OC Foundation框架 字典
Posted Billy Miracle
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了OC Foundation框架 字典相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
NSDictionary用于保存具有映射关系的数据。因此,NSDictionary集合里保存着两组值,一组值用于保存NSDictionary里的key,另一组值用于保存NSDictionary里的value。注意:key和value都可以是任何指针类型的数据,NSDictionary的key不允许重复。
key和value之间存在一对一关系即通过指定的key,总能找到唯一的、确定的value。从NSDictionary中取出数据时,只要给出指定的key,就可以取出对应的value。NSDictionary有类似下图的结构:
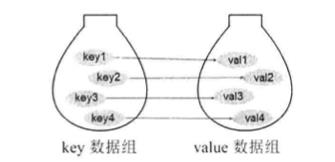
所有的key组成一个NSSet集合(key没有顺序,不能重复),实际上,NSDictionary确实包含一个allKeys方法,用于返回NSDictionary所有key组成的集合,但是,NSDictionary把allKeys方法的返回值设为NSArray,说明该方法经过了进一步的转换。
NSDictionary的功能与用法
NSDictionary分别提供了类方法和实例方法来创建NSDictionary,类方法以dictionary开头,实例方法则以init开头:
- dictionary:创建一个不包含任何key-value对的NSDictionary。
- dictionaryWithContentsOfFile:/initWithContentsOfFile::读取指定文件的内容,使用指定的文件内容来初始化NSDictionary。该文件通常是由NSDictionary输出生成的。
- dictionaryWithDictionary:/initWithDictionary::使用已有的NSDictionary包含的key-value对来初始化NSDictionary对象。
- dictionaryWithObject:forKey::使用单个key-value对来创建NSDictionary对像。
- dictionaryWithObjects:forKeys:/initWithObjects:forKeys::使用两个NSArray分别指定key、value集合,可以创建包含多个key-value对的NSDictionary。
- dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:/initWithObjectsAndKeys::调用该方法时,需要按value1,key1,value2,key2,…,nil的格式传入多个key-value对。
除此之外,还可以使用如下简化语法来创建NSDictionary对象:
@{key1: value1, key2: value2, key3 ...}
常用的访问该集合的key和value的方法有:
- count:返回所有key-value对数量。
- allKeys:返回全部key。
- allKeysForObject::返回指定value对应的全部key。
- allValues:返回包含的全部value。
- objectForKey::获取指定key对应value。
- objectForKeyedSubscript::通过该方法的支持,允许通过下标法来获取指定key对应的value。
- valueForKey::获取指定key对应的value。
- keyEnumerator:返回用于遍历该NSDictionary所有key的NSEnumerator对象。
- objectEnumerator:该方法返回用于遍历该NSDictionary所有value的NSEnumerator对象。
- enumerateKeysAndObjectsUsingBlock::使用指定的代码块来迭代执行该集合中所有的key-value对。
- enumerateKeysAndObjectsWithOptions:usingBlock::使用指定的代码块来迭代执行该集合中所有的key-value对。可以传入一个额外的NSEnumerationOptions参数。
- writeToFile:atomically::将该NSDictionary对象的数据写入指定文件。
示例程序:
该程序为了能更清晰地看到key-value对的详情,为NSDictionary类扩展了一个print类别,在该类别中扩展了一个print方法,用于打印NSDictionary中key-value对的详情。
该类接口部分:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface NSDictionary (print)
-(void) print;
@end
实现部分:
#import "NSDictionary+print.h"
@implementation NSDictionary (print)
-(void) print {
NSMutableString* result = [NSMutableString stringWithString:@"{"];
//快速枚举法遍历
//循环计数器将依次等于每个key
for(id key in self) {
[result appendString: [key description]];
[result appendString:@"="];
//使用下标法根据key获取对应的vakue
[result appendString:[self[key] description]];
[result appendString:@", "];
}
//获取字符串长度
NSUInteger len = [result length];
//去掉字符串最后两个字符
[result deleteCharactersInRange:NSMakeRange(len - 2, 2)];
[result appendString:@"}"];
NSLog(@"%@", result);
}
@end
通过key来获取value有两种方法:
- 调用NSDictionary的objectForKey:方法
- 直接使用下标法
也就是说,下面两行代码的功能是相同的:
[dictionary objectForKey:key];
dictionary[key];
测试:
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
NSDictionary* dict = [NSDictionary dictionaryWithObjectsAndKeys:
[[User alloc] initWithName:@"Billy" andPass:@"1234"],@"one",
[[User alloc] initWithName:@"Terasa" andPass:@"2345"],@"two",
[[User alloc] initWithName:@"Amy" andPass:@"3456"],@"three",
[[User alloc] initWithName:@"John" andPass:@"4567"],@"four",
[[User alloc] initWithName:@"Jimmy" andPass:@"5678"],@"five",
nil];
[dict print];
NSLog(@"dict包含%ld个key-value对", [dict count]);
NSLog(@"dict的所有key为:%@", [dict allKeys]);
NSLog(@"<User[name=Billy,pass=1234]>对应的key为:%@",[dict allKeysForObject:[[User alloc] initWithName:@"Billy" andPass:@"1234"]]);
//获取遍历dict所有value的枚举器
NSEnumerator* en = [dict objectEnumerator];
id value;
//使用枚举器来遍历dict中所有value
while(value = [en nextObject]) {
NSLog(@"%@", value);
}
//使用指定代码块来迭代执行该集合中所有的key-vakue对
[dict enumerateKeysAndObjectsUsingBlock:
//该集合包含多少个key-value对,下面的代码块就执行相应的次数
^(id key, id value, BOOL* stop) {
NSLog(@"key的值为:%@",key);
[value say:@"Bill"];
}];
}
return 0;
}
输出:
{one=<User[name=Billy,pass=1234]>, five=<User[name=Jimmy,pass=5678]>, three=<User[name=Amy,pass=3456]>, two=<User[name=Terasa,pass=2345]>, four=<User[name=John,pass=4567]>}
dict包含5个key-value对
dict的所有key为:(
one,
five,
three,
two,
four
)
<User[name=Billy,pass=1234]>对应的key为:(
one
)
<User[name=Billy,pass=1234]>
<User[name=Jimmy,pass=5678]>
<User[name=Amy,pass=3456]>
<User[name=Terasa,pass=2345]>
<User[name=John,pass=4567]>
key的值为:one
Billy说:Bill
key的值为:five
Jimmy说:Bill
key的值为:three
Amy说:Bill
key的值为:two
Terasa说:Bill
key的值为:four
John说:Bill
对NSDictionary的key排序
方法如下:
- keysSortedByValueUsingSelector::根据所有value指定方法的返回值对key排序;调用该方法必须返回NSOrderedAscending、NSOrderedDescending、NSOrderedSame这三个枚举值之一。
- keysSortedByValueUsingComparator::使用指定的代码块来遍历key-value对,并根据执行结果(必须返回NSOrderedAscending、NSOrderedDescending、NSOrderedSame这三个枚举值之一)对所有key进行排序。
- keysSortedByValueWithOptions:usingComparator::与前一个方法的功能类似,只是可以传入一个额外的NSEnumerationOptions参数。
示例程序:
#import "NSDictionary+print.h"
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
//
NSDictionary* dict = @{@"one": @"Billy",
@"two":@"Teresa",
@"three":@"Amy",
@"four":@"John"
};
//打印dict集合所有元素
[dict print];
//获取所有直接调用value的compare:方法对所有key进行排序
//返回排序好的所有key组成的NSArray
NSArray* keyArr1 = [dict keysSortedByValueUsingSelector:@selector(compare:)];
NSLog(@"%@", keyArr1);
NSArray* keyArr2 = [dict keysSortedByValueUsingComparator:
//对value进行比较,字符串越长,即可认为value越大
^(id value1, id value2){
//下面定义比较大小的标准:字符串越长,即可认为value越大
if([value1 length] > [value2 length]) {
return NSOrderedDescending;
} else if ([value1 length] < [value2 length]) {
return NSOrderedAscending;
} else {
return NSOrderedSame;
}
}];
NSLog(@"%@", keyArr2);
//将NSDictionary的内容输出到指定文件中
[dict writeToFile:@"mydict.txt" atomically: YES];
}
}
先使用compare:方法排序——字符串比较大小直接根据字符对应的编码进行。后面调用代码块对value比较大小,规则是value对应的字符串越长,系统就认为该value越大。程序的输出结果为:
{one=Billy, three=Amy, two=Teresa, four=John}
(
three,
one,
four,
two
)
(
three,
four,
one,
two
)
打开 mydict.txt 文件,可以看到如下内容:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE plist PUBLIC "-//Apple//DTD PLIST 1.0//EN" "http://www.apple.com/DTDs/PropertyList-1.0.dtd">
<plist version="1.0">
<dict>
<key>four</key>
<string>John</string>
<key>one</key>
<string>Billy</string>
<key>three</key>
<string>Amy</string>
<key>two</key>
<string>Teresa</string>
</dict>
</plist>
对NSDictionary的key进行过滤
NSDictionary还提供了方法对NSDictionary的所有key执行过滤,这些方法执行完将返回满足条件的key组成的NSSet。方法如下:
- keysOfEntriesPassingTest::使用代码块迭代处理NSDictionary的每个key-value对。对NSDictionary的key-value对进行过滤,该代码块必须返回BOOL类型的值,只有当该代码块返回YES时,该key才会被保留下来;该代码块可以接受3个参数,其中第一个参数代表正在迭代处理的key,第二个参数代表正在迭代处理的value,第三个参数代表是否还要继续迭代,如果将第三个参数设为NO,那么该迭代会立即停止。
- keysOfEntriesWithOptions:passingTest::该方法的功能与前一个方法的功能基本相同。只是该方法可以额外传入一个附加的NSEnumerationOptions选项参数。
如下程序示范了对NSDictionary进行过滤。
#import "NSDictionary+print.h"
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
NSDictionary* dict = @{
@"Billy":[NSNumber numberWithInt: 89],
@"Teresa":[NSNumber numberWithInt: 69],
@"Amy":[NSNumber numberWithInt: 78],
@"John":[NSNumber numberWithInt: 109]
};
[dict print];
//对NSDictionary的所有key进行过滤
NSSet* keySet = [dict keysOfEntriesPassingTest:
//使用代码块对NSDictionary的key-value对进行过滤
^(id key, id value, BOOL* stop) {
//当value的值大于80时返回YES
//这意味着只有value的值大于80的key才会被保存下来
return (BOOL)([value intValue] > 80);
}];
NSLog(@"%@", keySet);
}
}
输出:
{John=109, Billy=89, Amy=78, Teresa=69}
{(
Billy,
John
)}
使用自定义类作为NSDictionary的key
如果程序打算使用自定义类作为NSDictionary的key,则该自定义类必须满足如下需求:
- 该自定义类正确重写过isEqual: 和hash方法。所谓正确重写,是指当两个对象通过isEqual:方法判断相等时,两个对象的hash方法返回值也相等。
- 该自定义类必须实现了copyWithZone:方法,该方法最好返回该对象的不可变副本。
为什么要实现copyWithZone:方法呢?因为对于NSDictionary来说,key是非常关键的,NSDictionary需要根据key来访问value——从这个意义上看,key相当于NSDictionary的索引,如果key本身是可变的,且程序可以通过其他变量来修改NSDictionary的key,这就可能导致NSDictionary的“索引”值被破坏,从而导致NSDictionary的完整性被破坏。
为了让前面的User类作为NSDictionary的key,还需要让该User类实现NSCopying协议(可选的,通常建议实现),并让该User类实现copyWithZone:方法。User实现的copyWithZone:方法如下:
-(id) copyWithZone: (NSZone*) zone {
NSLog(@"--正在复制--");
//复制一个对象
User* newUser = [[[self class] allocWithZone:zone] init];
//将被复制的对象的实例变量的值赋给新对象的实例变量
newUser->_name = _name;
newUser->_pass = _pass;
return newUser;
}
User.h:
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
@interface User : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString* name;
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString* pass;
-(id) initWithName: (NSString*) aName andPass: (NSString*) aPass;
-(void) say: (NSString*) content;
@end```
User.m:
```objectivec
#import "User.h"
@implementation User
-(id) initWithName:(NSString *) name andPass:(NSString *) pass {
if (self = [super init]) {
self->_name = name;
self->_pass = pass;
}
return self;
}
-(void) say: (NSString*) content {
NSLog(@"%@说:%@",self.name, content);
}
//重写isEqual: 方法,重写比较方法为
//如果两个User的name、pass相等,既可以认为它们相等
-(BOOL) isEqual: (id) other {
if(self == other) {
return YES;
}
if([other class] == User.class) {
User* target = (User*) other;
return [self.name isEqualToString: target.name] && [self.pass isEqualToString: target.pass];
}
return NO;
}
//重写description方法,可以看到User状态
-(NSString*) description {
return [NSString stringWithFormat:@"<User[name=%@,pass=%@]>", self.name, self.pass];
}
-(NSUInteger) hash {
NSLog(@"===hash===");
NSUInteger nameHash = self.name == nil ? 0 : [self.name hash];
NSUInteger passHash = self.pass == nil ? 0 : [self.pass hash];
return nameHash *31 + passHash;
}
-(id) copyWithZone: (NSZone*) zone {
NSLog(@"--正在复制--");
//复制一个对象
User* newUser = [[[self class] allocWithZone:zone] init];
//将被复制的对象的实例变量的值赋给新对象的实例变量
newUser->_name = _name;
newUser->_pass = _pass;
return newUser;
}
@end
主函数:
#import "User.h"
#import "NSDictionary+print.h"
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
@autoreleasepool {
User* u1 = [[User alloc] initWithName:@"Billy" andPass:@"765"];
NSDictionary* dict = @{
[[User alloc] initWithName:@"Bill" andPass:@"123"]:@"one",
u1:@"two",
[[User alloc] initWithName:@"Bill" andPass:@"123"]:@"three",
[[User alloc] initWithName:@"Nick" andPass:@"890"]:@"four",
[[User alloc] initWithName:@"Polly" andPass:@"761"]:@"five"
};
//将u1的密码设为nil
u1.pass = nil;
//由于NSDictionary并未直接使用u1所指的User作为key
//而是先复制了u1所指向对象的副本,然后以该副本作为key
//因此程序将看到dict的key不会受到任何影响
[dict print];
}
}
当程序尝试使用任何对象作为key时,会先调用copy方法来复制该key的不可变副本,实际是以该副本作为NSDictionary的key。因此,上面程序对u1的pass进行修改时,NSDictionary的所有key并不会受到任何影响。
输出结果:
===hash===
--正在复制--
===hash===
--正在复制--
===hash===
===hash===
--正在复制--
===hash===
--正在复制--
===hash===
===hash===
===hash===
===hash===
{<User[name=Bill,pass=123]>=one, <User[name=Billy,pass=765]>=two, <User[name=Polly,pass=761]>=five, <User[name=Nick,pass=890]>=four}
其中两个User对象的name、pass完全相同,但这两个对象通过isEqual:方法会返回YES,并且hash方法返回值也相等,因此只会保留一个。
NSMutableDictionary的功能与用法
NSMutableDictionary继承了NSDictionary,它代表一个key-value对可变的NSDictionary集合。由于NSMutableDictionary可以动态地添加key-value对,因此,创建NSMutableDictionary集合时可以指定初始容量。
NSMutableDictionary主要新增了如下方法:
- setObject:forKey::设置一个key-value对。如果NSDictionary中没有包含与该key相同的key-value对,那么NSDictionary将会新增一个key-value对;否则该key-value对将覆盖已有的key-value对。
- setObject:forKeyedSubscript::通过该方法的支持,允许程序通过下标法来设置key-value对。
- addEntriesFromDictionary::将另一个NSDictionary中所有的key-value对复制到当前NSDictionary中。
- setDictionary::用另一个NSDictionary中所有的key-value对替换当前NSDictionary中的key-value对。
- removeObjectForKey::根据key来删除key-value对。
- removeAllObjects:清空该NSDictionary。
- removeObjectsForKeys::使用多个key组成的NSArray作为参数,同时删除多个key对应的key-value对。
示范程序:
int main以上是关于OC Foundation框架 字典的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章