工作量减半的开发神器,MyBatisPlus入门和部分源码讲解
Posted XiaoLin__Java
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了工作量减半的开发神器,MyBatisPlus入门和部分源码讲解相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
一、MyBatis回顾
1.1、回顾MyBatis
1.1.1、建库建表
CREATE TABLE `user` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`username` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
`password` varchar(255) DEFAULT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=7 DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
1.1.2、引入依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.mybatis.spring.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>1.3.2</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
1.1.3、application.properties
spring.datasource.druid.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.druid.url=jdbc:mysql:///db?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8
spring.datasource.druid.username=root
spring.datasource.druid.password=123456
1.1.4、编写Mapper接口
public interface UserMapper {
List<Employee> selectAll();
}
1.1.5、编写Mapper.xml
<select id="selectAll" resultMap="BaseResultMap">
select id,username,password
from user
</select>
1.1.6、MyBatis存在的缺点
我们可以发现传统的MyBatis存在很致命的问题,每个实体表对应一个实体类,对应一个Mapper.java接口,对应一个Mapper.xml配置文件每个Mapper.java接口都有重复的crud方法,每一个Mapper.xml都有重复的crud的sql配置。如果想解决这个问题,唯一的办法就是使用MyBatis-Plus。
二、了解Mybatis-Plus
MyBatis-Plus(简称 MP)是一个 MyBatis 的增强工具,在 MyBatis 的基础上只做增强不做改变,为简化开发、提高效率而生。
2.1、代码以及文档
文档地址:https://mybatis.plus/guide/
源码地址:https://github.com/baomidou/mybatis-plus
2.2、特性
- 无侵入:只做增强不做改变,引入它不会对现有工程产生影响,如丝般顺滑。
- 损耗小:启动即会自动注入基本 CURD,性能基本无损耗,直接面向对象操作。
- 强大的 CRUD 操作:内置通用 Mapper、通用 Service,仅仅通过少量配置即可实现单表大部分 CRUD 操作,更有强大的条件构造器,满足各类使用需求。
- 支持 Lambda 形式调用:通过 Lambda 表达式,方便的编写各类查询条件,无需再担心字段写错。
- 支持多种数据库:支持 MySQL、MariaDB、Oracle、DB2、H2、HSQL、SQLite、Postgre、SQLServer2005、SQLServer 等多种数据库。
- 支持主键自动生成:支持多达 4 种主键策略(内含分布式唯一 ID 生成器 - Sequence),可自由配置,完美解决主键问题。
- 支持 XML 热加载:Mapper 对应的 XML 支持热加载,对于简单的 CRUD 操作,甚至可以无 XML 启动。
- 支持 ActiveRecord 模式:支持 ActiveRecord 形式调用,实体类只需继承 Model 类即可进行强大的 CRUD 操
作。 - 支持自定义全局通用操作:支持全局通用方法注入( Write once, use anywhere )。
- 支持关键词自动转义:支持数据库关键词(order、key…)自动转义,还可自定义关键词。
- 内置代码生成器:采用代码或者 Maven 插件可快速生成 Mapper 、 Model 、 Service 、 Controller 层代码,
支持模板引擎,更有超多自定义配置等您来使用。 - 内置分页插件:基于 MyBatis 物理分页,开发者无需关心具体操作,配置好插件之后,写分页等同于普通 List查询。
- 内置性能分析插件:可输出 Sql 语句以及其执行时间,建议开发测试时启用该功能,能快速揪出慢查询。
- 内置全局拦截插件:提供全表 delete 、 update 操作智能分析阻断,也可自定义拦截规则,预防误操作。
- 内置 Sql 注入剥离器:支持 Sql 注入剥离,有效预防 Sql 注入攻击。
2.3、快速开始
2.3.1、导入依赖
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<exclusions>
<exclusion>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId>
</exclusion>
</exclusions>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--简化代码的工具包-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<!--mybatis-plus的springboot支持-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.1.1</version>
</dependency>
<!--mysql驱动-->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>5.1.47</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.slf4j</groupId>
<artifactId>slf4j-log4j12</artifactId>
</dependency>
2.3.2、log4j.properties
og4j.rootLogger=DEBUG,A1
log4j.appender.A1=org.apache.log4j.ConsoleAppender
log4j.appender.A1.layout=org.apache.log4j.PatternLayout
log4j.appender.A1.layout.ConversionPattern=[%t] [%c]-[%p] %m%n
2.3.3、编写实体类
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String type;
}
2.3.4、编写mapper
// 直接继承Myabtis-Plus的BaseMapper即可,泛型表示实体类
public interface UserMapper extends BaseMapper<User> {
}
2.3.5、编写启动类
@SpringBootApplication
// 设置mapper接口扫描包
@MapperScan("cn.linstudy.mapper")
public class DemoApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(DemoApplication.class, args);
}
}
2.3.6、测试
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class UserMapperTest {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
public void testSelect() {
List<User> userList = userMapper.selectList(null);
for (User user : userList) {
System.out.println(user);
}
}
}
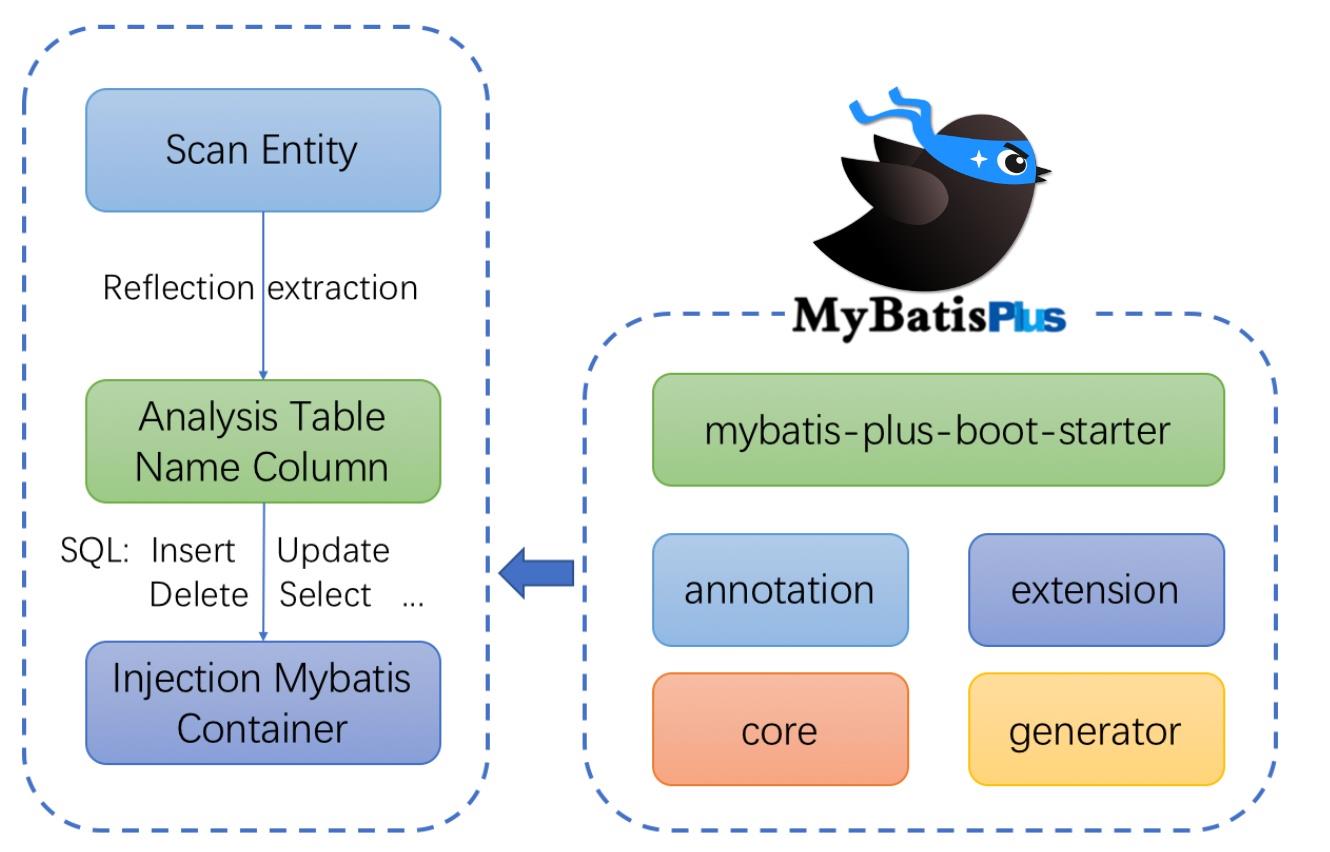
2.4、架构
三、常用注解
3.1、@TableName
MyBatis-Plus中默认表名是跟实体类名一致,当我们实体类的类名和表名不一致的时候,MyBatis-Plus就会报错,但是我们实际上又有这种需求的时候,我们就需要使用@TableName这个注解,来指定当前实体类映射哪张数据库表。
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@TableName("user")
public class User {
private Integer id;
private String username;
private String password;
private String type;
}
3.2、@TableId
我们在使用insert方法的时候会发现一个很奇怪的现象。他生成的ID格外长,这是因为他使用的算法是使用雪花算法生成的ID,我们想要的是自增的ID,所以我们需要设置主键增长的策略。
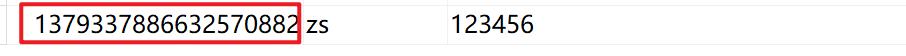
我们可以使用@TableId这个注解。他的作用是主键注解,标记当前属性映射表的主键,其中type是属性指定的主键类型,他有这几个值:
- IdType.AUTO:数据库ID自增。
- IdType.NONE:无状态,该类型为未设置主键类型(注解里等于跟随全局,全局里约等于 INPUT)。
- IdType.INPUT:insert前自行set主键值。
- IdType.ASSIGN_ID:分配ID(主键类型为Number(Long和Integer)或String)(since 3.3.0),使用接口IdentifierGenerator的方法nextId(默认实现类为DefaultIdentifierGenerator雪花算法)。
- 分配UUID,主键类型为String(since 3.3.0),使用接口IdentifierGenerator的方法nextUUID(默认default方法)
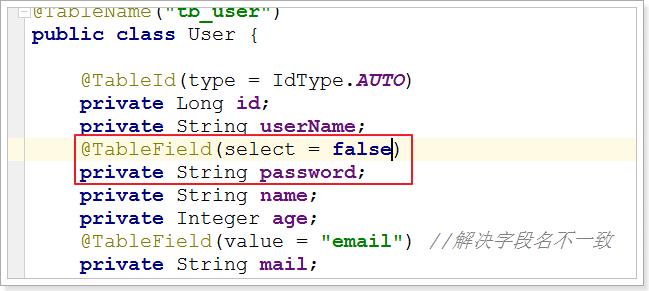
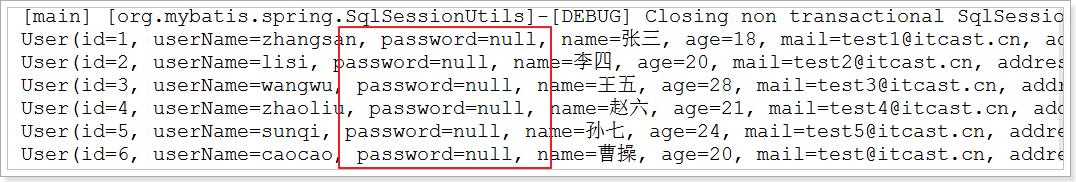
3.3、@TableField
我们有些时候,数据库的字段名和实体类的名字可能会不一样,或者是说实体类中有的字段而数据库中却没有,我们需要用@TableField这个注解。
@TableField注解用于标记非主键字段,他的作用是指定当前属性映射数据库表哪一列, 默认是跟属性名一致。常用于解决以下两个问题:
- 对象中的属性名和字段名不一致的问题(非驼峰)
- 对象中的属性字段在表中不存在的问题
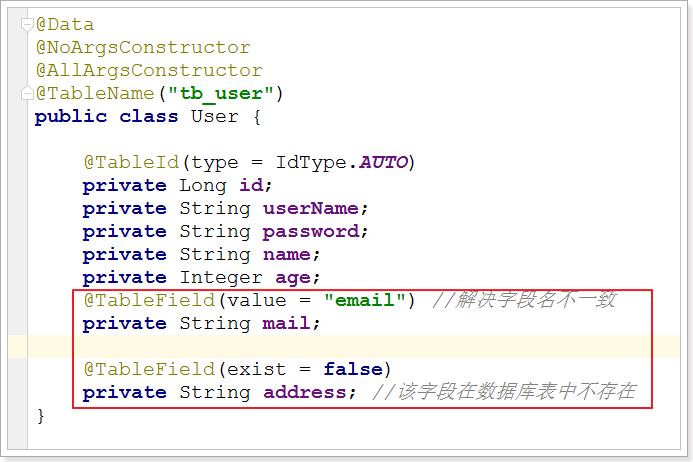
他还有另一种用法,就是指定某个字段不加入查询。
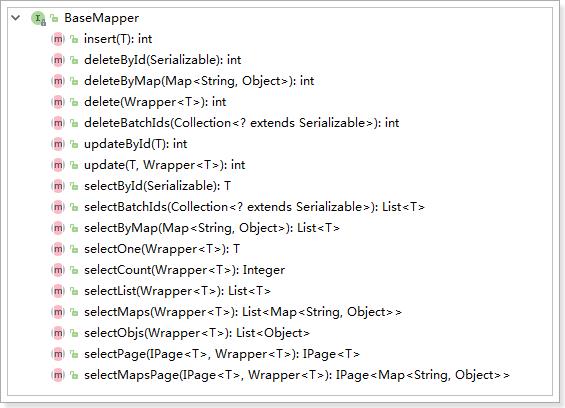
四、通用CRUD
我们之前学过,使用MyBatis-Plus的时候,Mapper接口里面的方法不需要我们再自己写了,只需要继承BaseMapper接口即可获取到各种各样的单表操作。
4.1、插入操作
4.1.1、方法定义
MyBatis-Plus中对于insert的方法定义是:
/**
* 插入一条记录
*
* @param entity 实体对象
*/
int insert(T entity);
4.1.2、测试
package cn.linstudy.test
import cn.itcast.mp.mapper.UserMapper;
import cn.itcast.mp.pojo.User;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.util.List;
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@SpringBootTest
public class UserMapperTest {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
@Test
public void testInsert() {
User user = new User();
user.setAge(20);
user.setEmail("test@itcast.cn");
user.setName("曹操");
user.setUserName("caocao");
user.setPassword("123456");
int result = this.userMapper.insert(user); //返回的result是受影响的行数,并不是自增后的id
System.out.println("result = " + result);
System.out.println(user.getId()); //自增后的id会回填到对象中
}
}
4.2、更新操作
4.2.1、updateById
4.2.1.1、方法定义
/**
* 根据 ID 修改
*
* @param entity 实体对象
*/
int updateById(@Param(Constants.ENTITY) T entity);
4.2.1.2、测试
// 需求: 将id=1用户名字修改为xiaolin
@Test
public void testUpdateById(){
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(1L);
employee.setName("xiaolin");
employeeMapper.updateById(employee);
}
// 注意: 拼接sql时,所有非null 字段都进行set 拼接
// UPDATE employee SET name=?, age=?, admin=? WHERE id=?
// 改进的方法是先查,再替换,最后更新
// 需求: 将id=1用户名字修改为xiaolin
@Test
public void testUpdateById2(){
Employee employee = employeeMapper.selectById(1L);
employee.setName("xiaolin");
employeeMapper.updateById(employee);
}
4.2.2、update
4.2.2.1、方法定义
/**
* 根据 whereEntity 条件,更新记录
*
* @param entity 实体对象 (set 条件值,可以为 null)
* @param updateWrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null,里面的 entity 用于生成 where 语句)
*/
int update(@Param(Constants.ENTITY) T entity, @Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T>
updateWrapper);
4.2.2.2、测试
public class UserMapperTest {
@Autowired
private UserMapper userMapper;
// 方法一:使用QueryWrapper
@Test
public void testUpdate() {
User user = new User();
user.setAge(22); //更新的字段
//更新的条件
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq("id", 6);
//执行更新操作
int result = this.userMapper.update(user, wrapper);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
//方法二: 通过UpdateWrapper进行更新
@Test
public void testUpdate(){
//更新的条件以及字段
UpdateWrapper<User> wrapper=new UpdateWrapper<>();
wrapper.eq("id",6).set("age",23);
//执行更新操作
int result=this.userMapper.update(null,wrapper);
System.out.println("result = "+result);
}
}
4.2.2.3、使用建议
-
知道id,并且所有更新使用
updateById -
部分字段更新,使用
update
4.3、删除操作
4.3.1、deleteById
4.3.1.1、方法定义
/**
* 根据 ID 删除
*
* @param id 主键ID
*/
int deleteById(Serializable id);
4.3.1.2、测试
@Test
public void testDeleteById() {
//执行删除操作
int result = this.userMapper.deleteById(6L);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
4.3.2、deleteByMap
4.3.2.1、方法定义
/**
* 根据 columnMap 条件,删除记录
*
* @param columnMap 表字段 map 对象
*/
int deleteByMap(@Param(Constants.COLUMN_MAP) Map<String, Object> columnMap);
4.3.2.2、测试
@Test
public void testDeleteByMap() {
Map<String, Object> columnMap = new HashMap<>();
columnMap.put("age",20);
columnMap.put("name","张三");
//将columnMap中的元素设置为删除的条件,多个之间为and关系
int result = this.userMapper.deleteByMap(columnMap);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
4.3.3、delete
4.3.3.1、方法定义
/**
* 根据 entity 条件,删除记录
*
* @param wrapper 实体对象封装操作类(可以为 null)
*/
int delete(@Param(Constants.WRAPPER) Wrapper<T> wrapper);
4.3.3.2、测试
@Test
public void testDeleteByMap() {
User user = new User();
user.setAge(20);
user.setName("张三");
//将实体对象进行包装,包装为操作条件
QueryWrapper<User> wrapper = new QueryWrapper<>(user);
int result = this.userMapper.delete(wrapper);
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
4.3.4、deleteBatchIds
4.3.4.1、方法定义
/**
* 删除(根据ID 批量删除)
*
* @param idList 主键ID列表(不能为 null 以及 empty)
*/
int deleteBatchIds(@Param(Constants.COLLECTION) Collection<? extends Serializable>
idList);
4.3.4.2、测试
@Test
public void testDeleteByMap() {
//根据id集合批量删除
int result = this.userMapper.deleteBatchIds(Arrays.asList(1L,10L,20L));
System.out.println("result = " + result);
}
4.4、查询操作
MyBatis-Plus提供了多种查询操作,包括根据id查询、批量查询、查询单条数据、查询列表、分页查询等操作。
4.4.1、selectById
4.4.1.1、方法定义
/**
* 根据 ID 查询
*
* @param id 主键ID
*/
T selectById(Serializable id);
4.1.1.2、测试
@Test
public void testSelectById() {
//根据id查询数据
User user = this.userMapper.selectById(2L);
System.out.println("result = " + user);
}
4.4.2、selectBatchIds
4.4.2.1、方法定义
/**
* 查询(根据ID 批量查询)
*
* @param idList 主键ID列表(不能为 null 以及 empty)
*/
List<T> selectBatchIds(@Param(Constants.COLLECTION) Collection<? extends Serializable>
idList);
4.2.2.2、测试
@Test
public void testSelectBatchIds() {
//根据id集合批量查询
List<User> users = this.userMapper.selectBatchIds(Arrays.asList(2L, 3L, 10L));
for (User user : users) 以上是关于工作量减半的开发神器,MyBatisPlus入门和部分源码讲解的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章