二叉树
Posted L_add
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了二叉树相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
二叉树
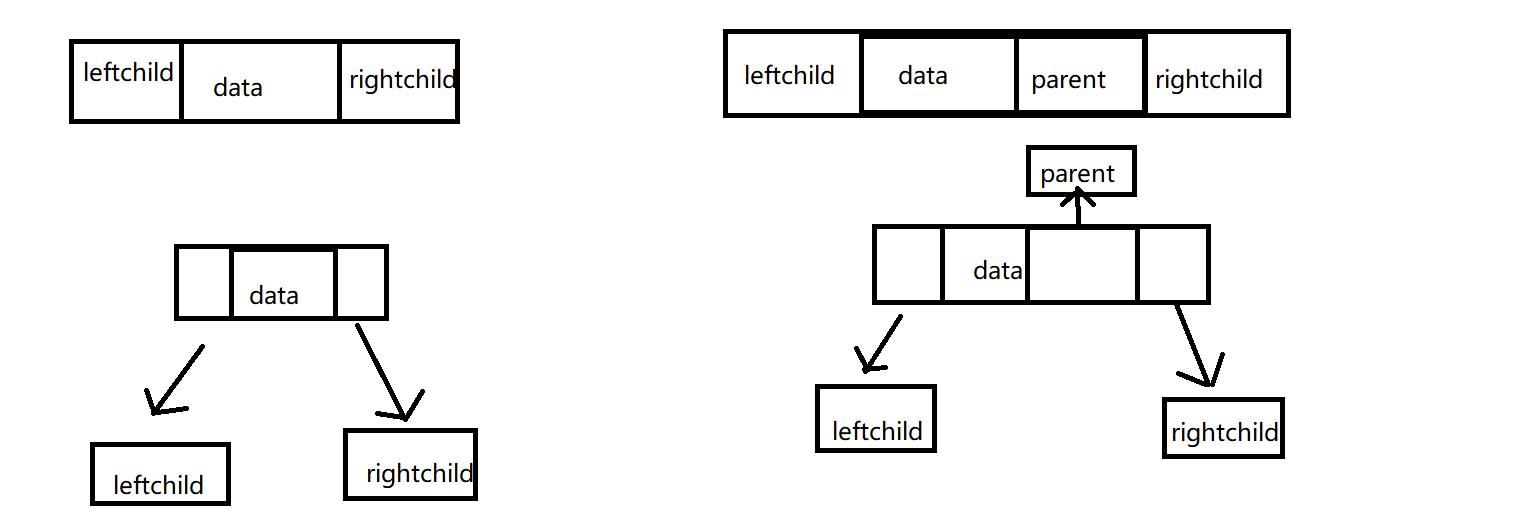
二叉树的存储结构
1、顺序存储:用数组来存储,只适用于完全二叉树(堆),因为会存在空间浪费,现实中只有堆才会用数组来存储。二叉树顺序存储在物理上是数组,在逻辑上是一颗二叉树。
2.链式存储:用链表来表示一颗二叉树。
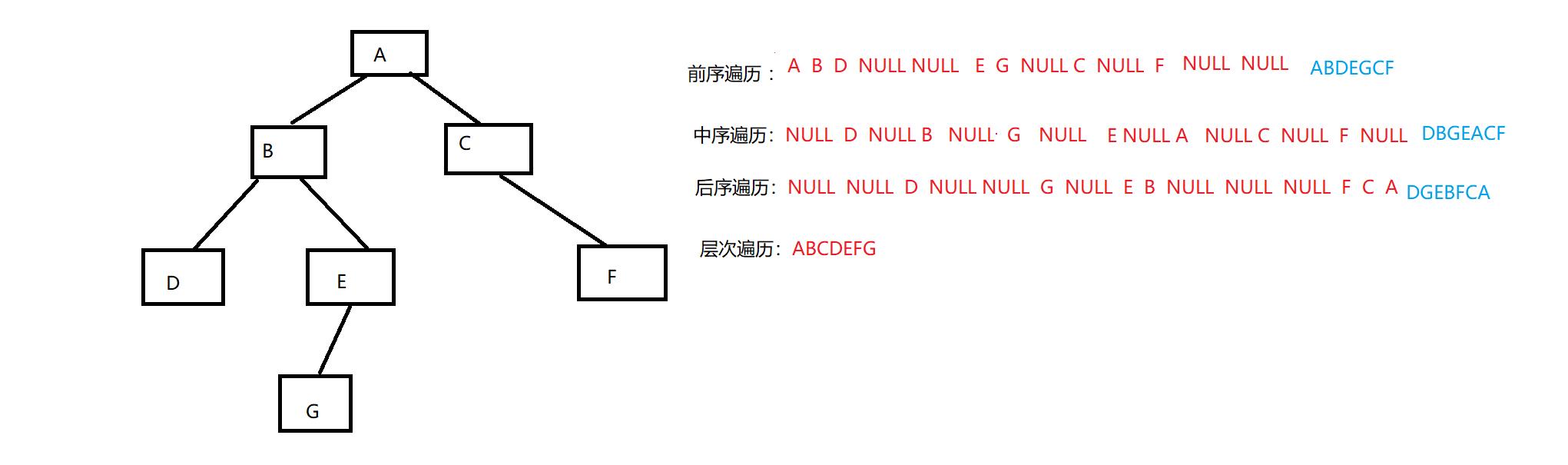
二叉树的遍历
四种遍历顺序:
1、前序遍历 先根遍历 根 -> 左 -> 右
2、中序遍历 中根遍历 左 -> 根 -> 右
3、后序遍历 后根遍历 左 -> 右 -> 根
4、层序遍历
普通二叉树增删查改没有意义,如果是为了存储数据,用线性表更简单,二叉树反而复杂。(极端情况下搜索二叉树退化效率为O(N))
哈夫曼树:哈夫曼编码 -> 文件压缩
搜索树:AVL树、红黑树(平衡树)
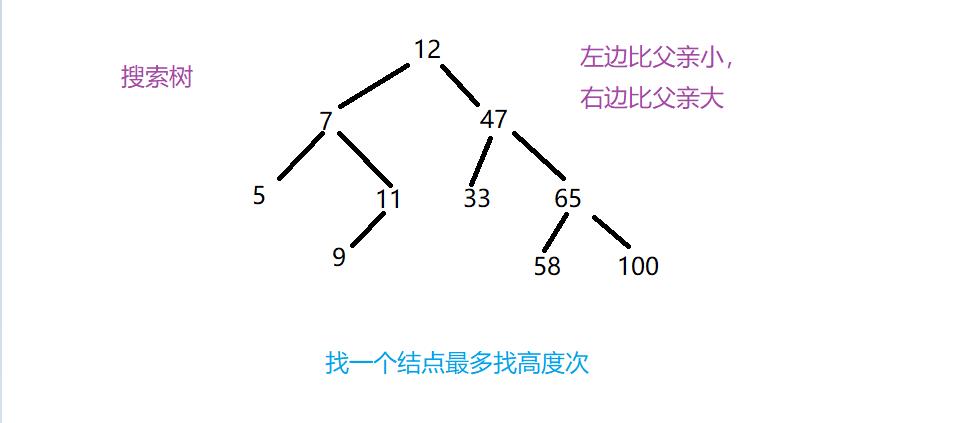
排序二叉树增删查改才有意义
二叉树的实现
1、表示
typedef char BTDataType;
typedef struct BinaryTreeNode
{
struct BinaryTreeNode* left;
struct BinaryTreeNode* right;
BTDataType data;
}BTNode;
2、创建结点
BTNode* CreateTreeNode(BTDataType x)
{
BTNode* node = (BTNode*)malloc(sizeof(BTNode));
node->data = x;
node->left = NULL;
node->right = NULL;
return node;
}
3、前、中、后序遍历
递归调用
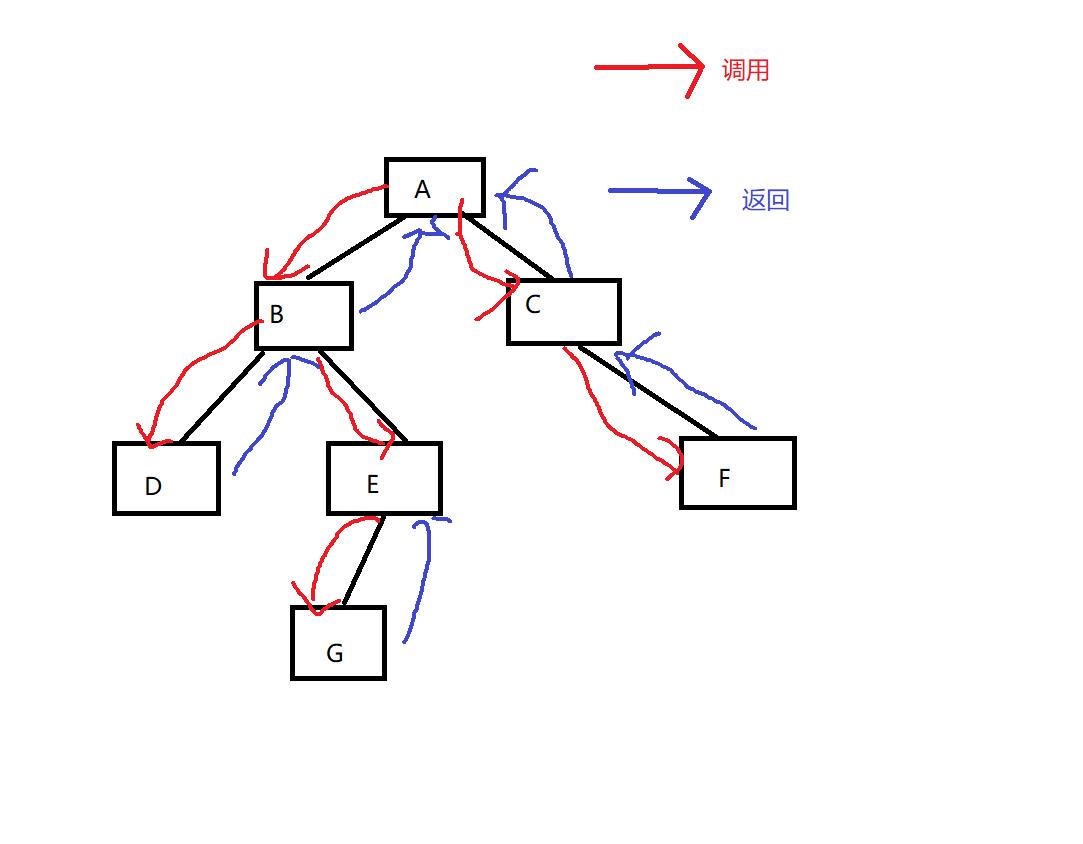
void PrevOrder(BTNode* root)//前序
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL");
return ;
}
printf("%c", root->data);
PrevOrder(root->left);
PrevOrder(root->right);
}
void InOrder(BTNode* root)//中序
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL");
return;
}
InOrder(root->left);
printf("%c", root->data);
InOrder(root->right);
}
void PostOrder(BTNode* root)//后序
{
if (root == NULL)
{
printf("NULL");
return;
}
PostOrder(root->left);
PostOrder(root->right);
printf("%c", root->data);
}
4、求树结点的个数
int TreeSize(BTNode* root)//树结点的个数
{
return root == NULL ? 0 : TreeSize(root->left) + TreeSize(root->right) + 1;
}
分治算法:分而治之
把大问题拆成小问题
思路:
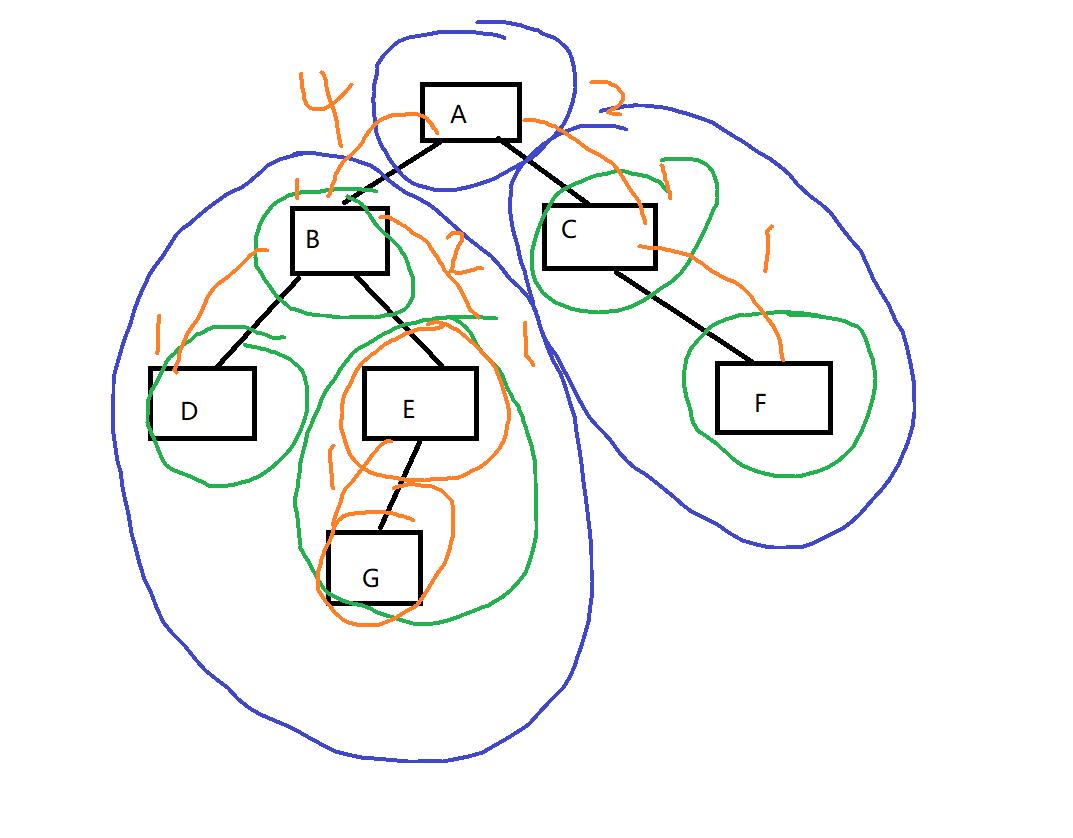
1、空 :返回0;
2、非空 :左子树结点个数 + 右结点个数 + 1(自己)
5、求叶子结点个数
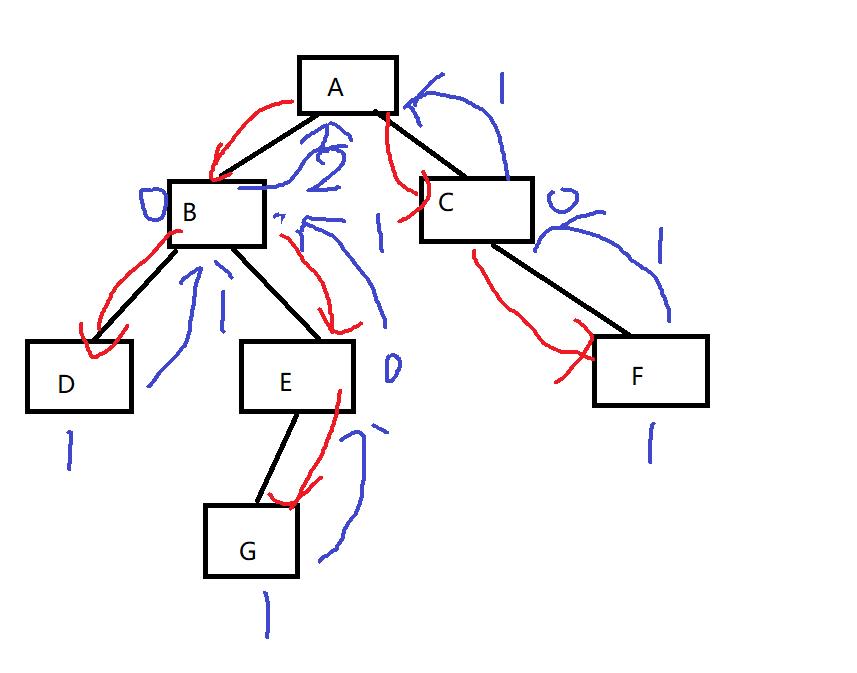
思路:
1、空 :返回0
2、叶子 :返回1
3、非空且不是叶子 :返回左子数叶子结点个数+右子树结点个数
int TreeLeafSize(BTNode* root)//叶子结点的个数
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
if (root->left == NULL&& root->right == NULL)
return 1;
return TreeLeafSize(root->left) + TreeLeafSize(root->right);
}
7、求第K层叶子结点个数
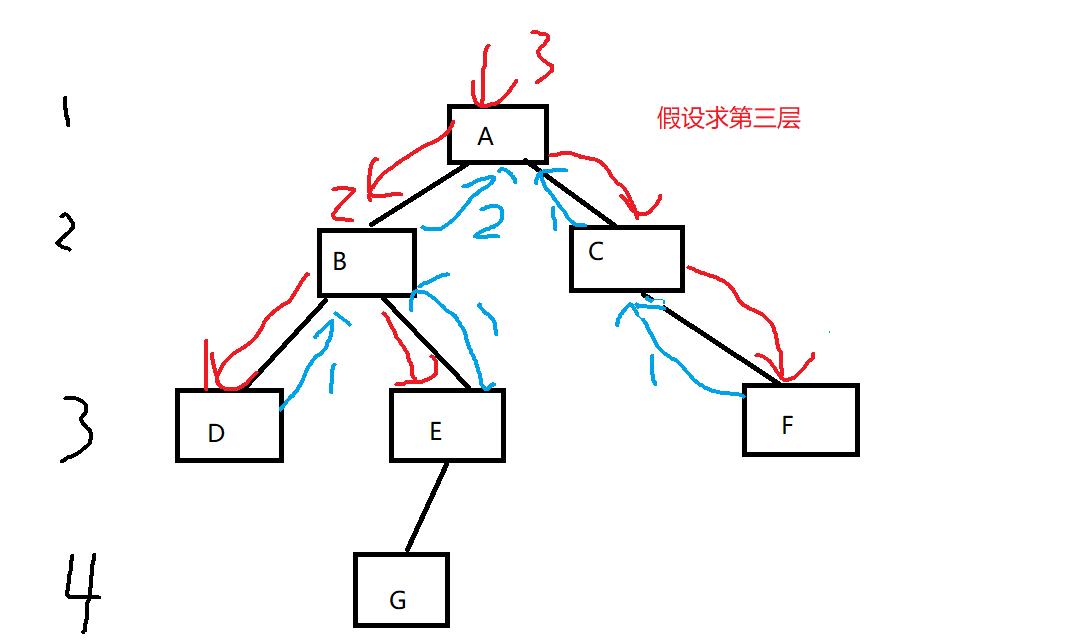
思路:
求第K层个数,转化为求K-1层个数
K-> K-1 -> K-2 ->… -> 2 -> 1 ->返回个数
int TreeKLevelSize(BTNode* root, int k)//第K层叶子结点个数
{
if (root == NULL)
return 0;
if (k == 1)
return 1;
return TreeKLevelSize(root->left, k - 1) +
TreeKLevelSize(root->right, k - 1);
}
8、找结点
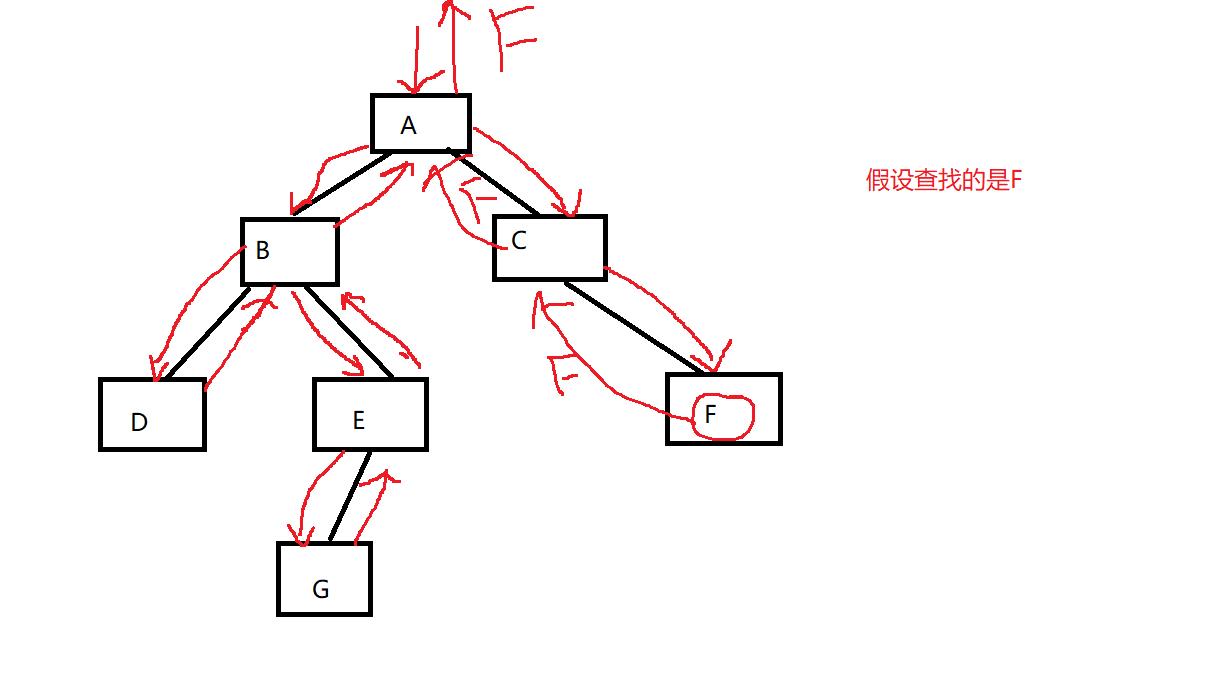
思路:
1、root == NULL return NULL
2、root 结点不是我们要找的,先去左树找,如果左树没有,再到右树找
3、左右都没有,当前树没有,return NULL
BTNode* TreeFind(BTNode* root, BTDataType x)
{
if (root == NULL)
return NULL;
//我自己不是
if (root->data == x)
return root;
//分别到左右子树寻找
BTNode* lret = TreeFind(root->left,x);
if (lret)
return lret;
BTNode* rret = TreeFind(root->right,x);
if (rret)
return rret;
//左右都没找到
return NULL;
}
9、销毁
void BinaryTreeDestoty(BTNode** proot)//后序销毁
{
//
if (*proot == NULL)
return;
BinaryTreeDestoty(&(*proot)->left);
BinaryTreeDestoty(&(*proot)->right);
free(*proot);
*proot = NULL;
}
二叉树的前、中、后序就是深度优先遍历
广度优先遍历
思路:
1、先把根入队列
2、出队头的数据,把它的下一层入队
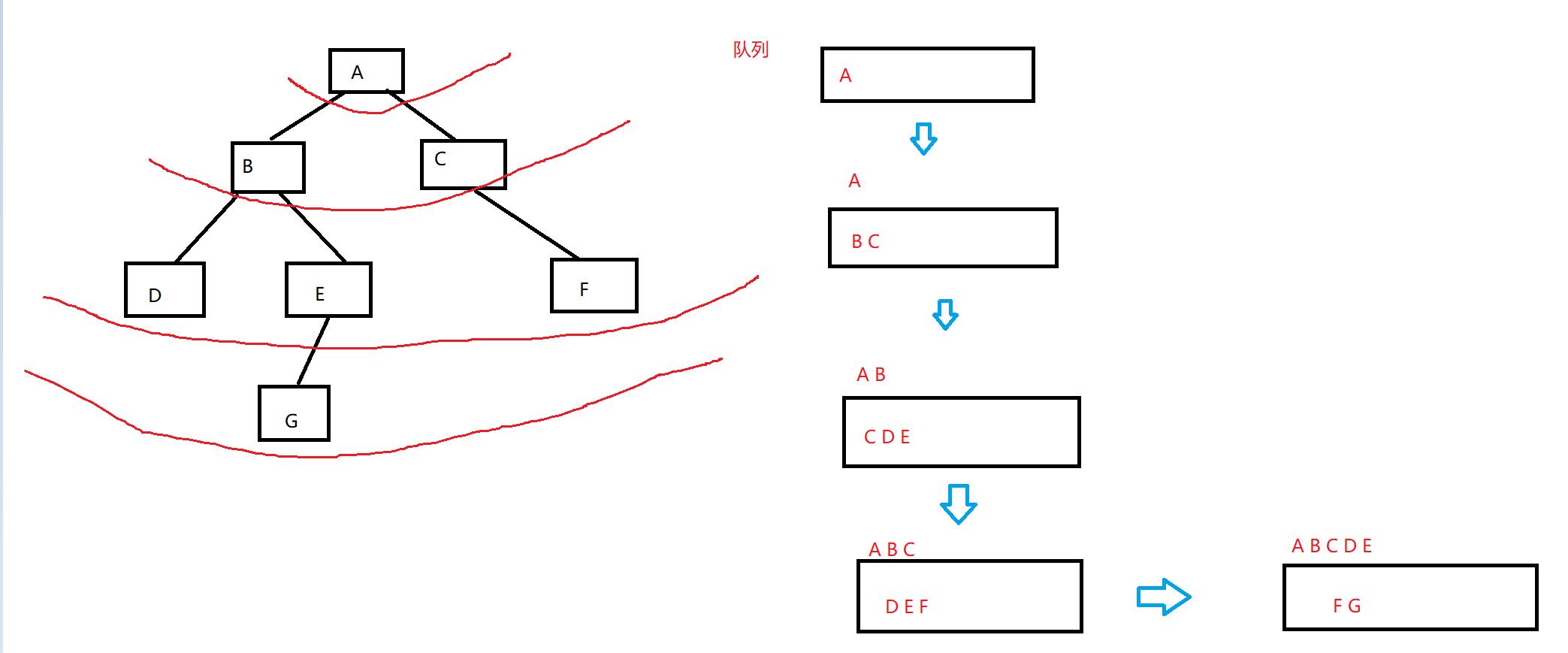
特点:借助队列先进先出的性质,
上一层出队,下一层入队
void TreeLevelOrder(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root == NULL)
{
QueuePush(&q, root->data);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
printf("%c", front->data);
if (front->left)
QueuePush(&q, front->left->data);
if (front->right)
QueuePush(&q, front->right->data);
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
}
10、判断是否为完全二叉树
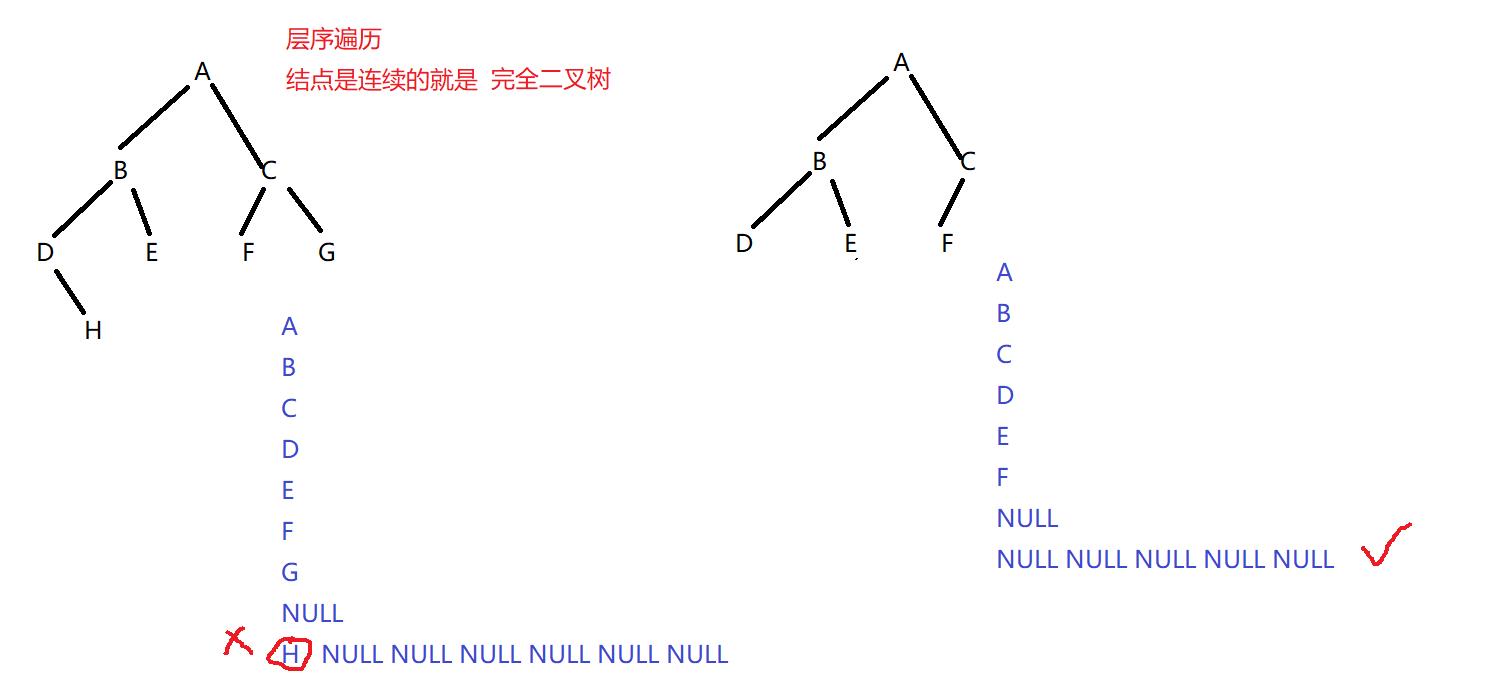
bool BinaryTreeCompelet(BTNode* root)
{
Queue q;
QueueInit(&q);
if (root)
QueuePush(&q, root->data);
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front == NULL)
break;
QueuePush(&q, front->left->data);
QueuePush(&q, front->right->data);
}
while (!QueueEmpty(&q))
{
BTNode* front = QueueFront(&q);
QueuePop(&q);
if (front)
return false;
}
QueueDestroy(&q);
return true;
}
注:队列的函数在另一篇博客:队列
以上是关于二叉树的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章