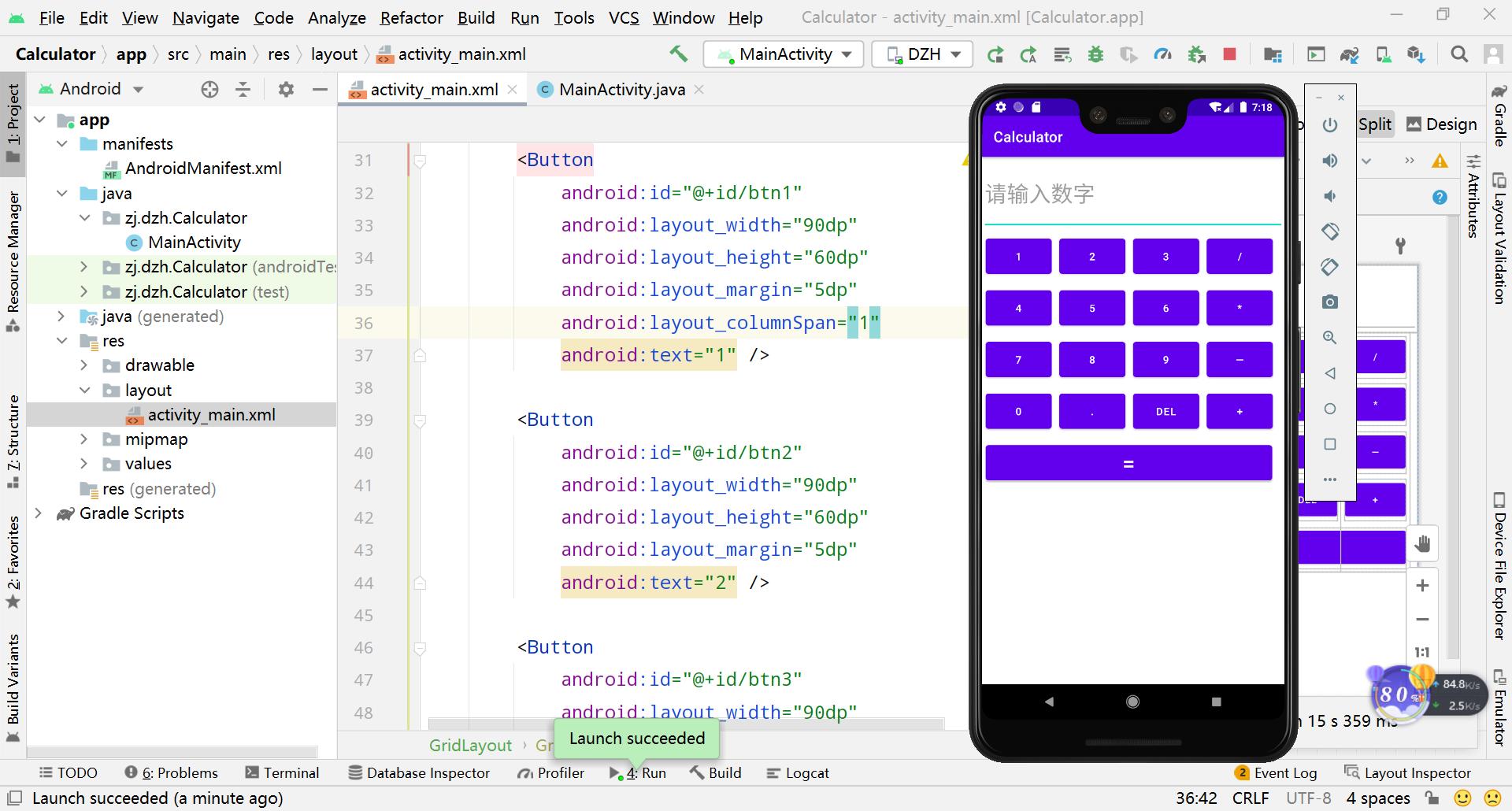
我们来看下界面预览:
2、主函数
2.1、控件定义
定义了很多button,分别代表0-9、加减乘除、小数点、等于和清零,这里变量名一定要简洁易懂,不要随意定义变量名,养成好习惯。
//运算符
private Button plus;//加号+
private Button sub;//减号-
private Button multi; //乘号*
private Button divide;// 除号/
private Button point; //小数点.
private Button equ; //等于=
private Button clean;//清除输入框
2.2、控件绑定
将刚刚定义的变量和已经设置好的控件通过id进行绑定,这样整个变量就代表了这个控件记住,写Android一定要先写layout,再写Main函数。
plus = findViewById(R.id.plus);// +
sub = findViewById(R.id.sub);// -
multi = findViewById(R.id.multi);// *
divide = findViewById(R.id.divide); // /
point = findViewById(R.id.point);//小数点
equ = findViewById(R.id.equ);//=
clean = findViewById(R.id.clean);//清空
2.3、控件设置监听器
将每个控件添加上点击事件,这是最常用的方法,系统监听到你的动作从而给出响应。
plus.setOnClickListener(this);
sub.setOnClickListener(this);
multi.setOnClickListener(this);
divide.setOnClickListener(this);
equ.setOnClickListener(this);
point.setOnClickListener(this);
clean.setOnClickListener(this);
2.4、控件设置点击事件
这里我们通过变量clear_flag来判断,它是清空标识,true就是清空,false就是未清空。
然后将数字、运算符、其他操作分类即可。
public void onClick(View view) {
//获取文本内容
String input = editText.getText().toString();
switch (view.getId()){//选择按钮id
case R.id.btn0:
case R.id.btn1:
case R.id.btn2:
case R.id.btn3:
case R.id.btn4:
case R.id.btn5:
case R.id.btn6:
case R.id.btn7:
case R.id.btn8:
case R.id.btn9:
case R.id.point:
if(clear_flag){
clear_flag = false;
editText.setText("");//赋值为空
}
editText.setText(input + ((Button)view).getText());//结果集就为本身
break;
case R.id.plus:
case R.id.sub:
case R.id.multi:
case R.id.divide://加减乘除一起
if(clear_flag){
clear_flag = false;
input = "";
editText.setText("");
}
editText.setText(input + " " + ((Button)view).getText() + " ");
break;
case R.id.clean://清除输入框
if(clear_flag){
clear_flag = false;
input = "";
editText.setText("");
}else if(input != null || !input.equals("")) {//如果获取到的内容为空
editText.setText(input.substring(0, input.length() - 1));//结果集为空
}
break;
case R.id.equ://运算结果等于
getResult();//调用处理结果集的方法
break;
}
}
2.5、运行结果
这部分方法就是计算两个数字运算结果,就是if-else语句,equals( )就是两个对象比较,如果相同则为true,否则为false,contains( ) 就是包含关系,包含为ture,否则为false。
//运算结果的方法
private void getResult(){
String exp = editText.getText().toString();//获取文本框的内容
if(exp==null||exp.equals("")){
return;
}
if(!exp.contains(" ")){
return;
}
if(clear_flag){
clear_flag = false;
return;
}
clear_flag = true;
double result = 0;
//进行截取
//运算符前的数字
String s1 = exp.substring(0,exp.indexOf(" "));
//运算符
String op = exp.substring(exp.indexOf(" ")+1,exp.indexOf(" ")+2);
//运算符后的数字
String s2 = exp.substring(exp.indexOf(" ")+3);
if(!s1.equals("")&&!s2.equals("")) {//如果包含小数点的运算
double d1 = Double.parseDouble(s1);//则数字都是double类型
double d2 = Double.parseDouble(s2);
if (op.equals("+")) {//如果是 +
result = d1 + d2;
} else if (op.equals("-")) {
result = d1 - d2;
} else if (op.equals("*")) {
result = d1 * d2;
} else if (op.equals("/")) {
if (d2 == 0) { //如果被除数是0
result = 0; //则结果是0
}
else {//否则执行正常是除法运算
result = d1 / d2;
}
}
if (!s1.contains(".") && !s2.contains(".") && !op.equals("/")) {//如果是整数类型
int r = (int) result; //都是整形
editText.setText(r + "");
} else{
editText.setText(result + "");
}
}else if(!s1.equals("") && s2.equals("")){//如果是只输入运算符前的数
editText.setText(exp);//直接返回当前文本框的内容
}else if(s1.equals("") && !s2.equals("")){//如果是只输入运算符后面的数
double d2 = Double.parseDouble(s2);
//运算符前没有输入数字
if (op.equals("+")) {
result = 0 + d2;
} else if (op.equals("-")) {
result = 0 - d2;
} else if (op.equals("*")) {
result = 0;
} else if (op.equals("/")) {
result = 0;
}
if (!s1.contains(".") && !s2.contains(".")) {
int r = (int) result;
editText.setText(r + "");
} else{
editText.setText(result + "");
}
}else {
editText.setText("");
}
}
四、项目效果
1、打开模拟器运行,输入两个数字
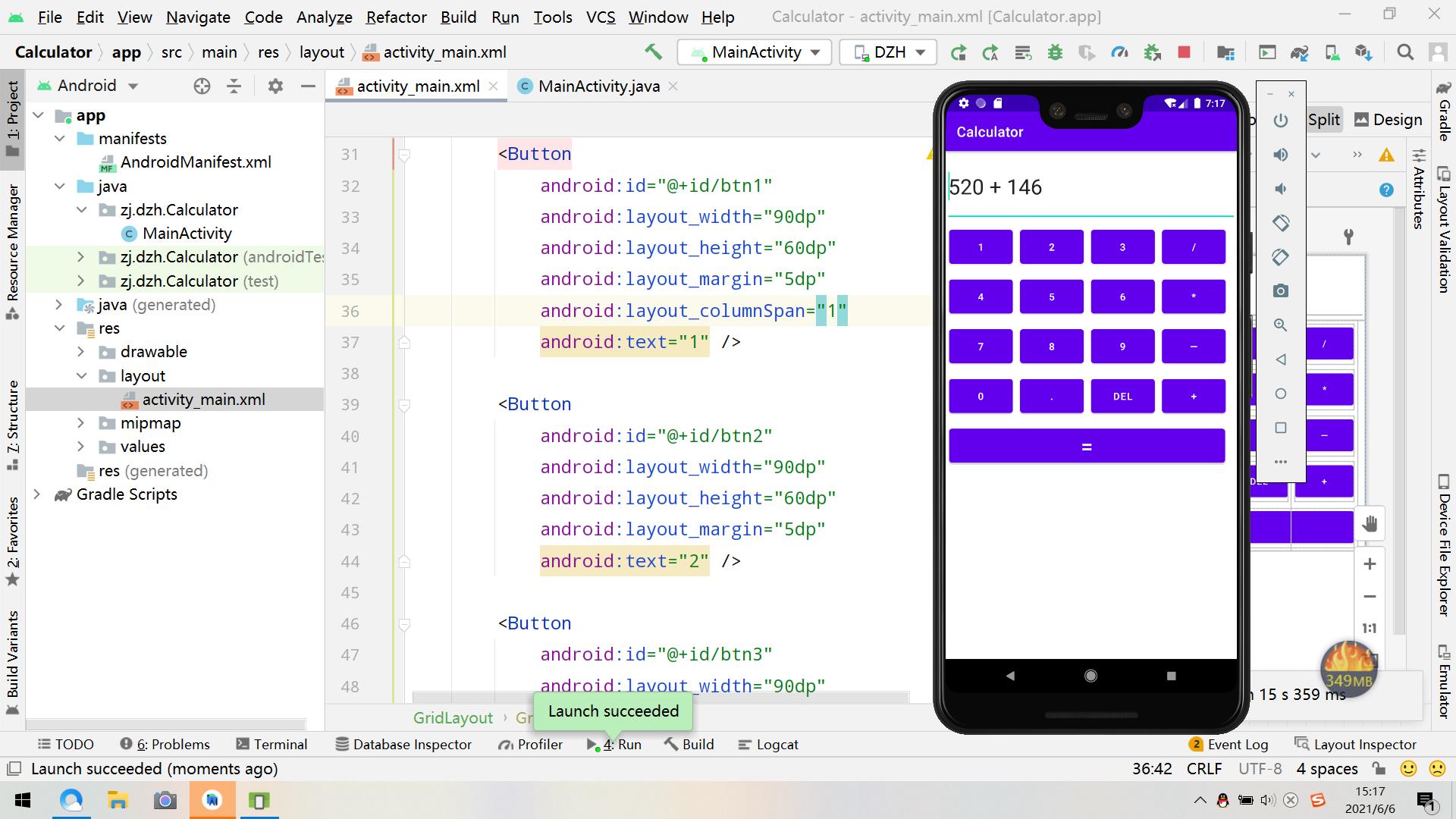
2、按等于键,得出结果
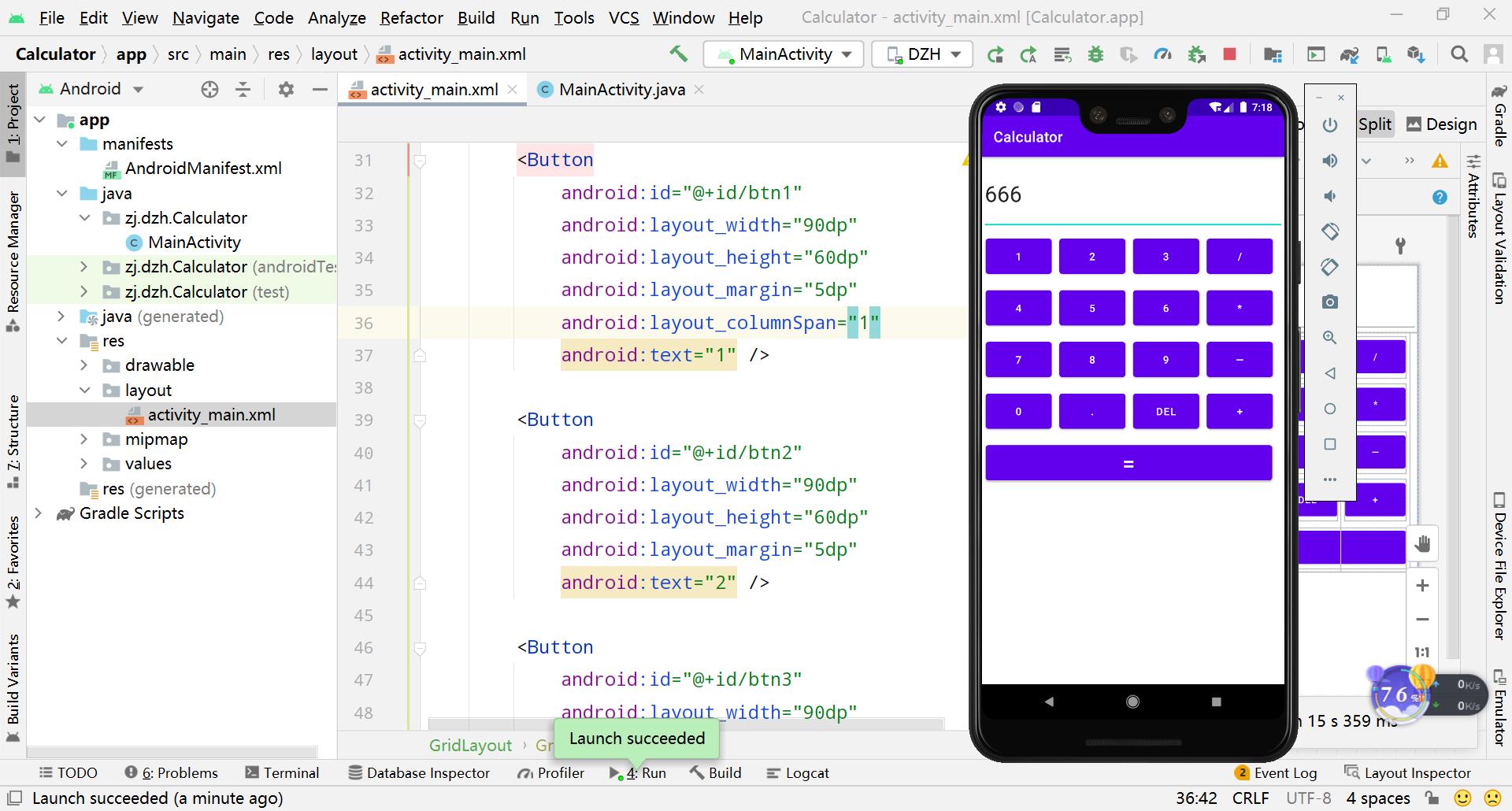
3、选择清空键,清除所有结果
五、项目总结
本次项目是比较基础的考验布局和控件的实例,对于初学者来说是非常好的example,可以作为Hello World之后第二个实例,认真消化里面的内容,以后做起来会非常快。
六、源码下载
需要源码学习的同学可以关注我的微信公众号,回复:计算器,即可免费获取源
以上是关于你们要的Android计算器,今天它来了!的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章