Spring 从入门到精通系列 11—— Spring 中的 JdbcTemplate
Posted Xiu Yan
tags:
篇首语:本文由小常识网(cha138.com)小编为大家整理,主要介绍了Spring 从入门到精通系列 11—— Spring 中的 JdbcTemplate相关的知识,希望对你有一定的参考价值。
本文针对 Spring 中的 JdbcTemplate 进行了分析,并实现对数据库的操作。

文章目录
一、JdbcTemplate 概述
它是 spring 框架中提供的一个对象,是对原始 Jdbc API 对象的简单封装。spring 框架为我们提供了很多的操作模板类。
- 操作关系型数据的:
jdbcTemplate
HibernateTemplate - 操作 nosql 数据库的:
RedisTemplate - 操作消息队列的:
JmsTemplate
JdbcTemplate在 spring-jdbc-5.0.2.RELEASE.jar 中,我们在导包的时候,除了要导入这个 jar 包
外,还需要导入一个 spring-tx-5.0.2.RELEASE.jar(它是和事务相关的),也可以在maven工程中也可以导入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>5.1.14.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-tx</artifactId>
<version>5.1.3.RELEASE</version>
</dependency>
二、JdbcTemplate 对象的创建
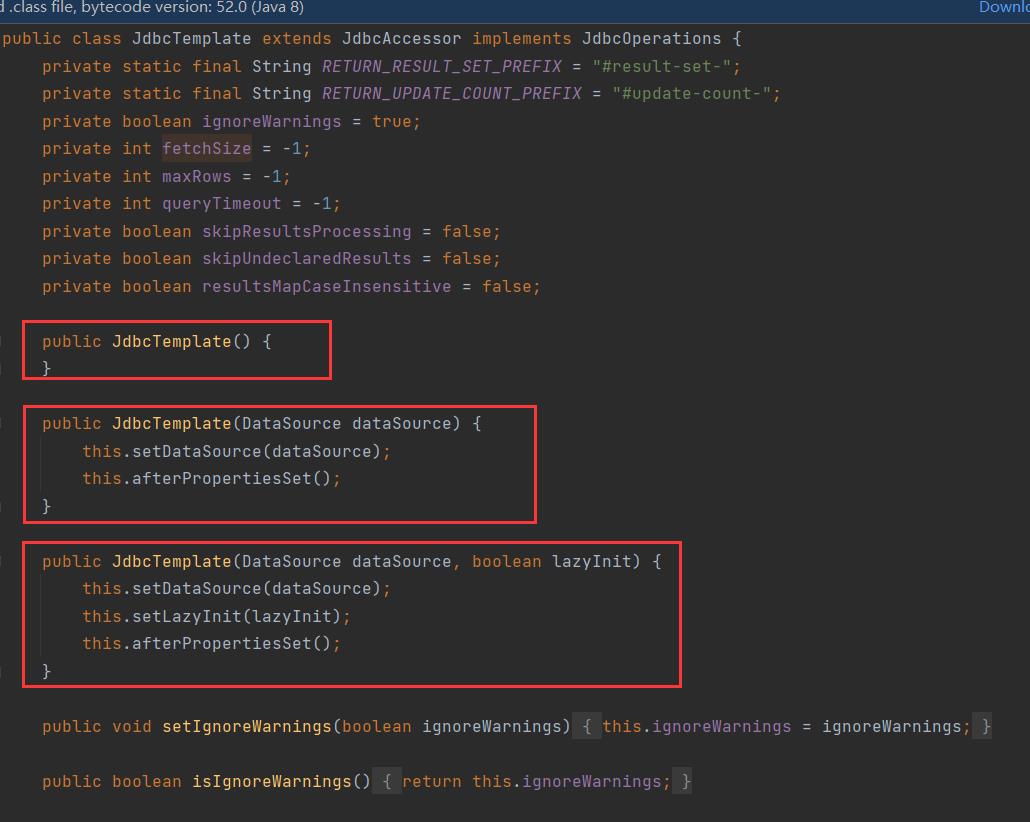
通过源码我们发现除了默认构造函数之外,都需要提供一个数据源。既然有set方法,依据我们之前学过的依赖注入,我们可以在配置文件中配置这些对象。
三、JdbcTemplate 的应用
下面我们通过案例演示 JdbcTemplate 的应用,工程目录如下:
3.1 JdbcTemplate 的简单使用
public class JdbctemplateDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//准备数据源
DriverManagerDataSource ds = new DriverManagerDataSource();
ds.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
ds.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springdb");
ds.setUsername("root");
ds.setPassword("000000");
//1. 创建jdbcTemplate对象
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate = new JdbcTemplate();
jdbcTemplate.setDataSource(ds);
//2. 执行操作
jdbcTemplate.execute("insert into account(name, money) values('ccc',1000)");
}
}
3.2 JdbcTemplate 的增删改查
public class JdbctemplateDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2. 获取对象
JdbcTemplate jt = ac.getBean("jdbcTemplate", JdbcTemplate.class);
//3. 执行操作
//增加
jt.update("insert into account(name, money) values(?, ?)", "eee", 333f);
//改
jt.update("update account set name=?, money=? where id=?", "abc", 1234f, 6);
//删除
jt.update("delete from account where id = ?",6 );
//查询所有
List<Account> accounts = jt.query("select * from account where money > ?", newBeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class), 500f);
for(Account account:accounts){
System.out.println(account);
}
//查询一个
List<Account> accounts1 = jt.query("select * from account where id = ?", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class), 1);
System.out.println(accounts1.isEmpty()?"没有内容":accounts1.get(0));
//查询返回一行一列(使用聚合函数,但不加group by 子句)
Integer count = jt.queryForObject("select count(*) from account where money > ?", Integer.class, 1000f);
System.out.println(count);
}
}
3.2 在 Spring 中应用 JdbcTemplate
3.2.1 编写 spring 的配置文件
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--配置账户的持久层-->
<bean id="accountDao" class="com.itheima.dao.impl.AccountDaoImpl">
<property name="jdbcTemplate" ref="jdbcTemplate"></property>
</bean>
<!--配置jdbcTemplate-->
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"></property>
</bean>
</beans>
注意: 此时数据源还没有配置
3.2.1 配置数据源
配置数据源的方式有三种,分别是:
- 配置 C3P0 数据源
- 配置 DBCP 数据源
- 配置 Spring 内置数据源
1. 配置 C3P0 数据源
<bean id="dataSource" class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource">
<property name="driverClass" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springdb"></property>
<property name="user" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="000000"></property>
</bean>
2. 配置 DBCP 数据源
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springdb"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="000000"></property>
</bean>
3. 配置 Spring 内置数据源
<bean id="dataSource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver"></property>
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/springdb"></property>
<property name="username" value="root"></property>
<property name="password" value="000000"></property>
</bean>
3.2.3 持久层及其实现类
/**
* 账户持久层接口
*/
public interface IAccountDao {
/**
* 根据id查询账户
*/
Account findAccountById(Integer accountId);
/**
* 根据名称查询
*/
Account findAccountByName(String accountName);
/**
* 更新账户
*/
void updateAccount(Account account);
}
/**
* 账户的持久层实现类
*/
public class AccountDaoImpl implements IAccountDao {
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void setJdbcTemplate(JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate) {
this.jdbcTemplate = jdbcTemplate;
}
public Account findAccountById(Integer accountId) {
List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where id = ?", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class), accountId);
return accounts.isEmpty()?null:accounts.get(0);
}
public Account findAccountByName(String accountName) {
List<Account> accounts = jdbcTemplate.query("select * from account where name = ?", new BeanPropertyRowMapper<Account>(Account.class), accountName);
if(accounts.isEmpty()){
return null;
}
if(accounts.size()>1){
throw new RuntimeException("结果集不唯一");
}
return accounts.get(0);
}
public void updateAccount(Account account) {
jdbcTemplate.update("update account set name = ? , money = ? where id = ?", account.getName(), account.getMoney(), account.getId());
}
}
3.2.4 测试方法
public class JdbctemplateDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1. 获取容器
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("bean.xml");
//2. 获取对象
IAccountDao accountDao = ac.getBean("accountDao", IAccountDao.class);
//3. 执行操作
Account account = accountDao.findAccountById(1);
System.out.println(account);
}
}
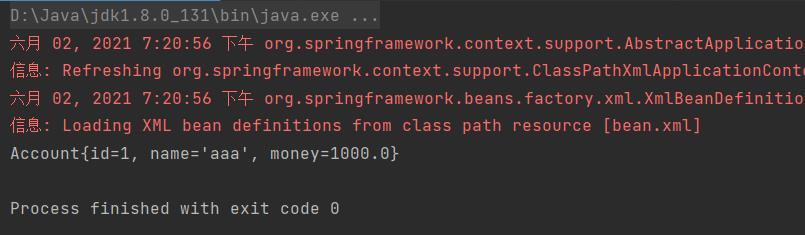
测试结果如下:
本文针对 Spring 中的 JdbcTemplate 进行了分析,并实现对数据库的操作。如果大家对文章内容还存在一些疑问,欢迎大家在评论区留言哦~
以上是关于Spring 从入门到精通系列 11—— Spring 中的 JdbcTemplate的主要内容,如果未能解决你的问题,请参考以下文章